
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 1141-1146.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160186
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Yao-Qin1, ZHENG Guo-Yuan1, MO Shu-Yi1, HE Li-Qiu2, WANG Dong-Sheng2, LONG Fei1
Received:2016-03-28
Revised:2016-05-02
Published:2016-10-20
Online:2016-09-23
About author:HUANG Yao-Qin. E-mail: m15296818093@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
HUANG Yao-Qin, ZHENG Guo-Yuan, MO Shu-Yi, HE Li-Qiu, WANG Dong-Sheng, LONG Fei. Liquid-assisted Hot-pressed Sintering of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 Targets[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1141-1146.
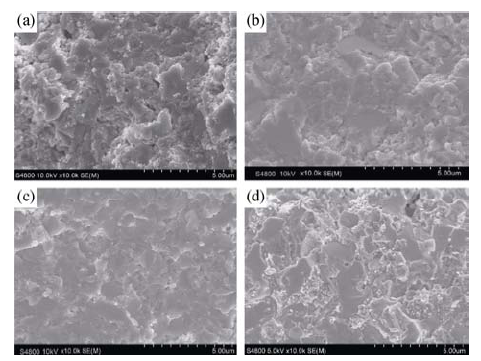
Fig. 5 Cross-sectional FESEM images of CIGS targets sintered at different temperatures from different formula powders (a) Formula A, T=600℃; (b) Formula A, T=625℃; (c) Formula B, T=550℃; (d) Formula B, T=575℃
| Sample | Additive CuSe | Temperature /℃ | Cu / at% | In / at% | Ga /at% | Se / at% | Loss on ignition / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw material | No | -- | 24.98 | 17.52 | 7.49 | 50.01 | -- |
| a | No | 550 | 25.18 | 17.44 | 7.49 | 49.89 | 3.11 |
| b | No | 575 | 24.96 | 17.41 | 7.56 | 50.07 | 3.44 |
| c | No | 600 | 25.22 | 17.43 | 7.39 | 49.96 | 3.75 |
| d | No | 625 | 25.19 | 17.49 | 7.59 | 49.73 | 3.88 |
| Raw material | Yes | -- | 25.02 | 17.49 | 7.47 | 50.02 | -- |
| e | Yes | 525 | 24.98 | 17.46 | 7.48 | 50.08 | 0.49 |
| f | Yes | 550 | 24.89 | 17.42 | 7.45 | 50.24 | 0.59 |
| g | Yes | 575 | 25.04 | 17.52 | 7.55 | 49.89 | 0.67 |
| h | Yes | 600 | 25.12 | 17.48 | 7.52 | 49.88 | 0.74 |
| i | Yes | 625 | 24.78 | 17.38 | 7.45 | 50.39 | 0.83 |
Table 1 Composition proportion and loss on ignition table of targets by different formula
| Sample | Additive CuSe | Temperature /℃ | Cu / at% | In / at% | Ga /at% | Se / at% | Loss on ignition / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw material | No | -- | 24.98 | 17.52 | 7.49 | 50.01 | -- |
| a | No | 550 | 25.18 | 17.44 | 7.49 | 49.89 | 3.11 |
| b | No | 575 | 24.96 | 17.41 | 7.56 | 50.07 | 3.44 |
| c | No | 600 | 25.22 | 17.43 | 7.39 | 49.96 | 3.75 |
| d | No | 625 | 25.19 | 17.49 | 7.59 | 49.73 | 3.88 |
| Raw material | Yes | -- | 25.02 | 17.49 | 7.47 | 50.02 | -- |
| e | Yes | 525 | 24.98 | 17.46 | 7.48 | 50.08 | 0.49 |
| f | Yes | 550 | 24.89 | 17.42 | 7.45 | 50.24 | 0.59 |
| g | Yes | 575 | 25.04 | 17.52 | 7.55 | 49.89 | 0.67 |
| h | Yes | 600 | 25.12 | 17.48 | 7.52 | 49.88 | 0.74 |
| i | Yes | 625 | 24.78 | 17.38 | 7.45 | 50.39 | 0.83 |
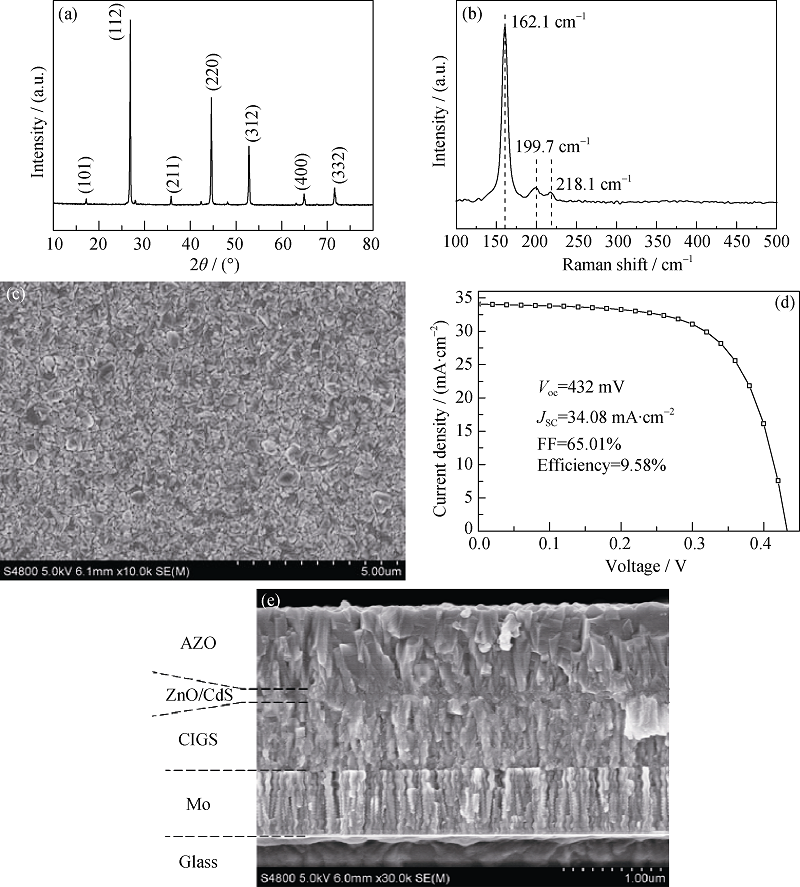
Fig. 7 XRD pattern(a), Raman pattern(b) and plan view (c) of CIGS thin film preparation by sputtering-heat treatment, and its I-V pattern(d) and cross-sectional view (e) FESEM image of a single battery
| [1] | SEIKE S, SHIOSAK K, KURAMOTO M, et al.Development of high-efficiency CIGS integrated submodules using in-line deposition technology.Solar Energy Material & Solar Cells, 2011, 95(1): 254-256. |
| [2] | ZHANG L, LIU F F, LI F Y, et al.Structural, optical and electrical properties of low-temperature deposition Cu(InxGa1-x)Se2 thin films.Solar Energy Material & Solar Cells, 2012, 99(10): 356-361. |
