
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 1204-1210.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140106
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
DU Quan-Chao1,2, Lü Gong-Xuan2
Received:2014-03-06
Revised:2014-04-22
Published:2014-11-20
Online:2014-10-24
About author:DU Quan-Chao. E-mail: duquanchao@126.com
CLC Number:
DU Quan-Chao, Lü Gong-Xuan. Visible Light Photocatalytic Properties of Bi2O3 Modified BiPO4 Nanorod Composite Photocatalyst[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(11): 1204-1210.
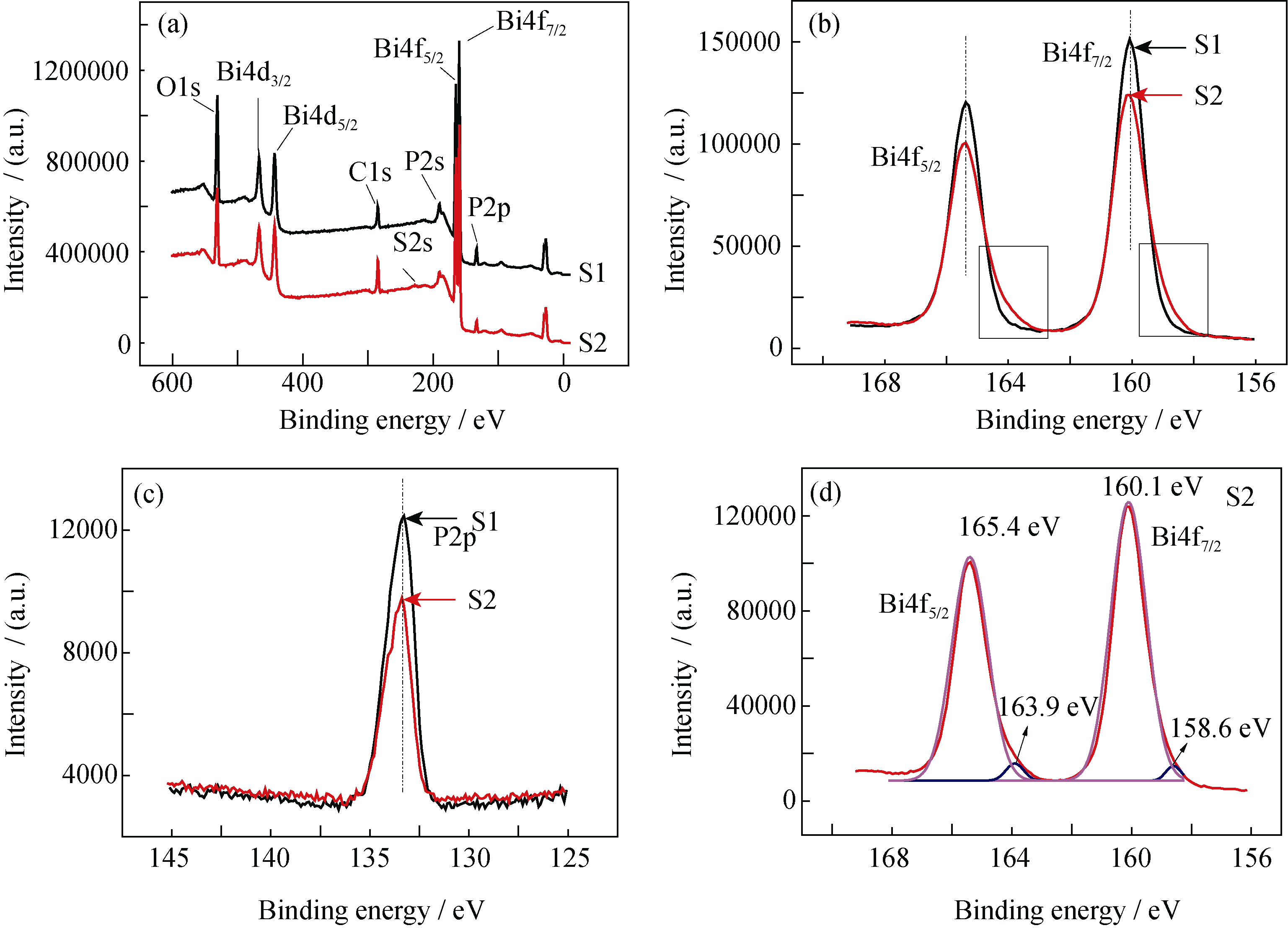
Fig. 3 The XPS survey spectra and the high-resolution XPS spectra of the S1 and S2 samples (a) The XPS survey spectra of sample S1 and S2; (b) High-resolution XPS spectra of Bi 4f in sample S1 and S2; (c) High-resolution XPS spectra of P 2p in sample S1 and S2; (d) The fitting curves of high-resolution XPS spectra for Bi 4f of sample S2
| Peak | Area fit | Center /eV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3450.66 | 158.6 |
| 2 | 135987.13 | 160.1 |
| 3 | 4431.80 | 163.9 |
| 4 | 108638.16 | 165.4 |
Table 1 XPS data of Bi 4f in sample S2
| Peak | Area fit | Center /eV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3450.66 | 158.6 |
| 2 | 135987.13 | 160.1 |
| 3 | 4431.80 | 163.9 |
| 4 | 108638.16 | 165.4 |
| Samples | SBET/(m²·g-1) | Vpore/(cm3·g-1) | dpore/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2.609 | 0.039 | 5.933 |
| S2 | 6.104 | 0.077 | 10.15 |
Table 2 The BET data of S1 and S2
| Samples | SBET/(m²·g-1) | Vpore/(cm3·g-1) | dpore/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2.609 | 0.039 | 5.933 |
| S2 | 6.104 | 0.077 | 10.15 |
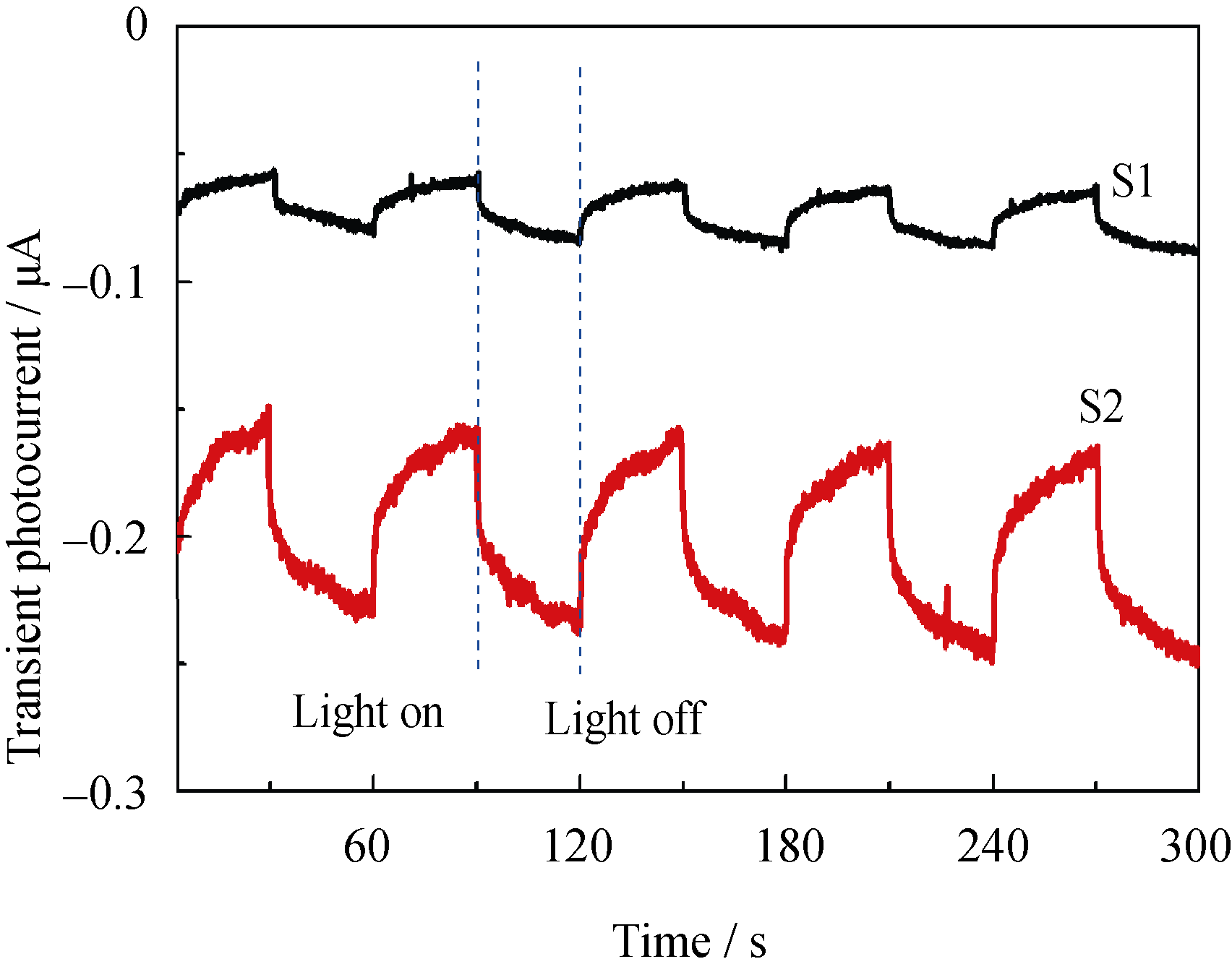
Fig. 6 The transient photocurrent-time curves of samples S1 and S2 Reaction conditions: 20 (V/V)% ethanol aqueous solution with 0.1 mol/L K2SO4, λ>420 nm
