
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 593-598.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140651
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Ka, WAN Kang, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Lin, CHEN Qiong, CHANG Yong-Qin, LONG Yi
Received:2014-12-16
Revised:2015-02-05
Published:2015-06-04
Online:2015-05-22
About author:WANG Ka. E-mail: wangka200888@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Ka, WAN Kang, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Lin, CHEN Qiong, CHANG Yong-Qin, LONG Yi. Fabrication and Irradiation of Nanocrystalline Yttrium-stabilized Cubic ZrO2 Film[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(6): 593-598.
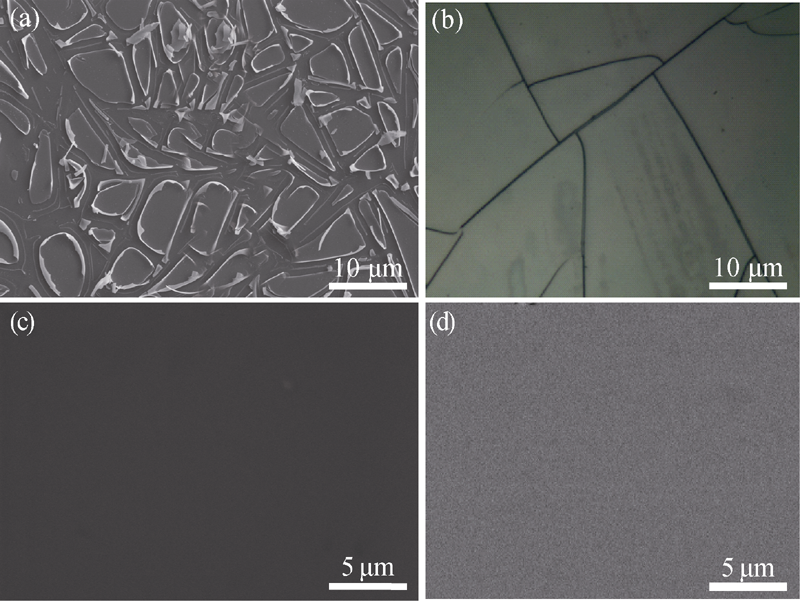
Fig. 1 (a) SEM image of YSZ film without adding PVA, (b) optical microscope image of YSZ film dried in air, SEM image (c) and BSD image (d) of YSZ film without cracks prepared under optimal conditions
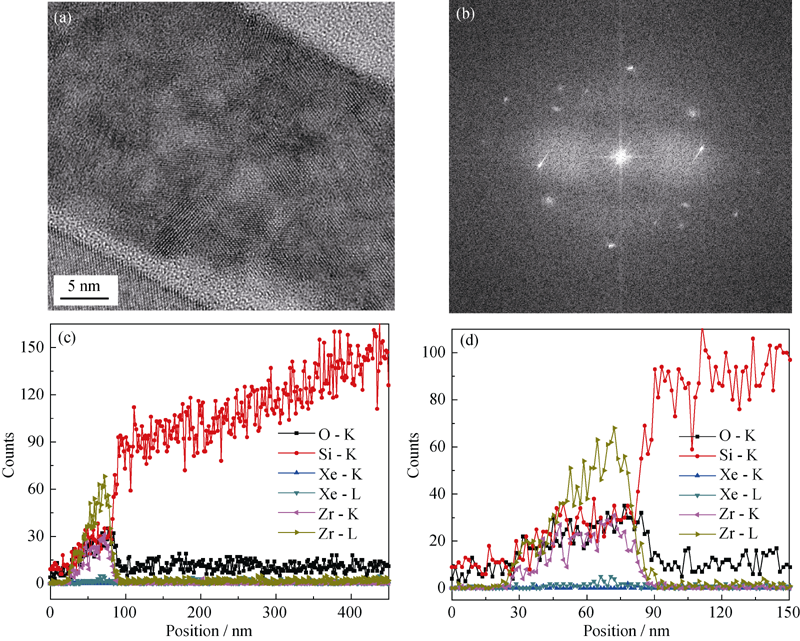
Fig. 4 Cross-sectional TEM image (a) and corresponding SAED pattern (b) of YSZ film, STEM-EDS line scan profile from the YSZ film to Si substrate (c) and its enlarged part (d)
| Element line | Flat site /at% | Crack site/at% |
|---|---|---|
| O K | 17.00 | 14.22 |
| Si K | 79.91 | 83.25 |
| Zr L | 3.10 | 2.53 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Table 1 Element compositions at flat and crack position on the surface of sample
| Element line | Flat site /at% | Crack site/at% |
|---|---|---|
| O K | 17.00 | 14.22 |
| Si K | 79.91 | 83.25 |
| Zr L | 3.10 | 2.53 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
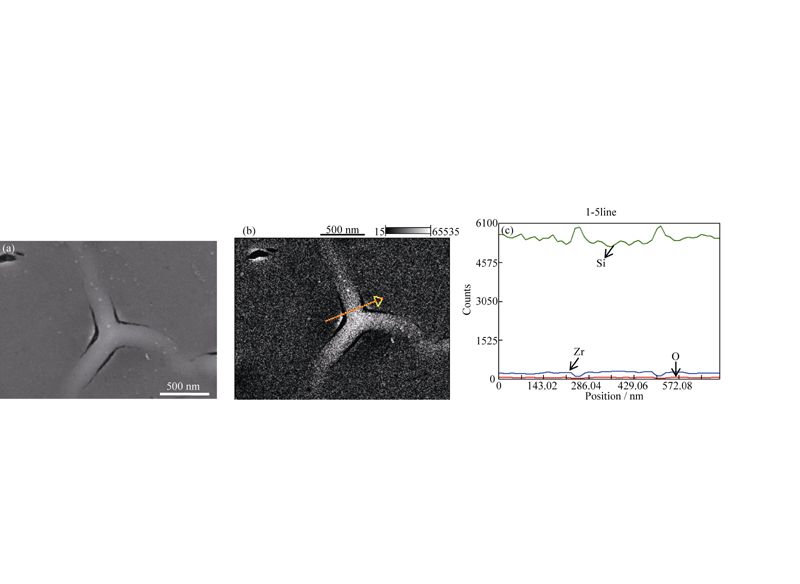
Fig. 6 High magnification SEM image of the YSZ films irradiated with 1.0 dpa irradiation dose (a), and corresponding BSD image (b) as well as its EDS line scan profile across the crack (c)
| [1] | SICKAFUS K E, MATZKE H, HARTMANN T, et al.Radiation damage effects in zirconia. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1999, 274(1): 66-77. |
| [2] | SASAJIMA N, MATSUI T, HOJOU K, et al.Radiation damage in yttria-stabilized zirconia under Xe ion irradiation.Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 1998, 141(1): 487-493. |
| [3] | EDMONDSON P D, WEBER W J, NAMAVAR F, et al.Determination of the displacement energies of O, p[Si and Zr under electron beam irradiation.Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2012, 422(1): 86-91. |
| [4] | ACKLAND G.Controlling radiation damage.Science, 2010, 327(5973): 1587-1588. |
| [5] | ZHANG YAN-WEN, JIANG WEI-LIN, WANG CHONG-MIN, et al.Grain growth and phase stability of nanocrystalline cubic zirconia under ion irradiation. Physical Review B, 2010, 82(18): 184105. |
| [6] | EDMONDSON P D, WEBER W J, NAMAVAR F, et al.Lattice distortions and oxygen vacancies produced in Au+-irradiated nanocrystalline cubic zirconia.Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65(8): 675-678. |
