
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 1051-1057.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160212
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Suo-Long, WANG Xiao-Fang, JIANG Chun-Li, ZHAO Ya-Wen, ZENG Rong-Guang, WANG Huai-Sheng, LAI Xin-Chun
Received:2016-03-31
Revised:2016-05-17
Published:2016-10-20
Online:2016-09-23
Supported by:CLC Number:
YANG Suo-Long, WANG Xiao-Fang, JIANG Chun-Li, ZHAO Ya-Wen, ZENG Rong-Guang, WANG Huai-Sheng, LAI Xin-Chun. Doping of InP Quantum Dots and Its Optical Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1051-1057.
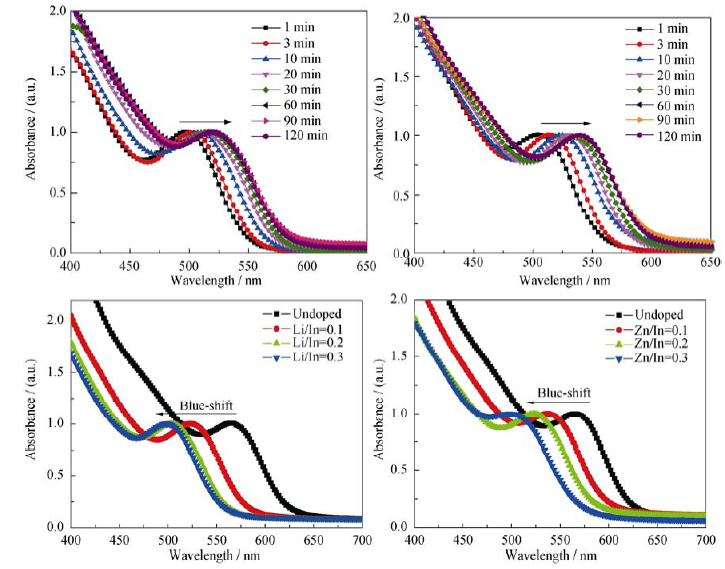
Fig. 1 Evolution absorption spectra of (a) Li: InP and (b) Zn: InP QDs. Absorption spectra of (c) Li: InP QDs and (d) Zn: InP QDs with different dopant contents
| Sample | Peak/nm | D/nm | Eg/eV | Sample | Peak/nm | D/nm | Eg/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undoped | 564 | 2.91 | 2.20 | Undoped | 564 | 2.91 | 2.20 |
| Zn/In=0.1 | 534 | 2.55 | 2.32 | Li/In=0.1 | 520 | 2.40 | 2.38 |
| Zn/In=0.2 | 518 | 2.38 | 2.39 | Li/In=0.2 | 499 | 2.20 | 2.48 |
| Zn/In=0.3 | 491 | 2.13 | 2.53 | Li/In=0.3 | 495 | 2.16 | 2.51 |
Table 1 Calculated D and Eg of Li: InP and Zn: InP QDs
| Sample | Peak/nm | D/nm | Eg/eV | Sample | Peak/nm | D/nm | Eg/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undoped | 564 | 2.91 | 2.20 | Undoped | 564 | 2.91 | 2.20 |
| Zn/In=0.1 | 534 | 2.55 | 2.32 | Li/In=0.1 | 520 | 2.40 | 2.38 |
| Zn/In=0.2 | 518 | 2.38 | 2.39 | Li/In=0.2 | 499 | 2.20 | 2.48 |
| Zn/In=0.3 | 491 | 2.13 | 2.53 | Li/In=0.3 | 495 | 2.16 | 2.51 |
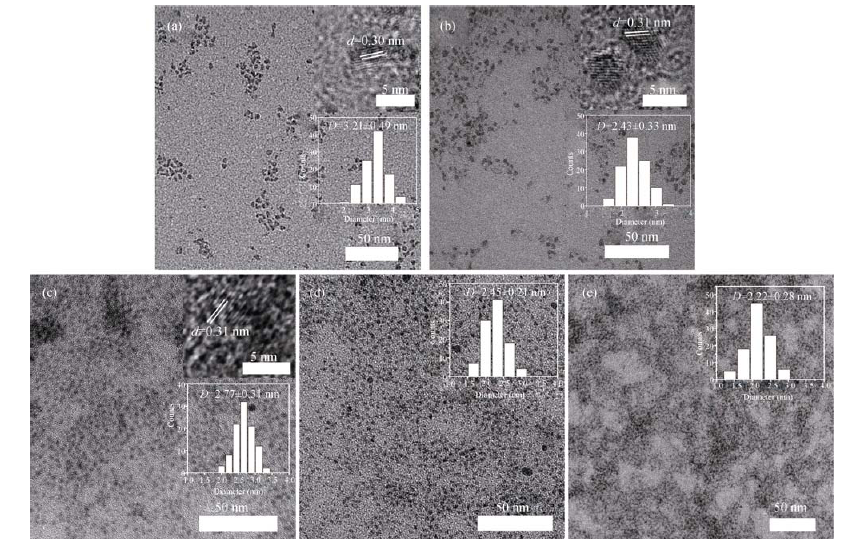
Fig. 2 TEM images of undoped InP QDs, Li: InP QDs and Zn: InP QDs QDs The insets are the corresponding HRTEM images (a-c) and size distribufion (a-e) (a) undoped InP QDs, (b) Li: InP QDs with Li/In=0.1, Zn: InP QDs QDs with (c) Zn/In=0.1 (d) Zn/In=0.2, (e) Zn/In=0.3
| [1] | TALAPIN D V, LEE J S, KOVALENKO M V, et al.Prospects of colloidal nanocrystals for electronic and optoelectronic applications.Chem. Rev., 2010, 110(1): 389-458. |
| [2] | WU P, YAN X P.Doped quantum dots for chemo/biosensing and bioimaging.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42(12): 5489-5521. |
| [3] | MUSHONGA P, ONANI M O, MADIEHE A M, et al.Indium phosphide-based semiconductor nanocrystals and their applications.Journal of Nanomaterials, 2012, 12(19): 5869-5878. |
| [4] | YANG S L, ZHAO P X, ZHAO X C, et al.InP and Sn: InP based quantum dot sensitized solar cells.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(43): 21922-21929. |
| [5] | SOENEN S J, MANSHIAN B B, AUBERT T, et al.Cytotoxicity of cadmium-free quantum dots and their use in cell bioimaging.Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2014, 27(6): 1050-1059. |
| [6] | ADAM S, TALAPIN D V, BORCHERT H, et al.The effect of nanocrystal surface structure on the luminescence properties: photoemission study of HF-etched InP nanocrystals.J. Chem. Phys., 2005, 123(8): 084706. |
| [7] | ADAM S, MCGINLEY C, MOLLER T, et al.Photoemission study of size selected InP nanocrystals: the relationship between luminescence yield and surface structure.Eur. Phys. J. D., 2003, 24(1): 373-376. |
| [8] | ZHENG J J, CAO S, GAO F M, et al.Synthesis of effective and qualified Cu-doped ZnSe quantum dots and their optical properties.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(2): 159-164. |
