
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 1279-1288.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150652
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Xue1, 2, ZHANG Wen-Qiang1, YU Bo1, CHEN Jing1
Received:2015-12-28
Revised:2016-02-09
Published:2016-12-16
Online:2016-11-23
About author:WANG Xue. E-mail: wxue225@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Xue, ZHANG Wen-Qiang, YU Bo, CHEN Jing. SOC Stack Impedance Characterization and Identification Based on DRT and ADIS Methods[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1279-1288.
| Item | Parameter |
|---|---|
| DC current/A | 5 |
| AC current/A | 2 |
| Frequency range /kHz | 10 |
| Number of test points | 10 |
Table 1 EIS test parameters
| Item | Parameter |
|---|---|
| DC current/A | 5 |
| AC current/A | 2 |
| Frequency range /kHz | 10 |
| Number of test points | 10 |
| Measurement | Cell-1 | Cell-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOFC | SOEC | SOFC | SOEC | |
| EIS/ (Ω·cm-2) | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| IV/ (Ω·cm-2) | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.19 |
Table 2 Comparison of ASR tested from I-V curves & impedance spectra
| Measurement | Cell-1 | Cell-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOFC | SOEC | SOFC | SOEC | |
| EIS/ (Ω·cm-2) | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| IV/ (Ω·cm-2) | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.19 |
