
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 1039-1045.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160214
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Xiu-Chun
Received:2016-03-31
Revised:2016-05-16
Published:2016-10-20
Online:2016-09-23
Supported by:CLC Number:
YANG Xiu-Chun. Influences of Ion Exchange and Thermal Treatment on Photoluminescence of Noble Metal Doped Silicate Glasses[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1039-1045.
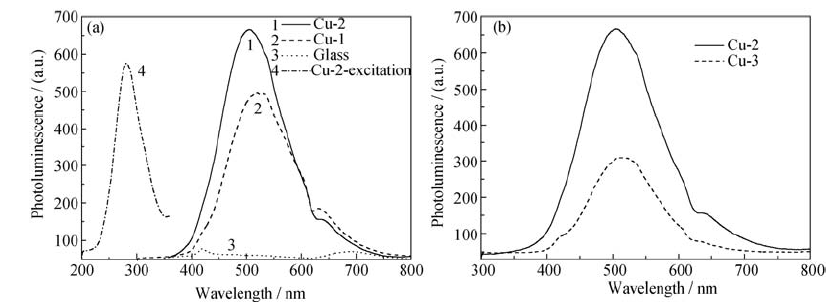
Fig. 1 Influences of ion-exchanged period (a) and temperature (b) on photoluminescence of Cu-doped silicate glasses PL spectra excited by 280 nm and PLE spectra detected by 500 nm
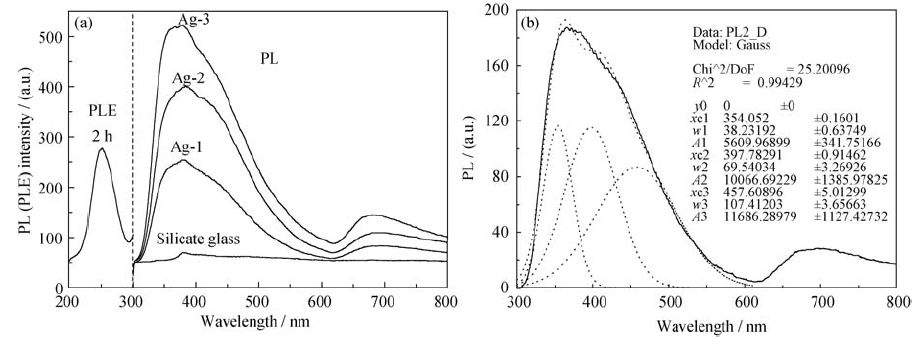
Fig. 4 (a) PL spectra of Ag-doped silicate glasses excited by 240 nm and a representative excitation spectrum detected by 360 nm emission; (b) PL differential spectrum of sample Ag-1 subtracting sodalime silicate glass (solid line) and the corresponding Gaussian fits (dot lines)
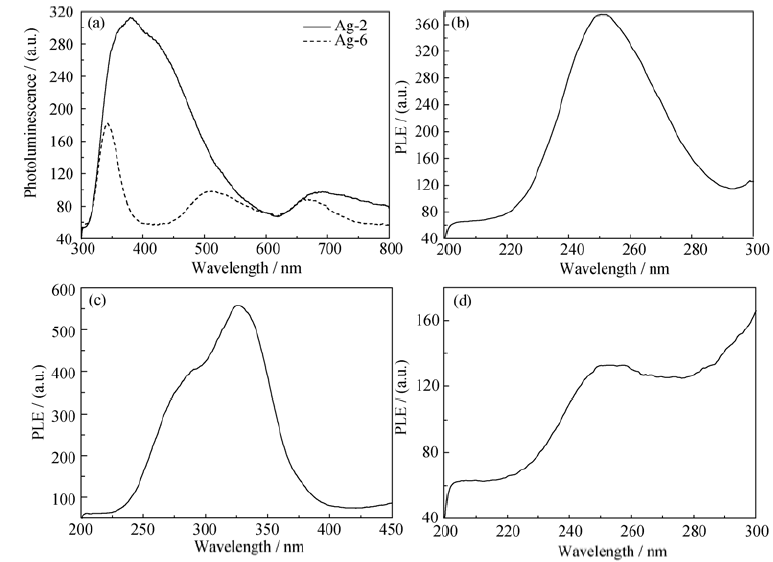
Fig. 6 PL and PLE spectra of samples Ag-2 and Ag-6 (a) PL spectra excited by 240 nm; (b-d) PLE spectra of Ag-6 detected by 345 nm, 510 nm and 670 nm, respectively
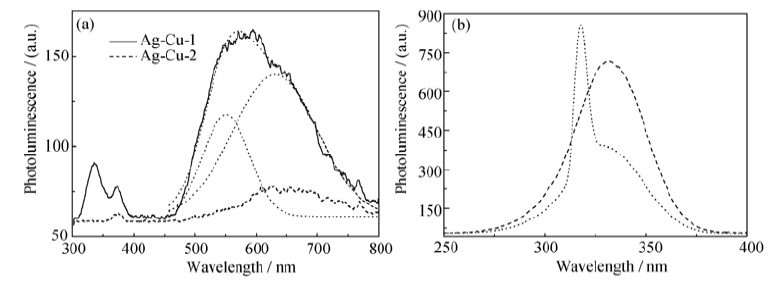
Fig. 7 PL and PLE spectra of samples Ag-Cu-1 and Ag-Cu-2 (a) PL spectra excited by 240 nm (b) PLE spectra of sample Ag-Cu-1 detected by 550 nm (dash curve) and 640 nm (dot curve), respectively
| [1] | KREIBIG U, VOLLMER M.Optical Properties of Metal Clusters. Berlin: Springer, 1995. 300. |
| [2] | FARADAY M. The Bakerian Lecture: On the relations of gold and other metals to light. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 8(8):356-361. |
| [3] | DOERINGg W E, NIE S M.Single-molecule and single-nanoparticle SERS: Examining the roles of surface active sites and chemical enhancementJ. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106(2):311-317. |
| [4] | CAMDEN J P, DIERINGER J A, ZHAO J, et al.Controlled plasmonic nanostructures for surface-enhanced spectroscopy and sensing.Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41(12): 1653-1661. |
| [5] | HAES A J, DUYNE R P V. A nanoscale optical biosensor: sensitivity and selectivity of an approach based on the localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of triangular silver nanoparticles.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124(35):10596-10604. |
| [6] | RASCHKE G, KOWARIK S, FRANZL T, et al.Biomolecular recognition based on single gold nanoparticle light scattering.Nano Lett., 2003, 3(7): 935-938. |
| [7] | JAIN P K, HUANG X H, EL-SAYED I H, et al. Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine.Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41(12):1578-1586. |
| [8] | COTTER D, MANNING R J, BLOK K J, et al.Nonlinear optics for high-speed digital information processing.Science, 1999, 286(5444):1523-1528. |
| [9] | EATON D F.Nonlinear optical materials.Science, 1991, 253(5017):281-287. |
