
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 950-956.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150077
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAI Yun-Gang1, DONG Wen-Jie1, GAO Yong-Ping1, NIU De-Chao1, CHEN Jian-Zhuang1, GU Jin-Lou1, LI Yong-Sheng1, SHI Jian-Lin1,2
Received:2015-02-03
Revised:2015-04-09
Published:2015-09-20
Online:2015-08-19
About author:ZHAI Yun-Gang. E-mail: zhaiyungang@126.com
CLC Number:
ZHAI Yun-Gang, DONG Wen-Jie, GAO Yong-Ping, NIU De-Chao, CHEN Jian-Zhuang, GU Jin-Lou, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin. Preparation of Superparamagnetic Gold Nanocomposites with Different Diameters and Their Imaging and Therapy Applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 950-956.
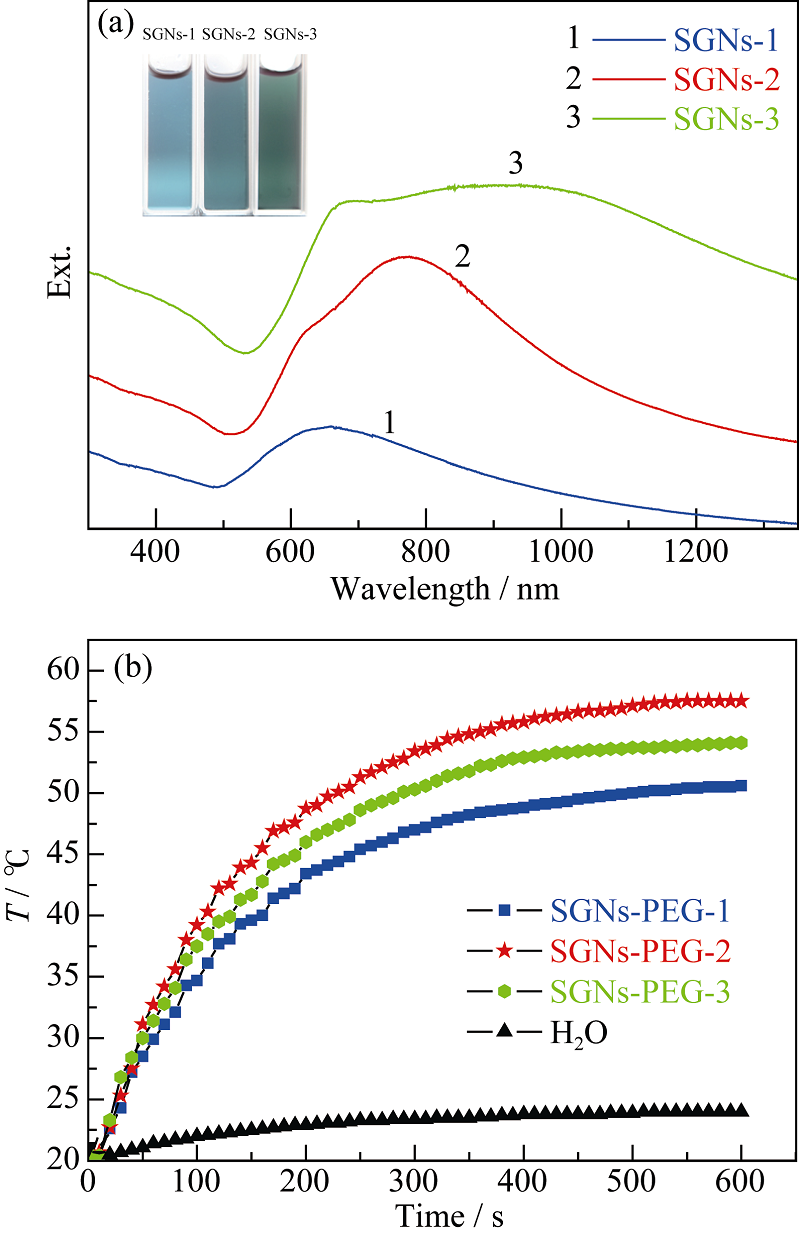
Fig. 4 UV-Vis spectra and digital photographs of SGNs with different diameters (a) and temperature change of SGNs-PEG with different diameters under irradiation time of 808 nm laser (b)
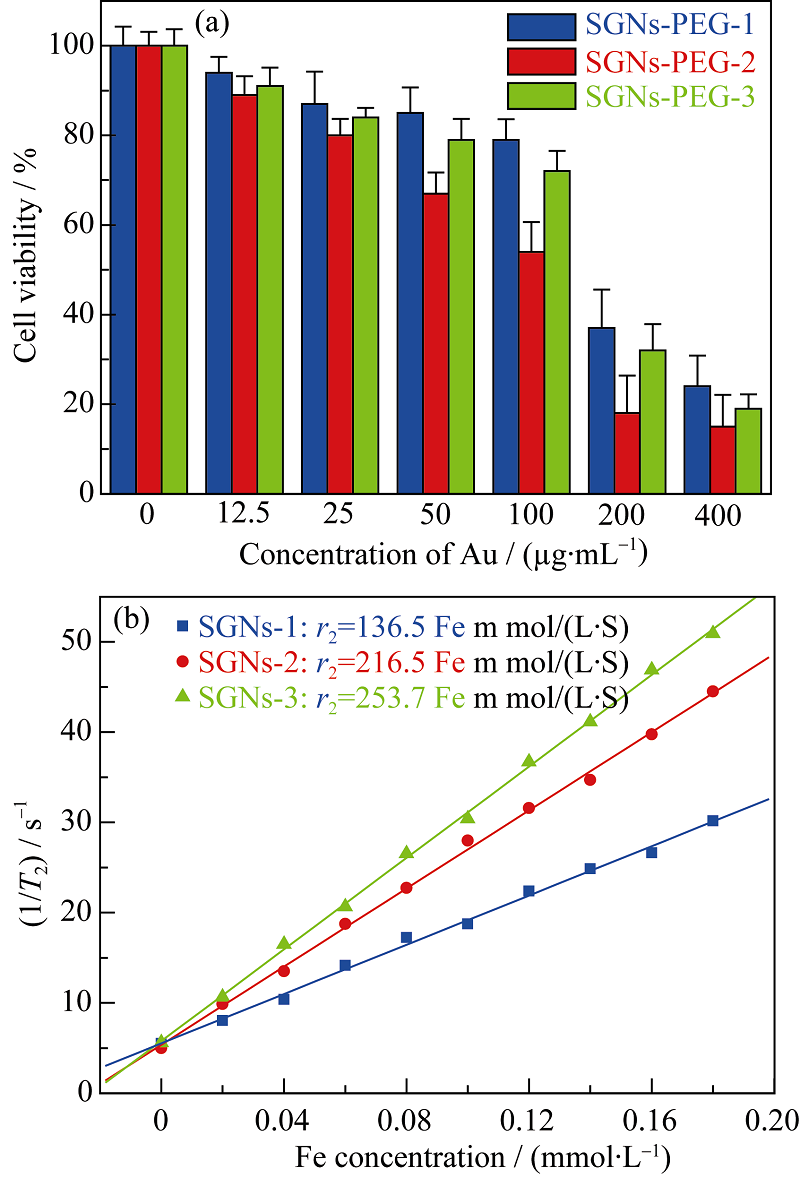
Fig. 5 MDA-MB-435 cell viability cultured with SGNs-PEG at different Au concentrations under 808 nm laser irradiation (a) and plots of inverse transverse relaxation time (1/T2) vs Fe concentration (b)
| [1] | HUANG X H, EL-SAYED I H, QIAN W, et al. Cancer cells assemble and align gold nanorods conjugated to antibodies to produce highly enhanced, sharp, and polarized surface raman spectra: a potential cancer diagnostic marker.Nano Letters, 2007, 7(6): 1591-1597. |
| [2] | ROSI N L, GILJOHANN D A, MIRKIN C A, et al.Oligonucletide- modified gold nanoparticles for intracellular gene regulation.Science, 2006, 312(5776): 1027-1030. |
| [3] | FUJIMOTO J G, BREZINSKI M E, SWANSON E A, et al.Optical biopsy and imaging using optical coherence tomography.Nature Medicine, 1995, 1: 970-972. |
| [4] | JAIN P K, HUANG X H, EL-SAYED M A, et al. Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine.Accounts of Chemical Research, 2008, 41(12): 1578-1586. |
| [5] | ARTHUR L, ADEN M K.Scattering of electromagnetic waves from two concentric spheres.Journal of Applied Physics, 1951, 22(10): 1242-1246. |
| [6] | OLDENBURG S J, AVERITT R D, HALAS N J, et al.Nanoengineering of optical resonances.Chemical Physics Letters, 1998, 288(1): 243-247. |
| [7] | WEST J L, HALAS N J.Engineered nanomaterials for biophotonics applications: improving sensing, imaging, and therapeutics.Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2003, 5(1): 285-292. |
