
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 972-978.DOI: 10.15541/jim20130686
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU You, LIU Xiu, WANG Fang, HAO Jian-Wei, DU Jian-Xin
Received:2013-12-30
Revised:2014-02-16
Published:2014-09-17
Online:2014-08-21
About author:ZHOU You. E-mail: ydzhouyou@126.com
CLC Number:
ZHOU You, LIU Xiu, WANG Fang, HAO Jian-Wei, DU Jian-Xin. Effect of Metal Oxides on Fire Resistance and Char Formation of Intumescent Flame Retardant Coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(9): 972-978.
| No. | Sample | Fire resistance time/s | V300℃a /(℃•s-1) | V400℃/(℃•s-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t300℃ | t400℃ | ||||
| 1 | EP/T-IFR | 200 | 1040 | 1.50 | 0.38 |
| 2 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% Fe2O3 | 230 | 2200 | 1.30 | 0.18 |
| 3 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 280 | 2360 | 1.07 | 0.17 |
| 4 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% Fe2O3 | 220 | 2010 | 1.36 | 0.20 |
| 5 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% ZnO | 320 | 1780 | 0.94 | 0.22 |
| 6 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 340 | 2140 | 0.88 | 0.19 |
| 7 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% ZnO | 530 | 1710 | 0.57 | 0.23 |
| 8 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% TiO2 | 220 | 1440 | 1.36 | 0.28 |
| 9 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 260 | 1520 | 1.15 | 0.26 |
| 10 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% TiO2 | 240 | 1380 | 1.25 | 0.29 |
Table 1 Effect of MO contents on the fire resistance properties of coatings
| No. | Sample | Fire resistance time/s | V300℃a /(℃•s-1) | V400℃/(℃•s-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t300℃ | t400℃ | ||||
| 1 | EP/T-IFR | 200 | 1040 | 1.50 | 0.38 |
| 2 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% Fe2O3 | 230 | 2200 | 1.30 | 0.18 |
| 3 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 280 | 2360 | 1.07 | 0.17 |
| 4 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% Fe2O3 | 220 | 2010 | 1.36 | 0.20 |
| 5 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% ZnO | 320 | 1780 | 0.94 | 0.22 |
| 6 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 340 | 2140 | 0.88 | 0.19 |
| 7 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% ZnO | 530 | 1710 | 0.57 | 0.23 |
| 8 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% TiO2 | 220 | 1440 | 1.36 | 0.28 |
| 9 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 260 | 1520 | 1.15 | 0.26 |
| 10 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% TiO2 | 240 | 1380 | 1.25 | 0.29 |
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR300℃ /% | △CRb300℃ /% | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | ||||
| EP/T-IFR | -/238 | - | -/86 | - | -/27 | - |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 242/271 | 29 | 87/91 | 4 | 29/39 | 10 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt%ZnO | 242/270 | 28 | 87/93 | 6 | 29/36 | 7 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 242/268 | 26 | 87/89 | 2 | 29/32 | 3 |
Table 2 TG data of EP/T-IFR and EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% MO coatings in air
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR300℃ /% | △CRb300℃ /% | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | ||||
| EP/T-IFR | -/238 | - | -/86 | - | -/27 | - |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 242/271 | 29 | 87/91 | 4 | 29/39 | 10 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt%ZnO | 242/270 | 28 | 87/93 | 6 | 29/36 | 7 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 242/268 | 26 | 87/89 | 2 | 29/32 | 3 |
