无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (8): 903-910.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240057
苗鑫1( ), 闫世强1, 韦金豆1, 吴超1, 樊文浩2, 陈少平1(
), 闫世强1, 韦金豆1, 吴超1, 樊文浩2, 陈少平1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-30
修回日期:2024-02-20
出版日期:2024-08-20
网络出版日期:2024-04-19
通讯作者:
陈少平, 教授. E-mail: chenshaoping@tyut.edu.cn作者简介:苗 鑫(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: miaoxin0242@link.tyut.edu.cn
基金资助:
MIAO Xin1( ), YAN Shiqiang1, WEI Jindou1, WU Chao1, FAN Wenhao2, CHEN Shaoping1(
), YAN Shiqiang1, WEI Jindou1, WU Chao1, FAN Wenhao2, CHEN Shaoping1( )
)
Received:2024-01-30
Revised:2024-02-20
Published:2024-08-20
Online:2024-04-19
Contact:
CHEN Shaoping, professor. E-mail: chenshaoping@tyut.edu.cnAbout author:MIAO Xin (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: miaoxin0242@link.tyut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
单质Te具有优异的热电优值(ZT), 但其与金属电极连接界面处的剧烈元素交互扩散及反应会引入较大的接触电阻率(ρc), 导致器件的转换效率(η)较低。因此, 寻找合适的阻挡层来优化Te与金属电极间的连接至关重要。本研究基于梯度结构报道了一种宽相场Ni-Te合金阻挡层NiTe2-m (NixTe(x=0.500~0.908))。结果表明, 当x=0.500时, Ni0.5Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni0.5Te器件的界面处无任何反应层及微观缺陷, ρc小于10 μΩ·cm2, η在180 K温差(热端温度473 K)时达到了理论值的75%。同时, 界面具有良好的热稳定性, 在473 K老化期间, 界面微观组织、ρc以及η无明显变化。当x>0.500时, 界面反应层厚度随x增大而逐渐减小, 即主导界面反应层生长行为的因素并非常规的界面反应能及浓度梯度等热力学因素。进一步分析表明, 反常生长源于动力学因素中的“原子空位”对反应层生成的迟滞作用。
中图分类号:
苗鑫, 闫世强, 韦金豆, 吴超, 樊文浩, 陈少平. Te基热电器件反常界面层生长行为及界面稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 903-910.
MIAO Xin, YAN Shiqiang, WEI Jindou, WU Chao, FAN Wenhao, CHEN Shaoping. Interface Layer of Te-based Thermoelectric Device: Abnormal Growth and Interface Stability[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 903-910.
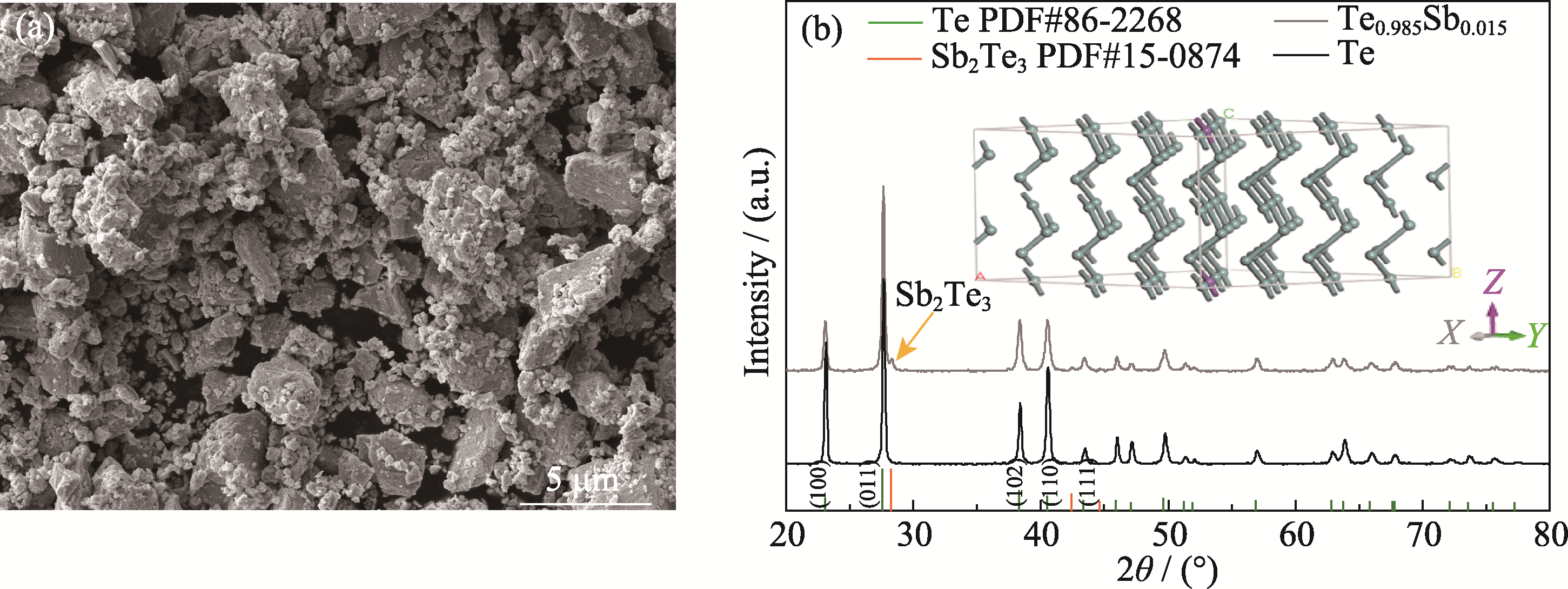
图1 Te0.985Sb0.015前驱粉末的微观形貌及成分组成
Fig. 1 Microstructure and composition of Te0.985Sb0.015 precursor powder (a) Backscattered SEM image; (b) XRD patterns and quasi-1D chain crystal structure of Te and Te0.985Sb0.015 powders; Colorful figures are available on website
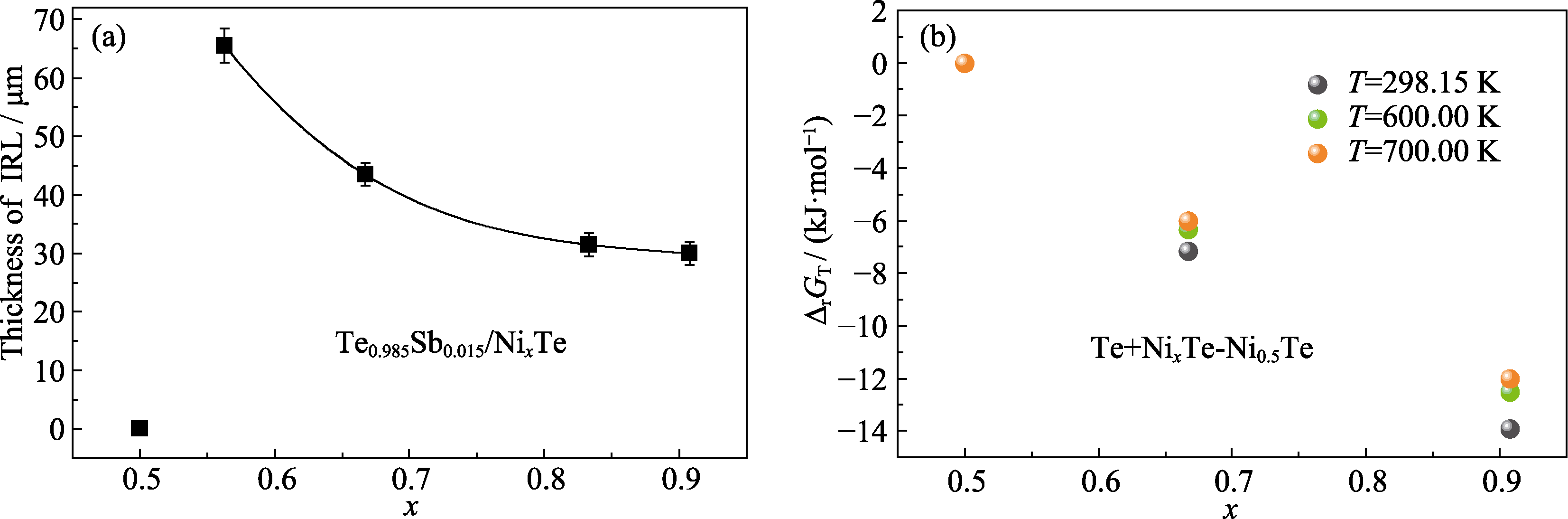
图3 (a) Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe各界面反应层(Interface Reaction Layers, IRLs)的厚度, (b)各界面产物的摩尔生成吉布斯自由能ΔrGT
Fig. 3 (a) Thicknesses of the interface reaction layers (IRLs) at the Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe interfaces, and (b) formation Gibbs free energies in molar (ΔrGT) of the interface products at the Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe interfaces
| Total migration of atoms | x=0.500 | x=0.563 | x=0.667 | x=0.833 | x=0.908 | Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN·l/(mol·cm-2) | 0 | 0.1297 | 0.2134 | 0.2810 | 0.3154 | 0.5653 |