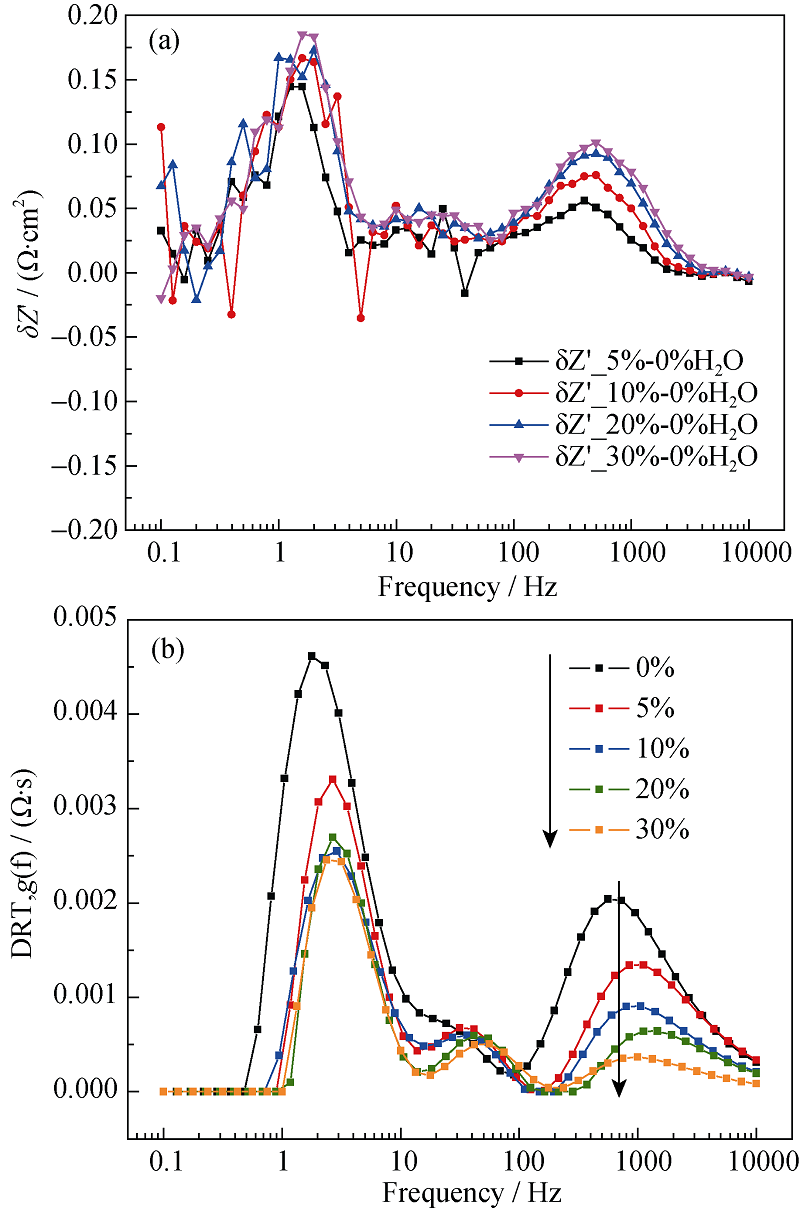
Fig. 9 Dependence of (a) ADIS plot and (b) DRT plot on steam content of the hydrogen electrode^(T = 700℃, SOFC mode, 0~30% H2O in the hydrogen electrode)
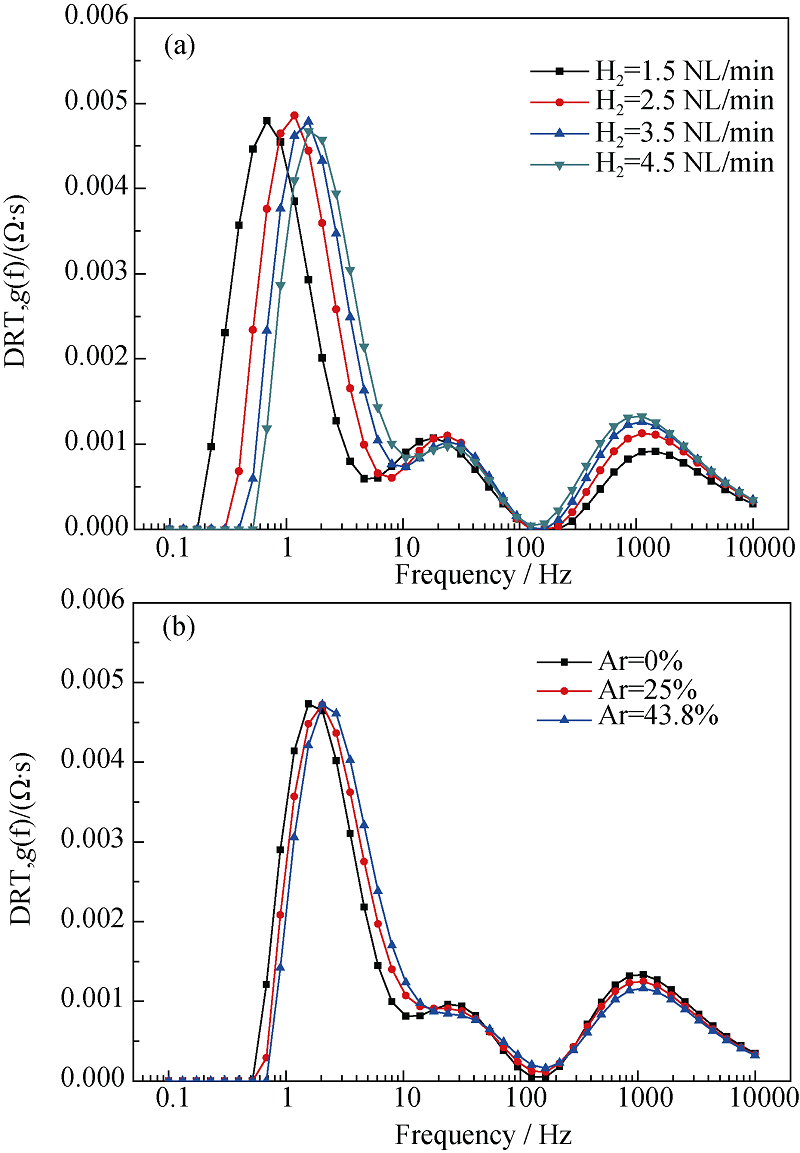
Fig. 10 Dependence of DRT plot on hydrogen flow rate of the hydrogen electrode (a), and on nitrogen flow rate of the hydrogen electrode (b)^(T = 700℃, SOFC mode, 100%H2 or 100%N2 in the hydrogen electrode)
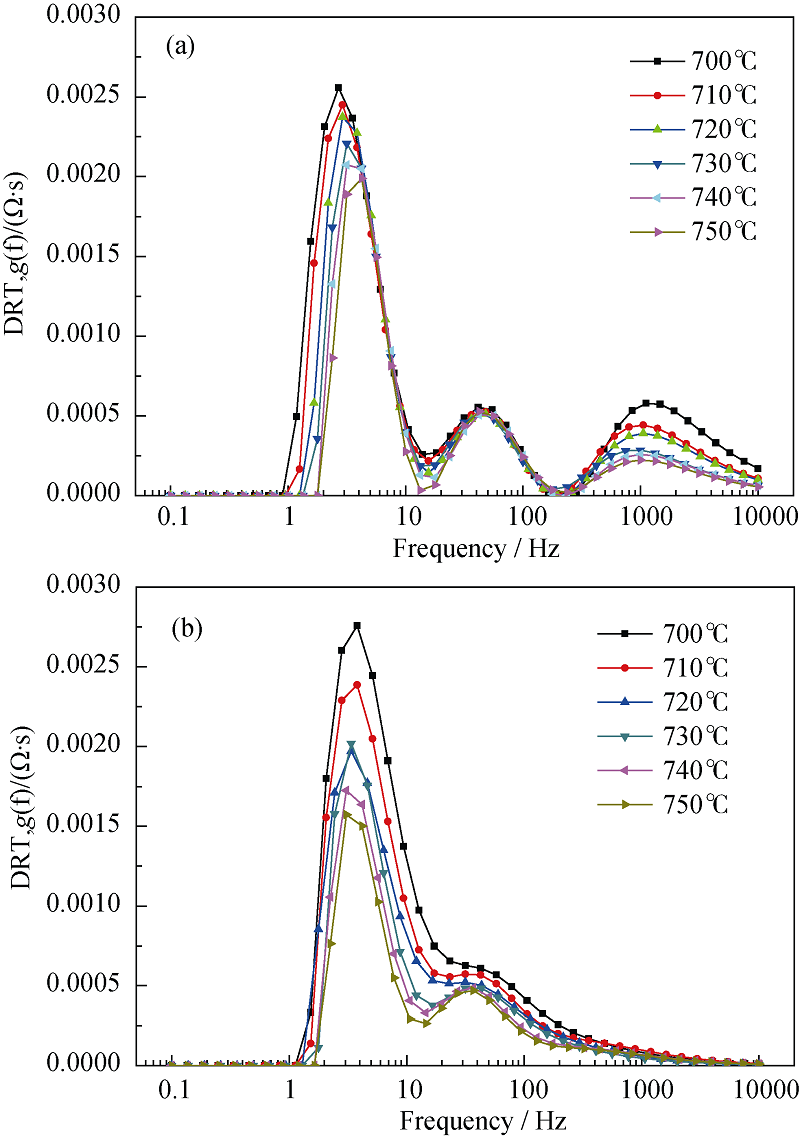
Fig. 12 Dependence of DRT plot on operating temperature^(a) SOFC mode, 20%H2O in the hydrogen electrode, air in the oxygen electrode; (b) SOEC mode, 80%H2O in the hydrogen electrode, air in the oxygen electrode
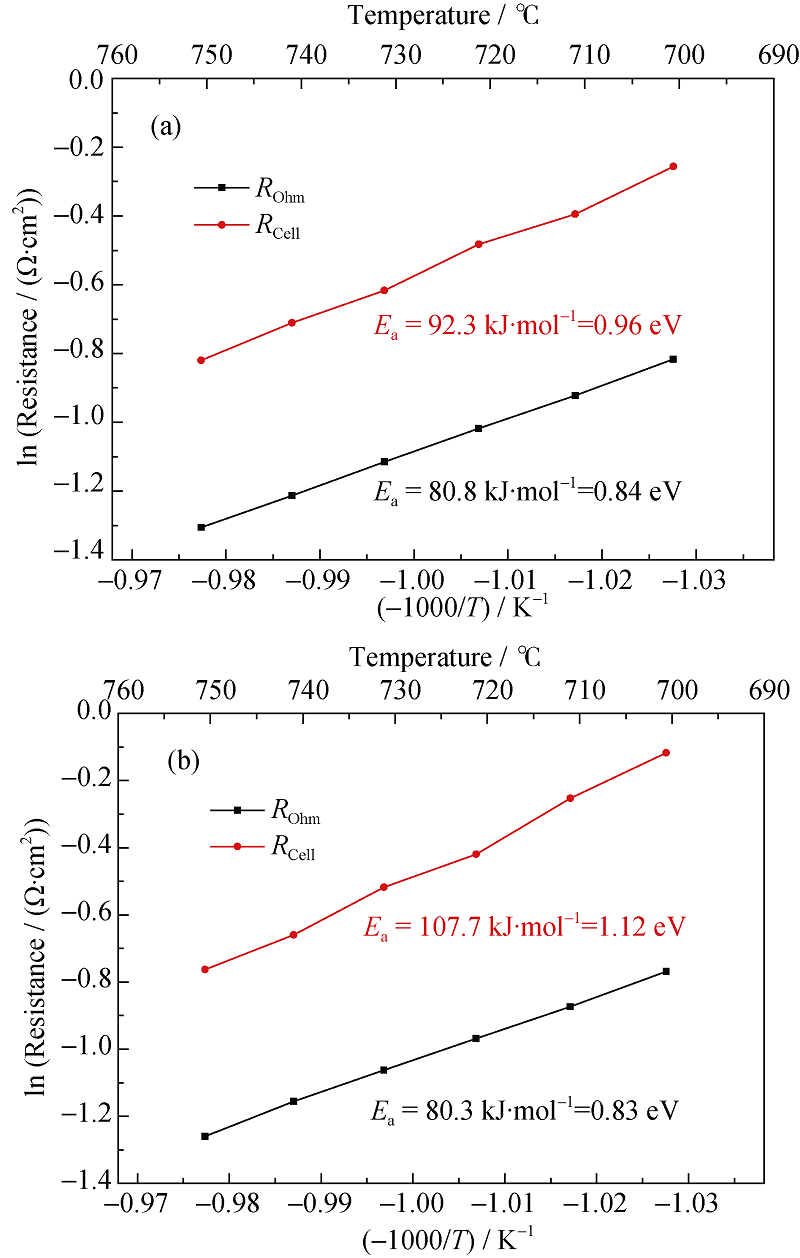
Fig. 13 Arrhenius plots of the reversible SOC^(a) SOFC mode; (b) SOEC mode (50%H2+50%H2O in the hydrogen electrode, air in the oxygen electrode, Temperature range: 700℃~750℃)
| Process | Equivalent circuit | Frequency range /Hz | Dependencies | Physical process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | RQ | 0.01-1 | | Gas diffusion in oxygen electrode |
| P2 | RQ | 1-10 | | Gas diffusion in substrate (fuel electrode) overlapped with gas conversion impedance |
| P3 | Gerischer | 10-100 | | Chemical surface exchange of O2 and O2- bulk diffusion in air electrode |
| P4 | RQ | 100-10000 | | Charge transfer reactions and ionic transport in YSZ and TPB |
