
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 845-849.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160012
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WAN Jian-Feng, HU De-Sheng, LU Peng-Hui, LIN Bi-Zhou, CHEN Yi-Lin, GAO Bi-Fen
Received:2016-01-05
Revised:2016-03-07
Published:2016-08-20
Online:2016-07-20
About author:WAN Jian-Feng. E-mail: 770673639@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WAN Jian-Feng, HU De-Sheng, LU Peng-Hui, LIN Bi-Zhou, CHEN Yi-Lin, GAO Bi-Fen. Preparation of Anatase TiO2 Nanocube with Exposed (001) Facet and Its Photocatalytic Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 845-849.
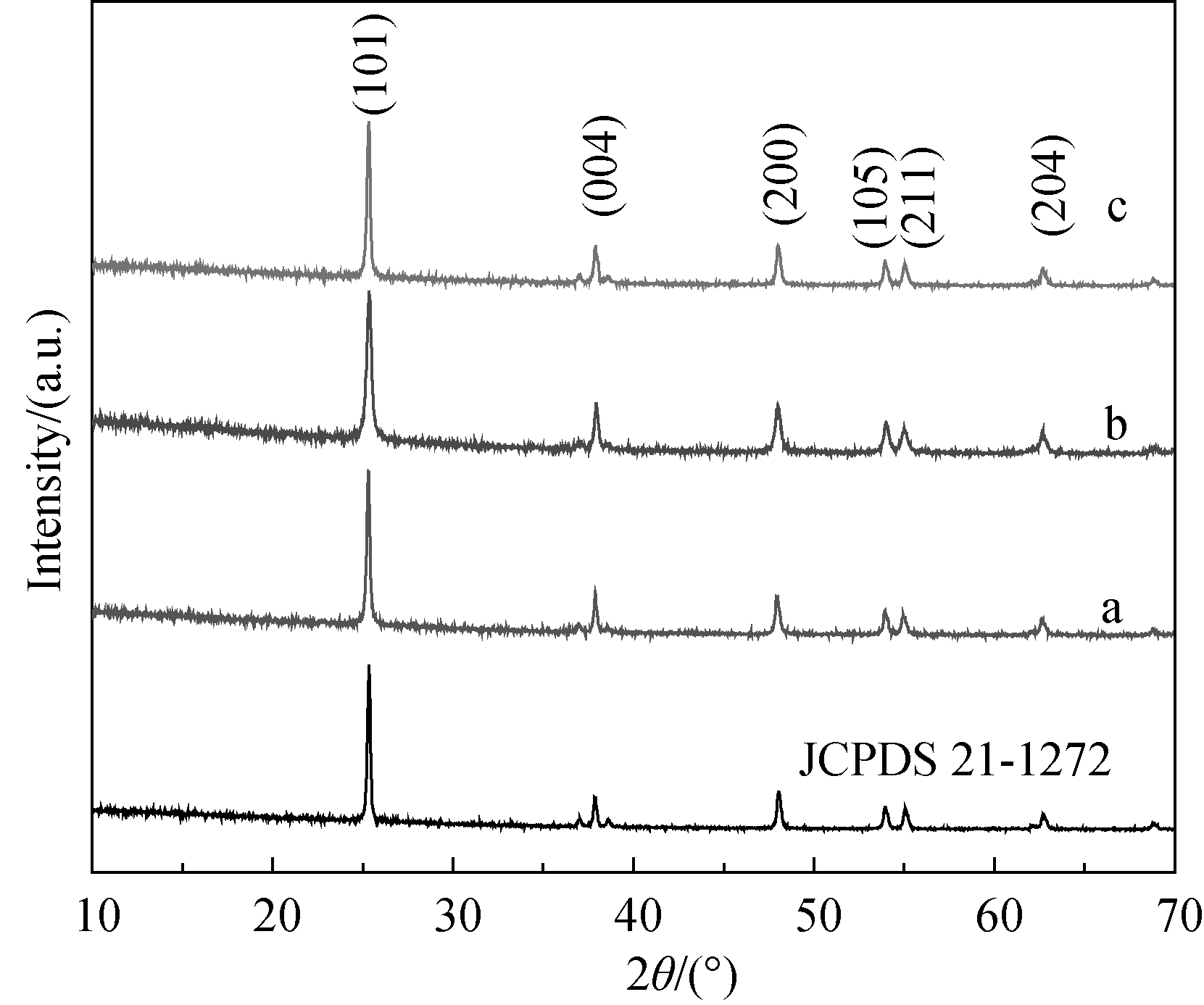
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of TiO2 samples synthesized at various hydrothermal temperatures(a) 160℃, (b) 180℃ and (c) 200℃. The hydrothermal treatment was kept for 20 h at pH 4
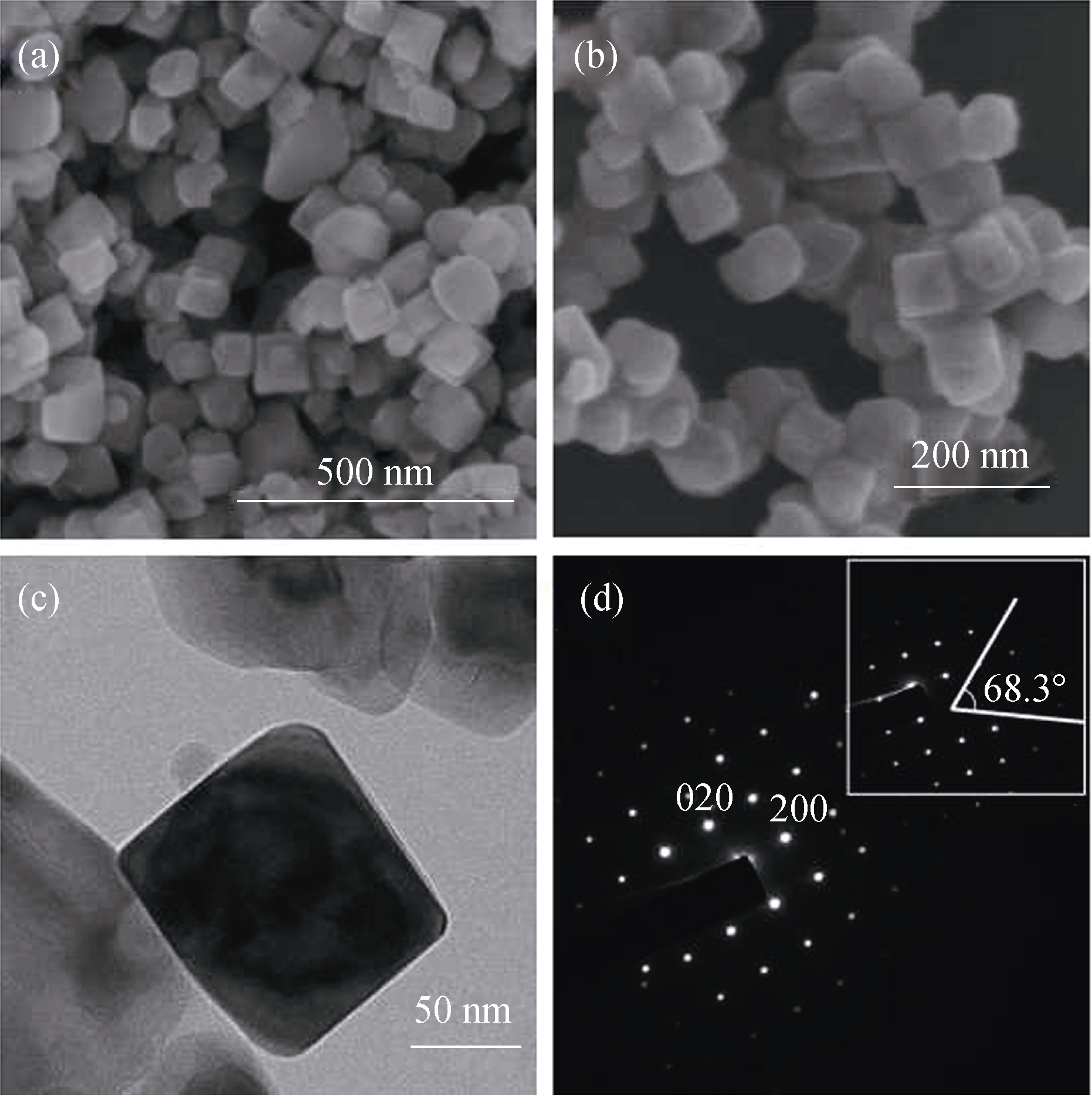
Fig. 2 SEM (a, b) and TEM (c, d) images of TiO2 nanocubes Inset of (d) shows the angle between (001) and (101) facets of the nanocube. The sample was obtained by hydrothermal treatment at 180℃ for 20 h at pH 4
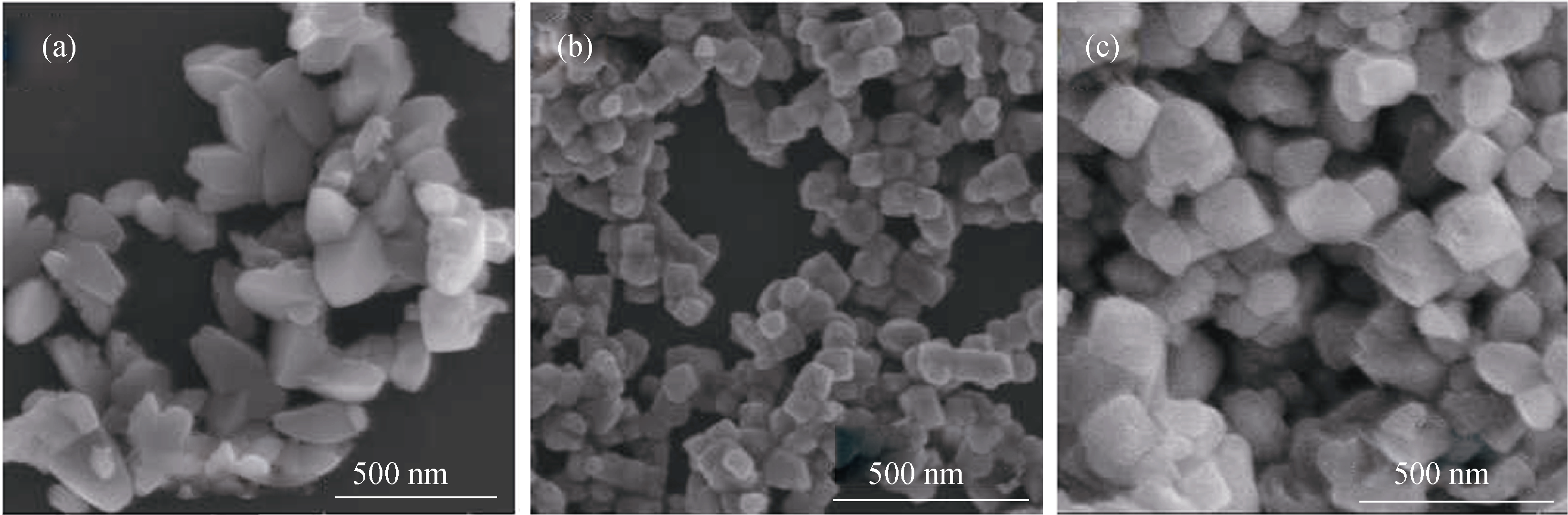
Fig. 3 FE-SEM images of anatase TiO2 synthesized at different hydrothermal temperatures(a) 160℃, (b) 180℃ and (c) 200℃. The hydrothermal treatment was kept for 20 h at pH 4
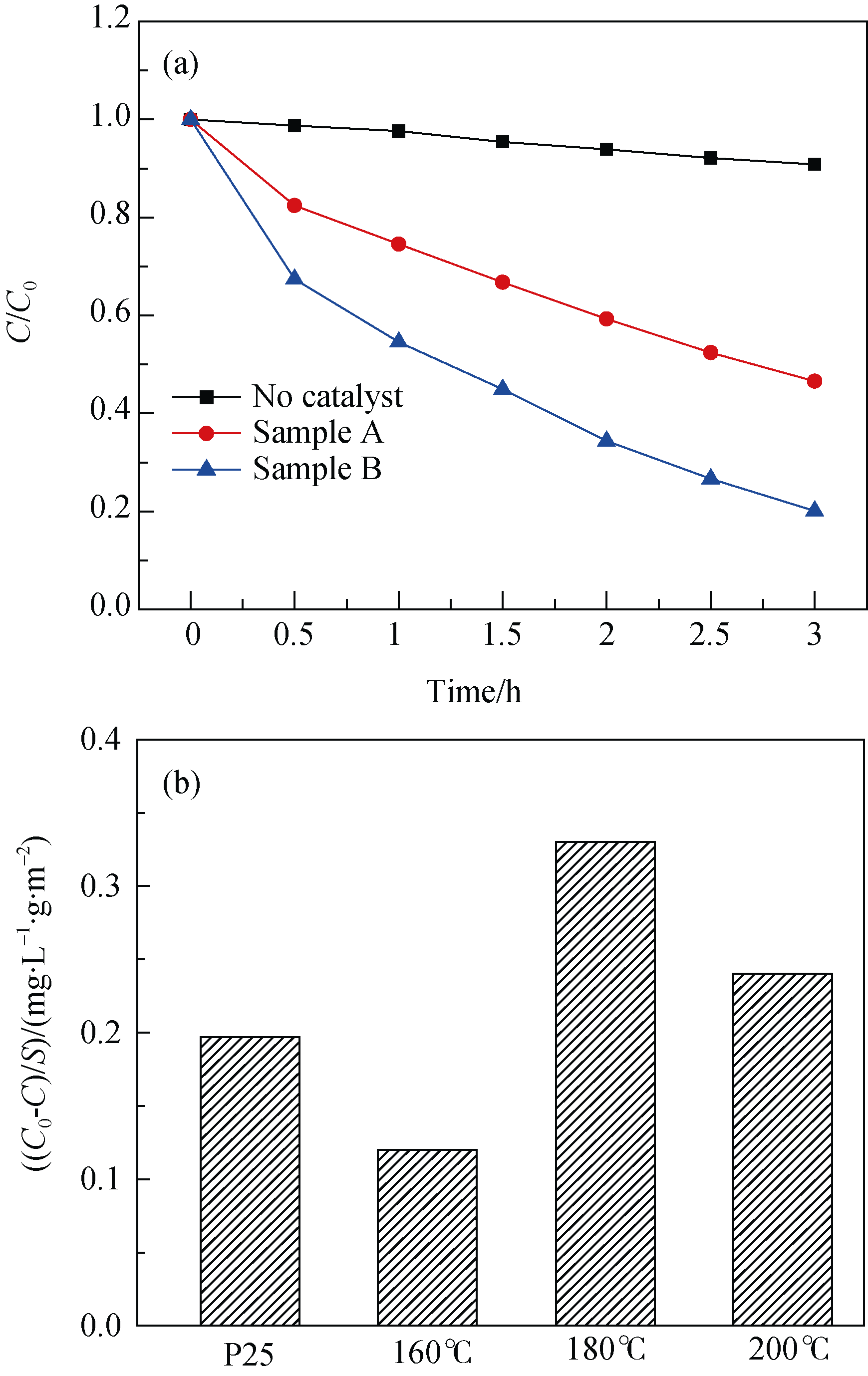
Fig. 6 (a) Photodegradation of acid red dye by TiO2 samples with different morphologies and (b) specific photocatalytic activity of P25 and TiO2 synthesized at different hydrothermal temperaturesMorphologies of sample A, tetragonal-dipyramid, and sample B, nanocube
| [1] | REN L, LI Y Z, HOU J G, et al.Preparation and enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanocrystals with internal pores.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2014, 6(3): 1608-1615. |