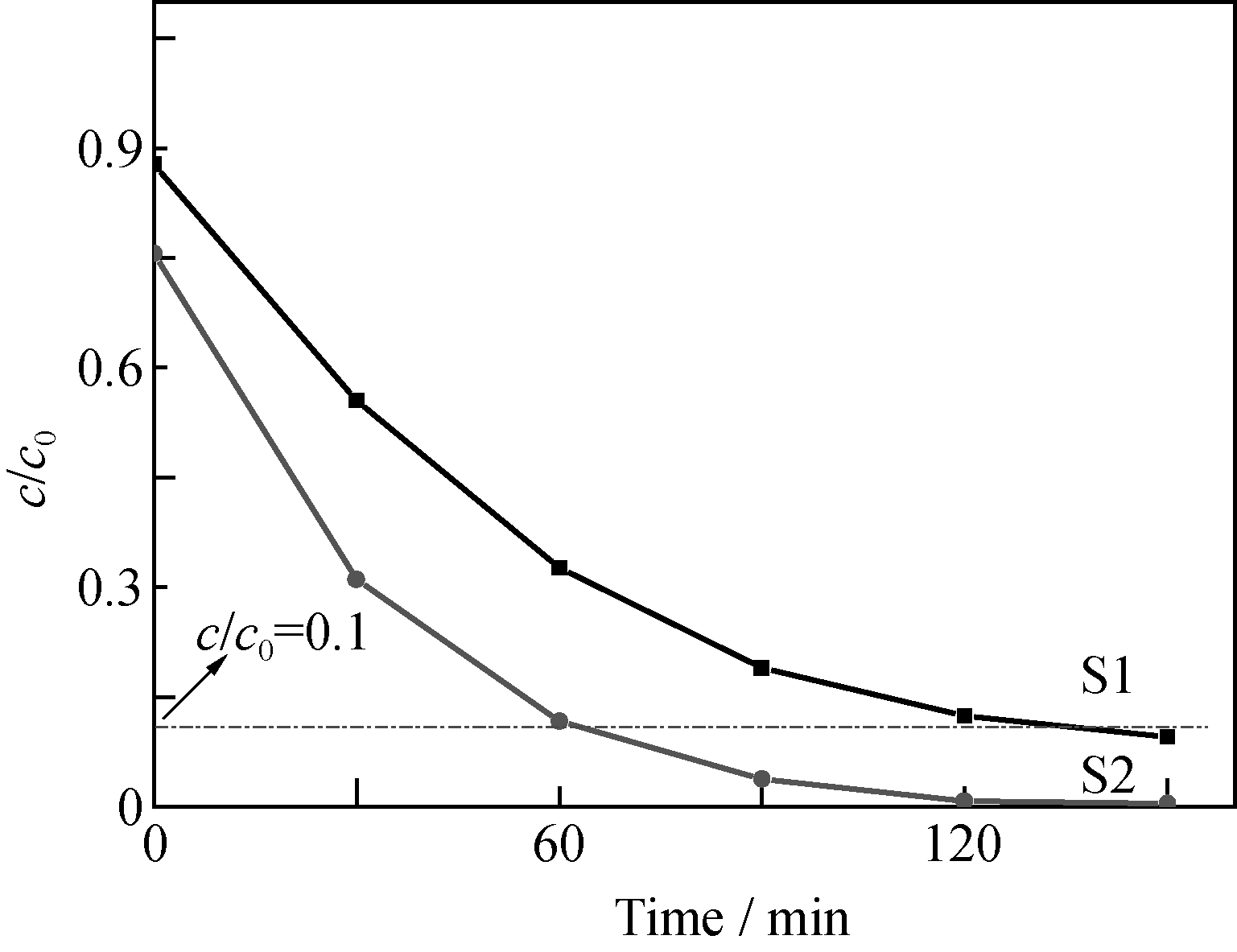
Fig. 7 Light degradation efficiency of S1 and S2 in methylene blue solution The light source is a xenon lamp, cut-off filter λ> 420 nm, the concentration of methylene blue is 10-5 g/L
| [1] | XIE Y Z, WU S H, ZHAO L, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of p-fluorobenzoic acid in sewage over Pt /TiO2. J. Mol. Catal. (China), 2012, 26: 449-455. |
| [2] | LI X Z, LI F B. Study of Au/Au3+-TiO2 Photocatalysts toward visible photooxidation for water and wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35: 2381-2387. |
| [3] | FENG YU, LIU XIN-YONG, JIANG ZHI, et al. Photocatalysis activity of Pt /TiO2 toward low concentration NO abatement. J. Mol. Catal. (China), 2013, 27: 76-82. |
| [4] | KUDO A, OMORI K, KATO H. A novel aqueous process for preparation of crystal form-controlled and highly crystalline BiVO4 powder from layered vanadates at room temperature and its photocatalytic and photophysical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121: 11459-11467. |
| [5] | LIN X P, HUANG T, HUANG F Q, et al. Photocatalytic activity of a Bi-based oxychloride Bi3O4Cl. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(48): 24629-24634. |
| [6] | DUNKLE S S, SUSLICK K S. Photodegradation of BiNbO4 powder during photocatalytic reactions. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(24): 10341-10345. |
| [7] | ZHAO X, XU T G, YAO W Q, et al. Photodegradation of dye pollutants catalyzed by γ-Bi2MoO6 nanoplate under visible light irradiation. App. Surf. Sci., 2009, 255: 8036-8040. |
| [8] | SHI R, LIN J, WANG Y J, et al. Visible-light photocatalytic degradation of BiTaO4 photocatalyst and mechanism of photocorrosion suppression. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114: 6472-6477. |