Table 3 Processes identified by DRT analysis
| Process | Equivalent circuit | Frequency range /Hz | Dependencies | Physical process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | RQ | 0.01-1 | | Gas diffusion in oxygen electrode |
| P2 | RQ | 1-10 | | Gas diffusion in substrate (fuel electrode) overlapped with gas conversion impedance |
| P3 | Gerischer | 10-100 | | Chemical surface exchange of O2 and O2- bulk diffusion in air electrode |
| P4 | RQ | 100-10000 | | Charge transfer reactions and ionic transport in YSZ and TPB |
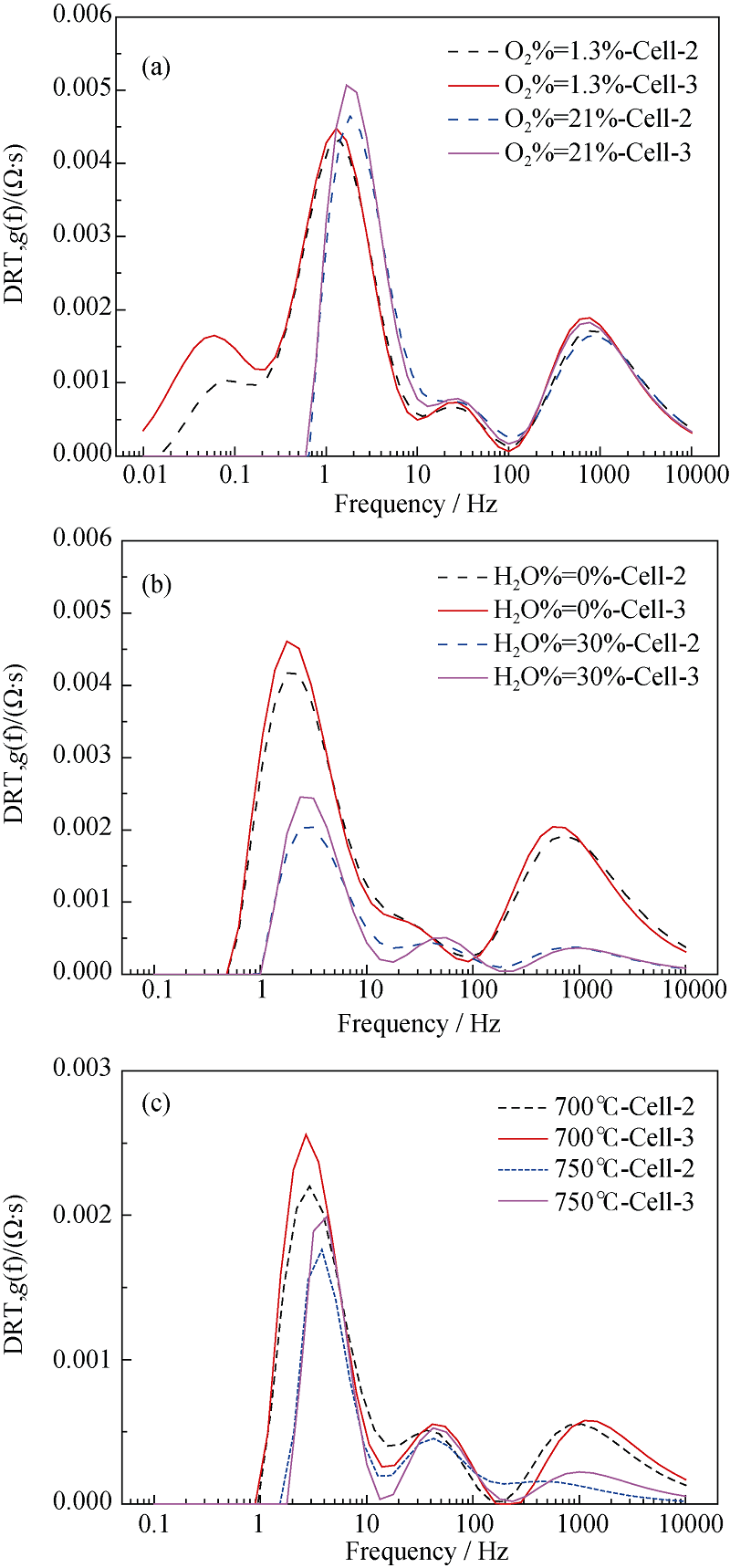
Fig. 14 DRT plots of the Cell-2 and Cell-3 under different conditions in SOFC mode Change of gas composition of hydrogen electrode (a), gas composition of oxygen electrode (b) and operating temperature (c)
| Before degradation | After degradation | Impedance growth rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-2 | Cell-3 | Cell-2 | Cell-3 | Cell-2 | Cell-3 | |
| Ohmic resistance/ (Ω·cm-2) | 0.612 | 0.471 | 1.010 | 0.485 | 65% | 3% |
| Polarization impedance /(Ω·cm-2) | 1.029 | 1.066 | 2.521 | 1.511 | 145% | 42% |
Table 4 Comparison of the resistances of cell-2 and cell-3 before and after degradation
| Before degradation | After degradation | Impedance growth rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-2 | Cell-3 | Cell-2 | Cell-3 | Cell-2 | Cell-3 | |
| Ohmic resistance/ (Ω·cm-2) | 0.612 | 0.471 | 1.010 | 0.485 | 65% | 3% |
