
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 1375-1382.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160136
Special Issue: 庆祝上海硅酸盐所独立建所60周年虚拟专刊!
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles
YAO Zheng1,2, QIU Peng-Fei2, LI Xiao-Ya2, CHEN Li-Dong2
Received:2016-03-09
Published:2016-12-16
Online:2016-11-23
About author:YAO Zheng(1988–), male, candidate of PhD. E-mail: yaozheng@student.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
YAO Zheng, QIU Peng-Fei, LI Xiao-Ya, CHEN Li-Dong. Investigation on Quick Fabrication of n-type Filled Skutterudites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1375-1382.

Fig. 1(a) represents the Co-Sb binary phase diagram from Ref.[26]. Due to the presence of a Co-Sb peritectic reaction at a temperature of about 876℃, the CoSb3 skutterudite phase could not be directly formed after quenching. This was confirmed by investigating the XRD pattern of the quenched ingot which experienced a 300 s induction-melting at 1353 K (see Fig. 1(b)). The ingot consisted of a mixture of CoSb, CoSb2, Sb and YbSb2. No X-ray diffraction peaks belonging to the Skutterudite phase were detected. SEM and EDS analyses shown in Fig. 1(c) further proved the coexistence of CoSb, CoSb2, and Sb in the quenched ingot. Presence of these phases formed typical dendrite networks, in which CoSb primary phases encircled with CoSb2 peritectic phases were unevenly distributed in the Sb matrix. Under higher magnification (see Fig. 1(d)), some bar-shape areas with brighter contrast were also observed in the Sb matrix, which were identified as YbSb2 by EDS. Such microstructure features are identical to that observed in the ingots prepared using a traditional long-term (48 h) melting process reported in Ref.[27]. However, the melting duration in this study is greatly reduced to as short as 300 s, which is meaningful for future industrial-level mass production.
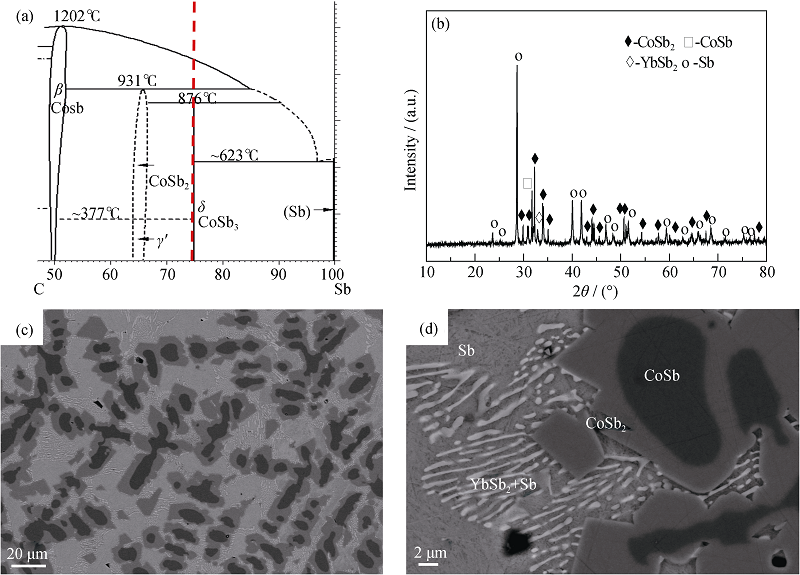
Fig. 1 (a) Co-Sb binary phase diagram from Ref. [26], (b) XRD patterns of the quenched sample, and (c, d) back scattering electron images of the quenched sample under different magnification
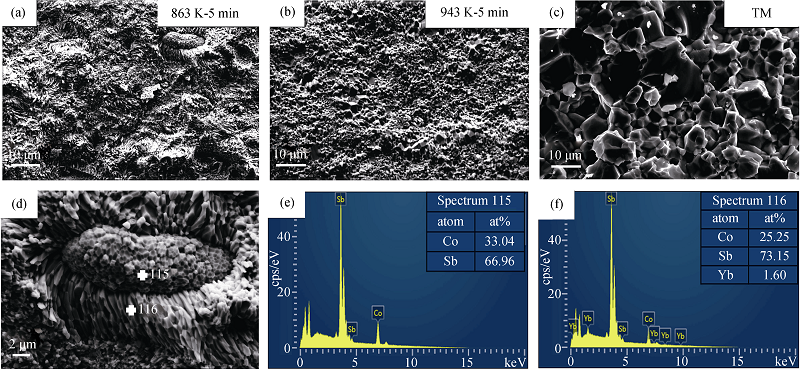
Fig. 5 Cross-section morphologies for the samples (a) 863 K-5 min, (b) 943 K-5 min and (c) TM, respectively, and (d) magnified image of (a), and (e, f) the EDS analyses on the two points (spectrum 115 and 116) shown in (d)
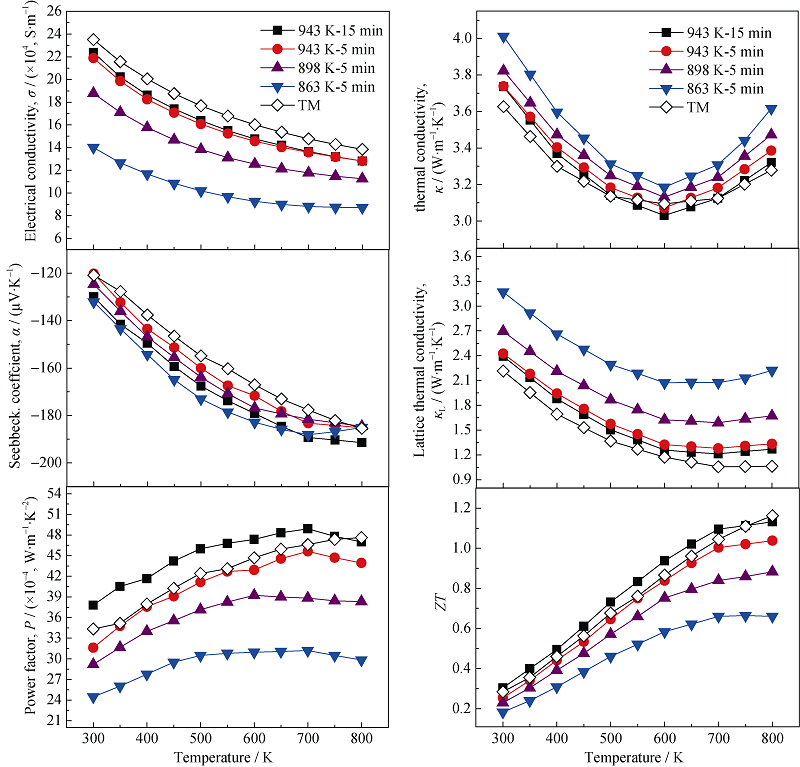
Fig. 7 Temperature dependences of TE properties of the samples prepared by the melting-quenching/SPS method The data for the TM sample are also included for comparison
| [1] | TRITT T M.Holey and unholey semiconductors.Science, 1999, 283(5403): 804-805. |
| [2] | SNYDER GERALD JEFFREY, ERIC S TOBERER.Complex thermoelectric materials.Nature Materials, 2008, 7: 105-114. |
| [3] | LIU HUI-LI, SHI XUN, XU FANG-FANG,et al. Copper ion liquid-like thermoelectric . Nature Materials, 2012, 11(5): 422-425. |
