
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 107-112.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160143
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles
MA Peng-Fei1, 2, LI Ri-Hong1, ZHANG Long1
Received:2016-03-14
Published:2017-01-20
Online:2016-12-15
About author:MA Peng-Fei (1989–), male, candidate of Master degree. Email: mapf@shanghaitech.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
MA Peng-Fei, LI Ri-Hong, ZHANG Long. Sol-Gel-derived Mesoporous Calcium Aluminum Phosphate Bioactive Glasses with High Surface Area[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 107-112.
| Glass code | CaO/mol% | AlO3/2/mol% | PO5/2/mol% | Annealing, T/℃ | Tc(℃) (glass), T/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5%CaO-MBG | 5 | 45 | 50 | 600 | 806.75 |
| 10%CaO-MBG | 10 | 40 | 50 | 600 | 738.00 |
| 15%CaO-MBG | 15 | 35 | 50 | 600 | 728.08 |
| 20%CaO-MBG | 20 | 30 | 50 | 600 | 717.66 |
| 25%CaO-MBG | 25 | 25 | 50 | 600 | 709.58 |
| 30%CaO-MBG | 30 | 20 | 50 | 600 | 701.10 |
Table 1 The phosphate coding, corresponding molar composition, annealing temperature and Tc temperature
| Glass code | CaO/mol% | AlO3/2/mol% | PO5/2/mol% | Annealing, T/℃ | Tc(℃) (glass), T/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5%CaO-MBG | 5 | 45 | 50 | 600 | 806.75 |
| 10%CaO-MBG | 10 | 40 | 50 | 600 | 738.00 |
| 15%CaO-MBG | 15 | 35 | 50 | 600 | 728.08 |
| 20%CaO-MBG | 20 | 30 | 50 | 600 | 717.66 |
| 25%CaO-MBG | 25 | 25 | 50 | 600 | 709.58 |
| 30%CaO-MBG | 30 | 20 | 50 | 600 | 701.10 |
| Glass code | Specific surface area/ (m²·g-1) | Pore volume/ (mL·g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5%CaO-MBG | 461.1 | 0.697 | 4.3 |
| 10%CaO-MBG | 332.6 | 0.412 | 3.0 |
| 15%CaO-MBG | 251.3 | 0.421 | 2.9 |
| 20%CaO-MBG | 246.2 | 0.380 | 2.7 |
| 25%CaO-MBG | 125.7 | 0.195 | 2.3 |
| 30%CaO-MBG | 25.6 | 0.066 | 1.9 |
Table 2 Specific surface area, pore volume and pore size of the series sample of different samples
| Glass code | Specific surface area/ (m²·g-1) | Pore volume/ (mL·g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5%CaO-MBG | 461.1 | 0.697 | 4.3 |
| 10%CaO-MBG | 332.6 | 0.412 | 3.0 |
| 15%CaO-MBG | 251.3 | 0.421 | 2.9 |
| 20%CaO-MBG | 246.2 | 0.380 | 2.7 |
| 25%CaO-MBG | 125.7 | 0.195 | 2.3 |
| 30%CaO-MBG | 25.6 | 0.066 | 1.9 |

Fig. 3 shows the DTA traces collected for the different compositions with the increasing calcium oxide. And the Tc temperatures are presented in Table 1. Due to the Sol-Gel methods and the thermal treatment at 600℃, the Tg temperature can’t be reflected clearly from the tracts of DTA. As seen from the Fig. 3, a decrease in Tc temperature is obtained with increasing content of calcium oxide.

Fig. 5 shows the FTIR spectra of the phosphate glass samples. Almost no change is seen in the samples with the increasing content of calcium oxide. Each FTIR spectra shows the characteristic 490 cm-1 which correspond to the flexural vibration of the O-P-O bond correspond to P=O at 1250 cm-1, which appears on the occasion of crystallization in phosphate glass, proving the amorphous form of phosphate glass. The result of FTIR spectra is in line with the conclusion of X-Ray diffraction patterns.

Fig. 6 shows the XRD patterns of the samples with the increasing content of calcium oxide before and after soaking in SBF solution. The presence of a broad band between 20° and 30° (2θ value) with no diffraction is observed, which confirms the amorphous structure of the phosphate matrix of glasses without dipping in SBF. After soaking, the major hydroxyapatite diffraction peaks [JCPDS 09-0432] (International Center for Diffraction Data, Swarthmore, PA, 2002) on the patterns at the different time periods, illustrating the change bioactive of the varying content glasses.