| Polarization impedance /(Ω·cm-2) | 1.029 | 1.066 | 2.521 | 1.511 | 145% | 42% |
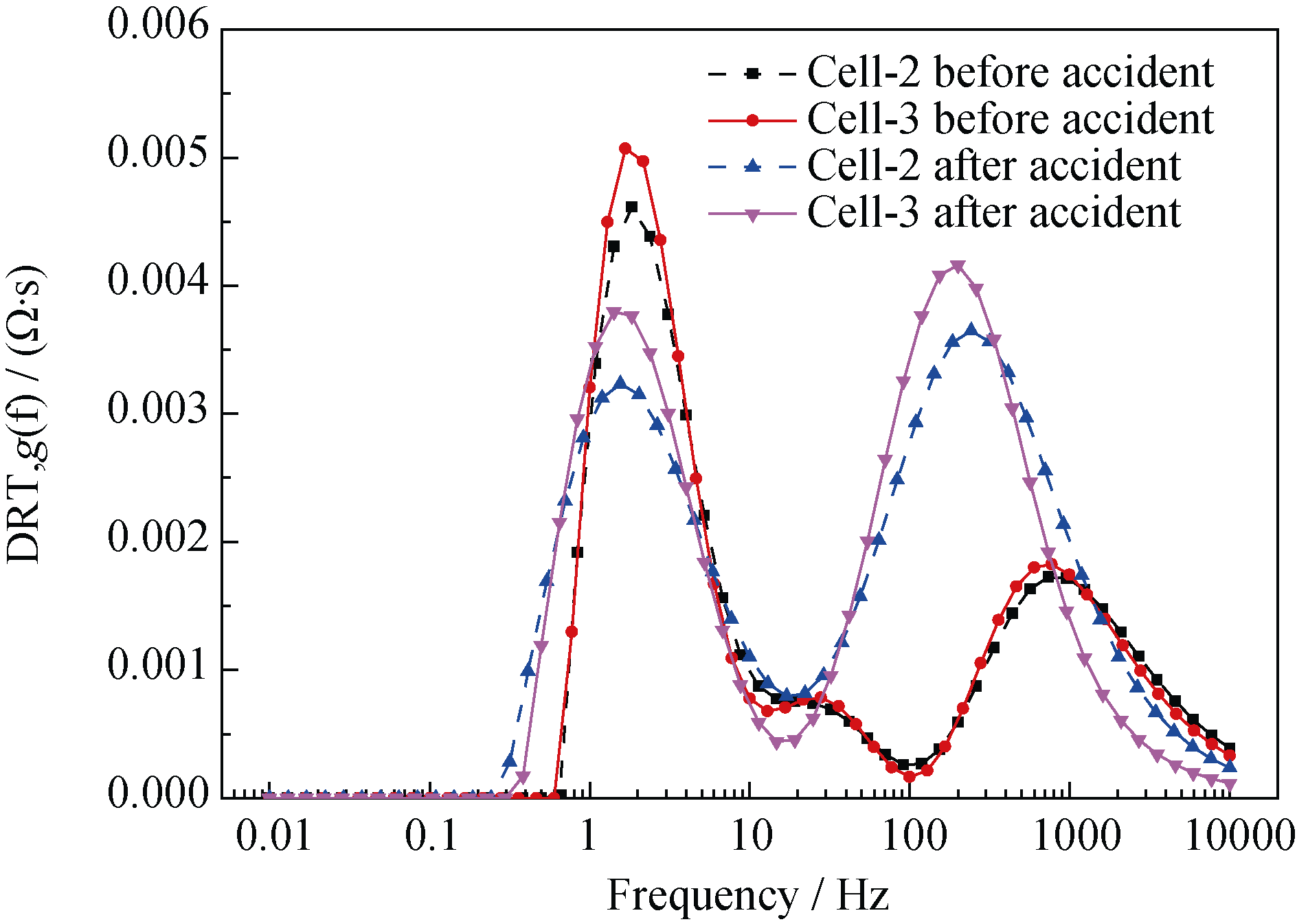
Fig. 17 DRT plots of the cell-2 and cell-3 before and after degradation^(T=700℃, SOECmode, 100%H2 in the hydrogen electrode, air in the oxygen electrode)
| [1] | WACHSMAN E D, LEE K T.Lowering the temperature of solid oxide fuel cells.Science, 2011, 334(6058): 935-939. |
| [2] | EBBESEN S D, JENSEN S H, HAUCH A,et al. High temperature electrolysis in alkaline cells, solid proton conducting cells, and solid oxide cells. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114: 10697-10734. |
| [3] | YU B, ZHANG W Q, XU J M,et al. Status and research of highly efficient hydrogen production through high temperature steam electrolysis at INET. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 35(7): 2829-2835. |
| [4] | MAWDSLEY J R, CARTER J D, KROPF A J,et al.Post-test evaluation of oxygen electrodes from solid oxide electrolysis stacks. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(9): 4198-4207. |
| [5] | MENZLER N H, BATFALSKY P, GROß S,et al. Post-Test characterization of an SOFC short-stack after 17, 000 hours of steady operation. ECS Transactions, 2011, 35(1): 195-206. |
| [6] | NECHACHE A, CASSIR M, RINGUEDÉ A.Solid oxide electrolysis cell analysis by means of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: review. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 258(15): 164-181. |
