无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 1063-1069.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240094
杨佳霖1( ), 王亮君1, 阮丝园1, 蒋秀林2,3, 杨长1(
), 王亮君1, 阮丝园1, 蒋秀林2,3, 杨长1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-01
修回日期:2024-04-09
出版日期:2024-09-20
网络出版日期:2024-04-19
通讯作者:
杨长, 研究员. E-mail: cyang@phy.ecnu.edu.cn作者简介:杨佳霖(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 51214700087@stu.ecnu.edu.cn
YANG Jialin1( ), WANG Liangjun1, RUAN Siyuan1, JIANG Xiulin2,3, YANG Chang1(
), WANG Liangjun1, RUAN Siyuan1, JIANG Xiulin2,3, YANG Chang1( )
)
Received:2024-03-01
Revised:2024-04-09
Published:2024-09-20
Online:2024-04-19
Contact:
YANG Chang, professor. E-mail: cyang@phy.ecnu.edu.cnAbout author:YANG Jialin (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 51214700087@stu.ecnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
近年来, 碘化铜(CuI)因其较高的本征霍尔迁移率、高光吸收和较大的激子结合能而成为一种新兴的p型宽带隙半导体。然而, 在传统半导体材料表面制备高质量CuI薄膜非常困难, 已有CuI基异质结器件的光谱响应和光电转换效率较低。本研究采用一种简易的金属碘化法制备了一种p-CuI/n-Si结构的光电二极管。虽然获得的CuI是带有明显结构缺陷的多晶薄膜, 但CuI/Si二极管具有很高的弱光灵敏度。其高达7.6×104的整流比表明该光电二极管具有良好的缺陷容忍度, 这与p+n型二极管的单边异质结这一特殊结构有关。本研究对该p+n型二极管的光电响应进行了较为系统的研究, 选择波长分别为400、505、635和780 nm的不同单色激光器进行光响应测试。在零偏置电压条件下, 该器件为单边异质结, 耗尽层仅在硅一侧, 因此只有可见光被吸收。当施加-3 V的偏置电压时, 光电二极管被切换到“紫外-可见”双波段响应的工作模式。因此, 通过调整偏置电压可以使检测波长在“可见”波段和“紫外-可见”波段之间切换。此外, 本研究所得到的CuI/Si二极管对弱光照非常敏感。在入射光功率密度低至0.5 μW/cm2时, 其具有高达1013~1014 Jones的探测率, 明显优于其他铜基光电二极管。相关研究结果证实了CuI在与传统硅工业集成时的高应用潜力。
中图分类号:
杨佳霖, 王亮君, 阮丝园, 蒋秀林, 杨长. 基于CuI/Si单边异质结的微光高灵敏双波段可切换光电探测器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1063-1069.
YANG Jialin, WANG Liangjun, RUAN Siyuan, JIANG Xiulin, YANG Chang. Highly Weak-light Sensitive and Dual-band Switchable Photodetector Based on CuI/Si Unilateral Heterojunction[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1063-1069.