| [2] | TONG T Z, HILL A N, ALSINA M A.Spectroscopic characterization of TiO2 polymorphs in wastewater treatment and sediment samples.Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett., 2015, 2(1): 12-18. |
| [3] | WENG Z G, GUO H, LIU X G, et al.Nanostructured TiO2 for energy conversion and storage.RSC Adv., 2013, 3(47): 24758-24775. |
| [4] | DUAN Y D, ZHENG J X, XU M, et al.Metal and F dual-doping to synchronously improve electron transport rate and lifetime for TiO2 photoanode to enhance dye-sensitized solar cells performances.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(10): 5692-5700. |
| [5] | HIRAYAMA J, KAMIYA K.Combining the photocatalyst Pt/TiO2 and the nonphotocatalyst SnPd/Al2O3 for effective photocatalytic purification of groundwater polluted with nitrate.ACS Catal., 2014, 4(7): 2207-2215. |
| [6] | KAMEGAWA T, ISHIGURO Y, SETO H, et al.Enhanced photocatalytic properties of TiO2-loaded porous silica with hierarchical macroporous and mesoporous architectures in water purification.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(5): 2323-2330. |
| [7] | YANG J L, WU Q L, HE S M, et al.Completely <001> oriented anatase TiO2 nanoarrays: topotactic growth and orientationrelated efficient photocatalysis.Nanoscale, 2015, 7(33): 13888-13897. |
| [8] | XU T Z, ZHENG H, SEKIGUCHI Y, et al.Hydrothermal preparation of nanoporous TiO2 films with exposed {001} facets and superior photocatalytic activity.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(37): 19115-19122. |
| [9] | YANG H G, SUN C H, QIAO S Z, et al.Anatase TiO2 single crystals with a large percentage of reactive facets.Nature, 2008, 453(7195): 638-642. |