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | |||
| EP | -/123 | - | -/5.7 | - |
| EP/5wt%Fe2O3 | 125/183 | 58 | 10.4/15.9 | 5.5 |
| EP/5wt%ZnO | 125/186 | 61 | 10.4/18.7 | 8.3 |
| EP/5wt%TiO2 | 125/172 | 47 | 10.4/12.6 | 2.2 |
Table 3 TG data of EP and EP /5wt% MO composites in N2
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | |||
| EP | -/123 | - | -/5.7 | - |
| EP/5wt%Fe2O3 | 125/183 | 58 | 10.4/15.9 | 5.5 |
| EP/5wt%ZnO | 125/186 | 61 | 10.4/18.7 | 8.3 |
| EP/5wt%TiO2 | 125/172 | 47 | 10.4/12.6 | 2.2 |
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | /℃ | Calcd./Exp. | /% | |
| T-IFR | -/320 | - | -/49 | - |
| T-IFR/Fe2O3 | 326/315 | -11 | 53/66 | 13 |
| T-IFR/ZnO | 326/312 | -14 | 53/62 | 9 |
| T-IFR/TiO2 | 326/318 | -8 | 53/57 | 4 |
Table 4 TG data of T-IFR and T-IFR / MO composites in N2
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | /℃ | Calcd./Exp. | /% | |
| T-IFR | -/320 | - | -/49 | - |
| T-IFR/Fe2O3 | 326/315 | -11 | 53/66 | 13 |
| T-IFR/ZnO | 326/312 | -14 | 53/62 | 9 |
| T-IFR/TiO2 | 326/318 | -8 | 53/57 | 4 |
| Sample | BE/eV | Ca/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | Cox/Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP/T-IFR | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /53.18 | 285.8 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/32.83 | 287.6 | -COO- /7.07 | 289.7 | -COOH /6.92 | 0.88 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /71.13 | 286.1 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/20.37 | 287.7 | -COO- /3.82 | 289.2 | -COOH /4.68 | 0.41 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /67.10 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/17.37 | 287.6 | -COO- /5.53 | 289.7 | -COOH /10.00 | 0.49 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /63.81 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/31.05 | 287.7 | -COO- /1.43 | 289.3 | -COOH /3.72 | 0.62 |
Table 5 Fitting results for the C1s spectra of char residues obtained from EP/T-IFR and EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% MO coatings at 650℃
| Sample | BE/eV | Ca/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | Cox/Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP/T-IFR | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /53.18 | 285.8 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/32.83 | 287.6 | -COO- /7.07 | 289.7 | -COOH /6.92 | 0.88 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /71.13 | 286.1 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/20.37 | 287.7 | -COO- /3.82 | 289.2 | -COOH /4.68 | 0.41 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /67.10 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/17.37 | 287.6 | -COO- /5.53 | 289.7 | -COOH /10.00 | 0.49 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /63.81 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/31.05 | 287.7 | -COO- /1.43 | 289.3 | -COOH /3.72 | 0.62 |
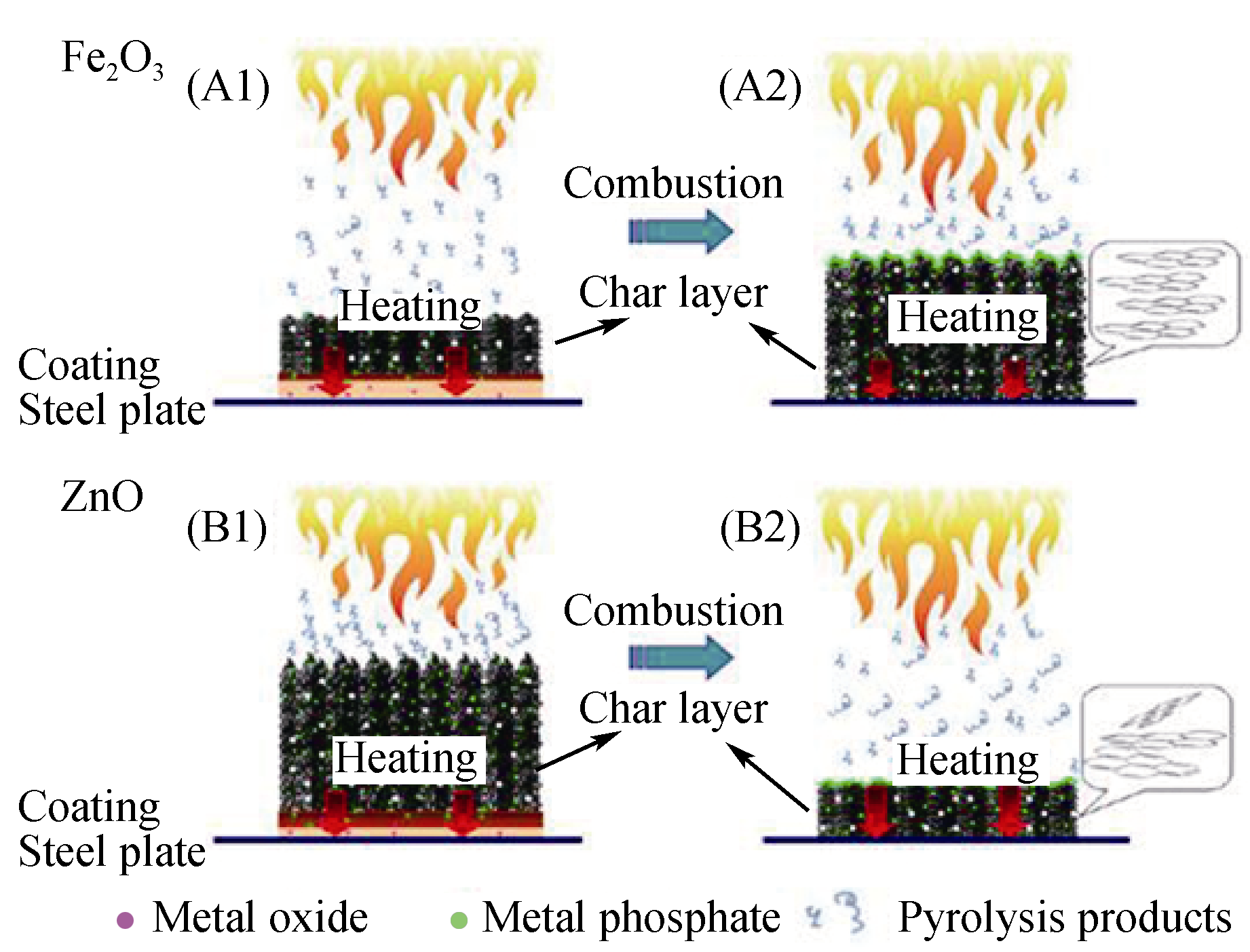
Fig. 6 Schematic drawing for the synergistic mechanism between MO and intumescent coating The initial combustion stage: A1 and B1; the end of combustion stage: A2 and B2
| [1] | CAMINO G, COSTA L, MARTINASSO G. Intumescent fire-retardant systems. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1989, 23(4): 359-376. |
| [2] | 杨荣杰,王建祺. 聚合物纳米复合物加工、热行为与阻燃性能. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 200-201. |
| [3] | DAI X H, WANG Y C, BAILEY C G. Effects of partial fire protection on temperature developments in steel joints protected by intumescent coating. Fire Saf. J., 2009, 44(3): 376-386. |
| [4] | ROBERT J A, BRIAN L, CHRIS M, et al. Thermo-physical performance of a fire protective coating for naval ship structures. Composites Part A, 2009, 40(1): 11-18. |
