
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 1347-1354.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160146
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Jian, ZHENG Yu-Ying, ZHANG Yan-Bing, ZOU Hai-Qiang, LU Xiu-Lian
Received:2016-03-15
Revised:2016-04-25
Published:2016-12-16
Online:2016-11-23
CLC Number:
CHEN Jian, ZHENG Yu-Ying, ZHANG Yan-Bing, ZOU Hai-Qiang, LU Xiu-Lian. Preparation of MnO2/MWCNTs Catalysts by a Redox Method and Their Activity in Low-temperature SCR[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1347-1354.
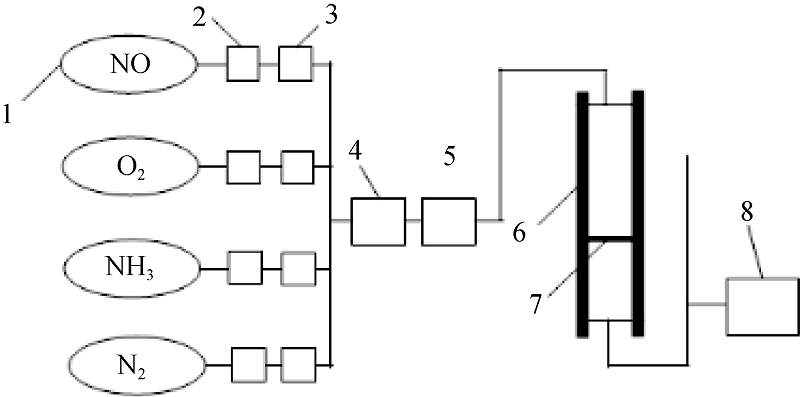
Fig. 2 Scheme of experiment apparatus^1. Air source; 2. Reducing valve; 3. Mass flowmeter; 4. Gas mixer; 5. Preheater; 6. Heater; 7. Sample; 8. Flue gas analyzer
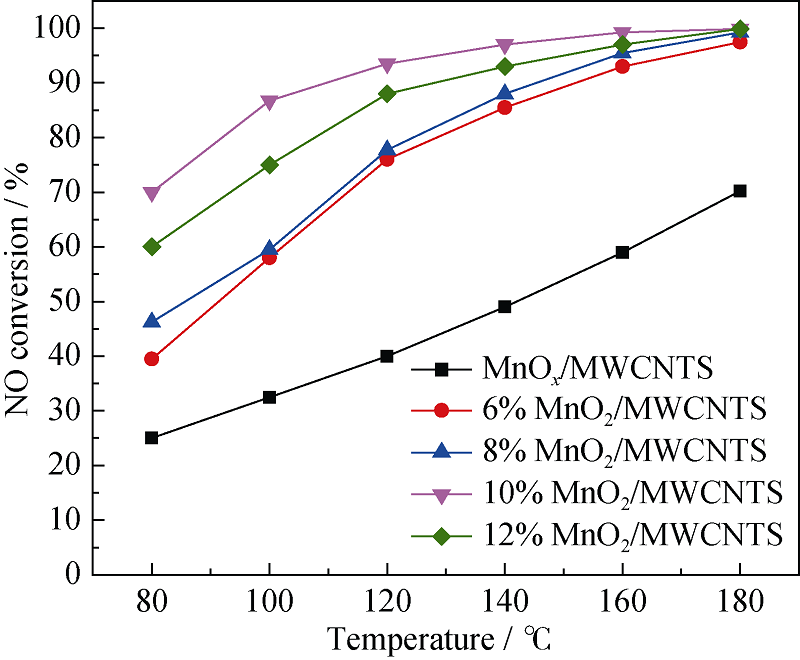
Fig. 3 SCR activity of MnO2/MWCNTs catalysts and MnOx/ MWCNTs catalyst^Reaction conditions: [NO]=[NH3]=400×10-6, [O2]=5%, N2 as balance gas, WHSV=210 L/(gcat·h), 200 mg sample
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Average pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine MWCNTs | 72 | 0.15 | 8.1 |
| Acid-treated MWCNTs | 91 | 0.18 | 7.7 |
| MnOx/MWCNTs | 69 | 0.15 | 9.0 |
| 6%MnO2/MWCNTs | 99 | 0.28 | 11.2 |
| 8%MnO2/MWCNTs | 100 | 0.29 | 11.6 |
| 10% MnO2/MWCNTs | 94 | 0.29 | 12.5 |
| 12% MnO2/MWCNTs | 111 | 0.31 | 11.3 |
Table 1 BET surface area, pore volumes and average pore size of pristine MWCNTs, acid-treated MWCNTs and different catalyst samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Average pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine MWCNTs | 72 | 0.15 | 8.1 |
| Acid-treated MWCNTs | 91 | 0.18 | 7.7 |
| MnOx/MWCNTs | 69 | 0.15 | 9.0 |
| 6%MnO2/MWCNTs | 99 | 0.28 | 11.2 |
| 8%MnO2/MWCNTs | 100 | 0.29 | 11.6 |
| 10% MnO2/MWCNTs | 94 | 0.29 | 12.5 |
| 12% MnO2/MWCNTs | 111 | 0.31 | 11.3 |
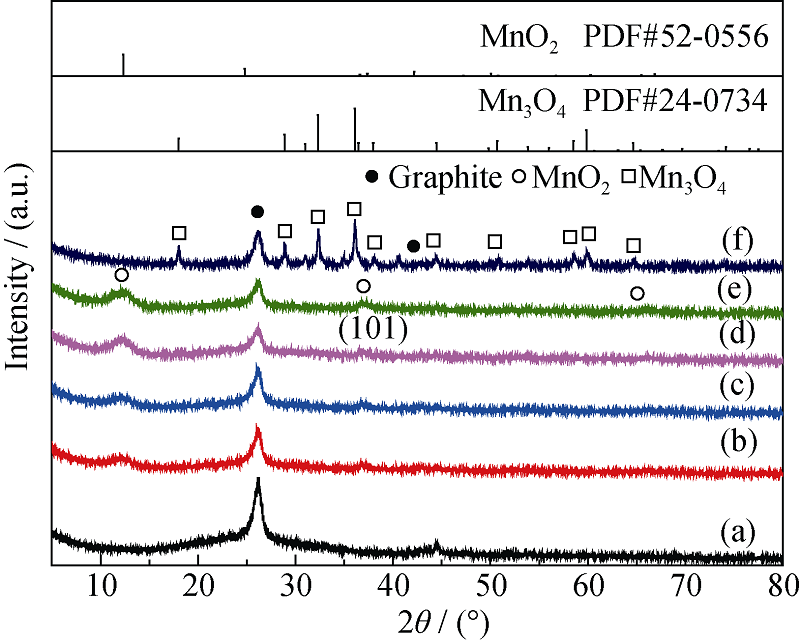
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of MnO2/MWCNTs catalysts and MnOx/ MWCNTs catalyst^(a) Pristine MWCNTs; (b) 6% MnO2/MWCNTs; (c) 8% MnO2/MWCNTs; (d) 10% MnO2/MWCNTs; (e) 12% MnO2/MWCNTs; (f) MnOx/MWCNTs
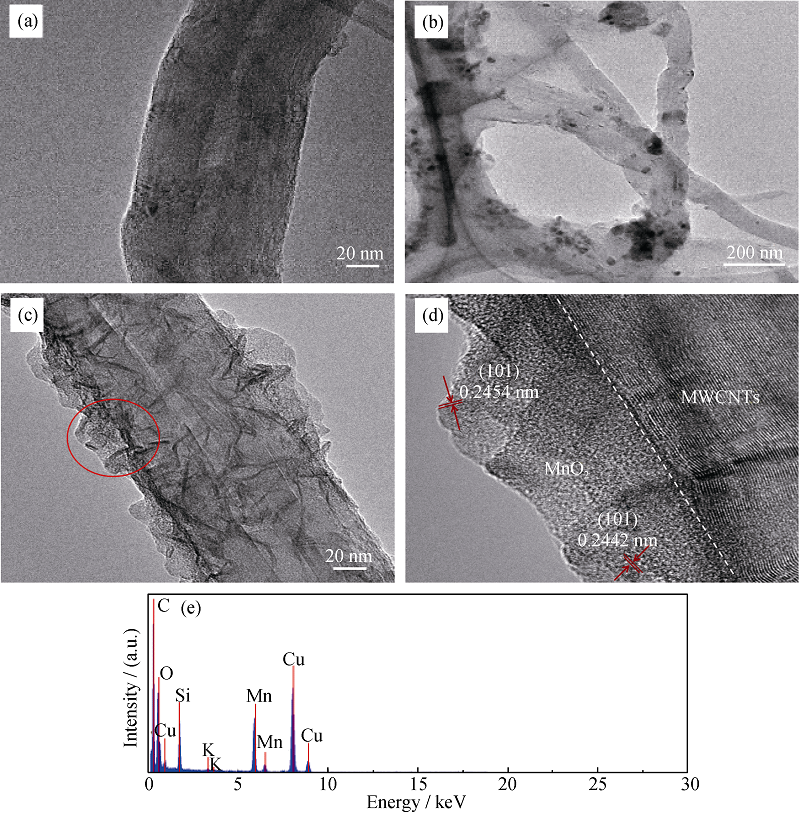
Fig. 6 TEM images of (a) pristine MWCNTs, (b) MnOx/MWCNTs catalyst and (c) 10% MnO2/MWCNTs catalyst and HRTEM image of 10% MnO2/MWCNTs catalyst, as well as (e) EDX pattern of 10% MnO2/MWCNTs catalyst from the annular region in (c)