表1 Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe界面处原子的总迁移量CN·l
Table 1 Total migration of atoms (CN·l) at Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe interface
| Total migration of atoms | x=0.500 | x=0.563 | x=0.667 | x=0.833 | x=0.908 | Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN·l/(mol·cm-2) | 0 | 0.1297 | 0.2134 | 0.2810 | 0.3154 | 0.5653 |
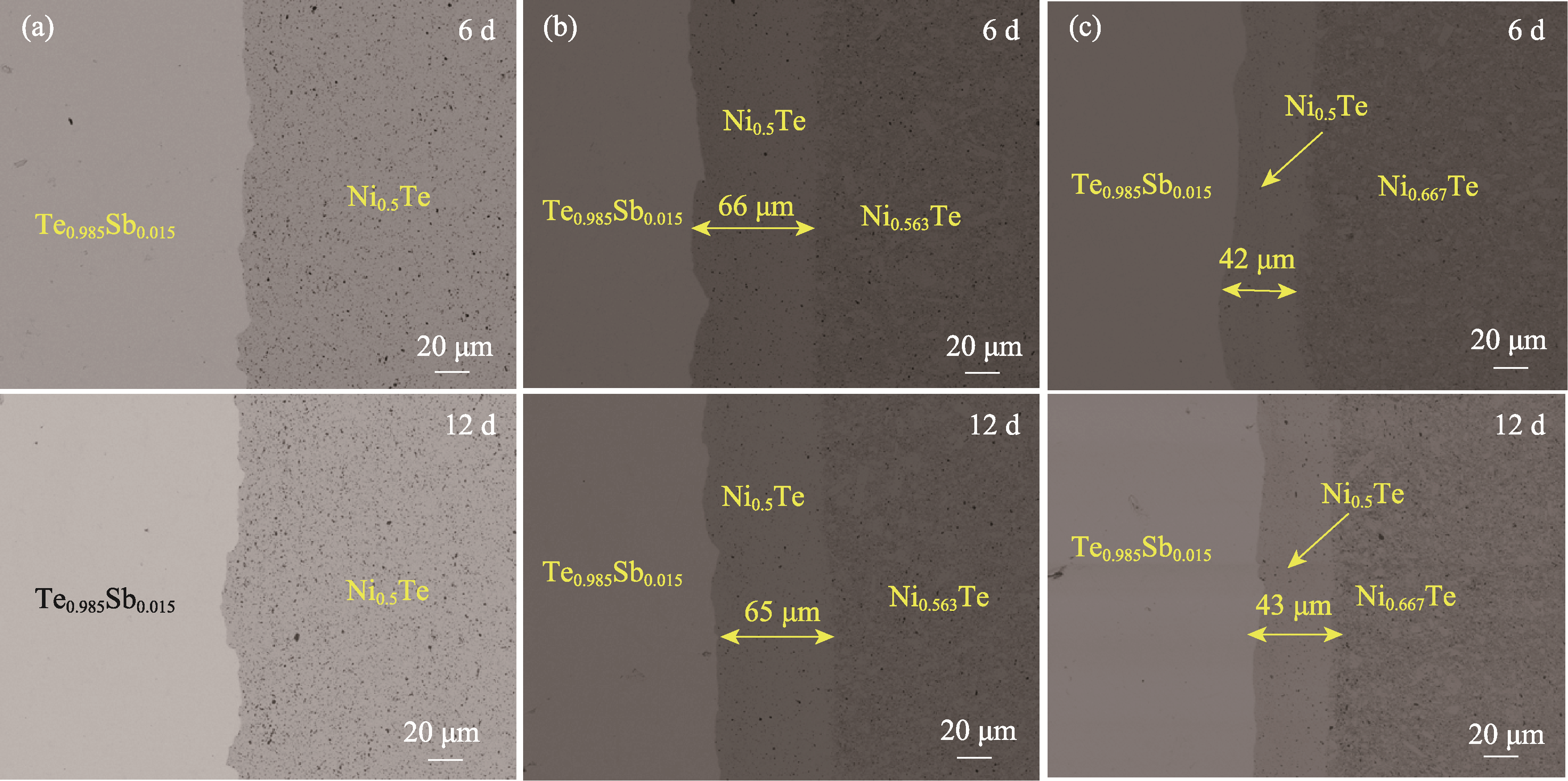
图5 473 K老化6及12 d后的Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe界面微观结构
Fig. 5 Microstructures of Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe interfaces after aging at 473 K for 6 and 12 d Backscattering SEM images for (a) x=0.500, (b) x=0.563, and (c) x=0.667
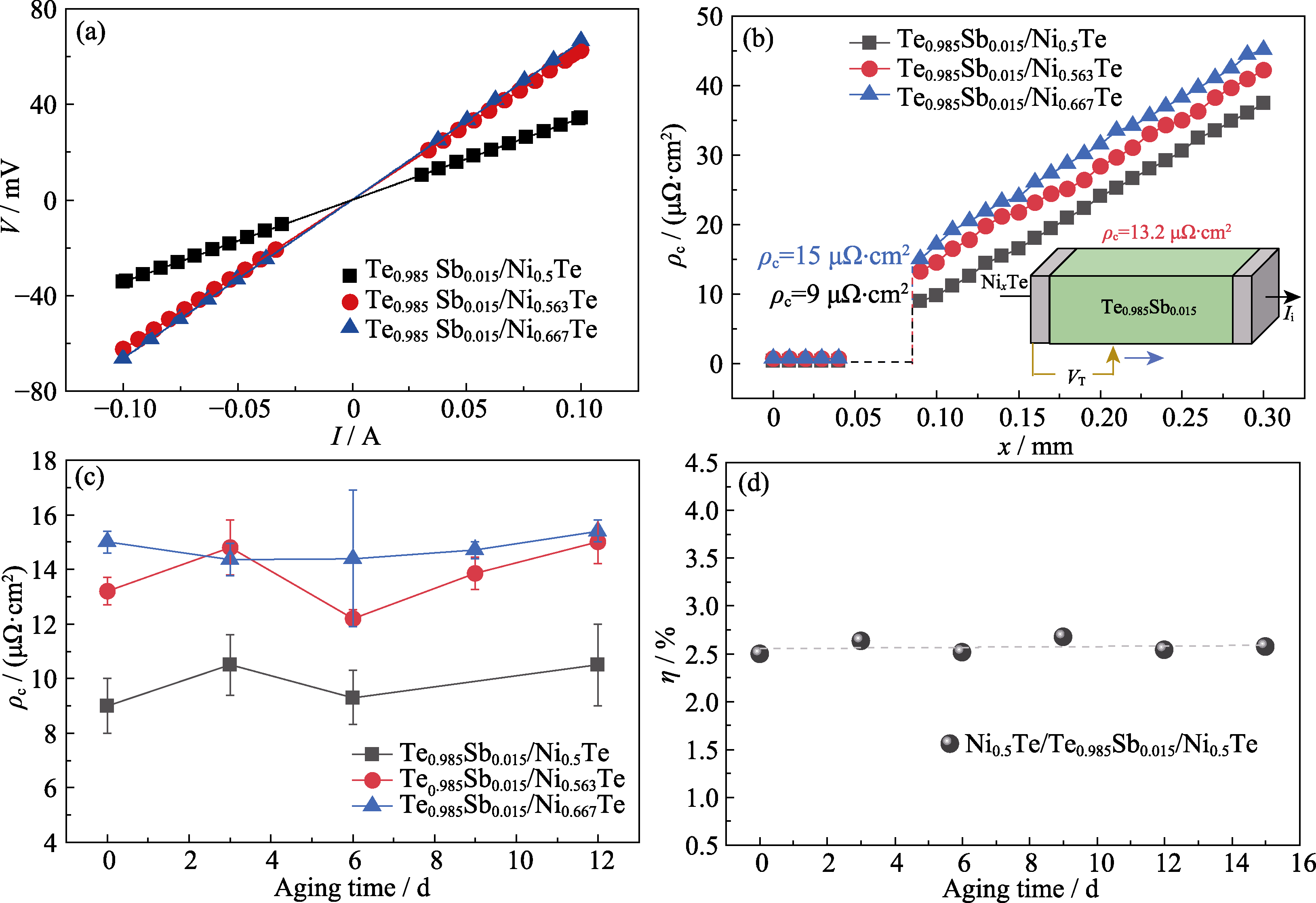
图6 NixTe/Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe (x=0.500, 0.563, 0.667)单臂器件的性能
Fig. 6 Performance of NixTe/Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe (x=0.500, 0.563, 0.667) single-leg devices (a, b) Room temperature V-I curves and contact resistivity, ρc, before aging; (c) Time-dependent room temperature ρc; (d) Time-dependent efficiency, η, under a temperature difference of 180 K (hot end: 473 K, cold end: 293 K)

图S1 烧结态Te0.985Sb0.015的断口形貌及元素分布
Fig. S1 Fracture microstructure and element distribution of sintered Te0.985Sb0.015 (a, b) Backscattered SEM images; (c) Corresponding EDS mapping
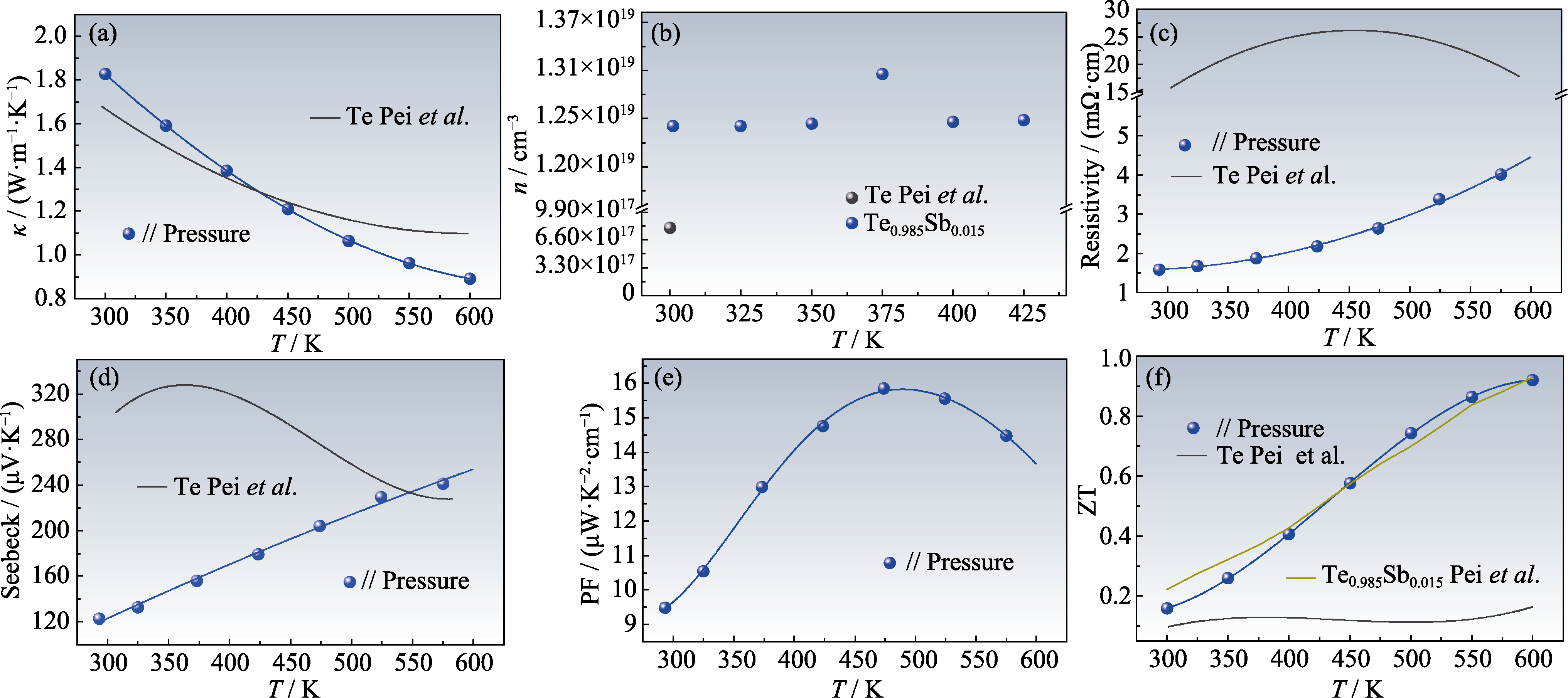
图S2 平行于烧结压力方向上的Te0.985Sb0.015的热电性能
Fig. S2 Thermoelectric performance of Te0.985Sb0.015 in the direction parallel to the sintering pressure (a) Total thermal conductivity, κ; (b) Carrier concentration, n; (c) Resistivity; (d) Seebeck coefficient; (e) Power factor, PF; (f) Dimensionless ZT of Te0.985Sb0.015; The test results of Pei et al.[15] are also drawn in the figures for comparison

图S4 烧结态Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe界面的微观形貌以及元素分布
Fig. S4 Microstructures and element distributions of sintered Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe interfaces Backscatter SEM images and EDS spectra for (a) x=0.500, (b) x=0.563, (c) x=0.667, (d) x=0.833, and (e) x=0.908
| Phase lable | Formula in reference | Formula used here | Temperature/K | ST/(J·mol-1·K-1) | HT/(kJ·mol-1) | GT/(kJ·mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ(-NiTe2-x, 52.2%-66.7% (in atom) Te) | Ni0.476Te0.524 | Ni0.908Te | 298.15 | 76.393 | -51.908 | -74.685 | [ |
| 600.00 | 112.729 | -36.120 | -103.758 | ||||
| 700.00 | 121.397 | -30.494 | -115.472 | ||||