| [4] | JUNG DO-YOUNG, KUROSAKI KEN, KIM CHANG-EUN,et al. Thermal expansion and melting temperature of the half-Heusler compounds: MNiSn (M=Ti, Zr, Hf) . Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 489(2): 328-331. |
| [5] | HE YING, LU PING, SHI XUN,et al. Ultrahigh thermoelectric performance in mosaic crystals . Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(24): 3639-3644. |
| [6] | HE YING, DAY TRISTAN, ZHANG TIAN-SONG,et al. High thermoelectric performance in non-toxic earth-abundant copper sulfide . Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(23): 3974-3978. |
| [7] | SHI XUN, YANG JIONG, SALVADOR JAMES R,et al. Multiple-filled skutterudites: high thermoelectric figure of merit through separately optimizing electrical and thermal transports . Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(20): 7837-7846. |
| [8] | ROGL G, GRYTSIV A, ROGL P,et al. n-type skutterudites (R,Ba,Yb)(y)Co4Sb12 (R = Sr, La, Mm, DD, SrMm, SrDD) approaching ZT approximate to 2.0 . Acta Materialia, 2014, 63: 30-43. |
| [9] | LIU WEI-SHU, JIE QING, KIM HEE SEOK,et al. Current progress and future challenges in thermoelectric power generation: from materials to devices. Acta Materialia, 2015, 87: 357-376. |
| [10] | YANG JI-HUI, STABLER FRANCIS R.Automotive applications of thermoelectric materials.Journal of Electronic Materials, 2009, 38(7): 1245-1251. |
| [11] | ZHANG QI-HAO, HUANG XIANG-YANG, BAI SHENG- QIANG,et al. Thermoelectric devices for power generation: recent progress and future challenges. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2016, 18(2): 194-213. |
| [12] | TANG YUN-SHAN, BAI SHENG-QIANG, REN DU-DI,et al. Interface structure and electrical property of Yb0.3Co4Sb12 Mo-Cu element prepared by welding using Ag-Cu-Zn solder. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 256. |
| [13] | RECKNAGEL C, REINFRIED N, HOHN P,et al. Application of spark plasma sintering to the fabrication of binary and ternary skutterudites. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2007, 8(5): 357-363. |
| [14] | SHI X, KONG H, LI C P,et al. Low thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric figure of merit in n-type BaxYbyCo4Sb12 double-filled skutterudites. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(18): 182101. |
| [15] | SU XIAN-LI, LI HAN, WANG GUO-YU,et al. Structure and transport properties of double-doped CoSb2.75Ge0.25-xTex(x= 0.125-0.20) with in situ nanostructure . Chemistry of Materials, 2011, 23(11): 2948-2955. |
| [16] | WU TING, BAI SHENG-QIANG, SHI XUN,et al. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of BaxEuyCo4Sb12 with very high filling fraction. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(2): 224-228. |
| [17] | YANG JUN-YOU, CHEN YUE-HUA, ZHU WEN,et al. Effect of La filling on thermoelectric properties of LaxCo3.6Ni0.4Sb12-filled skutterudite prepared by MA-HP method. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2006, 179(1): 212-216. |