| YANG H G, LIU G, QIAO S Z, et al.Solvothermal synthesis and photoreactivity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant {001} facets.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(11): 4078-4083. | |
| [10] | HAN X G, KUANG Q, JIN M S, et al.Synthesis of titania nanosheets with a high percentage of exposed (001) facets and related photocatalytic properties.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(9): 3152-3153. |
| [11] | LI H M, ZENG Y S, LIU M, et al.Controlled synthesis of anatase tio2 single crystals with dominant {001} facets from TiO2 powders.Chem Plus Chem., 2012, 77(11): 1017-1021. |
| [12] | LIU M, PIAO L G, WANG W J, et al.Anatase TiO2 single crystals with exposed {001} and {110} facets: facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalysis.Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(10): 1664-1666. |
| [13] | KIM J Y, LEE D, KIM H J, et al.Annealing-free preparation of anatase TiO2 nanopopcorns on Ti foil via a hydrothermal process and their photocatalytic and photovoltaic applications.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(19): 5982-5988. |
| [14] | GAO B F, LUO X Z, GU Z J, et al.Facile synthesis of TiO2 microspheres with reactive (001) facets for improved photocatalytic performance.J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2014, 14(5): 3969-3975. |
| [15] | JUN Y W, CASULA M F, SIM J H, et al.Surfactant-assisted elimination of a high energy facets as a means of controlling the shapes of TiO2 nanocrystals.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(51): 15981-15985. |
| [16] | DAI Y, COBLEY C M, SUN Y M, et al.Synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with exposed {001} facets.Nano Lett., 2009, 9(6): 2455-2459. |