| Ni0.4Te0.6 | Ni0.667Te | 298.15 | 66.917 | -47.833 | -67.785 | [ | |
| 600.00 | 98.732 | -33.987 | -93.226 | ||||
| 700.00 | 106.415 | -29.000 | -103.491 | ||||
| Ni0.333Te0.667 | Ni0.5Te | 298.15 | 60.135 | -43.778 | -61.707 | [ | |
| 600.00 | 88.253 | -31.552 | -84.504 | ||||
| 700.00 | 95.001 | -27.172 | -93.673 | ||||
| Te | Te | Te | 298.15 | 49.497 | 0.000 | -14.757 | [ |
| 600.00 | 69.537 | 8.766 | -32.956 | ||||
| 700.00 | 74.694 | 12.114 | -40.171 | ||||
| Ni | Ni | Ni | 298.15 | 29.874 | 0.000 | -8.907 | [ |
| 600.00 | 50.419 | 9.008 | -21.243 | ||||
| 700.00 | 55.546 | 12.326 | -26.557 |
表S1 热力学数据
Table S1 Thermodynamic data. Values of entropy (ST), enthalpy (HT), and Gibbs free energy (GT) at 298.15, 600.00 and 700.00 K, respectively
| Phase lable | Formula in reference | Formula used here | Temperature/K | ST/(J·mol-1·K-1) | HT/(kJ·mol-1) | GT/(kJ·mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ(-NiTe2-x, 52.2%-66.7% (in atom) Te) | Ni0.476Te0.524 | Ni0.908Te | 298.15 | 76.393 | -51.908 | -74.685 | [ |
| 600.00 | 112.729 | -36.120 | -103.758 | ||||
| 700.00 | 121.397 | -30.494 | -115.472 | ||||
| Ni0.4Te0.6 | Ni0.667Te | 298.15 | 66.917 | -47.833 | -67.785 | [ | |
| 600.00 | 98.732 | -33.987 | -93.226 | ||||
| 700.00 | 106.415 | -29.000 | -103.491 | ||||
| Ni0.333Te0.667 | Ni0.5Te | 298.15 | 60.135 | -43.778 | -61.707 | [ | |
| 600.00 | 88.253 | -31.552 | -84.504 | ||||
| 700.00 | 95.001 | -27.172 | -93.673 | ||||
| Te | Te | Te | 298.15 | 49.497 | 0.000 | -14.757 | [ |
| 600.00 | 69.537 | 8.766 | -32.956 | ||||
| 700.00 | 74.694 | 12.114 | -40.171 | ||||
| Ni | Ni | Ni | 298.15 | 29.874 | 0.000 | -8.907 | [ |
| 600.00 | 50.419 | 9.008 | -21.243 | ||||
| 700.00 | 55.546 | 12.326 | -26.557 |
| Chemical reaction equation | Temperature/K | ΔrST/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔrHT/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔrGT/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25Te+0.75Ni0.667Te→Ni0.5Te | 298.15 | -2.427 | -7.903 | -7.180 |
| 600.00 | -3.180 | -8.253 | -6.345 | |
| 700.00 | -3.484 | -8.451 | -6.012 | |
| 0.449Te+0.551Ni0.908Te→Ni0.5Te | 298.15 | -4.182 | -15.177 | -13.930 |
| 600.00 | -5.083 | -15.586 | -12.536 | |
| 700.00 | -5.426 | -15.809 | -12.010 | |
| 1.5Ni+Te→Ni1.5Te | 298.15 | 5.692 | -57.500 | -59.197 |
| 600.00 | 5.969 | -57.318 | -60.899 | |
| 700.00 | 8.110 | -56.023 | -61.700 |
表S2 298.15, 600.00和700.00 K条件下各界面反应产物的摩尔生成吉布斯自由能∆rGT
Table S2 Molar formation Gibbs free energies (ΔrGT) of interface products at 298.15, 600.00 and 700.00 K, respectively
