
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 1056-1062.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150118
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Jian-Ying, HOU Lin-Lin, JIA Ran, GAO Lu, WU Kang-Ning, LI Sheng-Tao
Received:2015-03-05
Revised:2015-05-13
Published:2015-10-20
Online:2015-09-30
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Jian-Ying, HOU Lin-Lin, JIA Ran, GAO Lu, WU Kang-Ning, LI Sheng-Tao. Influences of CuAl2O4 Doping on the Dielectric Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1056-1062.
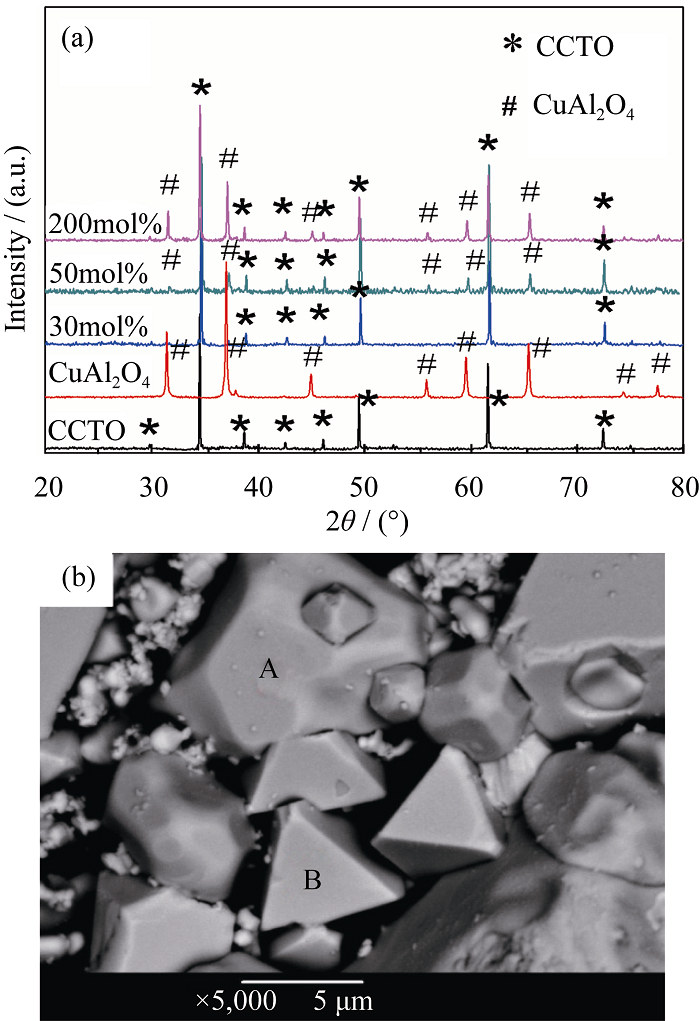
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of CCTO-xCuAl2O4 (x=0, 30mol%, 50mol%, 200mol%) composite ceramics and CuAl2O4 samples sintered at 1100℃ for 4 h (a) and BSEM image of sample with 200mol% CuAl2O4 (b)
| Element /at% | A | B |
|---|---|---|
| O | 10.54 | 13.53 |
| Al | 2.84 | 27.91 |
| Ca | 10.68 | 6.55 |
| Ti | 38.93 | 10.90 |
| Cu | 37.01 | 41.11 |
Table 1 EDS results for the marked points in Fig. 1(b)
| Element /at% | A | B |
|---|---|---|
| O | 10.54 | 13.53 |
| Al | 2.84 | 27.91 |
| Ca | 10.68 | 6.55 |
| Ti | 38.93 | 10.90 |
| Cu | 37.01 | 41.11 |
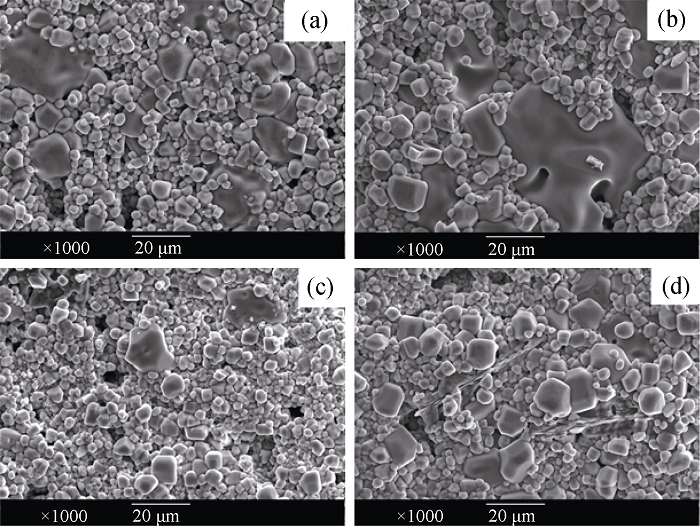
Fig. 2 SEM image of CCTO ceramics CCTO ceramics sintered at 1100℃ for 4 h (a) and 10 h (b); CCTO- 50mol% CuAl2O4 ceramics sintered at 1100 ℃ for 4 h (c) and 10 h (d)
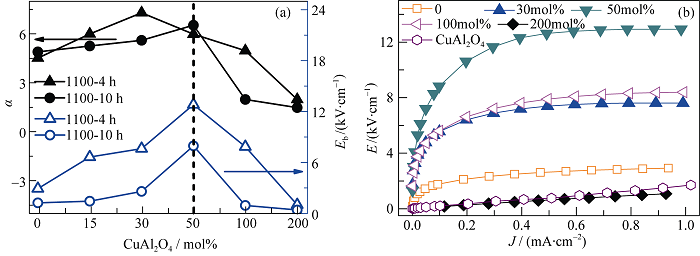
Fig. 3 α, Eb and J-E characteristics of the samples at room temperature (a) Dependence ofα and Eb on CuAl2O4 addition; (b) J-E characteristics of the samples sintered at 1100 ℃ for 4 h with different CuAl2O4 additions
| Doping ratio | Rgb/MΩ | Rg/Ω |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 37 | 47 |
| 15mol% | 274 | 140 |
| 30mol% | 426 | 190 |
| 50mol% | 2008 | 203 |
| 100mol% | 520 | 264 |
| 200mol% | 0.23 | - |
Table 2 Resistivity for both bulk and grain boundary of the samples sintered at 1100℃ for 4 h at room temperature
| Doping ratio | Rgb/MΩ | Rg/Ω |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 37 | 47 |
| 15mol% | 274 | 140 |
| 30mol% | 426 | 190 |
| 50mol% | 2008 | 203 |
| 100mol% | 520 | 264 |
| 200mol% | 0.23 | - |
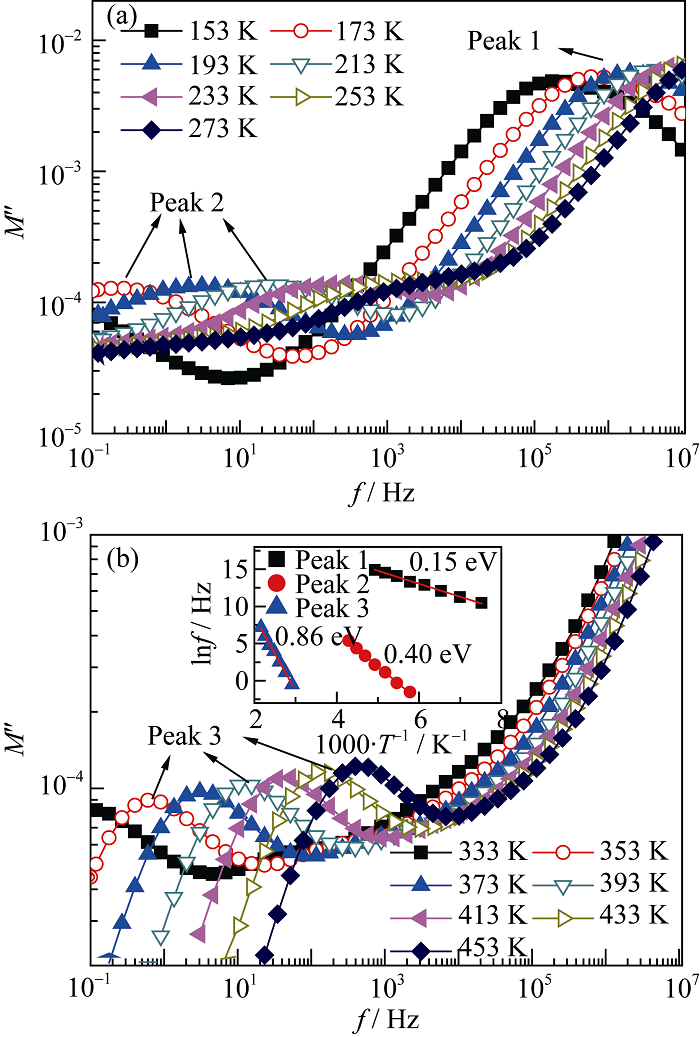
Fig. 6 Frequency and temperature dependence of electric modulus for CCTO-50mol% CuAl2O4 composite ceramics sintered at 1100 ℃ for 4 h (a) 153-273 K, (b) 333-433 K. the inset in (b) shows the energy levels of defect relaxation calculated by Arrhenius law
| Sample | Peak1/eV | Peak2/eV | Peak3/eV | Eb/(kV·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x=0 | 0.11 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 3.0 |
| x=50mol% | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.86 | 13.0 |
| x=200mol% | 0.15 | 0.22 | — | 1.0 |
Table 3 Energy levels and breakdown field Eb of CCTO-xCuAl2O4 (x=0, 50mol%, 200mol%) ceramics sintered at 1100 ℃ for 4 h
| Sample | Peak1/eV | Peak2/eV | Peak3/eV | Eb/(kV·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x=0 | 0.11 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 3.0 |