| [17] | SELCUK S, SELLONI A.Surface structure and reactivity of anatase TiO2 crystals with dominant {001} facets.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(12): 6358-6362. |
| [18] | ZHOU Y, WANG X Y, WANG H.Enhanced dye-sensitized solar cells performance using anatase TiO2 mesocrystals with the Wulff construction of nearly 100% exposed {101} facets as effective light scattering layer.Dalton Trans., 2014, 43(12): 4711-4719. |
| [19] | ZHANG H M, WANG Y, ZHAO H J, et al.Anatase TiO2 crystal facet growth: mechanistic role of hydrofluoric acid and photoelectrocatalytic activity.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2011, 3(7): 2472-2478. |
| [20] | RYU J, CHOI W.Substrate-specific photocatalytic activities of TiO2 and multiactivity test for water treatment application.Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 42(1): 294-300. |
| [21] | PRINGUET A, PAGNOUX C, VIDECOQ A, et al.Granulating titania powder by colloidal route using polyelectrolytes.Langmuir, 2008, 24(19): 10702-10708. |
| [22] | GAO Y, WAHI R, KAN A T, et al.Adsorption of cadmium on anatase nanoparticles effect of crystal size and pH.Langmuir., 2004, 20(22): 9585-9593. |
| [23] | WU GUO-TAO, ZHENG SHU-KAI, LÜ XIAO.First-principles calculation of Bi-doped anatase TiO2.Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(1): 9-14. |
| [24] | YUAN X, GAO B F, SHI J X, et al.Morphologically-tunable anatase TiO2 with exposed (001) facet and related photocatalytic performance.Materials Letters., 2014, 128: 167-169. |
| [25] | LIU G, SUN C, WANG L Z, et al.Nanosized anatase TiO2 single crystals for enhanced photocatalytic activity.Chem Commun., 2010, 46(5): 755-757. |