| Chemical reaction equation | Temperature/K | ΔrST/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔrHT/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔrGT/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25Te+0.75Ni0.667Te→Ni0.5Te | 298.15 | -2.427 | -7.903 | -7.180 |
| 600.00 | -3.180 | -8.253 | -6.345 | |
| 700.00 | -3.484 | -8.451 | -6.012 | |
| 0.449Te+0.551Ni0.908Te→Ni0.5Te | 298.15 | -4.182 | -15.177 | -13.930 |
| 600.00 | -5.083 | -15.586 | -12.536 | |
| 700.00 | -5.426 | -15.809 | -12.010 | |
| 1.5Ni+Te→Ni1.5Te | 298.15 | 5.692 | -57.500 | -59.197 |
| 600.00 | 5.969 | -57.318 | -60.899 | |
| 700.00 | 8.110 | -56.023 | -61.700 |
| Item | NiTe2 (Ni0.5Te) | NiTe1.776 (Ni0.563Te) | NiTe1.5 (Ni0.667Te) | NiTe1.2 (Ni0.833Te) | NiTe1.1 (Ni0.908Te) | Ni | Te | NiTe0.667 (Ni1.5Te) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/(g·mol-1) | 313.893 | 285.311 | 250.093 | 211.813 | 199.053 | 58.693 | 127.600 | 143.802 |
| n | 2.000 | 1.776 | 1.500 | 1.200 | 1.100 | 0.000 | - | 0.667 |
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | 7.701 | 7.565 | 7.363 | 7.086 | 6.976 | 8.910 | - | 8.126 |
表S3 各层材料的密度ρ、摩尔质量M以及每摩尔物质中结合态Te的物质的量n
Table S3 Density (ρ), molar mass (M) and moles of the bound Te per mole substance
| Item | NiTe2 (Ni0.5Te) | NiTe1.776 (Ni0.563Te) | NiTe1.5 (Ni0.667Te) | NiTe1.2 (Ni0.833Te) | NiTe1.1 (Ni0.908Te) | Ni | Te | NiTe0.667 (Ni1.5Te) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/(g·mol-1) | 313.893 | 285.311 | 250.093 | 211.813 | 199.053 | 58.693 | 127.600 | 143.802 |
| n | 2.000 | 1.776 | 1.500 | 1.200 | 1.100 | 0.000 | - | 0.667 |
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | 7.701 | 7.565 | 7.363 | 7.086 | 6.976 | 8.910 | - | 8.126 |

图S6 老化前在180 K温差(热端473 K, 冷端293 K)条件下Ni0.5Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni0.5Te单臂器件的性能
Fig. S6 Performance of Ni0.5Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni0.5Te single-leg devices under a temperature difference of 180 K (Hot end: 473 K, Cold end: 293 K) (a) Current-dependent output voltage, Uout; (b) Current-dependent heat flux, Q
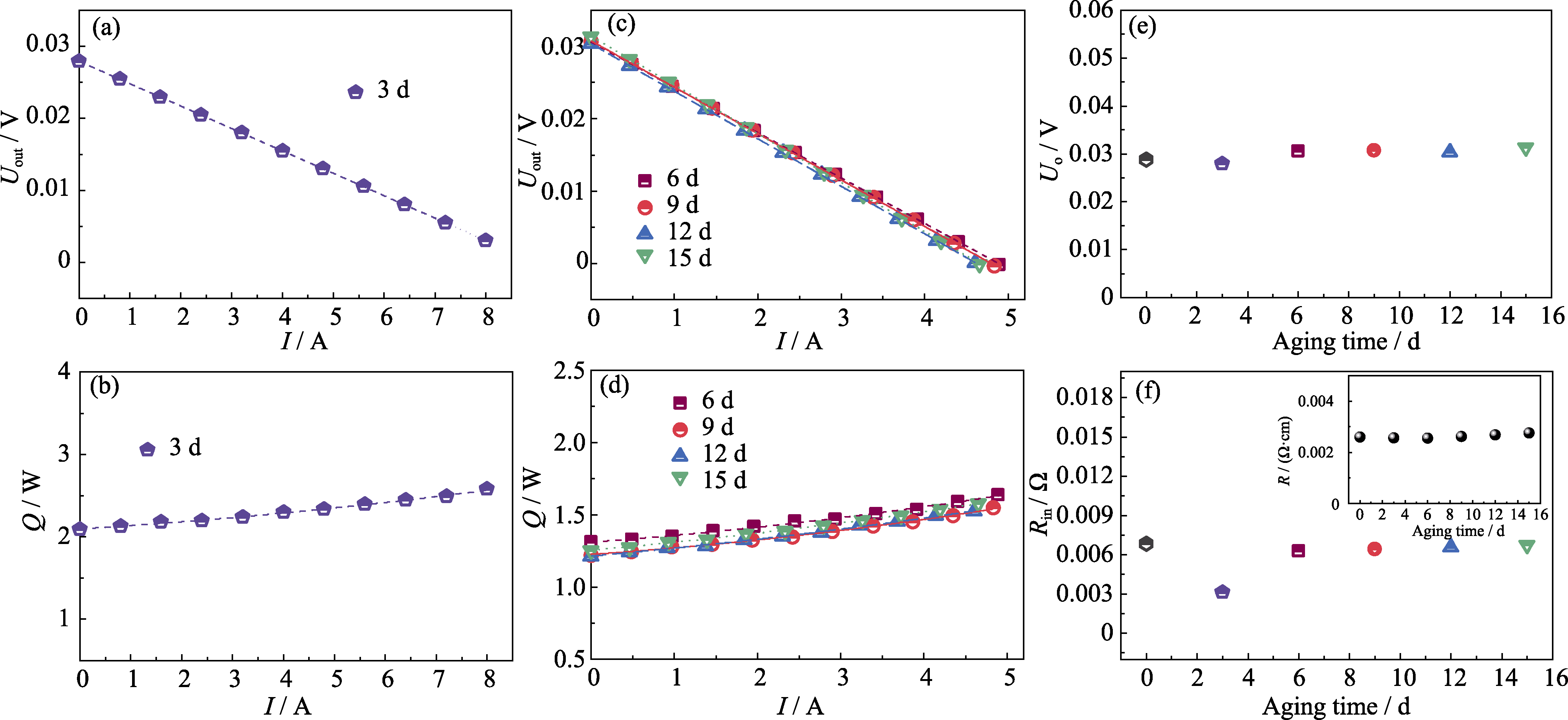
图S7 180 K温差 (热端473 K, 冷端293 K)条件下Ni0.5Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni0.5Te单臂器件的性能随老化时间的变化
Fig. S7 Aging-time dependent performance of Ni0.5Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni0.5Te single-leg devices under a temperature difference of 180 K (Hot end: 473 K, Cold end: 293 K) (a, c) Current-dependent output voltages, Uout and (b, d) current-dependent heat flux, Q, after aging for (a, b) 3 and (c, d) 6-15 d; Aging-time dependent (e) open-circuit voltage, Uo and (f) internal resistance, Rin with inset in (f) showing internal resistivity, R, of the devices
