
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 699-705.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140599
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Yang-Long1, ZHENG Yu-Ying2, SHANG Peng-Bo2
Received:2014-11-19
Revised:2015-01-21
Published:2015-07-20
Online:2015-06-25
About author:LIU Yang-Long. E-mall: 865528602@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Yang-Long, ZHENG Yu-Ying, SHANG Peng-Bo. Preparation, Characterization and Photocatalytic Property of Eu-doped TiO2 Hollow Microspheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(7): 699-705.
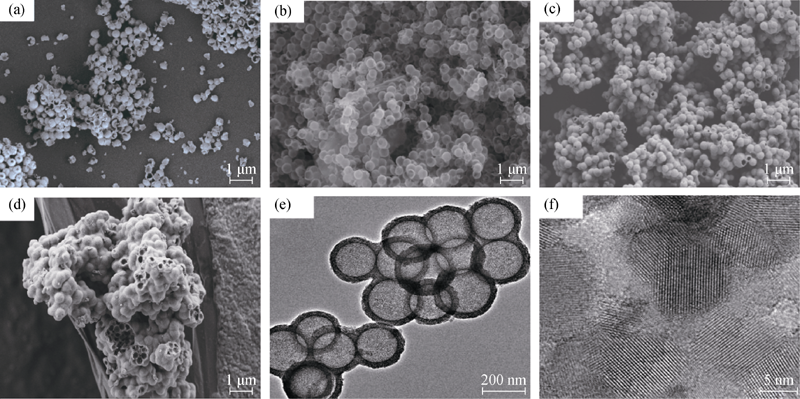
Fig. 2 SEM images of hollow microspheres prepared from solution with different quantities of TBOT (a-d) and TEM (e) and HRTEM (f) images of hollow microspheres by adding 1.5 mL TBOT (a) TBOT, 0.5 mL; (b) TBOT, 1 mL; (c) TBOT, 1.5 mL; (d) TBOT, 2 mL
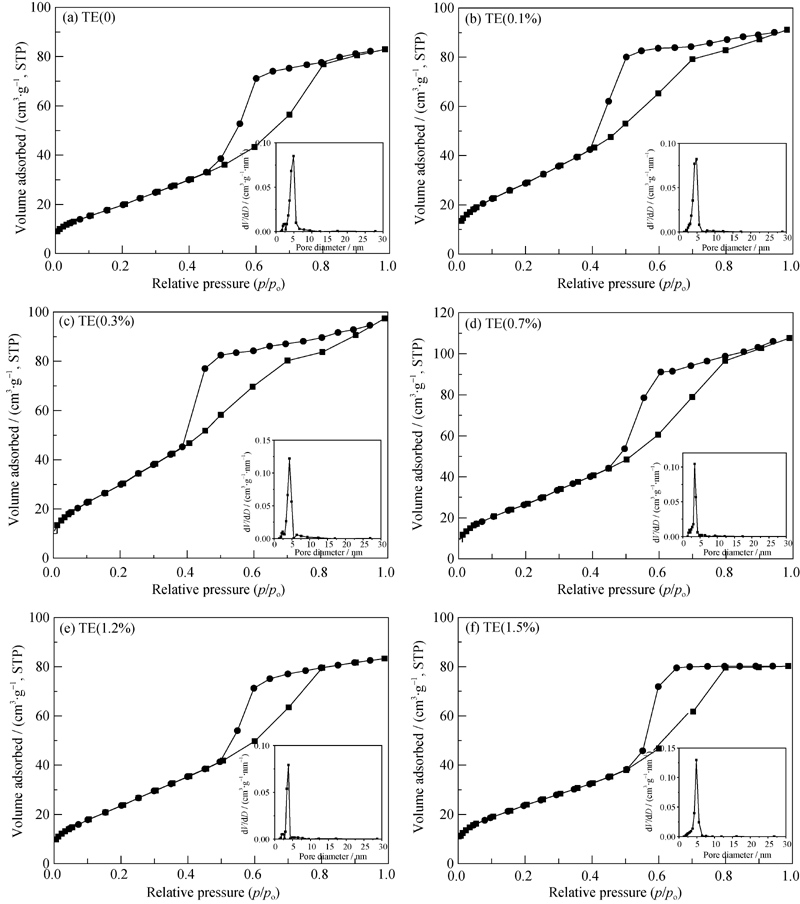
Fig. 5 N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and corresponding pore size distribution of TiO2 hollow microsphere samples with different Eu doping concentrations
| Sample | Crystallize size/nm | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| TE(0) | 12.9 | 221 | 5.5 |
| TE(0.1%) | 10.7 | 256 | 4.9 |
| TE(0.3%) | 9.5 | 275 | 4.2 |
| TE(0.7%) | 8.3 | 298 | 3.5 |
| TE(1.2%) | 10.0 | 268 | 4.5 |
| TE(1.5%) | 11.2 | 250 | 5.1 |
Table 1 Physical parameters of TiO2 hollow microsphere samples with different Eu doping concentrations
| Sample | Crystallize size/nm | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| TE(0) | 12.9 | 221 | 5.5 |
| TE(0.1%) | 10.7 | 256 | 4.9 |
| TE(0.3%) | 9.5 | 275 | 4.2 |
| TE(0.7%) | 8.3 | 298 | 3.5 |
| TE(1.2%) | 10.0 | 268 | 4.5 |
| TE(1.5%) | 11.2 | 250 | 5.1 |
| [1] | ALLINSON G, STAGNITTI F, COLVILLE S, et al.Growth of floating aquatic macrophytes in alkaline industrial wastewaters.Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2000, 126(12): 1103-1107. |
| [2] | GOSWAMI D Y.A review of engineering developments of aqueous phase solar photocatalytic detoxification and disinfection processes.Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, 1997, 119(3): 101-107. |
| [3] | ZHAO W, MA W H, CHEN C C.Efficient degradation of toxic organic pollutants with Ni2O3/TiO2-xBx under visible irradation.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(15): 4782-4783. |
| [4] | ZHANG QING-HONG, GAO LIAN, GUO JING-KUN.Photocatalytic activity of nanosized TiO2.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2000, 15(3): 556-560. |
| [5] | JI BONG JOO, QIAO ZHANG, IIKEUN LEE, et al.Mesoporous anatase titania hollow nanostructures though silica-protected calcination.Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(1): 166-174. |
| [6] | SUN B, VORONTSOV AV, SMIRNIOTIS PG.Role of platinum deposited on TiO2 in phenol photocatalytic oxidation.Langmuir, 2003, 19(8): 3151-3156. |
