
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 763-768.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2014.13519
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
DUAN Lian-Feng1,2, ZHANG Yu2, WANG Li-Min1, JIN Song-Zhe2, WU Hua2
Received:2013-10-10
Revised:2013-12-06
Published:2014-07-20
Online:2014-06-20
CLC Number:
DUAN Lian-Feng, ZHANG Yu, WANG Li-Min, JIN Song-Zhe, WU Hua. Synthesis and Characterization of MnFe2O4 with Different Morphologies and Their Application in Water Treatment[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 763-768.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Samples | S2 | S3 | S4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ms /(Am2·kg-1) | 58.7 | 76.7 | 61.3 |
| Mr /(Am2·kg-1) | 6.5 | 1.3 | 7.4 |
| Hc /(kA·m-1) | 6.23 | 0.95 | 6.87 |
Table 1 Magnetism parameters of different samples
| Samples | S2 | S3 | S4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ms /(Am2·kg-1) | 58.7 | 76.7 | 61.3 |
| Mr /(Am2·kg-1) | 6.5 | 1.3 | 7.4 |
| Hc /(kA·m-1) | 6.23 | 0.95 | 6.87 |
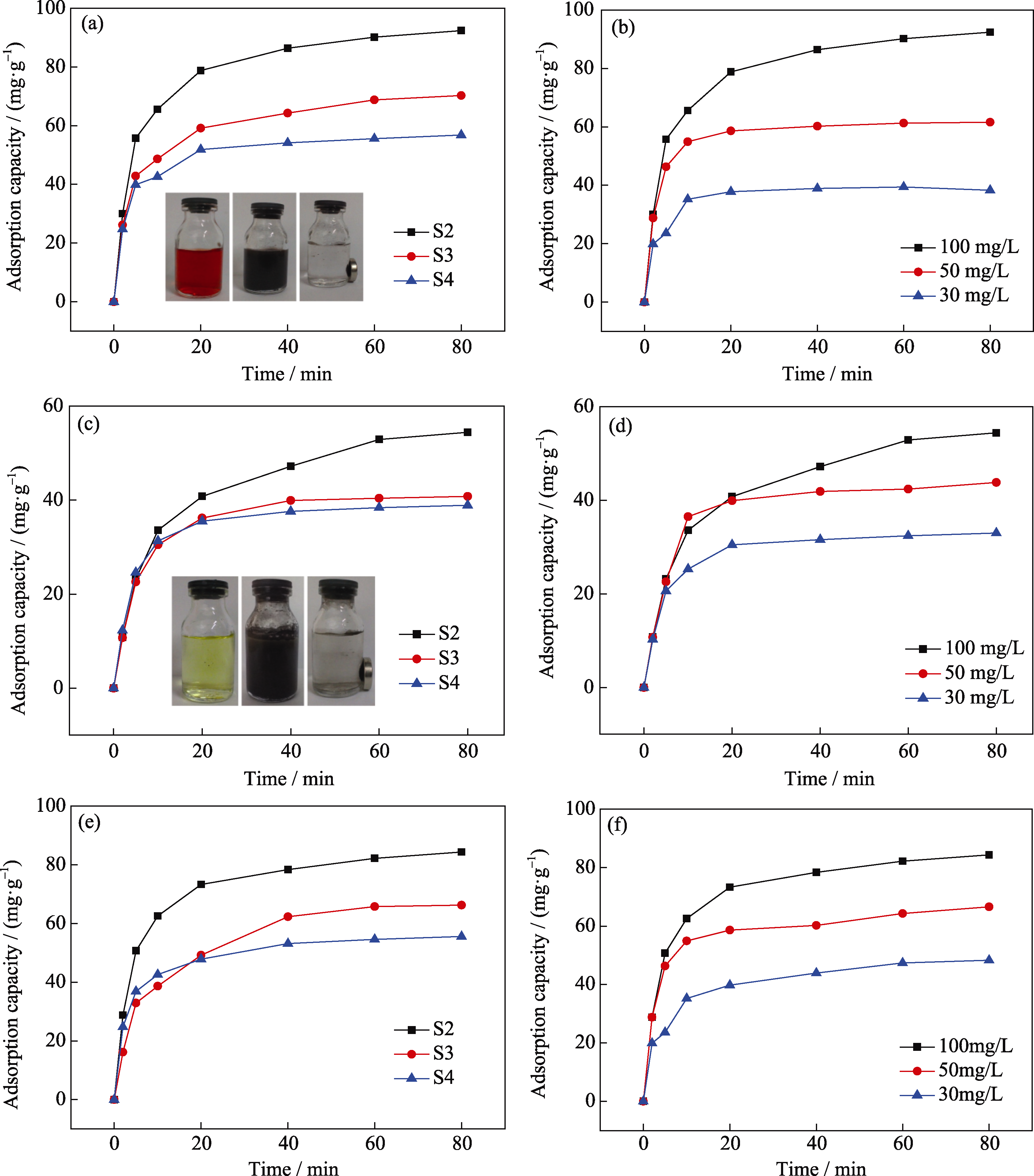
Fig. 5 Adsorption capacity of samples S2, S3 and S4 adsorbed CR, Cr6+ and Pb2+ solution (a, c and e) and adsorption capacity of sample S2 adsorbed CR, Cr6+ and Pb2+solution (b, d and f) with different concentrations
| [1] | CUI Y, LIEBER C M. Functional nanoscale electronic devices assembled using silicon nanowire building blocks. Science, 2001, 291(851): 851-853. |
| [2] | WANG X, ZHUANG J, PENG Q, et al. A general strategy for nanocrystal synthesis. Nature, 2005, 437(121-124): 121-124. |
| [3] | DUAN L F, JIA S S, ZHAO L J. Study on morphologies of Co microcrystals produced by solvothermal method with different solvents. Materials Research Bulletin, 2010, 45(4): 373-376. |
| [4] | LIU Q,LV L,WANG Y. Electric and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4- BaTiO3 composites synthesized by hydrothermalmethod. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 33(1): 50-55. |
| [5] | FU F L, WANG Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J. Environ. Manage., 2011, 92(3): 407-418. |
| [6] | WANG Y H, LIN S H, JUAN R S. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using various low-cost adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater., 2003, 102(2/3): 291-302. |
| [7] | KURNIAWAN T A, CHAN G Y S, LO W H, et al. Physico- chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. , 2006, 118(1/2): 83-98. |
| [8] | LI M, QIAN F Y, LI X Y. Characterization of organic pollutants in bio-treated effluents of dyeing and textile wastewater and removal behavior during magnesium sulfate coagulation process. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(1): 88-93. |
| [9] | MERIC S, KAPTAN D, OLMEZ T. Color and COD removal from wast-e-water containing Reactive Black 5 using Fenton's oxidation process. Chemosphere, 2004, 54(3): 435-441. |
| [10] | PAN B J, PAN B C, ZHANG W M, et al. Development of polymeric and polymer-based hybrid adsorbents for pollutants removal from waters. Chem. Eng. J., 2009, 151(1/2/3): 19-29. |