| [1] | WEI J, YANG L, MA Z, et al. Review of current high-ZT thermoelectric materials. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(27): 12642. |
| [2] | LIU H T, SUN Q, ZHONG Y, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of n-type Nb-doped PbTe by compensating resonant level and inducing atomic disorder. Materials Today Physics, 2022, 24: 100677. |
| [3] | SU L, WANG D, WANG S, et al. High thermoelectric performance realized through manipulating layered phonon-electron decoupling. Science, 2022, 375(6587): 1385. |
| [4] | SUN J, WANG R, CUI W, et al. Percolation process-mediated rich defects in hole-doped PbSe with enhanced thermoelectric performance. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34(14): 6450. |
| [5] | AN D, WANG J, ZHANG J, et al. Retarding Ostwald ripening through Gibbs adsorption and interfacial complexions leads to high-performance SnTe thermoelectrics. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(10): 5469. |
| [6] | YANG J, LI G, ZHU H, et al. Next-generation thermoelectric cooling modules based on high-performance Mg3(Bi,Sb)2 material. Joule, 2022, 6(1): 193. |
| [7] | CHU J, HUANG J, LIU R, et al. Electrode interface optimization advances conversion efficiency and stability of thermoelectric devices. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2723. |
| [8] | BJØRK R. The universal influence of contact resistance on the efficiency of a thermoelectric generator. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2015, 44(8): 2869. |
| [9] | ZHANG Q H, BAI S Q, CHEN L D. Technologies and applications of thermoelectric devices: current status, challenges and prospects. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 279. |
| [10] | WU X, HAN Z, ZHU Y, et al. A general design strategy for thermoelectric interface materials in n-type Mg3Sb1.5Bi0.5 single leg used in TEGs. Acta Materialia, 2022, 226: 117616. |
| [11] | HU X K, ZHANG S M, ZHAO F, et al. Thermoelectric device: contact interface and interface materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 269. |
| [12] | SAKANO M, HIRAYAMA M, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Radial spin texture in elemental tellurium with chiral crystal structure. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 124(13): 136404. |
| [13] | REITZ J R. Electronic band structure of selenium and tellurium. Physical Review, 1957, 105(4): 1233. |
| [14] | 李蓉, 陈少平, 樊文浩, 等. 孤对电子对碲热电传输性能的影响. 材料导报, 2018, 32(21): 3726. |