| [7] | YANG TENG-FEI, HUANG XUE-JUN, WANG CHEN-XU, et al.Enhanced structural stability of nanoporous zirconia under irradiation of He.Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2012, 427(1): 225-232. |
| [8] | LU FENG-YUAN, ZHANG JIA-MING, HUANG MENG-BING, et al.Phase transformation of nanosized ZrO2 upon thermal annealing and intense radiation.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(15): 7193-7201. |
| [9] | HUANG R T, SHEN Y H, HUANG R H, et al.Characterization of the irradiation-induced phase transition in the monoclinic polymorph of zirconia.Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2014, 332: 293-297. |
| [10] | SHARMA A, VARSHNEY M, SHIN H, et al.Monoclinic to tetragonal phase transition in ZrO2 thin films under swift heavy ion irradiation: structural and electronic structure study.Chemical Physics Letters, 2014, 592: 85-89. |
| [11] | ROSE M, GORZAWSKI G, MIEHE G, et al.Phase stability of nanostructured materials under heavy ion irradiation.Nanostructured Materials, 1995, 6(5): 731-734. |
| [12] | LU FENG-YUAN, WANG JIAN-WEI, LANG M, et al.Amorphization of nanocrystalline monoclinic ZrO2 by swift heavy ion irradiation.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2012, 14(35): 12295-12300. |
| [13] | MELDRUM A, BOATNER L A, EWING R C.Size effects in the irradiation-induced crystalline-to-amorphous transformation.Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2003, 207(1): 28-35. |
| [14] | MELDRUM A, BOATNER L A, EWING R C.Nanocrystalline zirconia can be amorphized by ion irradiation.Physical review letters, 2001, 88(2): 025503. |
| [15] | LIAN JIE, ZHANG JIA-MING, NAMAVAR F, et al. Ion beam-induced amorphous-to-tetragonal phase transformation and grain growth of nanocrystalline zirconia.Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(24): 245303. |
| [16] | YANG HUA-MING, OUYANG JING, ZHANG XIAO-LONG, et al.Synthesis and optical properties of yttria-doped ZrO2 nanopowders.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 458(1): 474-478. |
| [17] | LIN CUI-KUN, ZHANG CUI-MIAO, LIN JUN.Phase transformation and photoluminescence properties of nanocrystalline ZrO2 powders prepared via the pechini-type Sol-Gel process.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(8): 3300-3307. |
| [18] | FÁBREGAS I O, LAMAS D G. Parametric study of the gel-com- bustion synthesis of nanocrystalline ZrO2-based powders. Powder Technology, 2011, 214(2): 218-228. |
| [19] | MEHNER A, KLÜMPER-WESTKAMP H, HOFFMANN F, et al. Crystallization and residual stress formation of Sol-Gel-derived zirconia films.Thin Solid Films, 1997, 308: 363-368. |
| [1] | MAN Xin, WU Nan, ZHANG Mu, HE Hongliang, SUN Xudong, LI Xiaodong. Lu2O3-MgO Nano-powder: Synthesis and Fabrication of Composite Infrared Transparent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1263-1269. |
| [2] | YANG Conggang, MI Le, FENG Aihu, YU Yang, SUN Dazhi, YU Yun. Synthesis and Performance of KH-560 Modified SiO2 Insulation Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1343-1348. |