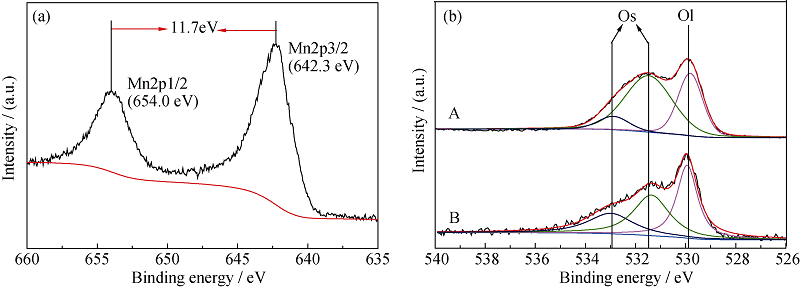
Fig. 7 Mn2p XPS spectra of 10% MnO2/MWCNTs catalyst (a) and O1s (b) spectra of different catalyst samples^(a) Mn2p; (b) O1s, (A) 10% MnO2/MWCNTs, (B) MnOx/MWCNTs
| Sample | OS/% | OL/% |
|---|---|---|
| 10% MnO2/MWCNTs | 66.7 | 33.3 |
| MnOx/MWCNTs | 61.1 | 38.9 |
Table 2 Relative content of O for 10% MnO2/MWCNTs and MnOx/MWCNTs catalyst
| Sample | OS/% | OL/% |
|---|---|---|
| 10% MnO2/MWCNTs | 66.7 | 33.3 |
| MnOx/MWCNTs | 61.1 | 38.9 |
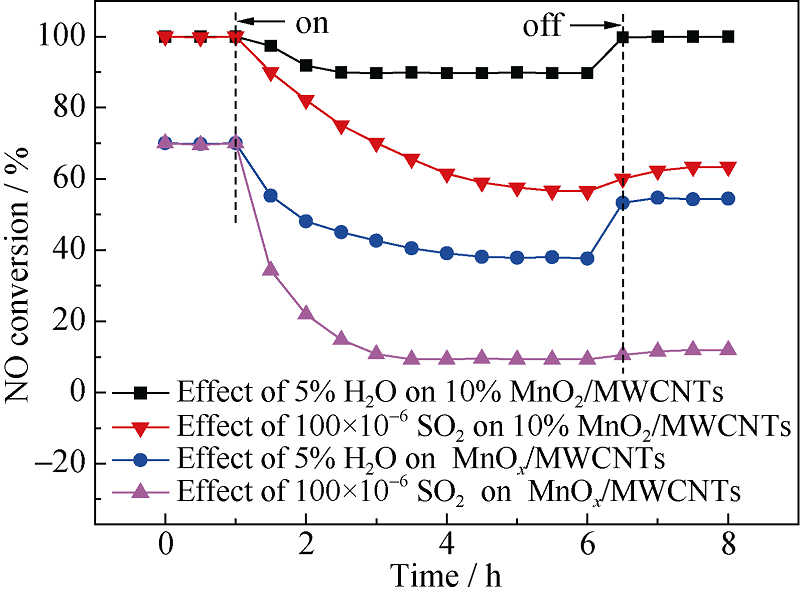
Fig. 9 Effect of H2O and SO2 on the SCR activities of catalysts at 180℃^Reaction conditions: [NO]=[NH3]=400×10-6, [O2]=5%, [H2O]=5%, [SO2]=100×10-6, N2 as balance gas, WHSV=210 L/(gcat·h), 200 mg sample
| [1] | WU D W, ZHANG Q L, LIN T, et al.. Effect of Fe on the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 at low temperature over Mn/CeO2-TiO2 catalyst.J. Inorg. Mater., 2012, 27(5): 495-500. |
| [2] | GAO R H, ZHANG D S, LIU X G,et al.. Enhanced catalytic performance of V2O5-WO3/Fe2O3/TiO2 microspheres for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3(1): 191-199. |
| [3] | NIE J Y, WU X D, MA Z R,et al.. Tailored temperature window of MnOx-CeO2 SCR catalyst by addition acidic metal oxides. Chin. J. Catal., 2014, 35(8): 1281-1288. |
| [4] | FANG C, ZHANG D S, CAI S X,et al.Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over nanoflaky MnOx on carbon nanotubes in situ prepared via a chemical bath deposition route. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(19): 9199-9207. |
| [5] | POURKHALIL M, MOGHADDAM A Z, RASHIDI A,et al.. Preparation of highly active manganese oxides supported on functionalized MWNTs for low temperature NOx reduction with NH3. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 279: 250-259. |
| [6] | YAO G H, WANG F, WANG X B,et al.. Magnetic field effects on selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over Fe2O3 catalyst in a magnetically fluidized bed. Energy, 2010, 35(5): 2295-2300. |
| [7] | KAPTEIJN F, SINGOREDJO L, ANDREINI A.Activity and selectivity of pure manganese oxides in the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. Appl.Catal. B: Environ., 1994, 3(2): 173-189. |
| [8] | QI G S, YANG R T, CHANG R.MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by co-precipitation for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl.Catal. B: Environ., 2004, 51(2): 93-106. |
