
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 385-390.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140430
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIAO Yu, JIN Teng, YU Sheng-Wang, HE Zhi-Yong, SHEN Yan-Yan
Received:2014-08-21
Revised:2014-10-12
Published:2015-04-29
Online:2015-03-26
About author:QIAO Yu. E-mail: qiaoyu91421@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
QIAO Yu, JIN Teng, YU Sheng-Wang, HE Zhi-Yong, SHEN Yan-Yan. Effect of Annealing Atmosphere on Thermal Evolution of Ag Nanoparticles Embedded in SiO2 Thin Surface Layers[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 385-390.

Fig. 1 AFM images of samples before and after annealing at elevated temperatures under different atmospheres (a) As-implanted; (b) Annealed in Ar; (c) Annealed in N2; (d) Annealed in air
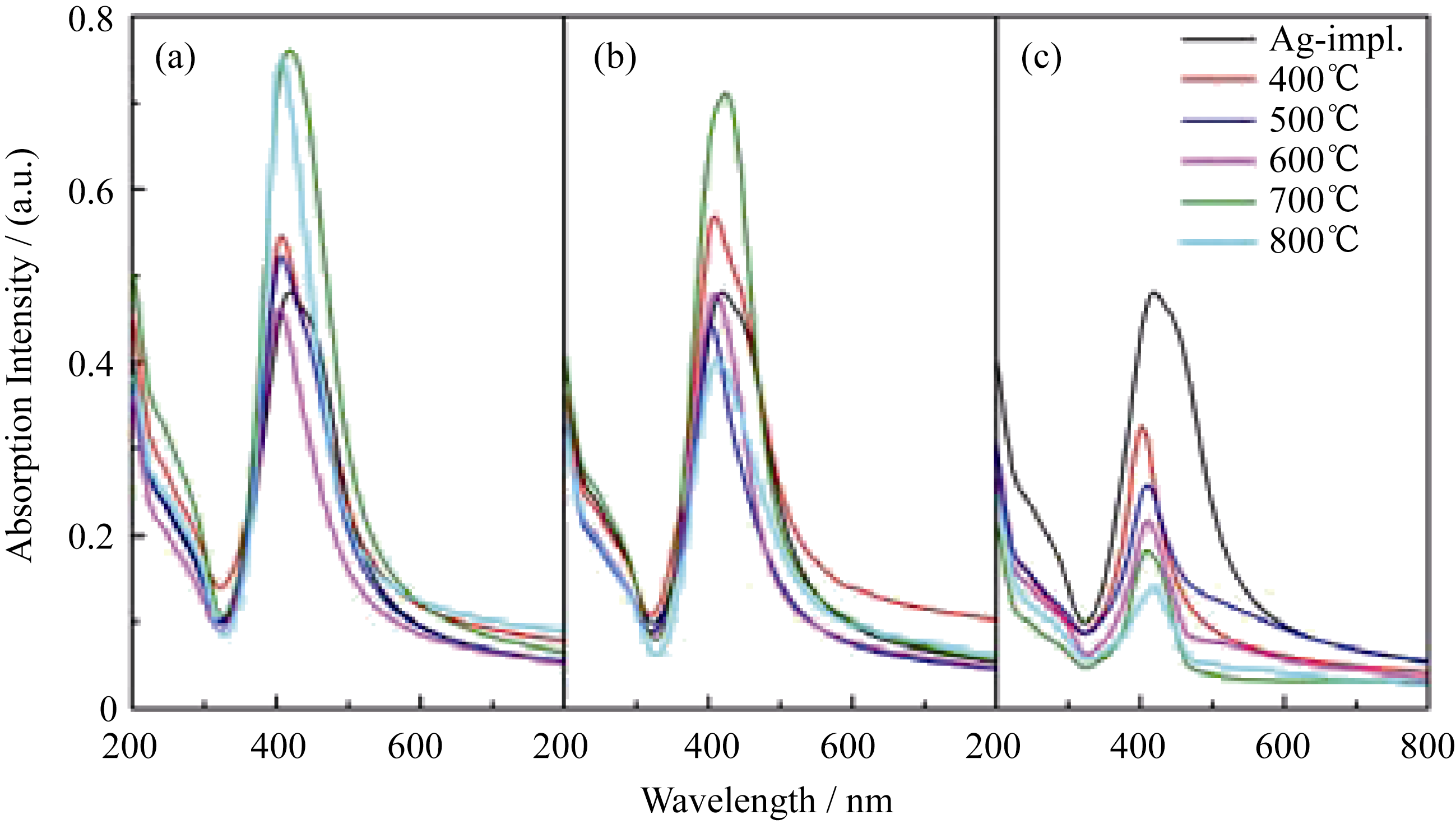
Fig. 2 UV-Vis optical absorption spectra of samples before and after annealing at elevated temperatures under different atmospheres (a) Annealed in Ar; (b) Annealed in N2; (c) Annealed in air
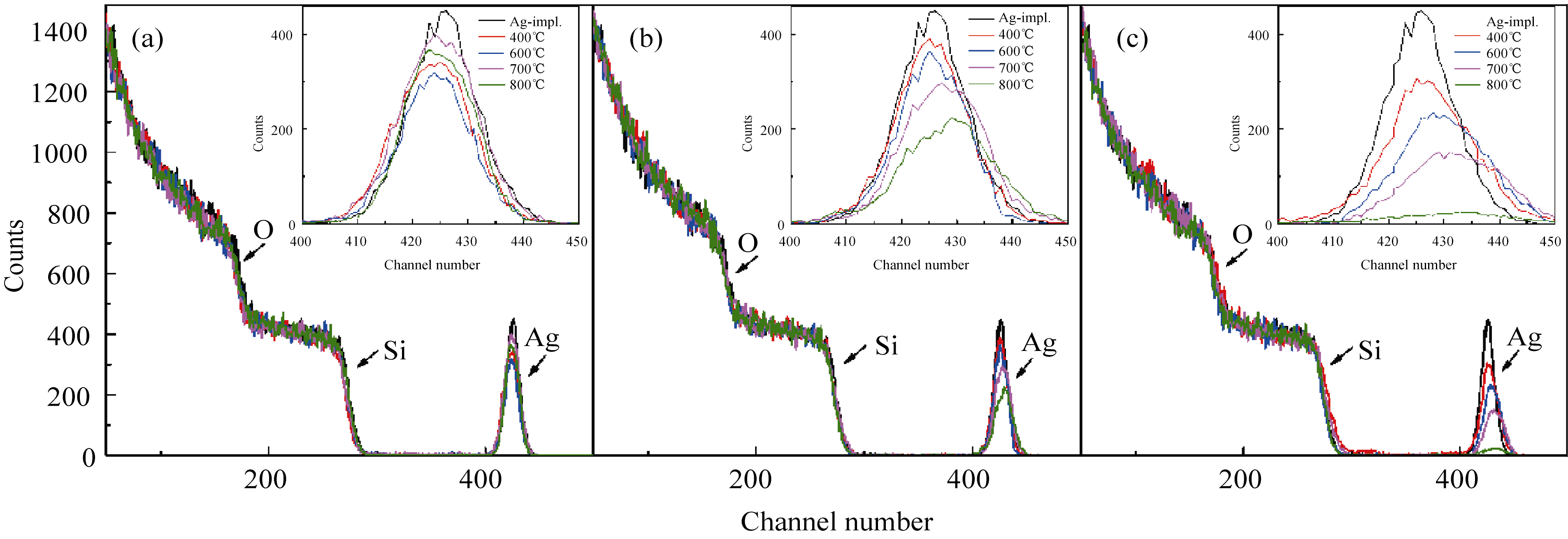
Fig. 4 RBS spectra of samples before and after annealing at elevated temperatures under different atmospheres (a) Annealed in Ar; (b) Annealed in N2; (c) Annealed in air (The insets show the corresponding magnified profiles for clarity)
| [1] | INOUYE H, TANAKA K, TANAHASHI I, et al.Ultrafast optical switching in a silver nanoparticle system. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2000, 39(9A): 5132-5133. |
| [2] | DONG P P, LIN Y Y, DENG J J, et al.Ultrathin gold-shell coated silver nanoparticles onto a glass platform for improvement of plasmonic sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(7): 2392-2399. |
| [3] | SHARMA A K, JHA R, GUPTA B D.Fiber-optic sensors based on surface plasmon resonance: a comprehensive review.IEEE Sens. J., 2007, 7(8): 1118-1129. |
| [4] | FUERTES G, SANCHEZ-MUNOZ O L, PEDRUEZA E, et al. Switchable bactericidal effects from novel silica-coated silver nanoparticles mediated by light irradiation.Langmuir, 2011, 27(6): 2826-2833. |
| [5] | KELLY K L, CORONADO E, ZHAO L L, et al.The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment.J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(3): 668-677. |
| [6] | ZHANG L, JIANG C Z, REN F, et al.Optical absorption of nanoclusters by sequentially implanting into SiO2 glass and subsequently annealing in a selected atmosphere.Acta Phys. Sin., 2004, 53(9): 2910-2914. |
