
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 51-55.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160268
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHUO Shi-Yi, LIU Xi, GAO Pan, YAN Cheng-Feng, SHI Er-Wei
Received:2016-04-18
Revised:2016-07-22
Published:2017-01-20
Online:2016-12-15
About author:ZHUO Shi-Yi. E-mail: syzhuo@mail.sic.ac.cn
CLC Number:
ZHUO Shi-Yi, LIU Xi, GAO Pan, YAN Cheng-Feng, SHI Er-Wei. Luminescence of Donor-acceptor-pair in Fluorescent 4H-SiC Doped with Nitrogen, Boron and Aluminum[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 51-55.
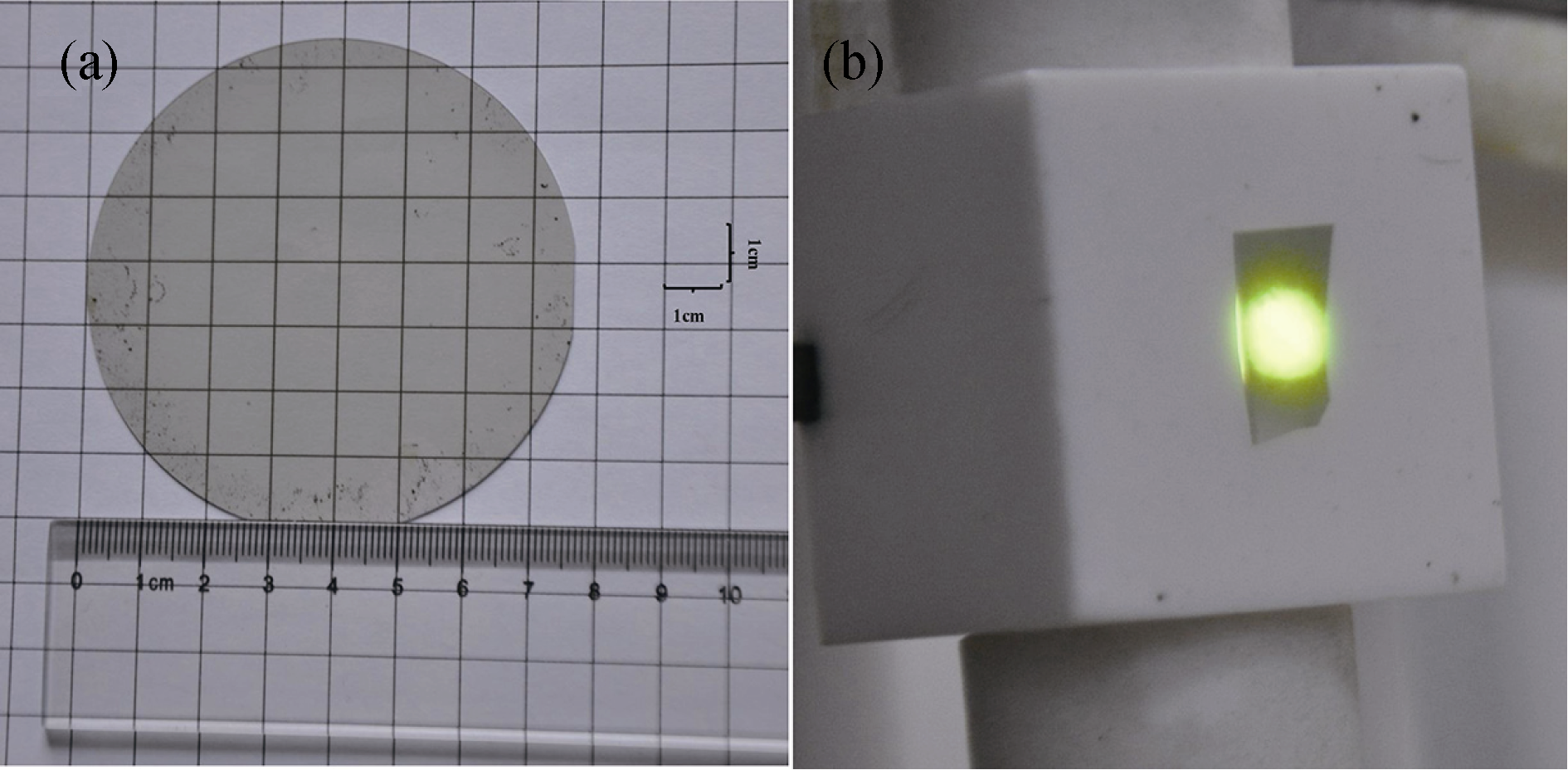
Fig. 1 (a) Photographs of 3-inch fluorescent 4H-SiC wafer grown by PVT method; (b) a visible light emitting fluorescent 4H-SiC sample excited by 325 nm pulsed laser source with a power of 5 mJ. The spot diameter of 325 nm laser source is about 10 mm
| Sample | [B]/cm-3 | [Al]/cm-3 | [N]/cm-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 9.68×1018 | 8.81×1016 | 8.49×1018 |
| b | 9.05×1018 | 1.77×1016 | 7.60×1018 |
| c | 1.09×1019 | 3.30×1016 | 8.12×1018 |
| d | 8.08×1018 | 7.19×1015 | 6.91×1018 |
| e | 1.05×1019 | 6.10×1015 | 3.49×1018 |
| f | 1.08×1019 | 3.91×1015 | 7.01×1018 |
| g | 5.66×1017 | 3.34×1016 | 1.20×1018 |
Table 1 SIMS results of N, B, Al doping concentration ([B], [Al], [N]) in samples a-g
| Sample | [B]/cm-3 | [Al]/cm-3 | [N]/cm-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 9.68×1018 | 8.81×1016 | 8.49×1018 |
| b | 9.05×1018 | 1.77×1016 | 7.60×1018 |
| c | 1.09×1019 | 3.30×1016 | 8.12×1018 |
| d | 8.08×1018 | 7.19×1015 | 6.91×1018 |
| e | 1.05×1019 | 6.10×1015 | 3.49×1018 |
| f | 1.08×1019 | 3.91×1015 | 7.01×1018 |
| g | 5.66×1017 | 3.34×1016 | 1.20×1018 |
| Sample | τ1/μs | τ2/μs | τ/μs |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 72.60 | 1542.13 | 910.38 |
| b | 93.12 | 1838.96 | 1167.66 |
| c | 78.79 | 1699.81 | 1040.48 |
| d | 88.58 | 1910.29 | 1247.37 |
| e | 79.29 | 1822.03 | 1142.43 |
| f | 100.80 | 2093.37 | 1407.54 |
| g | 171.02 | 1341.72 | 1021.90 |
Table 2 Fluorescence life time of samples a-g
| Sample | τ1/μs | τ2/μs | τ/μs |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 72.60 | 1542.13 | 910.38 |
| b | 93.12 | 1838.96 | 1167.66 |
| c | 78.79 | 1699.81 | 1040.48 |
| d | 88.58 | 1910.29 | 1247.37 |
| e | 79.29 | 1822.03 | 1142.43 |
| f | 100.80 | 2093.37 | 1407.54 |
| g | 171.02 | 1341.72 | 1021.90 |
| Sample | IQE/% | Abs | EQE/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 7.86 | 0.689 | 5.41 |
| b | 9.67 | 0.937 | 9.07 |
| c | 8.71 | 0.678 | 5.90 |
| d | 11.13 | 0.939 | 10.45 |
| e | 10.17 | 0.937 | 9.53 |
| f | 11.88 | 0.928 | 11.03 |
| g | 1.07 | 0.628 | 0.67 |
Table 3 Values of absorbance and internal and external quantum efficiencies (IQE and EQE) evaluated from PL spectra
| Sample | IQE/% | Abs | EQE/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 7.86 | 0.689 | 5.41 |