| [9] | PAN C S, ZHU Y F. Size-controlled synthesis of BiPO4 nanocrystals for enhanced photocatalytic performance. J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21: 4235-4241. |
| [10] | LUMETTA G. J, MCNAMARA B K, BUCK E C, et al. Characterization of high phosphate radioactive tank waste and simulant development. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009, 43(20): 7843-7848. |
| [11] | PAN C S, XU J, CHEN Y, et al. Influence of OH-related defects on the performances of BiPO4 photocatalyst for the degradation of rhodamine B. Appl. Catal B: Environ., 2012, 115-116: 314-319. |
| [12] | ROSE C L, MOONEY S. Polymorphic forms of bismuth phosphate. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie, Bd. , 1962, 117: 371-385. |
| [13] | BALTASAR R, SEBASTIAN B, MIGUEL A G ARANDA, et al. Syntheses, crystal structures, and characterization of bismuth phosphates. Inorg. Chem., 1994, 33: 1869-1874. |
| [14] | LI G F, DING Y, ZHANG Y F, et al. Microwave synthesis of BiPO4 nanostructures and their morphology-dependent photocatalytic performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 363: 497-503. |
| [15] | FU X Z, WALTER A Z, YANG Q, et al. Catalytic hydrolysis of dichlorodifluoromethane (CFC-12) on Sol-Gel-derived titania unmodified and modified with H2SO4. J. Catal., 1997, 168(2): 482-490. |
| [16] | László K, SZILVIA P, IMRE B, et al. Surface and bulk composition, structure, and photocatalytic activity of phosphate-modified TiO2. Chem. Mater., 2007, 19(19): 4811-4819. |
| [17] | BI Y P, OUYANG S X, NAOTO U, et al. Facet effect of single-crystalline Ag3PO4 Sub-microcrystals on photocatalytic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(17): 6490-6492. |
| [18] | JI F, LI C L, ZHANG J H. Hydrothermal synthesis of Li9Fe3(P2O7)3(PO4)2 nanoparticles and their photocatalytic properties under visible-light illumination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2(6): 1674-1678. |