| x=50mol% | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.86 | 13.0 |
| x=200mol% | 0.15 | 0.22 | — | 1.0 |
| [1] | SUBRAMANIAN M A, LI D, DUAN N, et al.High dielectric constant in ACu3Ti4O12 and ACu3Ti3FeO12 phases.Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2000, 151(2): 323-325. |
| [2] | HOME C C, VOGT T, SHAPIRO S, et al.Optical response of high-dielectric-constant perovskite-related oxide.Science, 2001, 293(5530): 673-676. |
| [3] | COHEN M H, NEATON J B, HE L X, et al.Extrinsic models for the dielectric response of CaCu3Ti4O12.Journal of Applied physics, 2003, 94(5): 3299-3306. |
| [4] | CHUNG S Y, KIM I D, KANG S J L. Strong nonlinear current-voltage behavior in perovskite-derivative calcium copper titanate.Nature Materials, 2004, 3(11): 774-778. |
| [5] | LIN Y H, CAI J N, LI M, et al.High dielectric and nonlinear electrical behaviors in TiO2-rich CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(17): 172902. |
| [6] | MARQUES V P B, BUENO P R, SIMÕES A Z, et al. Nature of potential barrier in (Ca1/4, Cu3/4)TiO3 polycrystalline perovskite.Solid State Communications, 2006, 138(1): 1-4. |
| [7] | LIU Y, WITERS R L, WEI X Y.Structurally frustrated relaxor ferroelectric behavior in CaCu3Ti4O12.Physics Review B, 2005, 72(13): 134104. |
| [8] | KROHNS S, LUNKENHEIMER P, EBBINGHAUS S G, et al.Colossal dielectric constants in single-crystalline and ceramic CaCu3Ti4O12 investigated by broadband dielectric spectroscopy.Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103(8): 084107. |
| [9] | HAO W T, ZHANG J L, TAN Y Q.Origin of giant dielectric permittivity in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(10): 1058-1062. |
| [10] | SINCAIR D C, ADAMS T B, MORRISON F D, et al.CaCu3Ti4O12: one-step internal barrier layer capacitor.Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 80(12): 2153-2155. |
| [11] | LUO X J, YANG C P, SONG X P, et al.Slow relaxation processes in CCTO detected by capacitance versus voltage curves.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(1): 253-258. |
| [12] | ADAMS T B, SINCAIR D C, WEST A R.Giant barrier layer capacitance effects in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(18): 1321-1323. |
| [13] | YUAN W X, HARK S K.Investigation on the origin of the giant dielectric constant in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics through analyzing CaCu3Ti4O12-HfO2 composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(2): 465-470. |
| [14] | YUAN J C, LIN Y H, LU H F, et al.Dielectric and varistor behavior of CaCu3Ti4O12-MgTiO3 composite ceramics.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(7): 1966-1969. |
| [15] | JIA R, GU F, WU Z Y, et al.Dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics prepared by a simplified coprecipitation method. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(20): 466-472. |
| [16] | ZHANG L, TANG Z J.Polaron relaxation and variable- range-hopping conductivity in the giant-dielectric-constant material CaCu3Ti4O12.Physics Review B, 2004, 70(17): 174306. |