| [7] | CHOI W K, EAS TERMIN, MICHAEL R. HOFFMANN. The role of metal ion dopants in quantum-sized TiO2: correlation between photoreactivity and charge carrier recombination dynamic.The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1994, 98(51): 13669-13679. |
| [8] | KARTHIK K, VICTOR JAYA N.High pressure electrical resistivity studies on Ni-doped TiO2 nanoparticles.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(16): 5173-5176. |
| [9] | BAE E, CHOI W.Highly enhanced photoreductive degradation of perchlorinated compounds on dye-sen-sitized metal/TiO2 under visible light.Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37(1): 147-152. |
| [10] | LIANG YU-CHUAN, WANG CHIH-CHIEH, KEI CHI-CHUNG, et al.Photocatalysis of Ag-loaded TiO2 nanotube arrays formed by atomic layer deposition.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(19): 9498-9502. |
| [11] | ZHONG LIANG-SHU, HU JIN-SONG, CUI ZHI-MIN, et al.In-situ loading of noble metal nanoparticles on hydroxyl- ground-rich titania precursor and their catalytic applications.Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(18): 4557-4562. |
| [12] | ZHOU WEI, ZHENG YU-HUI, WU GUANG-HUI.Novel luminescent RE/TiO2(RE=Eu, Gd)catalysts prepared by in-situation Sol-Gel approach construction of multi-functional precursors and their photo or photocatalytic oxidation properties.Applied Surface Science, 2006, 253(3): 1387-1392. |
| [13] | RANJIT K T, WILLNER I, BOSSMANN S H, et al.Lanthanide oxide doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts: effective photocatalysts for the enhanced degradation of salicylic acid and t-cinnamic acid.Journal of Catalysis, 2001, 204(2): 305-310. |
| [14] | LI F B, LI X Z, AO C H, et al.Enhaned photocatalytic degradation of VOCs using Ln3+-TiO2 catalysts for indoor air purification.Chemosphere, 2005, 59(6): 787-800. |
| [15] | LIANG CHUN-HUA, HOU MEI-FANG, ZHOU SHUN-GUI, et al. The effect of erbium on the adsorption and photodegradation of orange I in aqueous Er3+-TiO2 suspension. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 138(3): 471-478. |
| [16] | SYOUFIAN A, SATRIYAA O H, NAKASHIMA K.Photocatalytic activity of titania hollow spheres: photodecomposition of methylene blue as a target molecule.Catalysis Communications, 2007, 8(5): 755-759. |
| [17] | YU JIA-GUO, ZHANG LI-JUAN, BEI CHENG, et al.Hydrothermal preparation and photocatalytic activity of hierarchically sponge-like macro-/mesoporous titania.The Journal of Physical Chemistry. C, 2007, 111(28): 10582-10589. |
| [18] | SUN XIAO-MING, LI YA-DONG. Ga2O3 and GaN semiconductor hollow spheres. Angewandte Chemie, 2004, 43(29): 3827-3831. |
| [19] | YU JIA-GUO, LIU SHENG-WEI, YU HUO-GEN.Microstructures and photoactivity of mesoporous anatase hollow microspheres fabricated by fluoride-mediated self-transformation.Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 249(1): 59-66. |