| [18] | LIU WEI-SHU, ZHANG BO-PING, LI JING-FENG,et al. Enhanced thermoelectric properties in CoSb3-xTex alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(10): 103717. |
| [19] | BISWAS KRISHNENDU, MUIR SEAN, SUBRAMANIAN M A.Rapid microwave synthesis of indium filled skutterudites: an energy efficient route to high performance thermoelectric materials.Materials Research Bulletin, 2011, 46(12): 2288-2290. |
| [20] | ZHANG JIAN-JUN, XU BO, WANG LI-MIN,et al.High-pressure synthesis of phonon-glass electron-crystal featured thermoelectric LixCo4Sb12. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(3): 1246-1251. |
| [21] | LIANG TAO, SU XIAN-LI, YAN YONG-GAo,et al. Ultra-fast synthesis and thermoelectric properties of Te doped skutterudites. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(42): 17914-17918. |
| [22] | LI HAN, TANG XIN-FENG, ZHANG QING-JIE,et al. Rapid preparation method of bulk nanostructured Yb0.3Co4Sb12+ycompounds and their improved thermoelectric performance . Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(25): 252109. |
| [23] | LI HAN, TANG XIN-FENG, ZHANG QING-JIe,et al. High performance InxCeyCo4Sb12 thermoelectric materials with in situ forming nanostructured InSb phase. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(10): 102114. |
| [24] | YU JIAN, ZHAO WEN-YU, ZHOU HONG-YU,et al. Rapid preparation and thermoelectric properties of Ba and In double-filled p-type skutterudite bulk materials. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 68(8): 643-646. |
| [25] | ZHAO X Y, SHI X, CHEN L D,et al. Synthesis and thermoelectric properties of Sr-filled skutterudite SryCo4Sb12. Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 99(5): 053711 . |
| [26] | HANNINGER G, IPSER H, TERZIEFF P,et al. The Co-Sb phase- diagram and some properties of NiAs-type Co1+/-xSb. Journal of the Less-Common Metals, 1990, 166(1): 103-114. |
| [27] | YAO ZHENG, LI XIAO-YA, TANG YUN-SHAN,et al. Genomic effects of the quenching process on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties of Yb0.3Co4Sb12. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2014, 44(6): 1890-1895. |
| [28] | ZHAO XUE-YIN, SHI XUN, CHEN LI-DONG,et al. Synthesis of YbyCo4Sb12/Yb2O3 composites and their thermoelectric properties. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(9): 092121. |
| [29] | ZHOU H.Preparation and Thermoelectric Properties of Nonequilibrium-structure Filled Skutterudite Based Thermoelectric Materials. Wuhan University of Technology, 2011: 41. |
| [1] | WANG Bo, YU Jian, LI Cuncheng, NIE Xiaolei, ZHU Wanting, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Service Stability of Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermo-electro-magnetic Gradient Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [2] | WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [3] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [4] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [5] | XIA Qian, SUN Shihao, ZHAO Yiliang, ZHANG Cuiping, RU Hongqiang, WANG Wei, YUE Xinyan. Effect of Boron Carbide Particle Size Distribution on the Microstructure and Properties of Reaction Bonded Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 636-642. |