| [9] | LI J H, CHEN J J, KE R, et al.. Effects of precursors on the surface Mn species and the activities for NO reduction over MnOx/TiO2 catalysts.Catal. Commun., 2007, 8(12): 1896-1900. |
| [10] | KIJLSTRA W S, BRANDS D S, POELS E K,et al.Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over MnOx/Al2O3. Catal., 1997, 171(1): 208-218. |
| [11] | SHEN B X, GUO B B, WU C F,et al.Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by MnOx/ACF. Environ. Pollut. Control, 2006, 28(11): 801-803. |
| [12] | WANG H J, WANG X H, ZHENG J D,et al.Pt/MoO3- WO3/CNTs catalyst with excellent performance for methanol electrooxidation. Chinese J. Catal., 2014, 35(10): 1687-1694. |
| [13] | TAN Z Q, ABE H, NAITO M, et al. Arrangement of palladium nanoparticles templated by supramolecular self-assembly of SDS wrapped on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun.Arrangement of palladium nanoparticles templated by supramolecular self-assembly of SDS wrapped on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun., 2010,46(24): 4363-4365 |
| [14] | MA S B, AHN KY, LEE E S,et al.Synthesis and characterization of manganese dioxide spontaneously coated on carbon nanotubes. Carbon, 2007, 45(2): 375-382. |
| [15] | JIN X B, ZHOU W Z, ZHANG S W,et al.Nanoscale microelectro chemical cells on carbon nanotubes. Small, 2007, 3(9): 1513-1517. |
| [16] | WANG L S, HUANG B C, SU Y X,et al.Manganese oxides supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: catalytic activity and characterization. Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 192: 232-241. |
| [17] | WANG X, ZHENG Y Y, XU Z,et al.Amorphous MnO2 supported on carbon nanotubes as a superior catalyst for low temperature NO reduction with NH3. Rsc. Adv., 2013, 3(29): 11539-11542. |
| [18] | HU J, YUAN A B, WANG Y Q,et al.Improved cyclability of nano-MnO2/CNT composite supercapacitor electrode derived from room-temperature solid reaction. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2009, 25(5): 987-993. |
| [19] | ZHU G, DENG L J, WANG J F,et al.Hydrothermal preparation and the capacitance of hierarchical MnO2 nanoflower. Colloid. Surface. A, 2013, 434: 42-48. |
| [20] | BAYKAL A, KAVAS H, DURMUS Z,et al. Sonochemical synthesis and chracterization of Mn3O4 nanoparticles. Cent. Eur. J. Chem., 2010, 8(3): 633-638. |