| b | 9.67 | 0.937 | 9.07 |
| c | 8.71 | 0.678 | 5.90 |
| d | 11.13 | 0.939 | 10.45 |
| e | 10.17 | 0.937 | 9.53 |
| f | 11.88 | 0.928 | 11.03 |
| g | 1.07 | 0.628 | 0.67 |
| [1] | KAMIYAMA S, MAEDA T, NAKAMURA Y, et al. Extremely high quantum efficiency of donor-acceptor-pair emission in N-and-B-doped 6H-SiC.Journal of Applied Physics, 2006,99(9): 093108-1-4. |
| [2] | OU H, OU Y Y, ARGYAKI A, et al. Advances in wide bandgap SiC for optoelectronics.The European Physical Journal B, 2014, 87(3): 58-74. |
| [3] | SUN J W, ROBERT T, ANDREADOU A, et al. Shockley-Frank stacking faults in 6H-SiC.Journal of Applied Physics,2012, 11(11): 113527-1-9. |
| [4] | OU Y Y, JOKUBAVICIUS V, KAMIYAMA S,et al.Donor- acceptor-pair emission characterization in N-B doped fluorescent SiC.Optical Materials Express, 2011, 1(8): 1439-1446. |
| [5] | SYVAJARVI M, MULLER J, SUN J W, et al.Fluorescent SiC as a new material for white LEDs.Physica Scripta,2012, T148: 014002-1-5. |
| [6] | KAMIYAMA S, IWAYA M, TAKEUCHI T,et al.White light- emitting diode based on fluorescent SiC.Thin Solid Films, 2012, 522: 23-25. |
| [7] | LIU X, ZHUO S Y, GAO P, et al. Donor-acceptor-pair emission in fluorescent 4H-SiC grown by PVT method.AIP Advances,2015,5(4): 047133-1-7. |
| [8] | SUN J W, JOKUBAVICIUS V, LILJEDAHL R,et al.Room Temperature luminescence properties of fluorescent SiC as white light emiting diode medium.Thin Solid Films, 2012, 522: 33-35. |
| [9] | CHUNG H J, SKOWRONSKI M.High-resoution X-ray diffraction and optical absorption study of heavily nitrogen-doped 4H-SiC.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2003, 259(1/2): 52-60. |
| [10] | IVANOV G, MAGUSSON B, JANZEN E, et al. Analysis of the sharp donor-acceptor pair luminescence in 4H-SiC doped with nitrogen and aluminum.Physical Review B, 2003, 67(16)67(16): 165211-1-8. |
| [11] | WANG X X, YANG L, LIU H,et al.Optical properties of ZnS:Co+Cr nanocrystals synthesized by a low temperature hydrothermal process.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1049-1054. |
| [12] | GAVRYUSHIN V, GULBINAS K, GRIVICKAS V, et al. Examination of photoluminescence temperature dependencies in N-B co-doped 6H-SiC.Materials Science and Engineering, 2014, 56(1): 012003-1-5. |
| [13] | SCHIMMEL S, KAISER M, JOKUBAVICIUS V, et al. The role of defects in fluorescent silicon carbide layers grown by sublimation epitaxy.Materials Science and Engineering, 2014, 56(1): 012002- 1-6. |
| [1] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [2] | LIU Qi, ZHU Can, XIE Guizhen, WANG Jun, ZHANG Dongming, SHAO Gangqin. Optical Absorption and Photoluminescence Spectra of Ce-doped SrMgF4 Polycrystalline with Superlattice Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 897-902. |