| [10] | WANG W, YANG G, CHEN Z, et al.Iron nanoparticles in amorphous BaTiO3 thin films with large third-order optical nonlinearity.Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 92(12):7242-7245 |
| [11] | DONG Z W, YANG X C, LI Z H, et al.Ultrafast dynamics of copper nanoparticles embedded in soda-lime silicate glass fabricated by ion exchange.Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517(21): 6046-6049. |
| [12] | YANG X C, LI Z H, LI W J, et al.Optical nonlinearity and ultrafast dynamics of ion exchanged silver nanoparticles embedded in soda-lime silicate glass.Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(5): 695-699. |
| [13] | YANG X C, DONG Z W, LIU H X, et al.Effects of thermal treatment on the third-order optical nonlinearity and ultrafast dynamics of Ag nanoparticles embedded in silicate glasses.Chemical Physics Letters, 2009, 475(4/5/6): 256-259. |
| [14] | YANG X C, LI W J, LI Z H, et al.Nonlinear optical properties of Ag nanoparticles/glass composites measured on a femtosecond time scale.Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2007, 22(Suppl.): 69-71. |
| [15] | TERVONEN A, WEST B R, HONKANEN S.Ion-exchanged glass waveguide technology: a review.Optical Engineering, 2011, 50(7): 71107-71114. |
| [16] | GONELLA F, MAZZOLDI P.Metal Nanocluster Composite Glasses, in H. S. Nalwa(Ed), Handbook of Nanostrured Materials and Nanotechnology. New York: Academic Press, 2000: 81. |
| [17] | YANG X C, DU T L, CHEN S, et al.Forming mechanism of Ag nanoparticles in silicate glasses by optical spectroscopy.Journal of Functional Materials & Devices, 2006, 12(3):177-181. |
| [18] | YANG X C, XU J X, LI Z H, et al.The formation mechanism of Cu nanoparticles and local structures of copper atoms in silicate glass.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008, 36(7): 990-993. |
| [19] | XU J X, YANG X C, LIU H X, et al.The formation process of Ag-Cu nanoparticles in silicate glass.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2009, 37(6): 953-959. |
| [20] | LIU H X, YANG X C, ZHAO J F, et al.The absorption spectra of silver nanoparticles/silicate glass composite materials.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2010, 38(10):1922-1926. |
| [21] | ZHAO J F, YANG X C, HUANG M, et al.Local structure of Ag-Cu nano-particles in composite materials.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 40(2):312-316. |
| [22] | YANG X C.Influences of preparation conditions on the formation and depth dispersion of Ag nanoparticles in soda-lime silicate glass.Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2015, 430(15): 87-93. |
| [23] | YANG X C, LI L L, HUANG M, et al.In situ synthesis of Ag-Cu bimetallic nanoparticles in silicate glass by a two-step ion-exchange route.Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2011, 357(11/12/13): 2306-2308. |
| [24] | YANG X C, LI W J, Dubiel M, et al.Silver structure environments in ion-exchanged silicate glasses studied by x-ray absorption fine structure.J. Nanosci. Nanotech., 2009, 9(2):1659-1662. |