| [19] | LONG B H, HUANG J H, WANG X C. Photocatalytic degradation of benzene in gas phase by nanostructured BiPO4 catalysts. Materials International, 2012, 22(6): 644-653. |
| [20] | PAN C S, ZHU Y F. New type of BiPO4 oxy-acid salt photocatalyst with high photocatalytic activity on degradation of dye. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44: 5570-5574. |
| [21] | LV T, PAN L K, LIU X J, et al. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by BiPO4-CdS composites synthesized using a microwave-assisted method. RSC Adv., 2012, 2: 12706-12709. |
| [22] | XU H, XU Y G, LI H M, et al. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic property of AgBr/BiPO4 heterojunction photocatalyst. Dalton Trans., 2012, 41: 3387-3394. |
| [23] | CHEN C C, MA W H, ZHAO J C. Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutants under visible-light irradiation. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39: 4206-4219. |
| [24] | YOU X F, CHEN F, ZHANG J L, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange on TiO2 promoted by silver. Chin. J. Catal., 2006, 27: 270-274. |
| [25] | SUBRAMANIAN V, WOLF E E, KAMAT P V. Catalysis with TiO2/gold nanocomposites: Effect of metal particle size on the Fermi level equilibration. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126: 4943-4950. |
| [26] | KIM W, TACHIKAWA T, MAJIMA T, et al. Photocatalysis of dye- sensitized TiO2 nanoparticles with thin overcoat of Al2O3: enhanced activity for H2 production and dechlorination of CCl4. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113: 10603-10609. |