| [5] | STAGGS J E J, CREWE R J, BUTLER R. A theoretical and experimental investigation of intumescent behaviour in protective coatings for structural steel. Chem. Eng. Sci., 2012, 71: 239-251. |
| [6] | WANG G J, YANG J Y. Influences of glass flakes on fire protection and water resistance of waterborne intumescent fire resistive coating for steel structure. Prog. Org. Coat., 2011, 70(2/3): 150-156. |
| [7] | YEW M C, SULONG N H R. Fire-resistive performance of intumescent flame-retardant coatings for steel. Mater. Des., 2012, 34: 719-724. |
| [8] | WU K, ZHANG Y K, ZHANG K, et al. Effect of microencapsulation on thermal properties and flammability performance of epoxy composite. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2012, 94: 196-201. |
| [9] | SUN L S, QU Y T, LI S X. Co-microencapsulate of ammonium polyphosphate and pentaerythritol in intumescent flame-retardant coatings. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2013, 111(2): 1099-1106. |
| [10] | 屈红强. 聚硅氧烷对聚磷酸铵的表面包覆改性及其在环氧树脂中的阻燃应用研究. 北京: 北京理工大学博士论文, 2013. |
| [11] | LI B, XU M J. Effect of a novel charring-foaming agent on flame retardancy and thermal degradation of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2006, 91(6): 1380-1386. |
| [12] | LI Y T, LI B, DAI J F, et al. Synergistic effects of lanthanum oxide on a novel intumescent flame retardant polypropylene system. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2008, 93(1): 9-16. |
| [13] | HAO JIAN-WEI, CHEN SU, DU JIAN-XIN, et al. An investigation on caged bicyclic phosphate applied to intumescent flame retar dant coating. J. Beijing. Inst. Technol., 2007, 27(11): 1027-1031. |
| [14] | HAO JIAN-WEI, WEN HAI-XU, DU JIAN-XIN, et al. Studies on fire resistance mechanism of intumescent flame retarded epoxy coating containing zinc borate as a synergistic agent. J. Beijing. Inst. Technol., 2012, 32(10): 1091-1100. |
| [15] | WANG Z Y, HAN E H, KE W. Influence of nano-LDHs on char formation and fire-resistant properties of flame-retardant coating. Prog. Org. Coat., 2005, 53(1): 29-37. |
| [16] | XIA LIAO-YUAN, WU YI-QIANG, HU YUN-CHU. Study on smoke catalytic conversion by Sn-substituted mesoporous silica composite in wood fire retardance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 532-536. |
| [17] | HU YUN-CHU, WU ZHI-PING, SUN HAN-ZHOU, et al. Synthesis of nano zinc borate fire retardant by solid state reaction. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(4): 815-820. |
| [18] | WANG Z Y, HAN E H, KE W. Effect of nanoparticles on the improvement in fire-resistant and anti-ageing properties of flame- retardant coating. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 200(20/21): 5706-5716. |
| [19] | ZOU MIN, WANG QI-LIN. Improvement of performance of steel structural fireproofing dope with ZnO whisker and nanometer TiO2. Nano Technol. Precis. Eng, 2009, 7(1): 25-30. |
| [20] | CAMINO G, MARTINASSO G, COSTA L. Thermal degradation of pentaerythritol diphosphate, model compound for fire retardant intumescent systems: Part I—Overall thermal degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1990, 27(3): 285-296. |
| [21] | CAMINO G, MARTINASSO G, COSTA L, et al. Thermal degradation of pentaerythritol diphosphate, model compound for fire retardant intumescent systems: Part II—Intumescence step. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1990, 28(1): 17-38. |
| [22] | MENACHEM L, ENDO M. Catalysis of intumescent flame retardancy of polypropylene by metallic compounds. Polym. Adv. Technol., 2003, 14(1): 3-11. |