| [6] | HONG Du, NIU Yaran, LI Hong, ZHONG Xin, ZHENG Xuebin. Tribological Properties of Plasma Sprayed TiC-Graphite Composite Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [7] | XU Puhao, ZHANG Xiangzhao, LIU Guiwu, ZHANG Mingfen, GUI Xinyi, QIAO Guanjun. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiC Joint Brazed by Al-Ti Alloys as Filler Metal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 683-690. |
| [8] | HUANG Longzhi, YIN Jie, CHEN Xiao, WANG Xinguang, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Selective Laser Sintering of SiC Green Body with Low Binder Content [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 347-352. |
| [9] | WU Xishi, ZHU Yunzhou, HUANG Qing, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Pore Structure of Organic Resin-based Porous Carbon on Joining Properties of Cf/SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280. |
| [10] | SUN Luchao, ZHOU Cui, DU Tiefeng, WU Zhen, LEI Yiming, LI Jialin, SU Haijun, WANG Jingyang. Directionally Solidified Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 and Al2O3/Yb3Al5O12 Eutectic Ceramics Prepared by Optical Floating Zone Melting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 652-658. |
| [11] | HUANG Xinyou, LIU Yumin, LIU Yang, LI Xiaoying, FENG Yagang, CHEN Xiaopu, CHEN Penghui, LIU Xin, XIE Tengfei, LI Jiang. Fabrication and Characterizations of Yb:YAG Transparent Ceramics Using Alcohol-water Co-precipitation Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 217-224. |
| [12] | ZHANG Junmin, CHEN Xiaowu, LIAO Chunjin, GUO Feiyu, YANG Jinshan, ZHANG Xiangyu, DONG Shaoming. Optimizing Microstructure and Properties of SiCf/SiC Composites Prepared by Reactive Melt Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1103-1110. |
| [13] | ZHU Danyang, QIAN Kang, CHEN Xiaopu, HU Zewang, LIU Xin, LI Xiaoying, PAN Yubai, MIHÓKOVÁ Eva, NIKL Martin, LI Jiang. Fine-grained Ce,Y:SrHfO3 Scintillation Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Isostatic Pressing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1118-1124. |
| [14] | CHEN Lei,WANG Kai,SU Wentao,ZHANG Wen,XU Chenguang,WANG Yujin,ZHOU Yu. Research Progress of Transition Metal Non-oxide High-entropy Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 748-758. |
| [15] | WU Xiaojun,YANG Jie,ZHENG Rui,ZHANG Zhaofu,YANG Yi. Effect of Ablation Surface Microstructure on Plasma Arc Ablation Properties of C/C Throat Insert Fabricated via CVI+HPIC Methods [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 654-660. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||