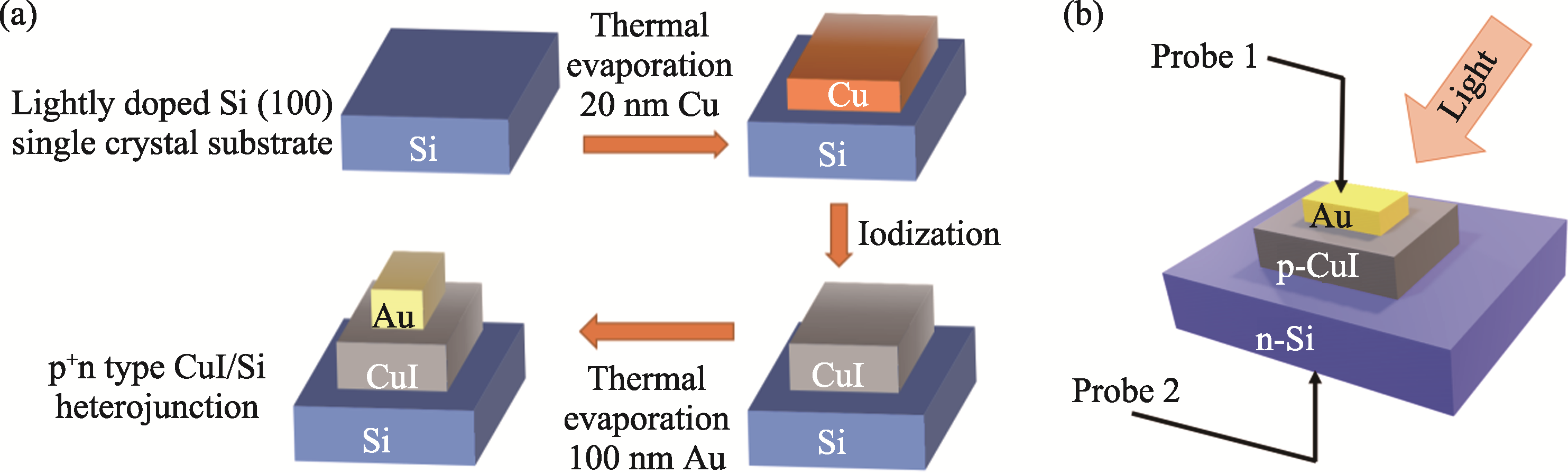
Fig. 1 Fabrication and testing schematic diagram (a) Schematic structure of the fabricated p+n type CuI/Si heterojunction diode; (b) Schematic diagram of the photodiode test
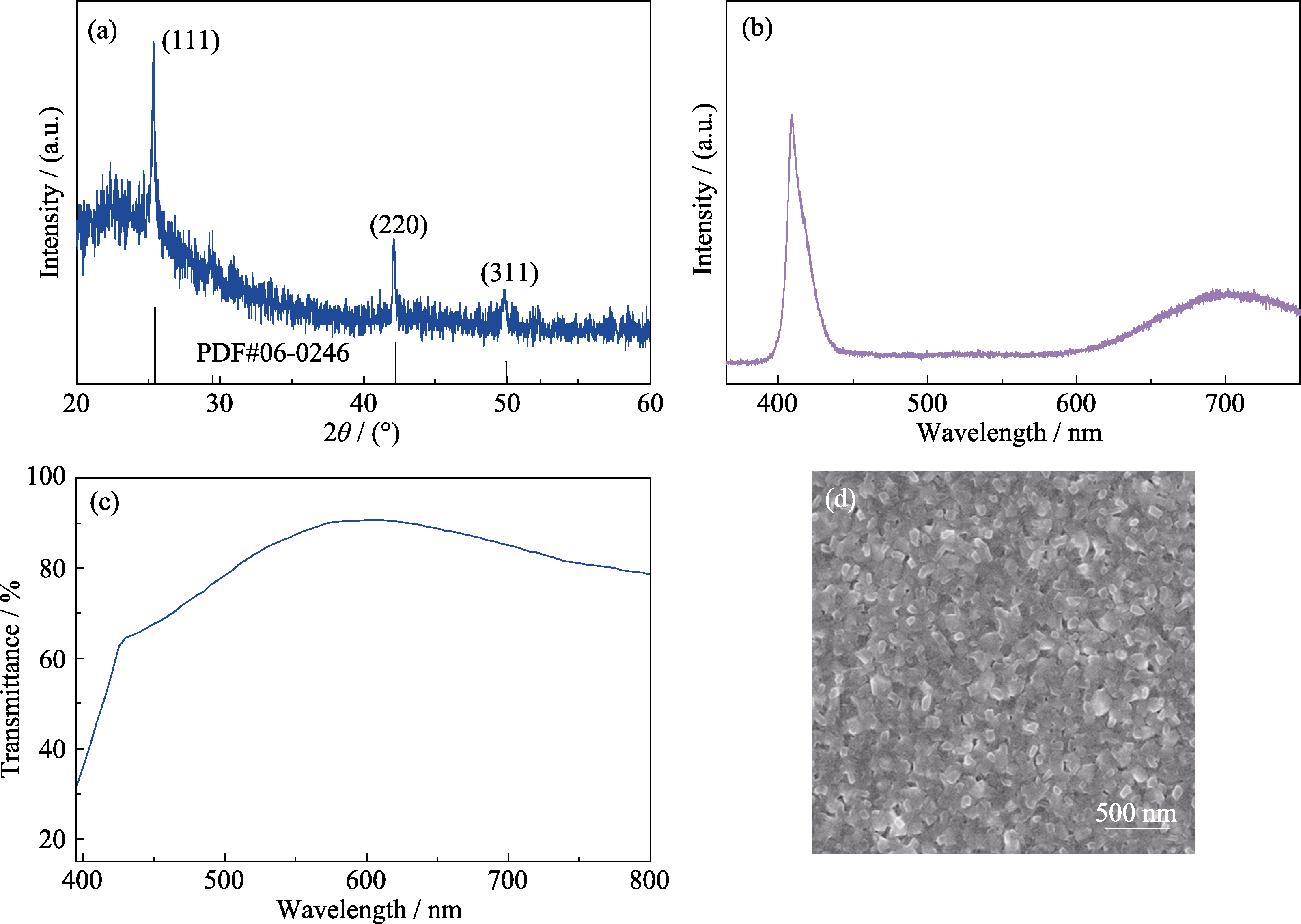
Fig. 2 Structural and electrical characterization of the obtained CuI thin film (a) XRD pattern; (b) PL spectrum; (c) Optical transmittance; (d) SEM image
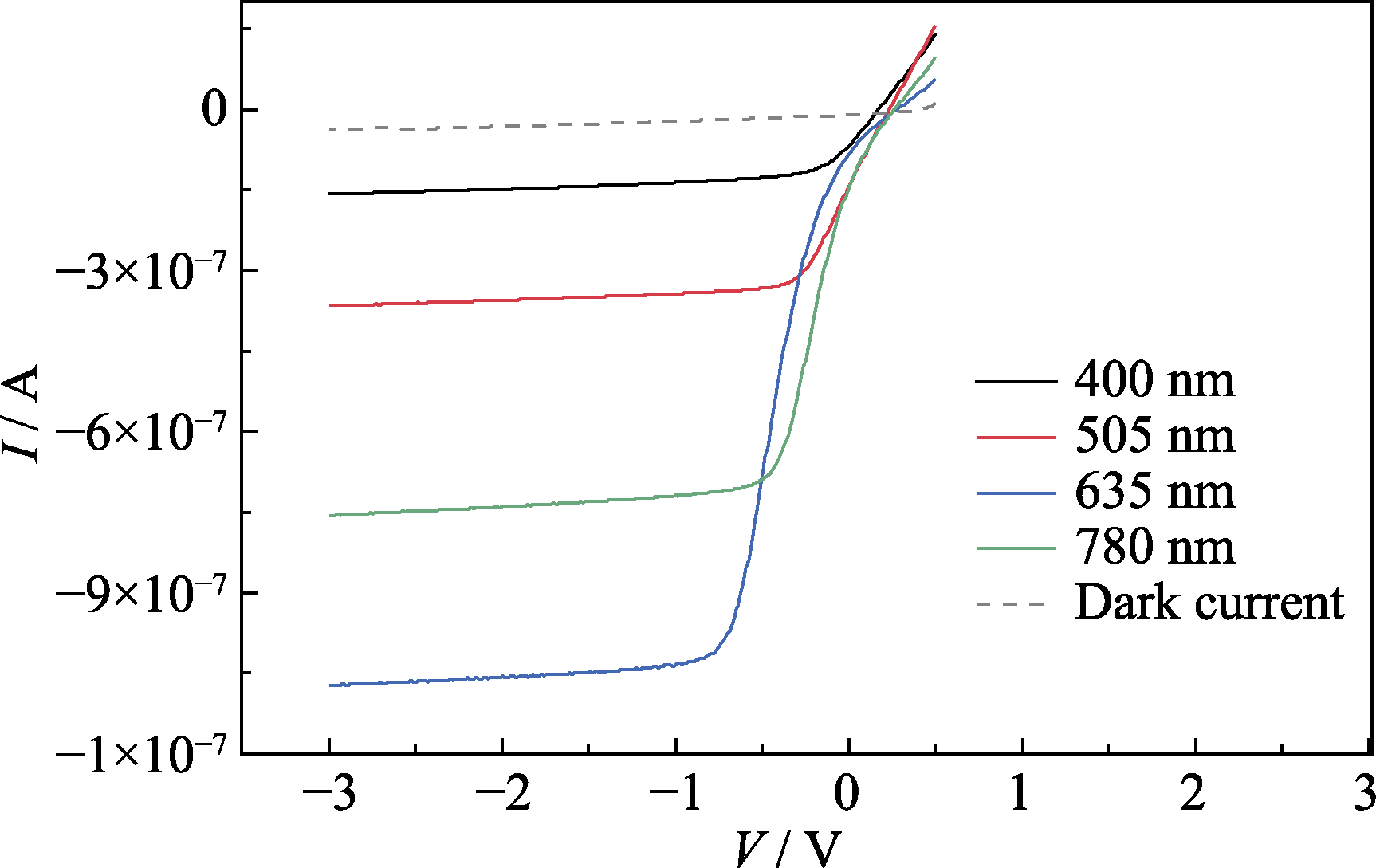
Fig. 4 I-V characteristic curves of the CuI/Si photodiode under different laser light wavelengths with a light power density of 50 μW/cm2 Dark current is plotted in dashed line; Colorful figure is available on website
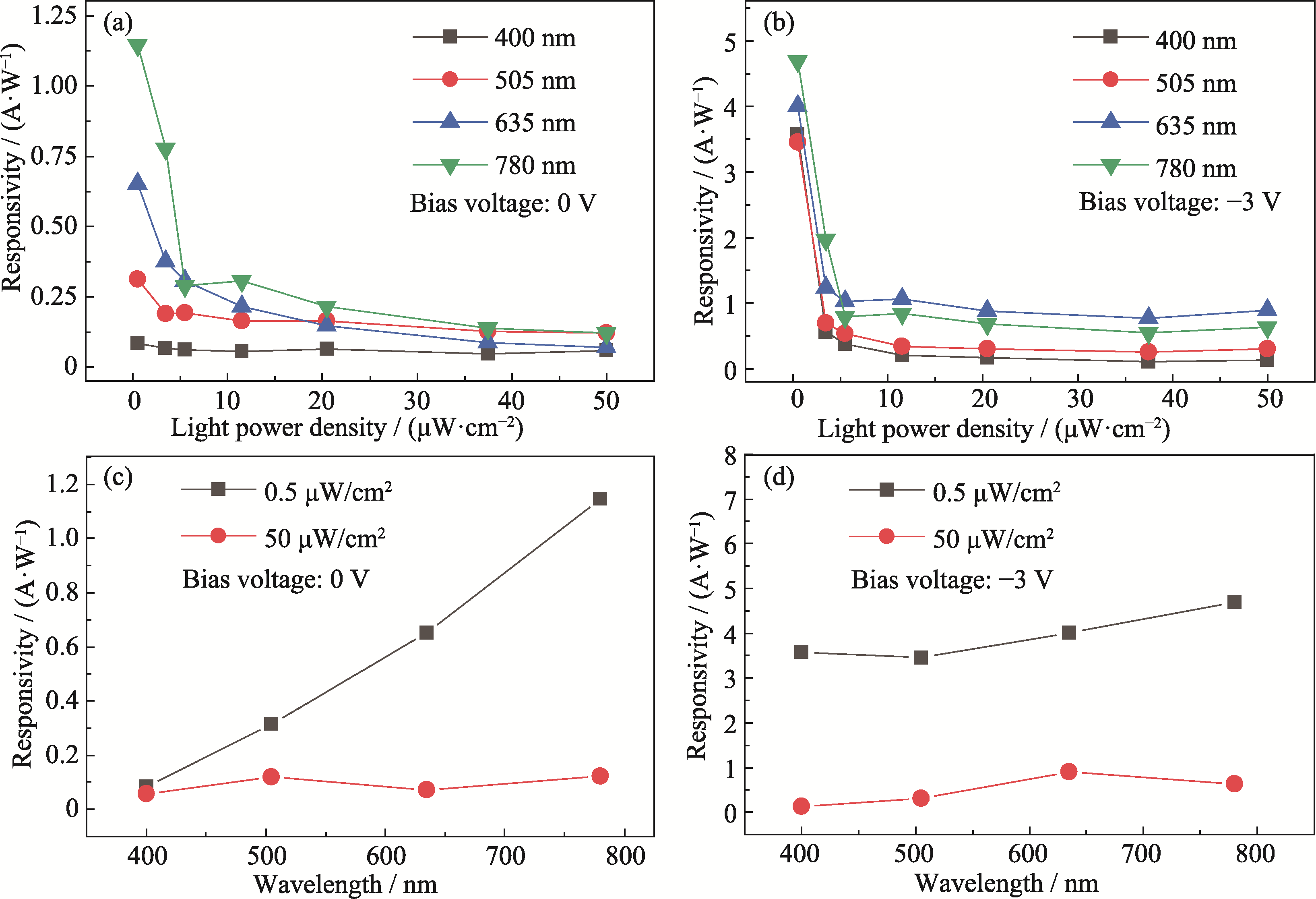
Fig. 5 Responsivity of the CuI/Si photodiode as a function of light power density and responsivity under specific light intensity (a) 0 V bias applied; (b) -3 V bias applied; (c) 0 V bias applied under specific light intensity; (d) -3 V bias applied under specific light intensity
| Wavelength/nm | Bias voltage/V | Responsivity (Weak/strong light)/(A·W-1) | D* (Weak/strong light)/ (×1013, Jones) | EQE (Weak/strong light)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 0 | 0.08/0.06 | 0.363/0.241 | 26/17 |
| -3 | 3.58/0.15 | 15.4/0.669 | 1109/48 | |
| 505 | 0 | 0.31/0.14 | 1.35/0.618 | 77/35 |
| -3 | 3.46/0.30 | 14.9/1.31 | 849/74 | |
| 635 | 0 | 0.65/0.13 | 2.82/0.561 | 127/25 |
| -3 | 4.00/0.90 | 17.3/3.88 | 782/175 | |
| 780 | 0 | 1.15/0.20 | 4.94/0.844 | 182/31 |
| -3 | 4.70/0.67 | 20.3/2.92 | 747/107 |
Table 1 Device parameters of the CuI/Si photodiodes
| Wavelength/nm | Bias voltage/V | Responsivity (Weak/strong light)/(A·W-1) | D* (Weak/strong light)/ (×1013, Jones) | EQE (Weak/strong light)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 0 | 0.08/0.06 | 0.363/0.241 | 26/17 |
