
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 667-672.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140688
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles
LIN Qing-Qing1,2,3, DONG Shao-Ming1,2, HE Ping1,2, ZHOU Hai-Jun1,2, HU Jian-Bao1,2
Received:2014-12-31
Published:2015-02-16
Online:2015-05-22
About author:LIN Qing-Qing(1987– ), female, candidate of master degree. E-mail: linqingqing_2006@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIN Qing-Qing, DONG Shao-Ming, HE Ping, ZHOU Hai-Jun, HU Jian-Bao. Microstructure and Property of TiB2 Reinforced Reaction-bonded B4C Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(6): 667-672.
| Specimen | Ti0 | Ti5 | Ti10 | Ti15 | Ti30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content of Ti in the perform/wt% | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
Table 1 Titanium content in the preforms
| Specimen | Ti0 | Ti5 | Ti10 | Ti15 | Ti30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content of Ti in the perform/wt% | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| Specimen | Density/ (g•cm-3) | Open porosity/ % | Flexural strength/ MPa | Elastic modulus/ GPa | Vickers hardness/ MPa | Fracture toughness/ (MPa•m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti0 | 2.52 | 1.6 | 286±12 | 332±11 | 22640±1950 | 4.74±0.73 |
| Ti5 | 2.54 | 1.1 | 295±8 | 338±10 | 21220±1660 | 5.10±0.14 |
| Ti10 | 2.59 | 0.9 | 320±10 | 323±2 | 21330±950 | 5.27±0.25 |
| Ti15 | 2.63 | 0.6 | 313±12 | 332±4 | 21080±1650 | 5.40±0.14 |
| Ti30 | 2.79 | 1.4 | 272±9 | 330±7 | 15510±700 | 4.97±0.23 |
Table 2 Properties of the reaction bonded B4C composites
| Specimen | Density/ (g•cm-3) | Open porosity/ % | Flexural strength/ MPa | Elastic modulus/ GPa | Vickers hardness/ MPa | Fracture toughness/ (MPa•m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti0 | 2.52 | 1.6 | 286±12 | 332±11 | 22640±1950 | 4.74±0.73 |
| Ti5 | 2.54 | 1.1 | 295±8 | 338±10 | 21220±1660 | 5.10±0.14 |
| Ti10 | 2.59 | 0.9 | 320±10 | 323±2 | 21330±950 | 5.27±0.25 |
| Ti15 | 2.63 | 0.6 | 313±12 | 332±4 | 21080±1650 | 5.40±0.14 |
| Ti30 | 2.79 | 1.4 | 272±9 | 330±7 | 15510±700 | 4.97±0.23 |
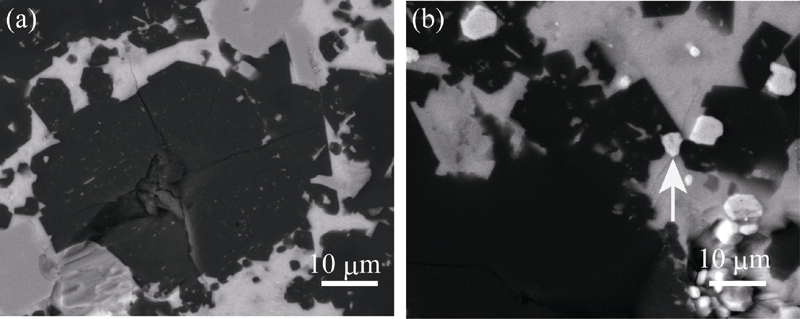
Fig. 5 SEM images showing the propagation behavior of indentation cracks in (a) sample Ti0 and (b) sample Ti15 The arrow in image (b) indicates the occurrence of crack deflection around a TiB2 particle
| [1] | THEVENOT F.A review on boron-carbide.Advanced Ceramics, 1991, 56: 59-88. |
| [2] | THUAULT A, MARINEL S, SAVARY E, et al.Processing of reaction- bonded B4C-SiC composites in a single-mode microwave cavity.Ceramics International, 2013, 39(2): 1215-1219. |
| [3] | LEE C H, KIM C H.Pressureless sintering and related reaction phenomena of Al2O3-doped B4C.Journal of Materials Science. 1992, 27(23): 6335-6340. |
| [4] | JUNG J W, KANG S H.Advances in manufacturing boron carbide- aluminum composites.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2004, 87(1): 47-54. |
| [5] | MALLICK D, KAYAL T K, GHOSH J, et al.Development of multi-phase B-Si-C ceramic composite by reaction sintering.Ceramics International, 2009, 35(4): 1667-1669. |
| [6] | CHEN H M, QI H Y, ZHENG F, et al, Thermodynamic assessment of the B-C-Si system.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 481(1/2): 182-189. |
| [7] | HAYUN S, WEIZMANN A, DARIEL M P, et al. The effect of particle size distribution on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of boron carbide-based reaction-bonded composites.Inernational Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2009, 6(4): 492-500. |
| [8] | SIGL L S, KLEEBE H J.Microcracking in B4C-TiB2 composites.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1995, 78(9): 2374-2380. |
| [9] | SKOROKHOD V, KRSTIC V D.High strength-high toughness B4C-TiB2 composites.Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2000, 19(3): 237-239. |