| [9] | THUY U T, MAURICE A, LIEM N Q, et al.Europium doped In(Zn)P/ZnS colloidal quantum dots.Dalton Trans., 2013, 42(35): 12606-12610. |
| [10] | SOMASKANDAN K, TSOI G M, WENGER L E, et al.Isovalent doping strategy for manganese introduction into III-V diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles: InP : Mn.Chem. Mater., 2005, 17(5): 1190-1198. |
| [11] | XIE R G, PENG X G.Synthesis of Cu-doped InP nanocrystals (d-dots) with ZnSe diffusion barrier as efficient and color-tunable NIR emitters.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(30): 10645-10651. |
| [12] | THUY U T, REISS P, LIEM N Q.Luminescence properties of In(Zn)P alloy core/ZnS shell quantum dots.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, 97(19): 193104. |
| [13] | BATTAGLIA D, PENG X G.Formation of high quality InP and InAs nanocrystals in a noncoordinating solvent.Nano Lett., 2002, 2(9): 1027-1030. |
| [14] | TUINENGA C, JASINSKI J, IWAMOTO T, et al.In situ observation of heterogeneous growth of CdSe quantum dots: effect of indium doping on the growth kinetics.ACS Nano, 2008, 2(7): 1411-1421. |
| [15] | MOCATTA D, COHEN G, SCHATTNER J, et al.Heavily doped semiconductor nanocrystal quantum dots.Science, 2011, 332(6025): 77-81. |
| [16] | GUZELIAN A A, KATARI J E B, KADAVANICH A V, et al. Synthesis of size-selected, surface-passivated InP nanocrystals.J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100(17): 7212-7219. |
| [17] | FU H X, ZUNGER A.Local-density-derived semiempirical nonlocal pseudopotentials for InP with applications to large quantum dots.Phys Rev B, 1997, 55(3): 1642-1653. |
| [18] | ZHANG Z L, LI D Z, XIE R G, et al.Insights into the energy levels of semiconductor nanocrystals by a dopant approach.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2013, 52(19): 5052-5055. |
| [19] | SCHWARTZ D A, NORBERG N S, NGUYEN Q P, et al.Magnetic quantum dots: synthesis, spectroscopy, and magnetism of CO2+- and Ni2+-doped ZnO nanocrystals.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(43): 13205-13218. |
| [20] | ROCKENBERGER J, ZUM FELDE U, TISCHER M, et al.Near edge x-ray absorption fine structure measurements (XANES) and extended x-ray absorption fine structure measurements (EXAFS) of the valence state and coordination of antimony in doped nanocrystalline SnO2.J. Chem. Phys., 2000, 112(9): 4296-4304. |
| [21] | PARK J, KIM S W.CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots by cation exchange and their blue-shifted photoluminescence.J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(11): 3745-3750. |
| [22] | VIRIEUX H, LE TROEDEC M, CROS-GAGNEUX A, et al.InP/ZnS nanocrystals: coupling NMR and XPS for fine surface and interface description.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(48): 19701-19708. |
| [23] | XU S, ZIEGLER J, NANN T.Rapid synthesis of highly luminescent InP and InP/ZnS nanocrystals.J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18(23): 2653-2656. |
| [24] | SHARMA M, MUSHRUSH M, WRIGHT R J, et al.Growth of polycrystalline zinc phosphide thin films by reactive radio frequency magnetron sputtering.Thin Solid Films, 2015, 591(A): 32-38. |
| [25] | HO M Q, ESTEVES R J A, KEDARNATH G, et al. Size-dependent optical properties of luminescent Zn3P2 quantum dots.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(19): 10576-10584. |