| [8] | LOO C, LOWERY A, HALAS N J, et al.Immunotargeted nanoshells for integrated cancer imaging and therapy.Nano Letters, 2005, 5(4): 709-711. |
| [9] | O'NEAL D P, HIRSCH L R, HALAS N J, et al. Photo-thermal tumor ablation in mice using near infrared-absorbing nanoparticles.Cancer letters, 2004, 209(2): 171-176. |
| [10] | HIRSCH L R, STAFFORD R J, WEST J L, et al.Nanoshell- mediated near-infrared thermal therapy of tumors under magnetic resonance guidance.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2003, 100(23): 13549-13554. |
| [11] | BARHOUMI A, HUSCHKA R, HALAS N J, et al.Light-induced release of DNA from plasmon-resonant nanoparticles: towards light-controlled gene therapy.Chemical Physics Letters, 2009, 482(4): 171-179. |
| [12] | CHENG L, YANG K, LIU Z, et al.Facile preparation of multifunctional upconversion nanoprobes for multimodal imaging and dual-targeted photothermal therapy.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(32): 7385-7390. |
| [13] | LIU H Y, LIU T L, TANG F Q, et al.Targeting gold nanoshells on silica nanorattles: a drug cocktail to fight breast tumors via a single irradiation with near-infrared laser light.Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(6): 755-761. |
| [14] | LIU H Y, CHEN D, TANG F Q, et al.Multifunctional gold nanoshells on silica nanorattles: a platform for the combination of photothermal therapy and chemotherapy with low systemic toxicity.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(4): 891-895. |
| [15] | BARDHAN R, CHEN W, HALAS N J, et al.Nanoshells with targeted simultaneous enhancement of magnetic and optical imaging and photothermal therapeutic response.Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(24): 3901-3909. |
| [16] | CHEN W, BARDHAN R, JOSHI A, et al.A molecularly targeted theranostic probe for ovarian cancer.Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 2010, 9(4): 1028-1038. |
| [17] | PRIYAM A, IDRIS N M, ZHANG Y.Gold nanoshell coated NaYF4 nanoparticles for simultaneously enhanced upconversion fluorescence and dark-field imaging.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(3): 960-965. |
| [18] | KIM J, PARK S, HYEON T, et al.Designed fabrication of multifunctional magnetic gold nanoshells and their application to magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(46): 7754-7758. |