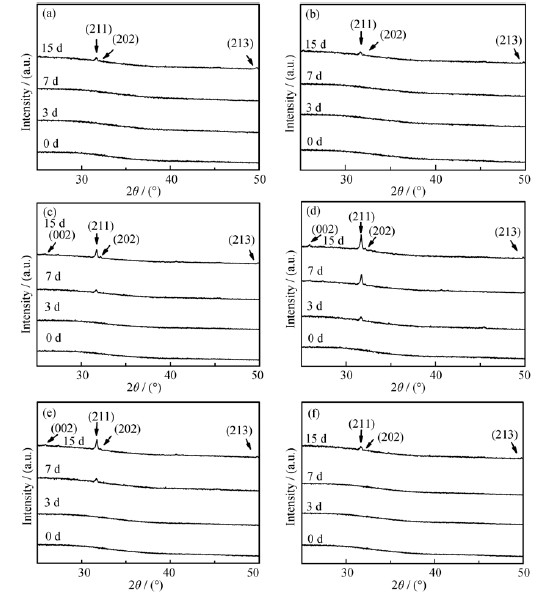
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of the samples before and after soaking in SBF solutiona) 5%CaO-MBG; b) 10%CaO-MBG; c) 15%CaO-MBG; d) 20%CaO-MBG; e) 25%CaO-MBG; f) 30%CaO-MBG
| [1] | QUINLAN E, PARTAP S, AZEVEDO M M,et al.Hypoxia-mimicking bioactive glass/collagen glycosaminoglycan composite scaffolds to enhance angiogenesis and bone repair.Biomaterials, 2015, 52: 358-366. |
| [2] | LIU HUI, CHEN XIAO-FENG, LI XIAN,et al.Gene transfection of bioactive glass fibers.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1023-1028. |
| [3] | ZHU Y, SHANG F, LI B,et al.Magnetic mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds: preparation, physicochemistry and biological properties.Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(9): 1279-1288. |
| [4] | ZHI-HONG D, ZHI-PING N, CHANG-CHUN Z.Bionic remineralization of acidic etched enamel induced by using mesoporous bioactive glass in natural oral saliva.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(1): 88-94. |
| [5] | AJITA J, SARAVANAN S, SELVAMURUGAN N.Effect of size of bioactive glass nanoparticles on mesenchymal stem cell proliferation for dental and orthopedic applications.Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2015, 53: 142-149. |
| [6] | LI Y, LIU Y Z, LONG T,et al.Mesoporous bioactive glass as a drug delivery system: fabrication, bactericidal properties and biocompatibility.Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2013, 24(8): 1951-1961. |
| [7] | HUANG S, KANG X, CHENG Z,et al.Electrospinning preparation and drug delivery properties of Eu3+/Tb3+ doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanofibers.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2012, 387(1): 285-291. |
| [8] | WANG X, WEN C.Corrosion protection of mesoporous bioactive glass coating on biodegradable magnesium.Applied Surface Science, 2014, 303: 196-204. |
| [9] | AL-NOAMAN A,RAWLINSON S C F,HILL R G. The role of MgO on thermal properties, structure and bioactivity of bioactive glass coating for dental implants.Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2012, 358(22): 3019-3027. |
| [10] | JONES J R.Review of bioactive glass: from Hench to hybrids.Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(1): 4457-4486. |
| [11] | YANG G J, LIN M, ZHANG L,et al.Progress of calcium sulfate and inorganic composites for bone defect repair.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(8): 795-803. |
| [12] | SHRUTI S, SALINAS A J, MALAVASI G,et al.Structural and in vitro study of cerium, gallium and zinc containing Sol-Gel bioactive glasses.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(27): 13698-13706. |
| [13] | CHEN J, QUE W, XING Y,et al.Molecular level-based bioactive glass-poly (caprolactone) hybrids monoliths with porous structure for bone tissue repair.Ceramics International, 2015, 41(2): 3330-3334. |
| [14] | HENDRIKX S, KASCHOLKE C, FLATH T,et al.Indirect rapid prototyping of sol-gel hybrid glass scaffolds for bone regeneration- effects of organic crosslinker valence, content and molecular weight on mechanical properties.Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 35: 318-329. |
| [15] | TAI H, MATHER M L, HOWARD D,et al.Control of pore size and structure of tissue engineering scaffolds produced by supercritical fluid processing.Eur. Cell Mater., 2007, 14: 64-77. |
| [16] | OKII N, NISHIMURA S, KURISU K,et al.In vivo histological changes occurring in hydroxyapatite cranial reconstruction.Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica, 2001, 41(2): 100-104. |
| [17] | EMADI R, TAVANGARIAN F, ESFAHANI S I R,et al.Nanostructured forsterite coating strengthens porous hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(9): 2679-2683. |
| [18] | FATHI M H, DOOSTMOHAMMADI A.Bioactive glass nanopowder and bioglass coating for biocompatibility improvement of metallic implant.Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(3): 1385-1391. |
| [19] | HENCH L L.Sol-Gel materials for bioceramic applications.Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 1997, 2(5): 604-610. |
| [20] | WANG X, LI X, ITO A,et al.Synthesis and characterization of hierarchically macroporous and mesoporous CaO-MO-SiO2-P2O5(M= Mg, Zn, Sr) bioactive glass scaffolds.Acta Biomaterialia, 2011, 7(10): 3638-3644. |
| [21] | MA Z, DONG G, LV C,et al.Core-shell glass fibers with high bioactivity and good flexibility.Materials Letters, 2012, 88: 136-139. |
| [22] | POOLOGASUNDARAMPILLAI G, WANG D, LI S,et al.Cotton-wool-like bioactive glasses for bone regeneration.Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10(8): 3733-3746. |