| [7] | MOCK J J, BARBIC M, SMITH D R, et al.Shape effects in plasmon resonance of individual colloidal silver nanoparticles.J. Chem. Phys., 2002, 116(15): 6755. |
| [8] | GANEEV R A, BABA M, RYASNYANSKY A I, et al.Characterization of optical and nonlinear optical properties of silver nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in various liquids.Optics Communications, 2004, 240(4): 437-448. |
| [9] | MA Y, LIN J, ZHU L F, et al.Optical properties of Ag nanoparticle embedded silicate glass prepared by field-assisted diffusion.Appl. Phys. A., 2011, 102(3): 521-525. |
| [10] | POPOK V N, STEPANOV A L, ODZHAEV V B.Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by the ion implantation method and investigation of their optical properties. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 2005, 72(2): 229-234. |
| [11] | STEPANOV A L, ZHIKHAREV V A, KHAIBULIN I B.Depth profiles of metal ions implanted in dielectrics at low energies.Phys. Sol. State, 2001, 43(4): 766-771. |
| [12] | ZHANG D C, SHEN Y Y, HUANG Y J, et al.Theoretical study of nanoparticles in insulators fabricated by metal ion implantation.Acta Phys. Sin., 2010, 59(11): 7974-7978. |
| [13] | JOSEPH B, SUCHAND SANDEEP C S, SEKHAR B R, et al. Nonlinear optical properties of MeV and keV ion beam synthesized Ag nanoclusters.Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. B, 2007, 265(2): 631-636. |
| [14] | STEPANOV A L, GANEEV R A, RYASNYANSKY A I, et al.Non-linear optical properties of metal nanoparticles implanted in silicate glass.Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. B, 2003, 206: 624-628. |
| [15] | REN F, JIANG C Z, LIU C, et al. Controlling the morphology of Ag nanoclusters by ion implantation to different doses and subsequent annealing. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(16): 165501-1-4. |
| [16] | OLIVER A, CHEANG-WONG J C, ROIZ J, et al. Metallic nanoparticle formation in ion-implanted silica after thermal annealing in reducing or oxidizing atmospheres.Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. B, 2002, 191(1): 333-336. |
| [17] | SAHU G, RATH S K, JOSEPH B, et al.Saturation effects observed in high fluence heavy ion implantation at few tens of keV.Vacuum, 2009, 83(5): 836-840. |