| [15] | LIN S Q, LI W, ZHANG X Y, et al. Sb induces both doping and precipitation for improving the thermoelectric performance of elemental Te. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2017, 4(6): 1066. |
| [16] | RAO F, DING K, ZHOU Y, et al. Reducing the stochasticity of crystal nucleation to enable subnanosecond memory writing. Science, 2017, 358(6369): 1423. |
| [17] | GUO J, FAN W, WANG Y, et al. Study on improving comprehensive property of Te-based thermoelectric joint. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 886: 161242. |
| [18] | 郭敬云, 陈少平, 樊文浩, 等. 改善Te基热电材料与复合电极界面性能. 物理学报, 2020, 69(14): 179. |
| [19] | HE Z, CHANG L G, LIN Y, et al. Real-time visualization of solid-phase ion migration kinetics on nanowire monolayer. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(17): 7968. |
| [20] | TASHIRO M, SUKENAGA S, IKEMOTO K, et al. Interfacial reactions between pure Cu, Ni, and Ni-Cu alloys and p-type Bi2Te3 bulk thermoelectric material. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(29): 16545. |
| [21] | FERRERES X R, AMINORROAYA YAMINI S, NANCARROW M, et al. One-step bonding of Ni electrode to n-type PbTe—a step towards fabrication of thermoelectric generators. Materials & Design, 2016, 107: 90. |
| [22] | ZHANG J, WEI P, ZHANG H, et al. Enhanced contact performance and thermal tolerance of Ni/Bi2Te3 joints for Bi2Te3-based thermoelectric devices. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(18): 22705. |
| [23] | CHEN J, FAN W, WANG Y, et al. Improvement of stability in a Mg2Si-based thermoelectric single-leg device via Mg50Si15Ni50 barrier. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 926: 166888. |
| [24] | WANG Y, CHEN J, JIANG Y, et al. Suppression of interfacial diffusion in Mg3Sb2 thermoelectric materials through an Mg4.3Sb3Ni/Mg3.2Sb2Y0.05/Mg4.3Sb3Ni-graded structure. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(29): 33419. |
| [25] | CHEN S, CHEN J, FAN W, et al. Improvement of contact and bonding performance of Mg2Si/Mg2SiNi3 thermoelectric joints by optimizing the concentration gradient of Mg. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2022, 51(5): 2256. |
| [26] | SUN Y, YIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Low contact resistivity and excellent thermal stability of p-type YbMg0.8Zn1.2Sb2/Fe-Sb junction for thermoelectric applications. Acta Materialia, 2022, 235: 118066. |
| [27] | SUN Z, CHEN X, ZHANG J, et al. Achieving reliable CoSb3 based thermoelectric joints with low contact resistivity using a high-entropy alloy diffusion barrier layer. Journal of Materiomics, 2022, 8(4): 882. |