| [21] | ZHANG Y B, ZHENG Y Y, WANG X,et al. Fabrication of Mn-CeOx/CNTs catalysts by a redox method and their performance in low-temperature NO reduction with NH3. RSC Adv., 2015, 5(36): 28385-28388. |
| [22] | JULIEN C M, MASSOT M, POINSIGNON C.Lattice vibrations of manganese oxides: Part I. Periodic structures.Spectrochim. Acta A, 2004, 60(3): 689-700. |
| [23] | DAI Y, LI J H, PENG Y,et al. Effects of MnO2 crystal structure and surface property on the NH3-SCR reaction at low temperature. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2012, 28(7): 1771-1776. |
| [24] | WANG Y L, WANG X J, ZHAN L,et al.Structure control of V2O5/CNFs/cordierite monolith catalyst and its catalytic performance on NO removal from flue gas. J. Inorg. Mater., 2012, 27(8): 800-806. |
| [25] | LIU F D, HE H, DING Y,et al. Effect of manganese substitution on the structure and activity of iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2009, 93(1): 194-204. |
| [26] | ETTIREDDY P R, ETTIREDDY N, MAMEDOV S,et al.. Surface characterization studies of TiO2 supported manganese oxide catalysts for low temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B, 2007, 76(1/2): 123-134. |
| [1] | BAI Xiangtao,BAN Liqing,ZHUANG Weidong. Research Progress on Coating and Doping Modification of Nickel Rich Ternary Cathode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 972-986. |
| [2] | WANG Jinmin, YU Hongyu, MA Dongyun. Progress in the Preparation and Application of Nanostructured Manganese Dioxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1307-1314. |
| [3] | LUO Qing,YUAN Qing,JIANG Qian-Qin,YU Nai-Sen. Cu-SSZ-13/SiC-waste Composite: Synthesis and Application for NH3-SCR [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 953-960. |
| [4] | LIU Jiao, WANG Wen-Qing, WU Hong-Ye, TIAN Ye, CAO Feng-Ze, ZHAO Jian-Jun. Electromagnetic Property of Co-doped La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 Perovskite Manganese Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1237-1247. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yuan-Yuan, TANG Xiao-Dong, CHEN Ying, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin. Electrical Transport Properties in La0.7Ca0.3-xSrxMnO3 Thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 274-278. |