| [3] | ZHU Ben-Bi,ZHANG Wang,ZHANG Zhi-Jian,ZHANG Jian-Zhong,IMRAN Zada,ZHANG Di. Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties of Titanium Dioxide (B)/Glass Fiber Cloth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 961-966. |
| [4] | Shao-Dan ZHANG, Wei-Wei BAO, Hai-Ping MA. Near-infrared Reflective Pigments Based on Cu 2+ and Tb 3+ Codoped BaZrO3: Preparation and Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 599-604. |
| [5] |
LIU Qian, ZHOU Zhen-Zhen.
Progress in Activated-synthesis of Si-based Oxynitrides Materials at Low Temperatures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 129-137. |
| [6] | ZHAO Hui-Yue, WANG Xiao-Dong, FENG Jian-Bin, LIU Yuan, HUANG Ji-Chen, SHEN Jun. Environmental Stable SiO2 Antireflective Coating Modified via NH3/HTMS Vapor Phase Treatment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1219-1224. |
| [7] | HE Fei, LI Ya, LUO Jin, FANG Min-Han, HE Xiao-Dong. Development of SiO2/C and SiC/C Composites Featuring Aerogel Structures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 449-458. |
| [8] | LU Shu-Juan, WANG Chang, ZHAO Bo-Wen, WANG Hao, LIU Jing-Bing, YAN Hui. Electrochromic Properties of PEG-modified Tungsten Oxide Thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 185-190. |
| [9] | CHEN Ting, ZHA Jian-Rui, ZHANG Xiao-Jun, JIANG Wei-Hui, JIANG Wan, LIU Jian-Min, WU Qian. Silane Coupling Agent on Synthesis and Antioxidation Property of Zircon Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1154-1158. |
| [10] | ZHENG Lei, LI Jin, LIU Hong-Bo. Carbon Aerogels Prepared Based on Sol-Gel Reaction of Cellulose Colloid with AEP and Its Adsorption of Copper Ions in Aqueous Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1159-1164. |
| [11] | MA Peng-Fei, LI Ri-Hong, ZHANG Long. Sol-Gel-derived Mesoporous Calcium Aluminum Phosphate Bioactive Glasses with High Surface Area [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 107-112. |
| [12] | HU Ya-Hua, GU Mu, ZHANG Zhi-Yuan, LIU Xiao-Lin, HUANG Shi-Ming, LIU Bo, ZHANG Juan-Nan. Fabrication and Characterization of Lu2O3 Nanowire Arrays by Sol-Gel Template Method Assisted with Ultrasonic Treatment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 807-811. |
| [13] | YIN Yue-Feng, LIANG Gui-Jie, ZHANG Qiang, PAN Zheng, LI Wang-Nan, LI Zai-Fang. Optimization of Dye-sensitized Solar Cells Prepared by Pechini Sol-Gel Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(7): 739-744. |
| [14] | ZHAO Yue, LI Jun-Ping, WANG Ting-Yu, LI Rui-Xing, FENG Zhi-Hai, CAI Hong-Nian. Synthesis of ZrB2 Nanoparticles by Using Xylitol [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 597-601. |
| [15] | DA Xiao-Wei, QIU Ming-Hui, FAN Yi-Qun. Fabrication and Characterization of Y-doped ZrO2 Nanofiltration Membranes by Aqueous Sol-Gel Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 621-626. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||