| [28] | ARVHULT C M, GUÉNEAU C, GOSSÉ S, et al. Thermodynamic assessment of the Ni-Te system. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(16): 11304. |
| [29] | LIAO C N, LEE C H, CHEN W J. Effect of interfacial compound formation on contact resistivity of soldered junctions between bismuth telluride-based thermoelements and copper. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2007, 10(9): 23. |
| [30] | XIA H, CHEN C L, DRYMIOTIS F, et al. Interfacial reaction between Nb foil and n-type PbTe thermoelectric materials during thermoelectric contact fabrication. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2014, 43(11): 4064. |
| [31] | LI C C, DRYMIOTIS F, LIAO L L, et al. Interfacial reactions between PbTe-based thermoelectric materials and Cu and Ag bonding materials. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(40): 10590. |
| [32] | WANG X, GU M, LIAO J C, et al. High temperature interfacial stability of Fe/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 thermoelectric elements. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 197. |
| [33] | TSUTOMU K, HIROMASA T, SATO H K, et al. Enhancement of average thermoelectric figure of merit by increasing the grain-size of Mg3.2Sb1.5Bi0.49Te0.01. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112(3): 33903. |
| [34] | AN D, CHEN S, LU Z, et al. Low thermal conductivity and optimized thermoelectric properties of p-type Te-Sb2Se3: synergistic effect of doping and defect engineering. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(31): 27788. |
| [35] | NORÉN L, TING V, WITHERS R L, et al. An electron and X-ray diffraction investigation of Ni1+xTe2 and Ni1+xSe2CdI2/NiAs type solid solution phases. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2001, 161(2): 266. |
| [36] | ANDERSON J S. Nonstoichiometric compounds: a critique of current structural views. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Chemical Sciences, 1984, 93(6): 861. |
| [37] | CHEN J, ZHANG Y, YU Z, et al. Interface growth and void formation in Sn/Cu and Sn0.7Cu/Cu systems. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(12): 2703. |
| [38] | LIN Y, WU X, LI Y, et al. Revealing multi-stage growth mechanism of Kirkendall voids at electrode interfaces of Bi2Te3-based thermoelectric devices with in-situ TEM technique. Nano Energy, 2022, 102: 107736. |
| [39] | LIU R, XING Y, LIAO J, et al. Thermal-inert and ohmic-contact interface for high performance half-Heusler based thermoelectric generator. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 7738. |