| -3 | 3.58/0.15 | 15.4/0.669 | 1109/48 | |
| 505 | 0 | 0.31/0.14 | 1.35/0.618 | 77/35 |
| -3 | 3.46/0.30 | 14.9/1.31 | 849/74 | |
| 635 | 0 | 0.65/0.13 | 2.82/0.561 | 127/25 |
| -3 | 4.00/0.90 | 17.3/3.88 | 782/175 | |
| 780 | 0 | 1.15/0.20 | 4.94/0.844 | 182/31 |
| -3 | 4.70/0.67 | 20.3/2.92 | 747/107 |
| Diode structure | Wavelength/ nm | Power density/ (μW·cm−2) | Bias voltage/V | D*/Jones | Responsivity/ (A·W-1) | EQE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnSe/Si | 405 | 10 | -4 | 3.4×1011 | 0.21 | - | [ |
| 405 | 300 | -4 | 3.0×1011 | 0.18 | - | ||
| 650 | 10 | 0 | 1.1×1011 | 0.20 | - | ||
| 650 | 300 | 0 | 1.0×1011 | 0.17 | - | ||
| MoS2/Si | 514 | 3 | -2 | 2.2×1011 | 1.25 | - | [ |
| 514 | 80 | -2 | 8.0×1011 | 0.90 | - | ||
| Graphene-Si | 730 | 10 | -2 | 2.1×108 | 0.35 | - | [ |
| Si/ZnO | 550 | - | -2 | - | 0.37 | - | [ |
| ZnTe-TeO2/Si | 350 | - | 0 | 4.0×1012 | 0.03 | - | [ |
| 850 | - | 0 | 1.4×1013 | 0.08 | - | ||
| CuI/Si | 400 | 0.5 | -3 | 1.54×1014 | 3.58 | 1109 | This work |
| 400 | 50 | -3 | 6.69×1012 | 0.15 | 48 | ||
| 780 | 0.5 | 0 | 4.94×1013 | 1.15 | 182 | ||
| 780 | 50 | 0 | 8.44×1012 | 0.20 | 31 |
Table 2 Summarization of photoelectric properties in Si-based photodiodes
| Diode structure | Wavelength/ nm | Power density/ (μW·cm−2) | Bias voltage/V | D*/Jones | Responsivity/ (A·W-1) | EQE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnSe/Si | 405 | 10 | -4 | 3.4×1011 | 0.21 | - | [ |
| 405 | 300 | -4 | 3.0×1011 | 0.18 | - | ||
| 650 | 10 | 0 | 1.1×1011 | 0.20 | - | ||
| 650 | 300 | 0 | 1.0×1011 | 0.17 | - | ||
| MoS2/Si | 514 | 3 | -2 | 2.2×1011 | 1.25 | - | [ |
| 514 | 80 | -2 | 8.0×1011 | 0.90 | - | ||
| Graphene-Si | 730 | 10 | -2 | 2.1×108 | 0.35 | - | [ |