| [20] | YU JIA-GUO, WANG GUO-HONG, CHENG BEI, et al.Effects of hydrothermaltemperature and time on the photocatalytic activity and microstructures of bimodal mesoporous TiO2 powders.Applied Catalysis B, 2007, 69(3): 171-180. |
| [21] | SYOUFIAN A, NAKASHIMA K.Degradation of methylene blue in aqueous dispersion of hollow titania photocatalyst: optimization of reaction by peroxydisulfate electron scavenger.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 313(1): 213-218. |
| [22] | LI GUI-CUN, ZHANG ZHI-KUN.Preparation and characterization of hollow titania microspheres.Journal of Functional Materials Contents, 2004, 35(1): 2786-2791. |
| [23] | AO YAN-HUI, XU JING-JING, FU DE-GANG, et al. A simple method to prepare N-doped titania hollow spheres with high photocatalytic activity under visible light. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1/2/3): 413-417. |
| [24] | ZHANG QING-HONG, GAO LIAN, ZHENG SHAN.Preparation of mesoporous TiO2. photocatalyst by selective dissolving of titania-silica binary oxides.Chemistry Letters, 2001, 11: 1124-1125. |
| [25] | ZHANG QING-HONG, GAO LIAN.Preparation of nanocrystalline titanium oxide by decomposition of molecular precursor alpha- (NH4)2TiO(SO4)2.Chemistry Letters, 2003, 32(5): 461-462. |
| [26] | ARNOUT I.Preparation and characterization of titania-coated polystyene spheres and hollow titania shells.Langmuir, 2001, 17(12): 3579-3585. |
| [27] | ANTHONY J P, WAYNE L, JAMES M N.Dispersion polymerization of styrene in polar solvents.Macromolecules, 1990, 23(12): 3104-3109. |
| [28] | SUN XIAO-MING, LI YA-DONG.Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles.Angewandte Chemie, 2004, 43(5): 597-601. |
| [29] | SPURR R A, HOWARD MYERS.Quantitative analysis of anatase- rutile mixtures with an X-ray diffractometer.Analytical Chemistry, 1957, 29(5): 760-762 |
| [30] | JAMES L GOLE, JOHN D STOUT.Highly efficient formation of visible light tunable TiO2-xNx photocatalysts and their transformation at the nanoscale.The Journal of Physical Chemistry, B, 2004, 108(4): 1230-1240. |
| [31] | MONA SAIF, ABDEL-MOTTALEB M S A. Titanium dioxide nanomaterial doped with trivalent lanthanide ions of Tb, Eu and Sm: Preparation, characterization and potential applications.Inorg. Chim . Acta, 2007, 360(9): 2863-2874. |
| [32] | XIE YI-BING, YUAN CHUN-WEI.Characterizationand photocatalysis of Eu3+-TiO2 sol in the hydrosol reaction system.Materials Research Bulletin, 2004, 39(4-5): 533-543. |
| [33] | AN XIAO-SHA, CHEN JUN-DE, ZHOU ZHI-YOU, et al.Rare earth Eu doped PtRu/C catalysts and their properties for methanol electrooxidation.Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2010, 26(5): 1207-1213. |
| [34] | LI JING-HONG, KANG WAN-LIN, YAN WEN-HUA, et al.Preparation of Eu3+ doped titania nanocrystals and photocatalytic degradation partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide.Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2008, 24(6): 1030-1034. |