| [25] | YANG X C, LI W J, LI Z H, et al.Depth profiles of Ag nanoparticles in silicate glass.Applied Physics A, 2008, 90(3):465-467. |
| [26] | BORSELLA E, VECCHIO A D, GARCIA M A, et al.Copper doping of silicate glasses by the ion-exchange technique: A photoluminescence spectroscopy study.Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 91(1): 90-98. |
| [27] | TANAKA K, YANO T, SHIBATA S, et al.Cu+-doped CaO-P2O5 glasses for lasers.J. Non-Crystalline Solids, 1994, 178(3): 9-14. |
| [28] | PODLIPENSKY A V, GREBENEV V, SEIFERT G, et al.Ionization and photomodification of Ag nanoparticles in soda-lime glass by 150 fs laser irradiation: a luminescence study.Journal of Luminescence, 2004, 109(3/4): 135-142. |
| [29] | EICHELBAUM M, RADEMANN K, HOELL A, et al.Photoluminescence of atomic gold and silver particles in soda-lime silicate glasses.Nanotechnology, 2008,19(13): 135701-135710. |
| [30] | BORSELLA E, BATTAGLIN G, GARCIA M A, et al.Structural incorporation of silver in soda-lime glass by the ion-exchange process: a photoluminescence spectroscopy study.Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Proocess, 2000, 71(2): 125-132. |
| [31] | MANIKANDANA D, MOHANC S, NAIR K G M. Absorption and luminescence of silver nanocomposite soda-lime glass formed by Ag+-Na+ ion-exchange.Materials Research Bulletin, 2003, 38(9/10):1545-1550. |
| [32] | VERON O, BLONDEAU P J, ABDELKRIM N, et al.Luminescence study of silver nanoparticles obtained by annealed ionic exchange silicate glasses.Plasmonics, 2010, 5(2):213-219. |
| [33] | BORSELLA E, GONELLA F, MAZZODI P, et al.Spectroscopic investigation of silver in soda-lime glass.Chemical Physics Letters, 1998, 284(5/6):429-434. |
| [34] | HE F, LI Q T, ZHANG Z Y.The photoluminescence properties of float glass doped with siliver.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2003, 31(7) : 711-714. |
| [35] | PAJE S E, GARCIA M A, LIOPIS J, et al.Optical spectroscopy of silver ion-exchanged As-doped glass.Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2003, 318(3):239-247. |
| [36] | WANG H Y, YE S, LIU T H, et al.Molecular-like Ag clusters and Eu3+ co-sensitized efficient broadband spectral modification with enhanced Yb3+ emission.J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2016, 99(7): 2376-2381. |
| [1] | LIU Qi, ZHU Can, XIE Guizhen, WANG Jun, ZHANG Dongming, SHAO Gangqin. Optical Absorption and Photoluminescence Spectra of Ce-doped SrMgF4 Polycrystalline with Superlattice Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 897-902. |
| [2] | GUAN Xufeng, LI Guifang, WEI Yunge. Microstructure and Thermal Quenching Characteristics of Na1-xMxCaEu(WO4)3 (M=Li, K) Red Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 676-682. |
| [3] | ZHANG Guoqing, QIN Peng, HUANG Fuqiang. Reversible Conversion between Space-confined Lead Ions and Perovskite Nanocrystals for Confidential Information Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 445-451. |
