
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 241-247.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150380
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIN Zhao( ), CHEN Qi-Han, ZHENG Meng-Jia, ZHAO Peng, LI Qian, CUI Xiao-Qiang(
), CHEN Qi-Han, ZHENG Meng-Jia, ZHAO Peng, LI Qian, CUI Xiao-Qiang( )
)
Received:2015-08-13
Revised:2015-11-06
Published:2016-03-20
Online:2016-02-24
Supported by:CLC Number:
JIN Zhao, CHEN Qi-Han, ZHENG Meng-Jia, ZHAO Peng, LI Qian, CUI Xiao-Qiang. Fabrication of Au Nanoparticles / Bilayer TiO2 Nanotube Periodical Structure and Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Ethanol[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 241-247.
| First time/V | 40 | 50 | 60 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Second time/V | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
Table 1 Anodization voltages for TiO2 nanotube fabrication
| First time/V | 40 | 50 | 60 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Second time/V | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| HAuCl4 concentration/(mmol·L-1) | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irradiation time/min | 30 | 90 | 150 |
Table 2 Concentration and irradiation time for Au nanoparticles decoration
| HAuCl4 concentration/(mmol·L-1) | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irradiation time/min | 30 | 90 | 150 |
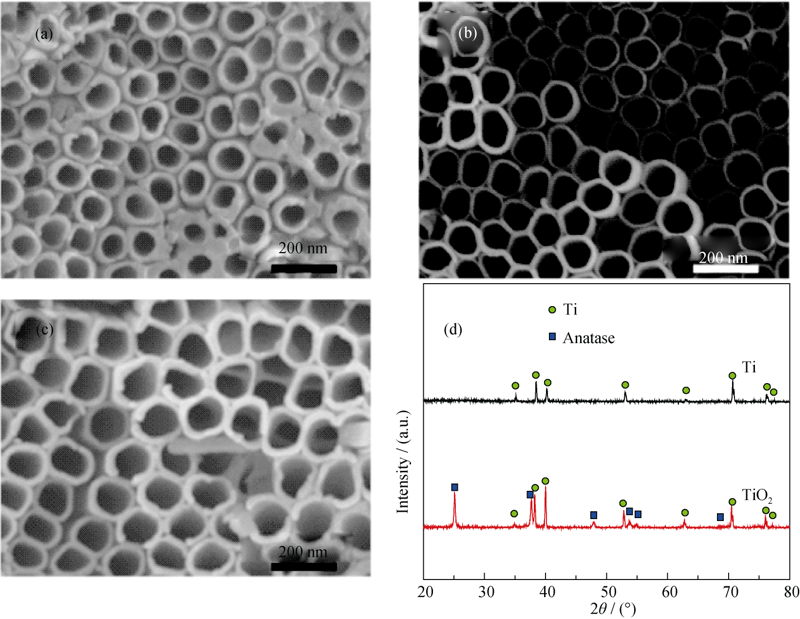
Fig. 1 SEM images (a-c) of TiO2 nanotubes after first anodizing under different voltages and corresponding XRD patterns(a) 40 V; (b) 50 V; (c) 60 V; (d) XRD pattern of Ti and TiO2 nanotubes after annealing
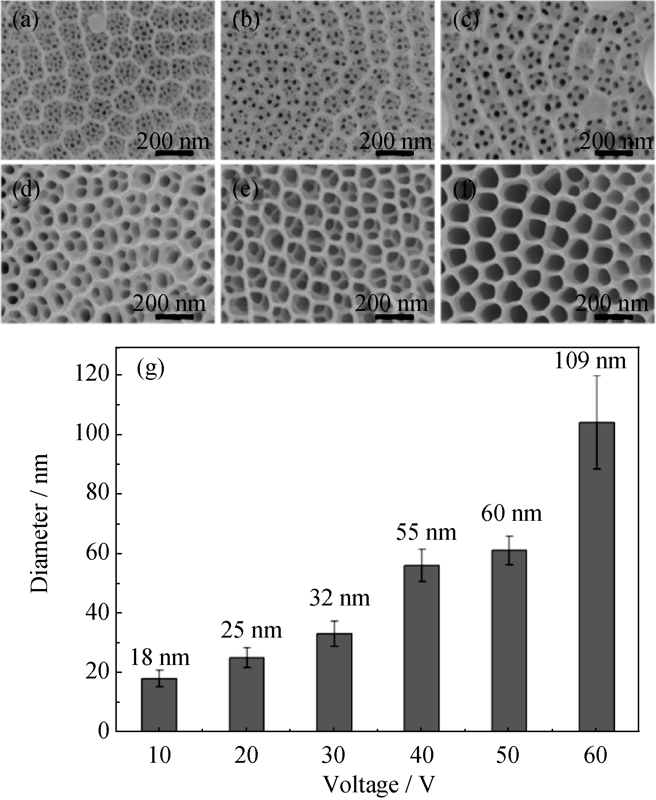
Fig. 2 SEM images (a-f) of TiO2 nanotubes after second anodizing under different voltages and histogram of nanotube diameter (g)(a) 10 V; (b) 20 V; (c) 30 V; (d) 40 V; (e) 50 V; (f) 60 V
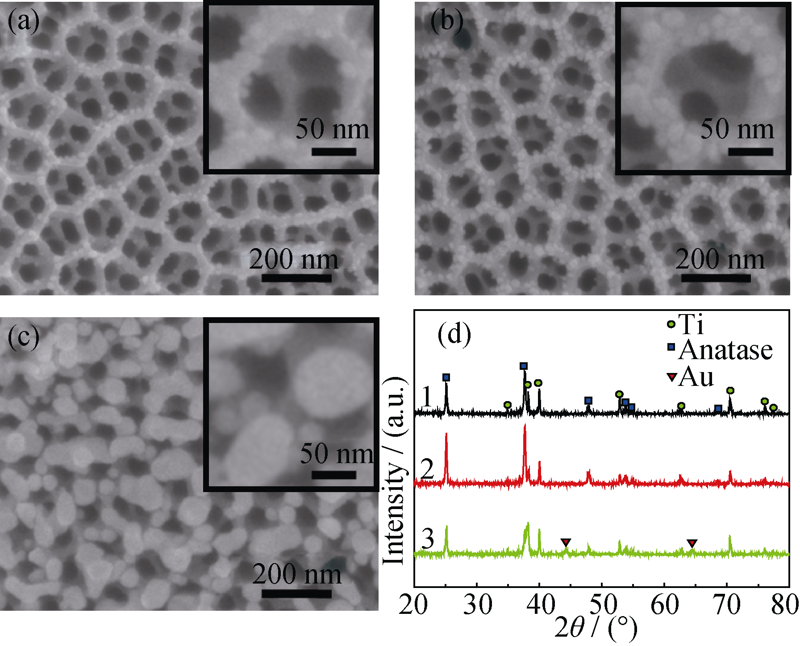
Fig. 3 SEM images (a-c) of TiO2 photoreduced in different concentrations of HAuCl4 and corresponding XRD patterns (d)(1) 0.01 mmol/L; (2) 0.05 mmol/L; (3) 0.09 mmol/L
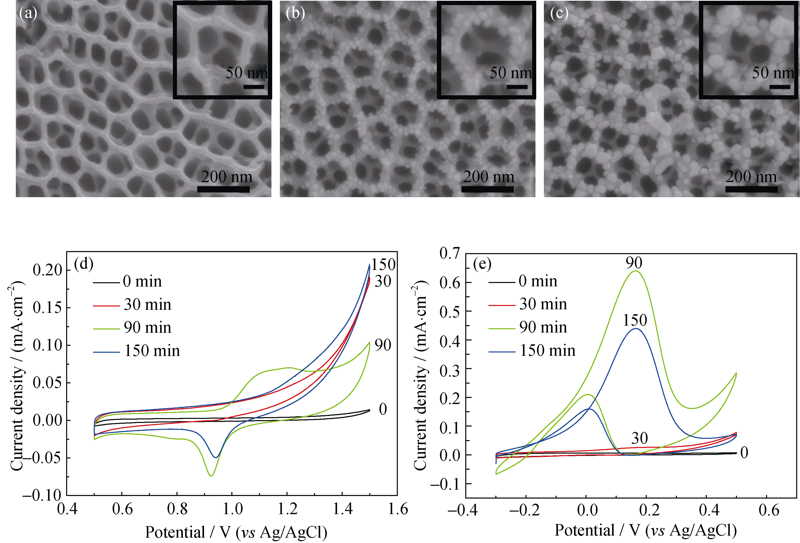
Fig. 4 SEM images (a-c) of TiO2 nanotubes photoreduced in different time and the corresponding CV characterization(a) 30 min; (b) 90 min; (c) 150 min; (d) CV measured in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4; (e) CV measured in KOH and ethanol
| [1] | MUN K S, ALVAREZ S D, CHOI W Y, et al. A stable, label-free optical interferometric biosensor based on TiO2 nanotube arrays. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(4): 2070-2076. |
| [2] | FAN L, ZHAO G, SHI H, et al. A femtomolar level and highly selective 17 beta-estradiol photoelectrochemical aptasensor applied in environmental water samples analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, 48(10): 5754-5761. |