| [1] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [2] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [3] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [4] | ZHANG Ye, YAO Dongxu, ZUO Kaihui, XIA Yongfeng, YIN Jinwei, ZENG Yuping. Combustion Synthesis of Si3N4-BN-SiC Composites by in-situ Introduction of BN and SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 574-578. |
| [5] | WANG Jing, XU Shoudong, LU Zhonghua, ZHAO Zhuangzhuang, CHEN Liang, ZHANG Ding, GUO Chunli. Hollow-structured CoSe2/C Anode Materials: Preparation and Sodium Storage Properties for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1344-1350. |
| [6] | ZHANG Wenjun, ZHAO Xueying, LÜ Jiangwei, QU Youpeng. Progresses on Hollow Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Preparation and Application in Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1192-1202. |
| [7] | ZHENG Yanning, JI Junrong, LIANG Xueling, LAI Zhengjie, CHENG Qifan, LIAO Dankui. Performance of Nitrogen-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres as Oxidase Mimic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 527-534. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xiaoshan, WANG Bing, WU Nan, HAN Cheng, WU Chunzhi, WANG Yingde. Micro-nano Ceramic Fibers for High Temperature Thermal Insulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 245-256. |
| [9] | MAN Xin, WU Nan, ZHANG Mu, HE Hongliang, SUN Xudong, LI Xiaodong. Lu2O3-MgO Nano-powder: Synthesis and Fabrication of Composite Infrared Transparent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1263-1269. |
| [10] | YANG Conggang, MI Le, FENG Aihu, YU Yang, SUN Dazhi, YU Yun. Synthesis and Performance of KH-560 Modified SiO2 Insulation Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1343-1348. |
| [11] | PAN Bichen,REN Penghe,ZHOU Tejun,CAI Zhenyang,ZHAO Xiaojun,ZHOU Hongming,XIAO Lairong. Microstructure and Property of Thermal Insulation Coating on the Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 947-952. |
| [12] | DU Juan, LIU Lei, YU Yifeng, ZHANG Yue, LÜ Haijun, CHEN Aibing. Hollow Carbon Sphere with Tunable Structure by Encapsulation Pyrolysis Synchronous Deposition for Cefalexin Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 608-616. |
| [13] | LIU Jinyun, ZHANG Yuting, HONG Zhou, LIU Hua, WANG Shengxian, GU Xuehong. Fabrication of Dual-layer Hollow Fiber Ceramic Composite Membranes by Co-extrusion [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1333-1339. |
| [14] | ZHU Ben-Bi,ZHANG Wang,ZHANG Zhi-Jian,ZHANG Jian-Zhong,IMRAN Zada,ZHANG Di. Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties of Titanium Dioxide (B)/Glass Fiber Cloth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 961-966. |
| [15] | Shao-Dan ZHANG, Wei-Wei BAO, Hai-Ping MA. Near-infrared Reflective Pigments Based on Cu 2+ and Tb 3+ Codoped BaZrO3: Preparation and Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 599-604. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||