| [10] | HAYUN S, DILMAN H, DARIEL M P, et al.The effect of aluminum on the microstructure and phase composition of boron carbide infiltrated with silicon.Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 118(2/3): 490-495. |
| [11] | TARIOLLE S, THEVENOT F, AIZENSTEIN M, et al.Boron carbide-copper infiltrated cermets.Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2004, 177(2): 400-406. |
| [12] | SINGH M.Thermodynamic analysis for the combustion synthesis of SiC-B4C composites.Scripta Materialia, 1996, 34(6): 923-927. |
| [13] | MIN XINMIN, LU YIJIN, AN JIMING, et al.Quantum chemistry study on boron carbides and Si-doped ones.J. Struct. Chem., 2000, 19(3): 212-216. |
| [14] | HAYUN S, WEIZMANN A, DARIEL M P, et al.Microstructural evolution during the infiltration of boron carbide with molten silicon.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(4): 1007-1014. |
| [15] | TANG JUN, TAN SHOUHONG, CHEN ZHONGMING, et al.Strengthening and toughening of B4C/TiB2 multiphase ceramics,Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1997, 12(2): 169-174. |
| [16] | BAHARVANDI H R, HADIAN A M.Pressureless sintering of TiB2- B4C composite.Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2008, 17(6): 838-841. |
| [1] | TUERHONG Munire, ZHAO Honggang, MA Yuhua, QI Xianhui, LI Yuchen, YAN Chenxiang, LI Jiawen, CHEN Ping. Construction and Photocatalytic Activity of Monoclinic Tungsten Oxide/Red Phosphorus Step-scheme Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 701-707. |
| [2] | GUO Tianmin, DONG Jiangbo, CHEN Zhengpeng, RAO Mumin, LI Mingfei, LI Tian, LING Yihan. Enhanced Compatibility and Activity of High-entropy Double Perovskite Cathode Material for IT-SOFC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 693-700. |
| [3] | JIN Sai, LIU Xiaogen, QI Shuang, ZHAO Runchang, LI Zhijun. Fused Silica Glass: Laser-induced Damage on Bending Strength Weakening and Safety Design [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 671-677. |
| [4] | SUN Qiangqiang, CHEN Zixuan, YANG Ziyue, WANG Yimeng, CAO Baoyue. Amorphous Vanadium Oxide Loaded by Metallic Nickel-copper towards High-efficiency Electrocatalyzing Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 647-655. |
| [5] | WANG Bo, YU Jian, LI Cuncheng, NIE Xiaolei, ZHU Wanting, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Service Stability of Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermo-electro-magnetic Gradient Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [6] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [7] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [8] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [9] | LIN Junliang, WANG Zhanjie. Research Progress on Ferroelectric Superlattices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [10] | ZHANG Shouchao, CHEN Hongyu, LIU Hongfei, YANG Yu, LI Xin, LIU Defeng. High Temperature Recovery of Neutron Irradiation-induced Swelling and Optical Property of 6H-SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 678-686. |
| [11] | YANG Yingkang, SHAO Yiqing, LI Bailiang, LÜ Zhiwei, WANG Lulu, WANG Liangjun, CAO Xun, WU Yuning, HUANG Rong, YANG Chang. Enhanced Band-edge Luminescence of CuI Thin Film by Cl-doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 687-692. |
| [12] | LI Yue, ZHANG Xuliang, JING Fangli, HU Zhanggui, WU Yicheng. Growth and Property of Ce3+-doped La2CaB10O19 Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 583-588. |
| [13] | NIU Jiaxue, SUN Si, LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Xiaodong, MU Xiaoyu. Copper-based Nanozymes: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [14] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xiangsong, LIU Yetong, WANG Yongying, WU Zirui, LIU Zhenzhong, LI Yi, YANG Juan. Self-assembled Platinum-iridium Alloy Aerogels and Their Efficient Electrocatalytic Ammonia Oxidation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 511-520. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||