| [11] | MISHRA S P, SINGH V K, TIWARI D. Radiotracer technique in adsorption study. 14. Efficient removal of mercury from aqueous solutions by hydrous zirco-nium oxide. Appl. Radiat. Isot. , 1996 47(1): 15-21. |
| [12] | VANBENSCHOTEN J E, REED B E, MATSUMOTO M R, et al. Metal removal by soil washing for an iron-oxide coated sandy soil. Water Environ. Res. , 1994(66): 168-174. |
| [13] | DING Z H, FENG J M. Surface characters of iron-(hydro) oxides andtheir adsorption of heavy metal ions. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2000(20): 349-352. |
| [14] | AGRAWAL A, SAHU K K. Kinetic and isotherm studies of cadmium adsorption on manganese nodule residue. J. Hazard. Mater., 2006(137): 915-924. |
| [15] | MANDAVIAN A R, MIRRAHIMI M A S. Efficient separation of heavy metal cations by anchoring polyacrylic acid on superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles through surface modification. Chem. Eng. J. , 2010, 159(1/2/3): 264-271. |
| [16] | ZHAO X, LV L, PAN B, et al. Polymer-supported nanoco-m-posites for environmental application-a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 170(2/3): 381-394. |
| [17] | ZHAO M Y, DUAN L F, WU H, et al. Synthesis of hollow Fe3O4 submicrospheres and their adsorption-desorption capability for Congo red. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 28(10): 2186-2192. |
| [18] | WANG Y Q, CHENG R M, WEN Z, et al. Synthesis and characteriz-ation of single-crystalline MnFe2O4 ferrite nanocrystals and their possible application in water treatment. Eur. J.Inorg.Chem., 2011, 19(1): 2942-2947. |
| [19] | ZHUO NA, LI LI, GAO YU, et al. CTAB-assisted synthesis of nano-composite Ag/ZnO-TiO2 and its UV photocatalytic activity. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(5): 991-998. |
| [20] | ZHU Y F, ZHAO W R, CHEN H R, et al. A Simple one-pot self-assem-bly route to nanoporous and monodispersed Fe3O4 particles with oriented attachment structure and magnetic property. Phys. J. Chem. C, 2007, 111(14): 5281-5285. |
| [21] | DIMITROV D A, WYSIN G M. Effects of surface anisotropy on hysteresis in fine magnetic particles. Phys. Rev. B, 1994, 50(5): 3077-3084. |
| [22] | KODOMA R H, BERKOWITZ A E. Atomic-scale magnetic modeling of oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B, 1999, 59(9): 6321-6336. |
| [23] | WANG L X, LI J C, JIANG Q, et al. Water-soluble Fe3O4 nanopart-icles with high solubility for removal of heavy-metal ions from waste water. Dalton Trans., 2012, 41(15): 4544-4551. |
| [24] | GUO MING, HUANG FENG-QIN, LIU MI-MI, et al. Performance of binding interaction between Cr(Ⅵ) and serum proteome. Chin. J. Inorg.Chem., 2013, 29(5): 1037-1044. |
| [25] | WANG X S, CHEN J P. Biosorption of congo red from aqueous solution using wheat bran and rice bran: batch studies. Sep.Sci. Technol. , 2009, 44(6): 1452-1466. |
| [26] | PANDAG C, DAS S K, GUHA A K. Effect of method of crystallization on the IV-III and IV-II polymorphic transitions of ammonium nitrate. J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 161(1): 373-379. |