| Si/ZnO | 550 | - | -2 | - | 0.37 | - | [ |
| ZnTe-TeO2/Si | 350 | - | 0 | 4.0×1012 | 0.03 | - | [ |
| 850 | - | 0 | 1.4×1013 | 0.08 | - | ||
| CuI/Si | 400 | 0.5 | -3 | 1.54×1014 | 3.58 | 1109 | This work |
| 400 | 50 | -3 | 6.69×1012 | 0.15 | 48 | ||
| 780 | 0.5 | 0 | 4.94×1013 | 1.15 | 182 | ||
| 780 | 50 | 0 | 8.44×1012 | 0.20 | 31 |
| [1] |
YU X, MARKS T, FACCHETTI A. Metal oxides for optoelectronic applications. Nature Materials, 2016, 15: 383.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | WOODS-ROBINSON R, HAN Y B, ZHANG H Y, et al. Wide band gap chalcogenide semiconductors. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(9): 4007. |
| [3] | ZHANG C, NICOLOSI V. Graphene and MXene-based transparent conductive electrodes and supercapacitors. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 16: 102. |
| [4] |
FANG H, ZHAO Z, WU W, et al. Progress in flexible electrochromic devices. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 140.
DOI |
| [5] | LIU H, LI H, TAO J, et al. Single crystalline transparent conducting F, Al, and Ga Co-doped ZnO thin films with high photoelectrical performance. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(18): 22195. |
| [6] | YUTAKA F, TARO H, YUKIO Y, et al. A transparent metal: Nb-doped anatase TiO2. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86(25): 252101. |
| [7] | WILLIS J, SCANLON D. Latest directions in p-type transparent conductor design. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2021, 9: 11995. |
| [8] | YANG C, KNEISS M, SCHEIN F L, et al. Room-temperature domain-epitaxy of copper iodide thin films for transparent CuI/ZnO heterojunctions with high rectification ratios larger than 109. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21937. |
| [9] |