| [3] | OUYANG Qin, WANG Yanfei, XU Jian, LI Yinsheng, PEI Xueliang, MO Gaoming, LI Mian, LI Peng, ZHOU Xiaobing, GE Fangfang, ZHANG Chonghong, HE Liu, YANG Lei, HUANG Zhengren, CHAI Zhifang, ZHAN Wenlong, HUANG Qing. Research Progress of SiC Fiber Reinforced SiC Composites for Nuclear Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [4] | GUAN Xufeng, LI Guifang, WEI Yunge. Microstructure and Thermal Quenching Characteristics of Na1-xMxCaEu(WO4)3 (M=Li, K) Red Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 676-682. |
| [5] | RUAN Jing, YANG Jinshan, YAN Jingyi, YOU Xiao, WANG Mengmeng, HU Jianbao, ZHANG Xiangyu, DING Yusheng, DONG Shaoming. Porous SiC Ceramic Matrix Composite Reinforced by SiC Nanowires with High Strength and Low Thermal Conductivity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [6] | ZHANG Guoqing, QIN Peng, HUANG Fuqiang. Reversible Conversion between Space-confined Lead Ions and Perovskite Nanocrystals for Confidential Information Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 445-451. |
| [7] | DU Aochen, DU Qiyuan, LIU Xin, YANG Yimin, XIA Chenyang, ZOU Jun, LI Jiang. Ce:YAG Transparent Ceramics Enabling High Luminous Efficacy for High-power LEDs/LDs [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 883-892. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zhijie,HUANG Hairui,CHENG Kun,GUO Shaoke. High Efficient Carbon Quantum Dots/BiOCl Nanocomposite for Photocatalytic Pollutant Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 491-496. |
| [9] | LUO Qing,YUAN Qing,JIANG Qian-Qin,YU Nai-Sen. Cu-SSZ-13/SiC-waste Composite: Synthesis and Application for NH3-SCR [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 953-960. |
| [10] | DAI Yan-Nan, YANG Shuai, SHEN Yang, SHAN Yong-Kui, YANG Fan, ZHAO Qing-Biao. Intense Yellow Emission from Gd0.5-yTb1.5REyW3O12 (RE=Eu, Sm) Phosphors Tuned through Full Range Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1210-1216. |
| [11] | LI Gui-Fang, YANG Qian, WEI Yun-Ge. Synthesis and Photoluminescence Properties of Double Perovskite NaLaMgWO6: Eu3+ Red Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(9): 936-942. |
| [12] | HE Fei, LI Ya, LUO Jin, FANG Min-Han, HE Xiao-Dong. Development of SiO2/C and SiC/C Composites Featuring Aerogel Structures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | YU Jie-Yi, HUANG Hao, GAO Jian, ZHOU Lei, GAO Song, DONG Xing-Long, QUAN Xie. Synthesis and Catalytic Performances of SiC Nanoparticles by DC Arc-discharge Plasma [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 351-356. |
| [14] | YAN Bo, PENG Ze-Yang, LV Bin, LIU Wei. Regrowth of CdTe Quantum Dots Induced by Circular Polarized Light and Its Effect on the Photoluminescence [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(12): 1321-1326. |
| [15] | WANG Feng, GAO Zhao-Fen, XU Jia-Qiang, ZENG Yu-Ping. Porous SiC Ceramics with Multiple Pore Structure Fabricated via Gelcasting and Solid State Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 305-310. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||