| [1] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [3] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [4] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [5] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [7] | LIU Xuechen, ZENG Di, ZHOU Yuanyi, WANG Haipeng, ZHANG Ling, WANG Wenzhong. Selective Oxidation of Biomass over Modified Carbon Nitride Photocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [9] | LIU Peng, WU Shimiao, WU Yunfeng, ZHANG Ning. Synthesis of Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS Photocatalyst for CO2 Reduction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [10] | WANG Luping, LU Zhanhui, WEI Xin, FANG Ming, WANG Xiangke. Application of Improved Grey Model in Photocatalytic Data Prediction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 871-876. |
| [11] | AN Weijia, LI Jing, WANG Shuyao, HU Jinshan, LIN Zaiyuan, CUI Wenquan, LIU Li, XIE Jun, LIANG Yinghua. Fe(III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6 Composite Photocatalyst Preparation and Phenol Degradation by Photocatalytic Fenton Synergy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 615-622. |
| [12] | XIAO Xiang, GUO Shaoke, DING Cheng, ZHANG Zhijie, HUANG Hairui, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3@TiO2 Core-shell Structure Nanocomposite as Water Stable and Efficient Visible-light-driven Photocatalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 507-512. |
| [13] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [14] | SHU Mengyang, LU Jialin, ZHANG Zhijie, SHEN Tao, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots/Ultrathin C3N4 Nanosheet 0D/2D Composite: Enhanced Stability and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1217-1222. |
| [15] | LIU Yaxin, WANG Min, SHEN Meng, WANG Qiang, ZHANG Lingxia. Bi-doped Ceria with Increased Oxygen Vacancy for Enhanced CO2 Photoreduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 88-94. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||