| [19] | JI X, SHAO R, LI C, et al.Bifunctional gold nanoshells with a superparamagnetic iron oxide-silica core suitable for both MR imaging and photothermal therapy.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(17): 6245-6251. |
| [20] | NIU D C, LI Y S, SHI J L, et al.A facile approach to fabricate functionalized superparamagnetic copolymer-silica nanocomposite spheres.Chemical Communications, 2008, 37: 4463-4465. |
| [21] | DONG W J, LIY S, SHI J L, et al.Facile synthesis of monodisperse superparamagnetic Fe3O4 core@hybrid@Au shell nanocomposite for biomodal imaging and photothermal therapy.Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(45): 5392-5397. |
| [22] | SUN S H, ZENG H, ROBINSON D B, et al.Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(1): 273-279. |
| [23] | DURAISWAMY S, KHAN S A.Plasmonic nanoshell synthesis in microfluidic composite foams.Nano Letters, 2010, 10(9): 3757-3763. |
| [24] | KE H T, WANG J R, LIU J B, et al.Gold-nanoshelled microcapsules: a theranostic agent for ultrasound contrast imaging and photothermal therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(13): 3017-3021. |
| [25] | PAQUET C, LEEK D M, SIMARD B, et al.Clusters of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles encapsulated in a hydrogel: a particle architecture generating a synergistic enhancement of the T2 relaxation.ACS Nano, 2011, 5(4): 3104-3112. |
| [26] | SPERLING R A, RIVERA G P, PARAK W J, et al.Biological applications of gold nanoparticles.Chemical Society Reviews, 2008, 37(9): 1896-1908. |
| [1] | TIAN Yu, ZHU Xiaojian, SUN Cui, YE Xiaoyu, LIU Huiyuan, LI Runwei. Intrinsically Stretchable Threshold Switching Memristor for Artificial Neuron Implementations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 413-420. |
| [2] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [3] | WANG Tongyu, RAN Haofeng, ZHOU Guangdong. Defect-induced Analogue Resistive Switching Behavior in FeOx-based Memristor and Synaptic Paired-pulse Facilitation Feature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 437-444. |
| [4] | HE Huikai, YANG Rui, XIA Jian, WANG Tingze, DONG Dequan, MIAO Xiangshui. High-uniformity Memristor Arrays Based on Two-dimensional MoTe2 for Neuromorphic Computing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 795-801. |