LI Z, HE J, LV X, et al. Optoelectronic properties and ultrafast carrier dynamics of copper iodide thin films. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 6346.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | YANG C, MAX K, MICHAEL L, et al. Room-temperature synthesized copper iodide thin film as degenerate p-type transparent conductor with a boosted figure of merit. Applied Physical Sciences, 2016, 113(46): 12929. |
| [11] | MARIUS G, FRIEDRICH S, MICHAEL L, et al. Cuprous iodide-a p-type transparent semiconductor: history and novel applications. Physica Status Solidi A, 2013, 210(9): 1671. |
| [12] | TANAKA T, KEISHI K, MASATAKA H. Transparent, conductive CuI films prepared by rf-dc coupled magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films, 1996, 281: 179. |
| [13] | KIM D, NAKAYAM M, KOJIM O, et al. Thermal-strain-induced splitting of heavy and light-hole exciton energies in CuI thin films grown by vacuum evaporation. Physical Review B, 1999, 60(19): 13879. |
| [14] | ZI M, LI J, ZHANG Z, et al. Effect of deposition temperature on transparent conductive properties of γ-CuI film prepared by vacuum thermal evaporation. Phys. Status Solidi, 2015, 212: 1466. |
| [15] | KANG H, LIU R, CHEN K, et al. Electrodeposition and optical properties of highly oriented γ-CuI thin films. Electrochim Acta, 2010, 55(27): 8121. |
| [16] | YAMADA N, KONDO Y, INO R. Low-temperature fabrication and performance of polycrystalline CuI films as transparent p-type semiconductors. Physica Status Solidi, 2019, 216(5): 1700782. |
| [17] | STORM P, BAR M, BENNDORF G, et al. High mobility, highly transparent, smooth, p-type CuI thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. APL Materials, 2020, 8(9): 091115. |