| [17] | ZHOU X L, DU P Y.Effects of preparation on giangt dielectric constant of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(2): 484-488. |
| [18] | HOMES C C, VOGT T, SHAPIRO S M, et al.Charge transfer in the high dielectric constant materials CaCu3Ti4O12 and CdCu3Ti4O12.Physics Review B, 2003, 67(9): 092106. |
| [19] | FANG T T, MEI L T, HO H F.Effects of Cu stoichiometry on the microstructures, barrier-layer structures, electrical conduction, dielectric responses and stability of CaCu3Ti4O12.Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(10): 2867-2875. |
| [20] | MEI L T, HSIANG H I, FANG T T.Effect pf copper-rich secondary phase at the grain boundary on the varistor properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(11): 3735-3737. |
| [21] | LI J Y, JIA R, TANG X, et al.Enhanced electric breakdown field of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics: tuning of grain boundary by a secondary phase.Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2013, 46(32): 325304. |
| [22] | JIA R, ZHAO X T, LI J Y, et al.Colossal breakdown electric field and dielectric response of Al-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Materials Science and Engineering B, 2014, 185: 79-85. |
| [23] | JACOB K T, ALCOCK C B.Thermodynamics of CuAlO2 and CuAl2O4 and phase equilibria in the system Cu2O-CuO-Al2O3.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1975, 58(5/6): 192-195. |
| [24] | SHAO S F, ZHANG J L, ZHENG P, et al.Microstructure and electrical properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Journal of applied physics, 2006, 99(8): 084106. |
| [25] | LI S T, WANG H, LIN C J, et al.Dielectric modulus response of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(8): 087701. |
| [26] | YANG Y, LI S T, LI X, et al.Investigation on relaxation properties of deep bulk trap in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 11(27): 1185-1190. |
| [27] | LI J Y, ZHAO X T, GU F, et al.Defects and dc electrical degradation in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics: role of oxygen vacancy migration.Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100(20): 202905. |
| [28] | 王振林, 李盛涛. 氧化锌压敏陶瓷制造及应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 31-35. |
| [1] | WEI Tingting, XU Huarui, ZHU Guisheng, LONG Shenfeng, ZHANG Xiuyun, ZHAO Yunyun, JIANG Xupeng, SONG Jinjie, GUO Ningjie, GONG Yipeng. Preparation and Properties of BaTiO3 Ceramics by Low Temperature Cold Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 903-910. |
| [2] | YAO Xiaogang, PENG Haiyi, GU Zhongyuan, HE Fei, ZHAO Xiangyu, LIN Huixing. Polyphenylene Oxide/Ca0.7La0.2TiO3 Microwave Composite Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 493-498. |
| [3] | Gang JIAN, Mei-Rui LIU, Chen ZHANG, Hui SHAO. Preparation of Fully-coated Ag@TiO2 Particle Fillers for High-k Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 641-645. |