| [3] | MOON D G, AHN S J, YUN J H, et al.Ex-situ and in-situ analyses on reaction mechanism of CuInSe2 (CIS) formed by selenization of sputter deposited CuIn precursor with Se vapor.Solar Energy Material & Solar Cells, 2011, 95(10): 2786-2794. |
| [4] | LI Z Q, LIU Q Q, LI J J, et al.Growth of Zn doped Cu(In, Ga)Se2 thin films by RF sputtering for solar cell applications.Solid-State Electronics, 2012, 68: 80-84. |
| [5] | OUYANG L Q, ZHUANG DM, ZHAO M, et al.Cu(In, Ga)Se2 solar cell with 16.7% active-area efficiency achieved by sputtering from a quaternary target.Physica Status Solidi A, 2015, 212(8): 1774-1778. |
| [6] | SHUI J H, LI Z Q, ZHANG D W, et al.Fabrication of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 thin films by sputtering from a single quaternary chalcogenide target.Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 2011, 19(2): 160-164. |
| [7] | 梅迪. 单靶磁控一步溅射制备CIGS薄膜. 成都: 电子科技大学硕士学位论文, 2011. |
| [8] | 孔慧. 单靶磁控溅射制备CIGS太阳能电池材料的研究. 长春: 东北师范大学博士学位论文, 2014. |
| [9] | SURYSNARAYANA C, IVANOV E, NOUFI R, et al.Synthesis and processing of a Cu-In-Ga-Se sputtering target.Thin Solid Films, 1998, 332: 340-344. |
| [10] | 田村友哉, 高见英生, 生泽正克, 等. Cu-In-Ga-Se 四元合金溅射靶, 中国, C23C14/34, ZL201080048413.7, 2014.08.27. |
| [11] | HSU W H, HSIANG H I, YEN F C, et al.Low-temperature sintered CuIn0.7Ga0.3Se2 prepared by colloidal processing.Journal European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(14): 3753-3757. |
| [12] | 王东生, 黄开盛, 龙飞, 等.太阳能电池铜铟镓硒薄膜关键靶材及其制备方法. 中国, C23C14/06, ZL200810073549.8. 2008.09.10. |
| [13] | ZHANG N, ZHUANG D M, ZHANG G.An investigation on preparation of CIGS targets by sintering process.Material Science Engineering: B, 2010, 166: 34-40. |
| [14] | LI XIAO-LONG, ZHUANG DA-MING, ZHAO MING, et al.Preparation and performance research of high dense rate of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 ceramic target.Journal of Solar Energy, 2013, 32(12): 2196-2199. |
| [15] | BEMARDINI G P, CATANI A.The Cu-Se system.Mineralium Deposita, 1968, 3(4): 375-380. |
| [16] | ROY S, GUHA P, KUNDU S N, et al.Characterization of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 films by Raman scattering.Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2002, 73(1): 24-30. |
| [17] | 乔英杰. 材料合成与制备. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012: 160-178. |
| [18] | KINGERY W D.Surface tension of some liquid oxides and their temperature coefficients.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1959, 42(1): 6-10. |
| [19] | KINGERY W D, WOULBROUN J M, CHARVAT F R.Effects of applied pressure on densification during sintering in the presence of a liquid phase.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1963, 46(8): 391-395. |
| [1] | MAN Xin, WU Nan, ZHANG Mu, HE Hongliang, SUN Xudong, LI Xiaodong. Lu2O3-MgO Nano-powder: Synthesis and Fabrication of Composite Infrared Transparent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1263-1269. |
| [2] | CHENG Xiaokun, ZHANG Yue, Lü Haijun, LIU Xinying, HOU Senlin, CHEN Aibing. Porous Carbon Nanomaterials Based Tumor Targeting Drug Delivery System: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 9-24. |