| [5] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [6] | WEI Chengxiong, JIN Xin, YIN Peinan, WU Chengwei, ZHANG Wei. Carbon Spheres for Photothermal Therapy of Tumor Cells: Rapid Preparation and High Photothermal Effect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1208-1216. |
| [7] | XIE Xue, WU Jianrong, CAI Xiaojun, HAO Junnian, ZHENG Yuanyi. Photothermal/pH Responsive B-CuS-DOX Nanodrug for Chemo-photothermal Synergistic Therapy of Tumor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 81-87. |
| [8] | ZHANG Chong, GENG Xiao-Wei, GAO Xiang-Di, ZHANG Xin, GUO Rao, WANG Yu-Jing, XU Jian-Zhong, MA Hai-Yun. Strontium Hydroxystannate Nanorods Encapsulated by Hybrid Polyphosphazene: Synthesis and Flame Retardancy on Epoxy Resin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 761-767. |
| [9] | LI Min, LUO Yuan, XU Wei-Jia, LIU Jia-Xiang. DMFC Anode Catalyst Fe3O4@Pt Particles: Synthesis and Catalytic Performanc [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(9): 916-922. |
| [10] | LIAO Fan, MA Jian-Qi, GE Hong-Guang. Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Core-satellite Ag/PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4 Magnetic Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 523-528. |
| [11] | JIANG Li, LIU Jia-Nan, FAN Wen-Pei, LIU Yan-Yan, NI Da-Long, BU Wen-Bo. Performance Study of TiO2-Au Photoelectric Nanocomposites for Novel Neuromodulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 550-554. |
| [12] | WANG Chao-Fei, LU Shuang, CHEN Hui-Long, GONG Fei-Long, GONG Yu-Yin, LI Feng. One-pot Synthesis and Application in Asymmetric Supercapacitors of Mn3O4@RGO Nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 581-587. |
| [13] | FU Hai-Li, ZHANG Wen, ZHANG Hua, SONG Shao-Bo, LI Wei. Preparation and Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan/Organic Laponite Nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 479-484. |
| [14] | LU Shao-Wei, LI Qian, XIONG Xu-Hai, MA Ke-Ming, XU Wei-Kai, JIA Cai-Xia. Microwave Abosrbing Properties of CNTs Composites Attached with Fe3O4/CNTs Hybrid Buckypaper [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(1): 23-28. |
| [15] | QIAO Yu-Lin, ZHAO Hai-Chao, ZANG Yan, ZHANG Qing. Tribological Properties of Graphene-based Fe3O4 Nanocomposite Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(1): 41-46. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||