| [18] | YANG C, ROSE E, YU W, et al. Controllable growth of copper iodide for high-mobility thin films and self-assembled microcrystals. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2020, 2(11): 3627. |
| [19] | GENG F, WU Y, SPLITH D, et al. Amorphous transparent Cu(S,I) thin films with very high hole conductivity. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2023, 14(26): 6163. |
| [20] | GENG F, WANG L, STRALKA T, et al. (111)-oriented growth and acceptor doping of transparent conductive CuI:S thin films by spin coating and radio frequency-sputtering. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2023, 25(11): 2201666. |
| [21] |
YANG C, SOUCHAY D, KNEISS M, et al. Transparent flexible thermoelectric material based on non-toxic earth-abundant p-type copper iodide thin film. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 16076.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | CHA J, JUNG D. Air-stable transparent silver iodide-copper iodide heterojunction diode. ACS Applied Materials Interfaces, 2017, 9(50): 43807. |
| [23] | NAOOMI Y, YUUMI K, XIANG C, et al. Visible-blind wide-dynamic-range fast-response self-powered ultraviolet photodetector based on CuI/In-Ga-Zn-O heterojunction. Applied Materials Today, 2019, 15: 153. |
| [24] | AKSHAI S, NANDAKUMAR A, RAMESH R, et al. Self-powered UV photodetectors based on heterojunctions composed of ZnO nanorods coated with thin films of ZnS and CuI. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023, 6(10): 8529. |
| [25] | ZHANG Y, LI S, YANG W, et al. Millimeter-sized single-crystal CsPbrB3/CuI heterojunction for high-performance self-powered photodetector. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2019, 10(10): 2400. |
| [26] | WANG Y, CHUANG C. Solution processed CuI/n-Si junction device annealed with and without iodine steam for ultraviolet photodetector applications. Journal of Materials Science, 2018, 29(21): 18622. |