| [1] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [3] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [4] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [5] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [7] | LIU Xuechen, ZENG Di, ZHOU Yuanyi, WANG Haipeng, ZHANG Ling, WANG Wenzhong. Selective Oxidation of Biomass over Modified Carbon Nitride Photocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [9] | LIU Peng, WU Shimiao, WU Yunfeng, ZHANG Ning. Synthesis of Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS Photocatalyst for CO2 Reduction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [10] | WANG Luping, LU Zhanhui, WEI Xin, FANG Ming, WANG Xiangke. Application of Improved Grey Model in Photocatalytic Data Prediction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 871-876. |
| [11] | AN Weijia, LI Jing, WANG Shuyao, HU Jinshan, LIN Zaiyuan, CUI Wenquan, LIU Li, XIE Jun, LIANG Yinghua. Fe(III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6 Composite Photocatalyst Preparation and Phenol Degradation by Photocatalytic Fenton Synergy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 615-622. |
| [12] | XIAO Xiang, GUO Shaoke, DING Cheng, ZHANG Zhijie, HUANG Hairui, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3@TiO2 Core-shell Structure Nanocomposite as Water Stable and Efficient Visible-light-driven Photocatalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 507-512. |
| [13] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [14] | SHU Mengyang, LU Jialin, ZHANG Zhijie, SHEN Tao, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots/Ultrathin C3N4 Nanosheet 0D/2D Composite: Enhanced Stability and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1217-1222. |
| [15] | LIU Yaxin, WANG Min, SHEN Meng, WANG Qiang, ZHANG Lingxia. Bi-doped Ceria with Increased Oxygen Vacancy for Enhanced CO2 Photoreduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 88-94. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||