| [18] | SHERRY L J, CHANG S H, SCHATZ G C, et al.Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver nanocubes.Nano Lett., 2005, 5(10): 2034-2038. |
| [19] | HAYNES C L, VAN DUYNE R P. Nanosphere lithography: a versatile nanofabrication tool for studies of size-dependent nanoparticle optics.J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105(24): 5599-5611. |
| [20] | CHAN G H, ZHAO J, HICKS E M, et al.Plasmonic properties of copper nanoparticles fabricated by nanosphere lithography.Nano Lett., 2007, 7(7): 1947-1952. |
| [21] | ROIZ J, OLIVER A, MUNOZ E, et al.Modification of the optical properties of Ag-implanted silica by annealing in two different atmospheres. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 95(4): 1783-1791. |
| [22] | BI H J, CAI W P, ZHANG L D.Annealing-induced reversible change in optical absorption of Ag nanoparticles.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 81(27): 5222-5224. |
| [23] | STEPANOV A L, POPOK V N. Nanostructuring of silicate glass under low-energy Ag-ion implantation. Surface Science, 2004, 566-568(Part2): 1250-1254. |
| [24] | STEPANOV A L, VALEEV V F, NUZHDIN V I, et al.Specificity of silver nanoparticle synthesis in quartz glass upon low-energy ion implantation.Nanotechnologies in Russia, 2011, 6(7/8): 490-495. |
| [25] | SEO H W, CHEN Q Y, RUSAKOVA I A, et al.Formation of silver nanoparticles in silicon by metal vapor vacuum arc ion implantation.Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. B, 2012, 292: 50-54. |
| [26] | CHEANG-WONG J C, OLIVER A, RODRIGUEZ-FERNANDEZ J, et al. Relationship between the Ag depth profiles and nanoparticle formation in Ag-implanted silica.J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 2001, 13(45): 10207-10209. |
| [27] | MARQUES C, SILVA R C, WEMANS A, et al.Optical properties tailoring by high fluence implantation of Ag ions on sapphire.Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. B, 2006, 242(1/2): 104-108. |
| [28] | WANG J, JIA G Y, MU X Y, et al. Quasi-two-dimensional Ag nanoparticle formation in silica by Xe ion irradiation and subsequent Ag ion implantation. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 102(13): 133102-1-4. |
| [29] | POPOK V N, GROMOV A V, NUZHDIN V I, et al.Optical and AFM study of ion-synthesised silver nanoparticles in thin surface layers of SiO2 glass.Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2010, 356(25/26/27): 1258-1261. |