| [3] | CHEN Haoyu, ZHANG Yiwen, WU Zhong, QIN Zhenbo, WU Shanshan, HU Wenbin. Room Temperature Magnetoresistance Property of Co-TiO2 Nanocomposite Film Prepared by Strong Magnetic Target Co-sputtering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1263-1267. |
| [4] | CHENG Yi-Tian, QIU Wan-Qi, ZHOU Ke-Song, LIU Zhong-Wu, JIAO Dong-Ling, ZHONG Xi-Chun, ZHANG Hui. Low-temperature Deposition of α-Al2O3 Films by Reactive Sputtering Al+α-Al2O3 Target [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 862-866. |
| [5] | Xin XU, Shu-Rong WANG, Xun MA, Shuai YANG, Yao-Bin LI, Hong-Bin YANG. Comparative Study of Cu2ZnSnS4 Thin Films Prepared by Chalcogenide and Single Targets [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 529-534. |
| [6] | HE Xu, REN Sheng-Qiang, LI Chun-Xiu, WU Li-Li, ZHANG Jing-Quan, DU Zheng. Zn1-xMgxO: Band Structure and Simulation as Window Layer for CdTe Solar Cell by SCAPS Software [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 635-640. |
| [7] | CAO Sheng, WU Li-Li, FENG Liang-Huan, WANG Wen-Wu, ZHANG Jing-Quan, YU Xiao-Qi, LI Xin-Xin, LI Wei, LI Bing. Effect of Substrate Temperature on CdTe Thin Film Property and Solar Cell Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(2): 141-147. |
| [8] | XIE Shou-Dong, WANG Gang, CHEN Hui-Yuan, LIN Hong, YAN Zhi-Nan, ZHANG Hui. Lycium ruthenicum Murray and Graphene Nanoplates for Dye Sensitized Solar Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1117-1122. |
| [9] | SUN Bao-Ping, PANG Shan, HU Bin-Bin, YANG Guang-Hong, WAN Shao-Ming, DU Zu-Liang. Influence of pH Value in Electrolyte on Photovoltaic Performance of CIGS Thin-films Prepared by Electrochemical Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(2): 141-145. |
| [10] | CUI Xu-Mei, ZUO Cheng-Yang, LAN De-Jun, WANG Jun. Preparation and Electrical Properties of TiO2/SnO2 Nanocrystalline Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(11): 1233-1236. |
| [11] | HUANG Shuai, LI Chen-Hui, SUN Yi-Hua, KE Wen-Ming. Influence of the Substrate Temperature on the Properties of Nb-doped TiO2 Films Deposited by DC Magnetron Sputtering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(1): 64-68. |
| [12] | ZHOU Zhen, ZHAO Kui, WANG Yao-Ming, HUANG Fu-Qiang. Surface Reconstructionof Epitaxial CIS Thin Films and Device Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(2): 113-118. |
| [13] | GU Wei, YANG Jian, QIU Tai, ZHU She-Ming. In-situ Synthesis and Mechanical Properties of (TiB2+TiC)/Ti3SiC2 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(10): 1081-1086. |
| [14] | ZHU Jia-Qi,LU Jia,TIAN Gui,TAN Man-Lin,GENG Da. Using Boron Doped Amorphous Diamond Films as Window Layer of Amorphous Silicon Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(5): 1064-1066. |
| [15] |
CHEN Zhu,ZHANG Shu-Ren,DU Shan-Yi,YANG Cheng-Tao,ZENG Ze-Yu,LI Bo,SUN Ming-Xia.
Li-doped ZnO Ceramic Target Preparation and RF Magnetron Sputtering ZnO Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(4): 1011-1017. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||