| [27] | LI W, SHI W. Growth habit and habit variation of γ-CuI crystallites under hydrothermal conditions. Crystal Research & Technology, 2002, 37(10): 1041. |
| [28] | ALIVOV Y, ÖZGÜR Ü, DOĞAN S, et al. Photoresponse of n-ZnO/p-SiC heterojunction diodes grown by plasma-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86(24): 241108. |
| [29] | LEE M, SEO S, KIM D, et al. A low-temperature grown oxide diode as a new switch element for high-density, nonvolatile memories. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(1): 73. |
| [30] | BRÖTZMANN M, VETTER U, HOFSÄSS H. BN/ZnO heterojunction diodes with apparently giant ideality factors. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 106(6): 063704. |
| [31] | SCHENK A, KRUMBEIN U. Coupled defect level recombination: theory and application to anomalous diode characteristics. Journal of Applied Physics, 1995, 78(5): 3185. |
| [32] | YASUHISA O, YOSHIAKI M, SHINGO S, et al. Revisiting the role of trap-assisted-tunneling process on current-voltage characteristics in tunnel field-effect transistors. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 123(16): 161549. |
| [33] | TALIN A, ALEC, LEONARD F, SWART B, et al. Unusually strong space-charge-limited current in thin wires. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 101: 076802. |
| [34] | YU W, BENNDORF G, JIANG Y, et al. Control of optical absorption and emission of sputtered copper iodide thin films. Physica Status Solidi (RRL)-Rapid Research Letters, 2020, 15(1): 2000431. |
| [35] |
YANG Y, SHAO Y, LI B, et al. Enhanced band-edge luminescence of CuI thin film by Cl-doping. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 687.