| [27] | JIANG M Q, WANG Q P, JIN X Y, et al. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using modified and unmodified kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 170(1): 332-339. |
| [28] | HU J, LO I M C, CHEN G H. Fast removal and recovery of Cr(VI) using surface-modified jacobsite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles. Langmuir, 2005, 21(24): 11173-11179. |
| [1] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [2] | WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [3] | WU Zhen, LI Huifang, ZHANG Zhonghan, ZHANG Zhen, LI Yang, LAN Jianghe, SU Liangbi, WU Anhua. Growth and Characterization of CeF3 Crystals for Magneto-optical Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 296-302. |
| [4] | QI Xuejun, ZHANG Jian, CHEN Lei, WANG Shaohan, LI Xiang, DU Yong, CHEN Junfeng. Macroscopic Defects of Large Bi12GeO20 Crystals Grown Using Vertical Bridgman Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 280-287. |
| [5] | QI Zhanguo, LIU Lei, WANG Shouzhi, WANG Guogong, YU Jiaoxian, WANG Zhongxin, DUAN Xiulan, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Progress in GaN Single Crystals: HVPE Growth and Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [6] | ZHANG Chaoyi, TANG Huili, LI Xianke, WANG Qingguo, LUO Ping, WU Feng, ZHANG Chenbo, XUE Yanyan, XU Jun, HAN Jianfeng, LU Zhanwen. Research Progress of ScAlMgO4 Crystal: a Novel GaN and ZnO Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [7] | CHEN Kunfeng, HU Qianyu, LIU Feng, XUE Dongfeng. Multi-scale Crystallization Materials: Advances in in-situ Characterization Techniques and Computational Simulations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [8] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [9] | YANG Jiaxue, LI Wen, WANG Yan, ZHU Zhaojie, YOU Zhenyu, LI Jianfu, TU Chaoyang. Spectroscopic and Yellow Laser Features of Dy3+: Y3Al5O12 Single Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 350-356. |
| [10] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [11] | XIA Qian, SUN Shihao, ZHAO Yiliang, ZHANG Cuiping, RU Hongqiang, WANG Wei, YUE Xinyan. Effect of Boron Carbide Particle Size Distribution on the Microstructure and Properties of Reaction Bonded Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 636-642. |
| [12] | HONG Du, NIU Yaran, LI Hong, ZHONG Xin, ZHENG Xuebin. Tribological Properties of Plasma Sprayed TiC-Graphite Composite Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [13] | XU Puhao, ZHANG Xiangzhao, LIU Guiwu, ZHANG Mingfen, GUI Xinyi, QIAO Guanjun. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiC Joint Brazed by Al-Ti Alloys as Filler Metal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 683-690. |
| [14] | HUANG Longzhi, YIN Jie, CHEN Xiao, WANG Xinguang, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Selective Laser Sintering of SiC Green Body with Low Binder Content [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 347-352. |
| [15] | MING Yue, HU Yue, MEI Anyi, RONG Yaoguang, HAN Hongwei. Application of Lead Acetate Additive for Printable Perovskite Solar Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 197-203. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||