| [4] | DU Aochen, DU Qiyuan, LIU Xin, YANG Yimin, XIA Chenyang, ZOU Jun, LI Jiang. Ce:YAG Transparent Ceramics Enabling High Luminous Efficacy for High-power LEDs/LDs [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 883-892. |
| [5] | WANG Zhihu,ZHANG Jumei,BAI Lijing,ZHANG Guojun. Mg(OH)2 Film on Micro-arc Oxidation Ceramic Coating of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy: Preparation and Corrosion Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 709-716. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhijie,HUANG Hairui,CHENG Kun,GUO Shaoke. High Efficient Carbon Quantum Dots/BiOCl Nanocomposite for Photocatalytic Pollutant Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 491-496. |
| [7] | DAI Yan-Nan, YANG Shuai, SHEN Yang, SHAN Yong-Kui, YANG Fan, ZHAO Qing-Biao. Intense Yellow Emission from Gd0.5-yTb1.5REyW3O12 (RE=Eu, Sm) Phosphors Tuned through Full Range Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1210-1216. |
| [8] | ZHENG Guo-Yuan, LI Jia-Cheng, SONG Li-Xin, ZHANG Tao. Simulation on Potassium Ion Concentration Profile of Engineered Stress Profile Glass by FDTD Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 693-698. |
| [9] | LI Gui-Fang, YANG Qian, WEI Yun-Ge. Synthesis and Photoluminescence Properties of Double Perovskite NaLaMgWO6: Eu3+ Red Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(9): 936-942. |
| [10] | YAN Bo, PENG Ze-Yang, LV Bin, LIU Wei. Regrowth of CdTe Quantum Dots Induced by Circular Polarized Light and Its Effect on the Photoluminescence [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(12): 1321-1326. |
| [11] | ZHUO Shi-Yi, LIU Xi, GAO Pan, YAN Cheng-Feng, SHI Er-Wei. Luminescence of Donor-acceptor-pair in Fluorescent 4H-SiC Doped with Nitrogen, Boron and Aluminum [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 51-55. |
| [12] | WAN Jian-Feng, HU De-Sheng, LU Peng-Hui, LIN Bi-Zhou, CHEN Yi-Lin, GAO Bi-Fen. Preparation of Anatase TiO2 Nanocube with Exposed (001) Facet and Its Photocatalytic Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 845-849. |
| [13] | YANG Feng-Jiu, LU Meng-Chen, ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Yan, WANG Lian-Jun, JIANG Wan. Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of Oil-Soluble PbSe Quantum Dots [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(7): 774-778. |
| [14] | CHEN Ting, JIANG Wei-Hui, ZHANG Xiao-Jun, XIE Zhi-Xiang, LIU Jian-Min, JIANG Wan. An Ionic Liquid-assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of CeO2 Nanorods [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 325-329. |
| [15] | HAN Bin, WANG Yi-Fei, LIU Qian, HUANG Qing. Microwave Assisted Sintering and Photoluminescence Properties of Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+ Green Phosphors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 330-336. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||