DOI |
| [36] | LUO F, ZHOU H, LIU Y, et al. High-performance self-driven SnSe/Si heterojunction photovoltaic photodetector. Chemosensors, 2023, 11: 406. |
| [37] | MUKHERJEE S, MAITI R, KATIYAR A, et al. Novel colloidal MoS2 quantum dot heterojunctions on silicon platforms for multifunctional optoelectronic devices. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 29016. |
| [38] | AN X, LIU F, JUNG Y, et al. Tunable graphenesilicon heterojunctions for ultrasensitive photodetection. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(3): 909. |
| [39] | LIM S, UM D, HA M, et al. Broadband omnidirectional light detection in flexible and hierarchical ZnO/Si heterojunction photodiodes. Nano Research, 2017, 10: 22. |
| [40] | SAHATIYA P, REDDY C, BADHULIKA S. Discretely distributed 1D V2O5 nanowires over 2D MoS2 nanoflakes for an enhanced broadband flexible photodetector covering the ultraviolet to near infrared region. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(48): 12728. |
| [41] | YIN W, YANG J, ZHAO K, et al. High responsivity and external quantum efficiency photodetectors based on solution-processed Ni-doped CuO films. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(10): 11797. |
| [42] | HONG Q, CAO Y, HU J, et al. Self-powered ultrafast broadband photodetector based on p-n heterojunctions of CuO/Si nanowire array. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(23): 20887. |
| [43] | SONG Z, LIU Y, WANG Q, et al. Self-powered photodetectors based on a ZnTe-TeO2 composite/Si heterojunction with ultra- broadband and high responsivity. Journal of Materials Science, 2018, 53: 7562. |
| [1] | 叶茂森, 王耀, 许冰, 王康康, 张胜楠, 冯建情. II/Z型Bi2MoO6/Ag2O/Bi2O3异质结可见光催化降解四环素[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 321-329. |
| [2] | 李腊, 沈国震. 二维MXenes材料在柔性光电探测器中的应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 186-194. |
| [3] | 胡盈, 李自清, 方晓生. 溶液法制备AgBi2I7薄膜及其光电探测性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1055-1061. |
| [4] | 蔡凯, 靳志文. 基于二维钙钛矿(PEA)2PbI4的光电探测器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1069-1075. |
| [5] | 李跃军, 曹铁平, 孙大伟. S型异质结Bi4O5Br2/CeO2的制备及其光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [6] | 吐尔洪·木尼热, 赵红刚, 马玉花, 齐献慧, 李钰宸, 闫沉香, 李佳文, 陈平. 单晶WO3/红磷S型异质结的构建及光催化活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 701-707. |
| [7] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [8] | 马润东, 郭雄, 施凯旋, 安胜利, 王瑞芬, 郭瑞华. MoS2/g-C3N4 S型异质结的构建及光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1176-1182. |
| [9] | 马心全, 李喜宝, 陈智, 冯志军, 黄军同. S型异质结BiOBr/ZnMoO4的构建及光催化降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [10] | 王如意, 徐国良, 杨蕾, 邓崇海, 储德林, 张苗, 孙兆奇. p-n异质结BiVO4/g-C3N4光阳极的制备及其光电化学水解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 87-96. |
| [11] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [12] | 高娃, 熊宇杰, 吴聪萍, 周勇, 邹志刚. 基于超薄纳米结构的光催化二氧化碳选择性转化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 3-14. |
| [13] | 刘彭, 吴仕淼, 吴昀峰, 张宁. Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS光催化材料的制备及其CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [14] | 赵宇鹏,贺勇,张敏,史俊杰. 新型二维Zr2CO2/InS异质结可见光催化产氢性能的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 993-998. |
| [15] | 许世超,朱天哲,乔阳,白学健,唐楠,郑春明. Z型BiVO4/GO/g-C3N4复合材料的制备及其可见光下催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 839-846. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||