| [40] | BALL R G J, DICKINSON S, CORDFUNKE E H P, et al. Thermochemical data acquisition. Part II. Luxembourg: Commission of the European Communities, 1992: 106. |
| [41] | BARIN I. Thermochemical data of pure substances. 3rd ed. Weinheim: VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, 1995: 1198. |
| [42] | 叶贡欣. 扩散控制固相反应动力学关系的研究. 合肥水泥研究设计院院刊, 1992(1): 10. |
| [43] | 陈立东, 刘睿恒, 史迅. 热电材料与器件. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 1. |
| [1] | 陈浩, 樊文浩, 安德成, 陈少平. 能带优化和载流子调控改善SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [2] | 胡忠良, 傅赟天, 蒋蒙, 王连军, 江莞. Nb/Mg3SbBi界面层热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 931-937. |
| [3] | 肖娅妮, 吕嘉南, 李振明, 刘铭扬, 刘伟, 任志刚, 刘弘景, 杨东旺, 鄢永高. Bi2Te3基热电材料的湿热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 800-806. |
| [4] | 李悦, 张旭良, 景芳丽, 胡章贵, 吴以成. 铈掺杂硼酸钙镧晶体的生长与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 583-588. |
| [5] | 王磊, 李建军, 宁军, 胡天玉, 王洪阳, 张占群, 武琳馨. CoFe2O4@Zeolite催化剂活化过一硫酸盐对甲基橙的强化降解: 性能与机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [6] | 孙晗, 李文俊, 贾子璇, 张岩, 殷利迎, 介万奇, 徐亚东. ACRT技术对大尺寸ZnTe晶体溶液法制备及其性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 310-315. |
| [7] | 华思恒, 杨东旺, 唐昊, 袁雄, 展若雨, 徐卓明, 吕嘉南, 肖娅妮, 鄢永高, 唐新峰. n型Bi2Te3基材料表面处理对热电单元性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 163-169. |
| [8] | 鲁志强, 刘可可, 李强, 胡芹, 冯利萍, 张清杰, 吴劲松, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. p型多晶Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3合金类施主效应与热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1331-1337. |
| [9] | 万家宝, 张明辉, 苏怀宇, 曹枝军, 刘学超, 谢坚生, 王祥远, 时英辉, 王亮, 雷水金. GeO2-La2O3-TiO2玻璃的结构、热学和光学性质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1230-1236. |
| [10] | 洪督, 牛亚然, 李红, 钟鑫, 郑学斌. 等离子喷涂TiC-Graphite复合涂层摩擦磨损性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [11] | 娄许诺, 邓后权, 李爽, 张青堂, 熊文杰, 唐国栋. Ge掺杂MnTe材料的热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [12] | 任培安, 汪聪, 訾鹏, 陶奇睿, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. Te与In共掺杂对Cu2SnSe3热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1079-1086. |
| [13] | 张岑岑, 王雪, 彭良明. 基于分步式双重调控n型(PbTe)1-x-y(PbS)x(Sb2Se3)y体系的热电传输特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 936-942. |
| [14] | 王旭, 顾明, 廖锦城, 宋庆峰, 史迅, 柏胜强, 陈立东. Fe/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3热电元件高温稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 197-202. |
| [15] | 杨枭, 苏贤礼, 鄢永高, 唐新峰. (GeTe)nBi2Te3的结构与热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 75-80. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||