| [4] | HAN Lin-Cai, DING Shi-Hua, SONG Tian-Xiu, HUANG Long, ZHANG Xiao-Yun, XIONG Zhong. ZBAS on the Structure and Dielectric Property of BaAl2Si2O8 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 883-888. |
| [5] | QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, LIU Fei, YUAN Chang-Lai, CHEN Guo-Hua, HUANG Xian-Pei. Heat-treatment on Crystallization and Dielecty Property of Mg-Al-Si-Ti-B Glass-ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(12): 1309-1315. |
| [6] | LIU Fei, HUANG Xian-Pei, YUAN Chang-Lai, CHEN Guo-Hua. Influence of Sintering Temperature and CaTiO3 Doping on Structure and Dielectric Properties for Instability Layered Can+1TinO3n+1 (n = 1) Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 489-494. |
| [7] | QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, SONG Xiao-Hui, YUAN Chang-Lai, LIU Fei. B-site Substitution by (Mg1/3Ta2/3)4+ on Structures and Dielectric Properties of New Sr-based (Sr, Nd, Ca)TiO3 Microwave Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(3): 293-298. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yao, DING Shi-Hua, LIU Yang-Qiong, DUAN Shao-Ying, XIAO Peng, HAN Lin-Cai. Crystal Structure and Microwave Dielectric Property of Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 91-95. |
| [9] | SUN Qing-Lei, ZHOU Hong-Qing, QIAN-Lei, WANG Ya-Zhou, ZHU Hai-Kui, YUE Zhen-Xing. Effects of MgO, SrO and La2O3 Co-doping on Structure and Properties of (Zr0.8Sn0.2)TiO4 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 812-818. |
| [10] | ZHANG Kang, LI Wei, LIN Hui-Xin. Effect of MgO/ Eu2O3 Co-doping on the Microwave Dielectric Properties of Al2O3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 984-988. |
| [11] | XIE Hui-Dong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao, XI Hai-Hong, SHI Ling. Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaPO4 Ceramics Synthesized by a Hydrothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 882-886. |
| [12] | XIE Hui-Dong, XI Hai-Hong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao. Microwave Dielectric Properties of BiMg2VO6 Ceramic with Low Sintering Temperature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(2): 202-206. |
| [13] | ZHAO Xue-Tong, REN Lu-Lu, LIAO Rui-Jin, LI Jian-Ying, WANG Fei-Peng. Effect of the Oxidizing Atmosphere on the Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1303-1309. |
| [14] | QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, JING Ben-Qin, LIU Fei, YUAN Chang-Lai. Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Property of (1-x)(Sr0.2Nd0.208Ca0.488)TiO3-xNd(Ti0.5Mg0.5)O3 Ceramics with High Quality Factor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(11): 1213-1217. |
| [15] | LI Wei, XIONG Zhao-Xian, XUE Hao. Preparation and Electrical Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Thin Ceramic Sheets via Water-based Tape Casting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(11): 1228-1232. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||