| [1] | KONG Guoqiang, LENG Mingzhe, ZHOU Zhanrong, XIA Chi, SHEN Xiaofang. Sb Doped O3 Type Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2 Cathode Material for Na-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 656-662. |
| [2] | YANG Yingkang, SHAO Yiqing, LI Bailiang, LÜ Zhiwei, WANG Lulu, WANG Liangjun, CAO Xun, WU Yuning, HUANG Rong, YANG Chang. Enhanced Band-edge Luminescence of CuI Thin Film by Cl-doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 687-692. |
| [3] | QI Zhanguo, LIU Lei, WANG Shouzhi, WANG Guogong, YU Jiaoxian, WANG Zhongxin, DUAN Xiulan, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Progress in GaN Single Crystals: HVPE Growth and Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [4] | WANG Zhiqiang, WU Ji’an, CHEN Kunfeng, XUE Dongfeng. Large-size Er,Yb:YAG Single Crystal: Growth and Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 329-334. |
| [5] | LU Chenhui, GE Wanyin, SONG Panpan, ZHANG Panfeng, XU Meimei, ZHANG Wei. Luminescence Property of Eu Doped SiAlON Phosphors for White LEDs [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 97-104. |
| [6] | WANG Yang, FAN Guangxin, LIU Pei, YIN Jinpei, LIU Baozhong, ZHU Linjian, LUO Chengguo. Microscopic Mechanism of K+ Doping on Performance of Lithium Manganese Cathode for Li-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [7] | JIAO Boxin, LIU Xingchong, QUAN Ziwei, PENG Yongshan, ZHOU Ruonan, LI Haimin. Performance of Perovskite solar cells Doped with L-arginine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 669-675. |
| [8] | WANG Xinjian, ZHU Yixuan, ZHANG Peng, YANG Wenlong, WANG Ting, HUAN Yu. Phase Structure and Piezoelectric Property of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1-xSnx)O3 Lead-free Piezoceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 513-519. |
| [9] | ZHANG Fengjuan, HAN Boning, ZENG Haibo. Perovskite Quantum Dot Photovoltaic and Luminescent Concentrator Cells: Current Status and Challenges [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 117-128. |
| [10] | LI Gaoran, LI Hongyang, ZENG Haibo. Recent Progress of Boron-based Materials in Lithium-sulfur Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 152-162. |
| [11] | LOU Xunuo, DENG Houquan, LI Shuang, ZHANG Qingtang, XIONG Wenjie, TANG Guodong. Thermal and Electrcial Transport Properities of Ge Doped MnTe Thermoelectrics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [12] | LIU Dingwei, ZENG Jiangtao, ZHENG Liaoying, MAN Zhenyong, RUAN Xuezheng, SHI Xue, LI Guorong. High Piezoelectric Property and Low Electric Field-strain Hysteresis of BiAlO3-doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1365-1370. |
| [13] | REN PeiAn, WANG Cong, ZI Peng, TAO Qirui, SU Xianli, TANG Xinfeng. Effect of Te and In Co-doping on Thermoelectric Properties of Cu2SnSe3 Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1079-1086. |
| [14] | GAN Hongyu, FENG Yan, YANG Dehong, TIAN Yubin, LI Yang, XING Tao, LI Zhi, ZHAO Xuebo, DAI Pengcheng. Heteroatom-doped Biochar for Direct Dehydrogenation of Propane to Propylene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1058-1064. |
| [15] | LI Bangxin, ZHANG Qian, XIAO Jie, XIAO Wenyan, ZHOU Ying. Iron-doping Enhanced Basic Nickel Carbonate for Moisture Resistance and Catalytic Performance of Ozone Decomposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 45-50. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||