| [7] | ORAZEM M E, TRIBOLLET B. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Wiley & Sons, Hobo-ken,New Jersey, 2008, 153-162. |
| [8] | VIRKAR A V.Transport through mixed proton, oxygen ion and electron (hole) conductors: Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz type equation.Journal of Power Sources , 2009, 194(2): 753-762. |
| [9] | YU B, LIU M Y, ZHANG W Q,et al. Polarization loss of single solid oxide electrolysis cells and microstructural optimization of the cathode. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2011, 27(2): 395-402. |
| [10] | SCHICHLEIN H,MÜLLER A C, VOIGTS M,et al. Deconvolution of electrochemical impedance spectra for the identification of electrode reaction mechanisms in solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2002, 32: 875-882. |
| [11] | LEONIDE A, SONN V, WEBER A,et al. Evaluation and modeling of the cell resistance in anode-supported solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2008, 155(1): B36-B41. |
| [12] | SCHONLEBER M, IVERS-TIFFEE E.Approximability of impedance spectra by RC elements and implications for impedance analysis.Electrochemistry Communications, 2015, 58(9): 15-19. |
| [13] | JENSEN S H, HAUCH A, HENDRIKSEN P V,et al. A method to separate process contributions in impedance spectra by variation of test conditions. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2007, 154(12): B1325-B1330. |