| [3] | XIANG Q, YU J, JARONIEC M.Synergetic effect of mos2 and graphene as cocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic H-2 production activity of tio2 nanoparticles.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(15): 6575-6578. |
| [4] | BASAHEL S N, LEE K, HAHN R, et al. Self-decoration of Pt metal particles on TiO2 nanotubes used for highly efficient photocatalytic H-2 production. Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(46): 6123-6125. |
| [5] | NEATU S, ANTONIO MACIA-AGULLO, CONCEPCION J P, et al. Gold-copper nanoalloys supported on TiO2 as photocatalysts for CO2 reduction by water. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(45): 15969-15976. |
| [6] | LUO H M, LIU Z Y, BAI C Y, et al. TiO2 nanotube based dye- sensitized photoanode. J. Inorg. Mater., 2013, 28(5): 521-526. |
| [7] | RAJA R, SUDHAGAR P, DEVADOSS A, et al. Pt-free solar driven photoelectrochemical hydrogen fuel generation using 1T MoS2 co-catalyst assembled CdS QDs/TiO2 photoelectrode. Chem. Commun., 2015, 51(3): 522-525. |
| [8] | ALBU S P, GHICOV A, ALDABERGENOVA S, et al. Formation of double-walled TiO2 nanotubes and robust anatase membranes. Adv. Mater., 2008, 20(21): 4135-4139. |
| [9] | KIM K, THIYAGARAJAN P, AHN H J, et al. Optimization for visible light photocatalytic water splitting: gold-coated and surface- textured TiO2 inverse opal nano-networks. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(14): 6254-6260. |
| [10] | ZHANG Z, WANG P.Optimization of photoelectrochemical water splitting performance on hierarchical TiO2 nanotube arrays.Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(4): 6506-6512. |
| [11] | YU W W, ZHANG Q H, SHI G Y, et al. Preparation of Pt-loaded TiO2 nanotubes/nanocrystals composite photocatalysts and their photocatalytic properties. J. Inorg. Mater., 2011, 26(7): 747-752. |
| [12] | KOWALSKI D, KIM D, SCHMUKI P.TiO2 nanotubes, nanochannels and mesosponge: self-organized formation and applications.Nano Today, 2013, 8(3): 235-264. |
| [13] | ZHANG Z, ZHANG L, HEDHILI M N, et al. Plasmonic gold nanocrystals coupled with photonic crystal seamlessly on TiO2 nanotube photoelectrodes for efficient visible light photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(1): 14-20. |
| [14] | ARABATZIS I M, STERGIOPOULOS T, ANDREEVA D, et al. Characterization and photocatalytic activity of Au/TiO(2) thin films for azo-dye degradation. J. Catal., 2003, 220(1): 127-135. |
| [15] | PRIMO A, CORMA A, GARCIA H.Titania supported gold nanoparticles as photocatalyst.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13(3): 886-910. |
| [16] | SU R, TIRUVALAM R, LOGSDAIL A J, et al. Designer titania- supported au-pd nanoparticles for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(4): 3490-3497. |