| [30] | XU J X, REN F, FU D J, et al.Effect of thermal annealing on the optical properties of low-energy Cu-implanted silica glass.Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2006, 373(2): 341-345. |
| [31] | REN F, JIANG C Z, LIU C, et al.Interface influence on the surface plasmon resonance of Ag nanocluster composites.Solid State Communications, 2005, 135(4): 268-272. |
| [32] | PAL S, DE G.Reversible transformations of silver oxide and metallic silver nanoparticles inside SiO2 films.Materials Research Bulletin, 2009, 44(2): 355-359. |
| [33] | BANIJAMALI S, AGHAEI A R, EFTEKHARI YEKTA B.Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics and microstructure of a silver doped calcium aluminophosphate glass.Ceramics International. 2012, 38(3): 2395-2402. |
| [1] | WU Ling, TAN Ji, QIAN Shi, GE Naijian, LIU Xuanyong. Biological Property Investigation of Nitinol Surface Implanted with Tantalum [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1217-1224. |
| [2] | LI Kun-Qiang,QIAO Yu-Qin,LIU Xuan-Yong. Titanium Modified by Copper Ion Implantation: Anti-bacterial and Cellular Behaviors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 158-164. |
| [3] | YANG Ming-Ming, MO Ya-Juan, WANG Xiao-Dan, ZENG Xiong-Hui, LIU Xue-Hua, HUANG Jun, ZHANG Ji-Cai, WANG Jian-Feng, XU Ke. Stress Induced Microstructure Evolution of AlN: Er Film at Different Annealing Temperature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 285-290. |
| [4] | YU Mei, LIU Peng-Rui, SUN Yu-Jing, LIU Jian-Hua, AN Jun-Wei, LI Song-Mei. Fabrication and Characterization of Graphene-Ag Nanoparticles Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(1): 89-94. |
| [5] | WAN Guo-Jiang,HUANG Nan,LENG Yong-Xiang,YANG Ping,CHEN Jun-Ying. Mechanical Properties of TiN Nano-film Deposited by Plasma Immersion Ion Implantation and Deposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(4): 904-910. |
| [6] | XIE Er-Qing,WANG Wen-Wu,JIANG Ning,HE De-Yan. Ion Beam Synthesis and Electrical Properties Study of Yttrium Silicide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2002, 17(4): 708-712. |
| [7] | TU Xian-Hua,LI Dao-Huo,ZHAO Hua-Zhen,ZHAN Ming-Sheng. Effects of Ion Implantation on the Structure of Nano-Si3N4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(2): 369-372. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||