| [6] | LI Jun, PAN Lei, WANG Ji-Tong, LONG Dong-Hui, QIAO Wen-Ming, LING Li-Cheng. Low-temperature Removal of NO by Spherical Activated Carbon Loaded with MnOx-CeO2 and Melamine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1205-1211. |
| [7] | LU Shu-Pei, FENG Li-Li, QI Lin, WANG Li-Li, QI Xing-Yi. Chemical Kinetics of Disproportionation Decomposition of tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Buserite-type Manganese Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(1): 14-20. |
| [8] | ZHENG Yi-Fan, ZHONG Shu-Bin, LV De-Yi, ZHOU Huan, HUAN Chang-Yong. Effect of Calcination Temperature of Cu-Mn/γ-Al2O3 Catalysts on Performance for Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(7): 694-698. |
| [9] |
LI Yun-Jiao, XU Hu, KONG Long, LI Hua-Cheng, LI Chun-Xia, ZHANG Xian-Zhen, HAN Qiang.
Synthesis and Electrochemical Characterizations of Co-doped Lithium Manganese Oxide Spinel Li1.035Mn1.965O4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(6): 661-666. |
| [10] | LI Yan-Yun, LI Song-Mei, LIU Jian-Hua, YU Mei. Preparation and Anti-mildew Properties of TPN-SDS-layered Double Hydroxide Nanohybrids [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(5): 515-522. |
| [11] | ZHANG Zhi-An, ZHOU Geng, PENG Bin, LU Hai, JIA Ming, LAI Yan-Qing, LI Jie. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Carbon Nanotubes/Cobalt Manganese Oxides Composite Materials for Lithium Air Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(9): 949-955. |
| [12] | HU Ying-Ying, WEN Zhao-Yin, JIN Jun. Rapid Low-cost Synthesis and Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Mesoporous Mn3O4 Nanorods [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(9): 1045-1050. |
| [13] | XIAO Xing-Zhong, YI Qing-Feng. Synthesis and Electrochemical Capacity of MnO2/SMWCNT/PANI Ternary Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(8): 825-830. |
| [14] | WU Da-Wang, ZHANG Qiu-Lin, LIN Tao, GONG Mao-Chu, CHEN Yao-Qiang. Effect of Fe on the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3 at Low Temperature over Mn/CeO2-TiO2 Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(5): 495-500. |
| [15] | LI Li, LIU Fang, WU Feng, CHEN Ren-Jie. Progress of Research on the Manganese Oxide Ion-sieve for Extracting Lithium [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(10): 1009-1016. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||