| [17] | MURDOCH M, WATERHOUSE G I N, NADEEM M A, et al. The effect of gold loading and particle size on photocatalytic hydrogen production from ethanol over Au/TiO2 nanoparticles. Nature Chemistry, 2011, 3(6): 489-492. |
| [18] | ZOPE B N, HIBBITTS D D, NEUROCK M, et al. Reactivity of the gold/water interface during selective oxidation catalysis. Science, 2010, 330(6000): 74-78. |
| [19] | TIAN Y, TATSUMA T.Mechanisms and applications of plasmon-induced charge separation at TiO2 films loaded with gold nanoparticles.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(20): 7632-7637. |
| [20] | GHICOV A, SCHMUKI P.Self-ordering electrochemistry: a review on growth and functionality of TiO2 nanotubes and other self-aligned MOx structures. Chem. Commun., 2009, (20): 2791-2808. |
| [21] | LU Q, ZHANG Z B, DONG C Q, et al. Improved visible-light photocatalytic activity of bi-crystalline mesoporous titania codoped with carbon and silver. J. Inorg. Mater., 2014, 29(12): 1333-1338. |
| [22] | YE M, GONG J, LAI Y, et al. High-efficiency photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen generation enabled by palladium quantum dots-sensitized TiO2 nanotube arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(38): 15720-15723. |
| [23] | TANAKA A, FUKU K, NISHI T, et al. Functionalization of Au/TiO2 plasmonic photocatalysts with Pd by formation of a core-shell structure for effective dechlorination of chlorobenzene under irradiation of visible light. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(33): 16983-16989. |
| [24] | ZHANG S, ZHANG S, PENG F, et al. Electrodeposition of polyhedral Cu2O on TiO2 nanotube arrays for enhancing visible light photocatalytic performance. Electrochem. Commun., 2011, 13(8): 861-864. |
| [25] | XU Z, YU J, LIU G.Enhancement of ethanol electrooxidation on plasmonic Au/TiO2 nanotube arrays.Electrochem. Commun., 2011, 13(11): 1260-1263. |
| [26] | WANG Y Q, WEI Z D, GAO B, et al. The electrochemical oxidation of methanol on a Pt/TNTs/Ti electrode enhanced by illumination. J. Power Sources, 2011, 196(3): 1132-1135. |
| [1] | YAO Yishuai, GUO Ruihua, AN Shengli, ZHANG Jieyu, CHOU Kuochih, ZHANG Guofang, HUANG Yarong, PAN Gaofei. In-situ Loaded Pt-Co High Index Facets Catalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 71-78. |
| [2] | ZHANG Dongqiang, LU Huihui, SU Na, LI Guixian, JI Dong, ZHAO Xinhong. Modulation of SAPO-34 Property with Activated Seeds and Its Enhanced Lifetime in Methanol to Olefins Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 101-106. |
| [3] | LYU Ziye, TANG Yiping, CAO Huazhen, ZHENG Guoqu, HOU Guangya. Effect of V Doping on Electrocatalytic Performance of Ni-Co-S on Bacterial Cellulose-derived Carbon Aerogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1142-1148. |
| [4] | LI Ya-Hui, ZHANG Jian-Feng, CAO Hui-Yang, ZHANG Xin, JIANG Wan. PtRu Particles Supported on Two-dimensional Titanium Carbide/Carbon Nanotubes: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 79-85. |