| [14] | EBBESEN S D, GRAVES C, HAUCH A,et al. Poisoning of solid oxide electrolysis cells by impurities. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(10): B1419-B1429. |
| [15] | KUZNECOV M, OTSCHIK P, OBENAUS P,et al. Diffusion controlled oxygen transport and stability at the perovskite/ electrolyte interface. Solid State Ionics, 2003, 157(1-4): 371-378. |
| [16] | WEESE J.A reliable and fast method for the solution of Fredhol integral equations of the first kind based on Tikhonov regularization.Computer Physics Communications, 1992, 69(1): 99-111. |
| [17] | BARFOD R, HAGEN A, RAMOUSSE S,et al. Break down of losses in thin electrolyte SOFCs. Fuel Cells, 2006, 6(2): 141-145. |
| [18] | JORGENSEN M J, MOGENSEN M.Impedance of solid oxide fuel cell LSM/YSZ composite cathodes.Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(5): A433-A442. |
| [19] | FU Y.Theoretical and Experimental Study of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) Using Impedance Spectra. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2014. |
| [1] | WANG Yue, CUI Changsong, WANG Shiwei, ZHAN Zhongliang. Symmetrical La3+-doped Sr2Fe1.5Ni0.1Mo0.4O6-δ Electrode Solid Oxide Fuel Cells for Pure CO2 Electrolysis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1323-1329. |
| [2] | LI Xiang, GE Wu-Jie, WANG Hao, QU Mei-Zhen. Research Progress on the Capacity Fading Mechanisms of High-Nickel Ternary Layered Oxide Cathode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 113-121. |
| [3] | SU Jing, WU Xing-Long, GUO Yu-Guo. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C Nanocomposite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(11): 1248-1254. |
| [4] | YU Bo, ZHANG Wen-Qiang, LIANG Ming-De, ZHANG Ping, XU Jing-Ming. Effect of PMMA Pore Former on Hydrogen Production Performance of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(8): 807-812. |
| [5] | KONG Jiang-Rong, ZHOU Tao, LIU Peng, ZHANG Yong, XU Jing-Ming. Preparation and Characterization of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ-based Composite Anode for Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(10): 1049-1052. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xue-Lin,JIANG Zhao-Hua,YAO Zhong-Ping,WU Zhen-Dong. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy during the Process ofPlasma Electrolytic Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(1): 111-116. |
| [7] |
GUAN Yong-Jun,XIA Yuan.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of PEO Coating on Aluminum Alloy in NaCl Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(4): 784-788. |
| [8] | CHEN Yu-Hong,TANG Zhi-Yuan,HE Yan-Bing. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of Layer Lithium Cobalt Nickel Manganese Oxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(3): 442-446. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||