| [23] | LIU GUO-SHENG, ZHOU YOU, HAO JIAN-WEI. Thermal degradation mechanism of Bi2O3 synergistic intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Chin. Synth. Res. Plast., 2013, 30(5): 15-19. |
| [24] | LI GUO-XIN, HE YAN-SHU, NAN FENG, et al. Influence of MoO3, MoSi2 and Fe2O3 on residual chars of intumescent fire-retardant coating. J. Build. Mater., 2012, 15(3): 349-355. |
| [25] | ZHOU YOU, HAO JIAN-WEI, LIU GUO-SHENG, et al. Influencing mechanism of transition metal oxide on thermal decomposition of ammonium polyphosphate. Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(6): 1115-1122. |
| [26] | JIMENEZ M, DUQUESNE S, BOURBIGOT S. Intumescent fire protective coating: toward a better understanding of their mechanism of action. Thermochim. Acta, 2006, 449(1/2): 16-26. |
| [27] | 胡 源,宋 磊. 阻燃聚合物纳米复合材料. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 156-157. |
| [28] | BAI Z M, WANG X, TANG G, et al. Structure-property relationships of synthetic organophosphorus flame retardant oligomers by thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta, 2013, 565(10): 17-26. |
| [29] | BOURBIGOT S, BRAS M L, GENGEMBRE L, et al. XPS study of an intumescent coating application to the ammonium polyphosphate/pentaerythritol fire-retardant system. Appl. Surf. Sci., 1994, 81(3): 299-307. |
| [30] | JIANG W Z, HAO J W, HAN Z D. Study on the thermal degradation of mixtures of ammonium polyphosphate and a novel caged bicyclic phosphate and their flame retardant effect in polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2012, 97(4): 632-637. |
| [31] | 韩维屏. 催化化学导论. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 392-393. |
| [32] | 麦松威,周公度,李伟基. 高等无机结构化学, 2版. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2001: 47-49. |
| [33] | ZHU J, UHL F M, MORGAN A B, et al. Studies on the mechanism by which the formation of nanocomposites enhances thermal stability. Chem. Mater., 2001, 13(12): 4649-4654. |
| [1] | ZHENG Shiyou, DONG Fei, PANG Yuepeng, HAN Pan, YANG Junhe. Research Progress on Nanostructured Metal Oxides as Anode Materials for Li-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1295-1306. |
| [2] | WANG Song-Can, TANG Feng-Qiu, WANG Lian-Zhou. Visible Light Responsive Metal Oxide Photoanodes for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting: a Comprehensive Review on Rational Materials Design [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 173-197. |
| [3] | TIAN Xiao-Dong, LI Xiao, YANG Tao, SONG Yan, LIU Zhan-Jun, GUO Quan-Gui. Recent Advances on Synthesis and Supercapacitor Application of Binary Metal Oxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 459-468. |
| [4] | WANG Wei-Qi, ZHENG Hui-Feng, LU Guan-Hong, LIU Yang-Qiao, SUN Jing, GAO Lian. Recent Progress on Applications of Nano Metal Oxides in Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(9): 897-907. |
| [5] | YANG Bin-Hua, LIU Xue-Qiang, ZHANG Wei, LI Xiang-Tan, ZHANG Li-Yan, HU Li-Li. Influences of the Dopants of Several Heavy Metal Oxides and GeO2 on Spectroscopic and Lasing Properties of Yb3+-doped Fluorophosphate Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(9): 961-966. |
| [6] | XU Li-Hua, ZENG Hong-Yan, LIAO Meng-Chen, XU Sheng, ZHANG Zhi-Qing, Li Qiao . Effect of Temperature on Microstructure and Cr(VI) Adsorption Capacity of MgAl Metal Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(5): 529-533. |
| [7] | WANG Zhi-Min,LI Li,HAN Ji-Xin,HAN Wei-Ping. Interaction, Non-crystalline Structure and Catalysis Property on the Interface of Five Binary Transition Metal Oxides (I) Suggestion of Interface Non-crystalline Dispersion and Bulk Crystal Residual Ratio [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(2): 385-392. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||