| [5] | ZHANG Ya-Ping, DING Wen-Ming, ZHU Hai-Feng, HUANG Cheng-Xing, YU Lian-Qing, WANG Yong-Qiang, LI Zhe, XU Fei. Photoelectrochemical Properties of MoSe2 Modified TiO2 Nanotube Arrays [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 797-802. |
| [6] | CHEN Chuan-Jie, WEI Li-Geng, WU Yue, HU Cheng-Pei, HU Yuan-Cong, JIANG Jiu-Xin. Synthesis of Metastable Vaterite Phase of CaCO3 via Ethanol-calcium Method and Ethanol-water Binary Solvent Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 755-760. |
| [7] | KE Yin-Huan, ZENG Min, JIANG Hong, XIONG Chun-Rong. Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol over N-doped TiO2 Nanofibers under Visible Irradiation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 839-844. |
| [8] | GUO Rui-hua, MO Yi-Jie, AN Sheng-Li, ZHANG Jie-Yu, ZHOU Guo-Zhi. Cerium Oxide Hollow Sphere: Controllable Synthesis and Its Effect on Electrocatalytic Performance of Pt-based Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(7): 779-786. |
| [9] | YAN Shi-Sheng, PENG Hong-Yan, ZHAO Zhi-Bin, PAN Meng-Mei, YANG Da-Li, A Jin-Hua, YE Guo-Lin, WANG Chong-Tai, GUO Xin-Wei. Nitrogen-doped Diamond Electrode Property and Anodic Catalytic Degradation of Nitrobenzene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 565-569. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Jian-Feng, YANG Shui-Xian, CAO Hui-Yang, HUANG Hua-Jie, JIANG Wan. Electrocatalytic Performance of Palladium Nanoparticle Supported by Two-dimensional Titanium Carbide-CNT Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 206-212. |
| [11] | WANG You-He, WANG Xiao-Dong, XU Jing-Wei, SUN Hong-Man, WU Cheng-Cheng, YAN Zi-Feng, JI Sheng-Fu. Hierarchical ZSM-5 Zeolite: Preparation by Sequential Desilication-dealumination and Catalytic Performance in Methanol to Gasoline Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1193-1200. |
| [12] | ZHAI Chun-Yang, SUN Ming-Juan, DU Yu-Kou, ZHU Ming-Shan. Noble Metal/Semiconductor Photoactivated Electrodes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(9): 897-903. |
| [13] | LI Min, LUO Yuan, XU Wei-Jia, LIU Jia-Xiang. DMFC Anode Catalyst Fe3O4@Pt Particles: Synthesis and Catalytic Performanc [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(9): 916-922. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yi, ZHANG Xiao-Feng, He Xiao-Lei, HUANG Huo-Di, LE Li-Juan, LIN Shen. Preparation and Electrocatalytic Property of Pt/{GN/CuPW11}n Composite Films toward Methanol Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(10): 1075-1082. |
| [15] | ZHAN Jing, LU Er-Ju, CAI Meng, MA Ya-Lin, ZHANG Chuan-Fu. Controlled Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Performance of Porous Nickel Cobaltite Rods [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 11-17. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||