| [23] | CUI Y, LI H, YI K,et al.Moisture absorption characteristics of a SiO2 film from 2 to 3 μm.Chinese Optics Letters, 2015, 13(2): 023101. |
| [24] | KNOWLES J C, FRANKS K, ABRAHAMS I.Investigation of the solubility and ion release in the glass system K2O-Na2O-CaO-P2O5.Biomaterials, 2001, 22(23): 3091-3096. |
| [25] | KOKUBO T, TAKADAMA H.How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity.Biomaterials, 2006, 27(15): 2907-2915. |
| [26] | AHMED I, LEWIS M, OLSEN I,et al.Phosphate glasses for tissue engineering: part 2. Processing and characterisation of a ternary-based P2O5-CaO-Na2O glass fibre system.Biomaterials, 2004, 25(3): 501-507. |
| [27] | FRANKS K, ABRAHAMS I, GEORGIOU G,et al.Investigation of thermal parameters and crytallisation in a ternary CaO-Na2O- P2O5-based glass system.Biomaterials, 2001, 22(5): 497-501. |
| [28] | SMITH J M, KING S P, BARNEY E R,et al.Structural study of Al2O3-Na2O-CaO-P2O5 bioactive glasses as a function of aluminium content.The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2013, 138(3): 034501. |
| [29] | EL-KHESHEN A A, KHALIAFA F A, SAAD E A, et al.Effect of Al2O3 addition on bioactivity, thermal and mechanical properties of some bioactive glasses.Ceramics International, 2008, 34(7): 1667-1673. |
| [30] | THIND K S, SINGH K, SHARMA G,et al.Influence of addition of Al2O3 on physical, structural, acoustical and in-vitro bioactive properties of phosphate glasses.Physica Status Solidi (a), 2009, 206(7): 1447-1455. |
| [1] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [2] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [3] | PANG Libin, WANG Deping. Drug Carrier Based on Mesoporous Borosilicate Glass Microspheres: Preparation and Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 780-786. |
| [4] | SHI Jixiang, ZHAI Dong, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Preparation and Characterization of Bioactive Glass-Manganese Dioxide Composite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 427-435. |
| [5] | TANG Jieyin, WANG Gang, LIU Cong, ZOU Xuenong, CHEN Xiaofeng. Dentin Remineralization Induced by Micro-nano Bioactive Glass Spheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 436-444. |
| [6] | SHU Chaoqin, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Cobalt-incorporated Chlorapatite: Preparation by Molten Salt Method, Anti-oxidation and Cytocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235. |
| [7] | CHEN Cheng, DING Jingxin, WANG Hui, WANG Deping. Nd-doped Mesoporous Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-ceramic Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1245-1258. |
| [8] | ZHANG Wenjun, ZHAO Xueying, LÜ Jiangwei, QU Youpeng. Progresses on Hollow Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Preparation and Application in Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1192-1202. |
| [9] | ZHU Zimin, ZHANG Minhui, ZHANG Xuanyu, YAO Aihua, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. In Vitro Mineralization Property of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass under DC Electric Field [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 1006-1012. |
| [10] | LIN Ziyang, CHANG Yuchen, WU Zhangfan, BAO Rong, LIN Wenqing, WANG Deping. Different Simulated Body Fluid on Mineralization of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-based Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [11] | MAN Xin, WU Nan, ZHANG Mu, HE Hongliang, SUN Xudong, LI Xiaodong. Lu2O3-MgO Nano-powder: Synthesis and Fabrication of Composite Infrared Transparent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1263-1269. |
| [12] | YANG Conggang, MI Le, FENG Aihu, YU Yang, SUN Dazhi, YU Yun. Synthesis and Performance of KH-560 Modified SiO2 Insulation Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1343-1348. |
| [13] | TANG Jiawei, WANG Yongbang, MA Cheng, YANG Haixiao, WANG Jitong, QIAO Wenming, LING Licheng. Methylnaphthalene Pitch-based Ordered Mesoporous Carbon: Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1031-1038. |
| [14] | HUANG Xieyi,WANG Peng,YIN Guoheng,ZHANG Shaoning,ZHAO Wei,WANG Dong,BI Qingyuan,HUANG Fuqiang. Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds Driven by Platinum Supported on Amorphous Phosphated Titanium Oxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 482-490. |
| [15] | FANG Mei-Rong,QIN Li-Mei,JIA Xiao-Bo,LI Yong-Sheng,NIU De-Chao,HU Ze-Lan. Construction of Polyethyleneimine-modified Dual-mesoporous Silica Gene Carrier [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 187-192. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||