无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 715-725.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230564
收稿日期:2023-12-07
修回日期:2024-02-26
出版日期:2024-06-20
网络出版日期:2024-05-24
通讯作者:
张侃, 教授. E-mail: kanzhang@jlu.edu.cn作者简介:张睿(2001-), 女, 博士研究生. E-mail: zhangr22@mails.jlu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Rui( ), ZHANG Kan(
), ZHANG Kan( ), YUAN Mengya, GU Xinlei, ZHENG Weitao
), YUAN Mengya, GU Xinlei, ZHENG Weitao
Received:2023-12-07
Revised:2024-02-26
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-05-24
Contact:
ZHANG Kan, professor. E-mail: kanzhang@jlu.edu.cnAbout author:ZHANG Rui (2001-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: zhangr22@mails.jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
高熵过渡金属氮化物(HENs)具有热稳定性, 抗腐蚀、抗氧化性以及优异的力学性质, 可用作结构部件及运动部件的表面防护薄膜。然而, 受HENs组元多样性的影响, 宽泛可调的金属组分与HENs力学性质之间的映射关系相当复杂。本工作以(NbMoTaW)Nx薄膜为研究对象, 基于磁控溅射方法调节薄膜生长过程中氮气流量, 制备了不同氮含量的(NbMoTaW)Nx (x = 0, 0.59, 0.80, 0.95)薄膜, 研究了(NbMoTaW)Nx薄膜的成分、结构、形貌与性能, 并对薄膜力学性质的主要影响机制进行了系统探究。结果表明, 通过调节氮空位, 实现了对氮原子及金属原子亚晶格畸变度的协同调控, 得益于氮原子和金属原子亚晶格的高畸变度, (NbMoTaW)N0.80样品具有最高的硬度与最好的耐磨损性能。排除电子结构、残余应力、晶粒尺寸等力学性质影响因素后, 进一步确认了HENs薄膜晶格畸变度与力学性质之间的直接关系。本研究寻找到一条简洁的晶格畸变度调控策略, 为调节、优化氮化物薄膜性能, 进而更好地解决复杂服役环境下防护薄膜的机械损伤问题提供了新的思路。
中图分类号:
张睿, 张侃, 袁梦雅, 谷鑫磊, 郑伟涛. 氮空位调控晶格畸变度强化(NbMoTaW)Nx薄膜的力学性质和耐磨损性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 715-725.
ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Kan, YUAN Mengya, GU Xinlei, ZHENG Weitao. Nitrogen Vacancy Regulated Lattice Distortion on Improvement of (NbMoTaW)Nx Thin Films: Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 715-725.

图1 (a) NbMoTaW, (b) (NbMoTaW)N0.59, (c) (NbMoTaW)N0.80和(d) (NbMoTaW)N0.95薄膜表面的SEM照片及相应的EDS元素分布
Fig. 1 SEM images and corresponding EDS mappings of the surfaces for (a) NbMoTaW, (b) (NbMoTaW)N0.59, (c) (NbMoTaW)N0.80, and (d) (NbMoTaW)N0.95 thin films
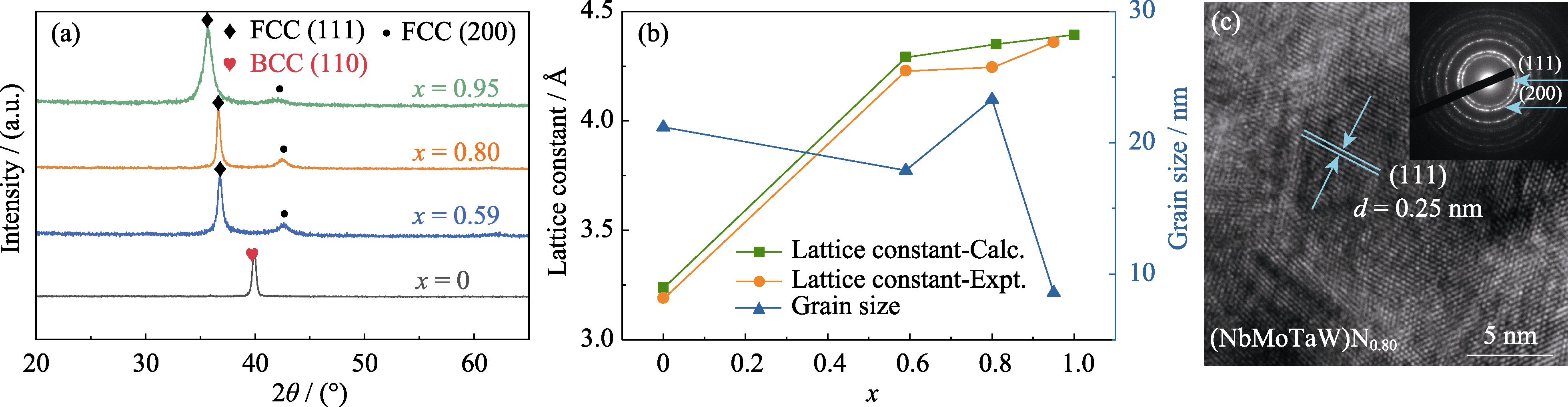
图2 结构变化趋势分析
Fig. 2 Analysis of the structural change trends (a) XRD patterns of (NbMoTaW)Nx thin films on Si(100) substrate; (b) Lattice constants of (NbMoTaW)Nx thin films obtained from XRD patterns and DFT calculations, and grain sizes of (NbMoTaW)Nx thin films calculated from XRD patterns; (c) HRTEM image and SAED pattern of (NbMoTaW)N0.80 sample
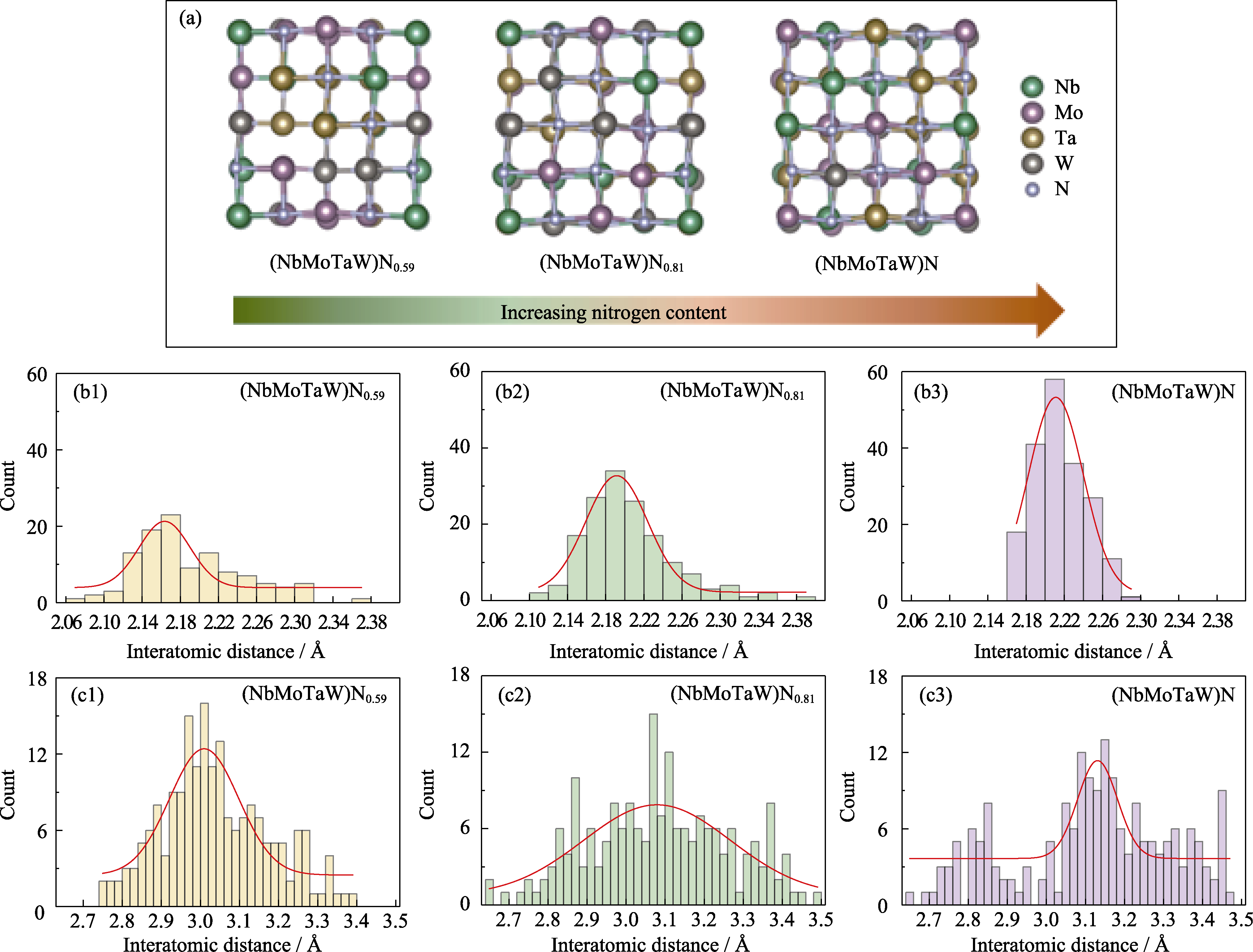
图3 (NbMoTaW)Nx(x = 0.59, 0.81, 1.00)的键长分布
Fig. 3 Bond-length distributions of (NbMoTaW)Nx (x = 0.59, 0.81, 1.00) (a) Schematic representation of the crystal structure after structural optimization; (b1-b3) 1NN atomic distance distribution of Me-N in the supercell and Gaussian fitting curves; (c1-c3) 1NN atomic distance distribution of Me-Me in the supercell and Gaussian fitting curves
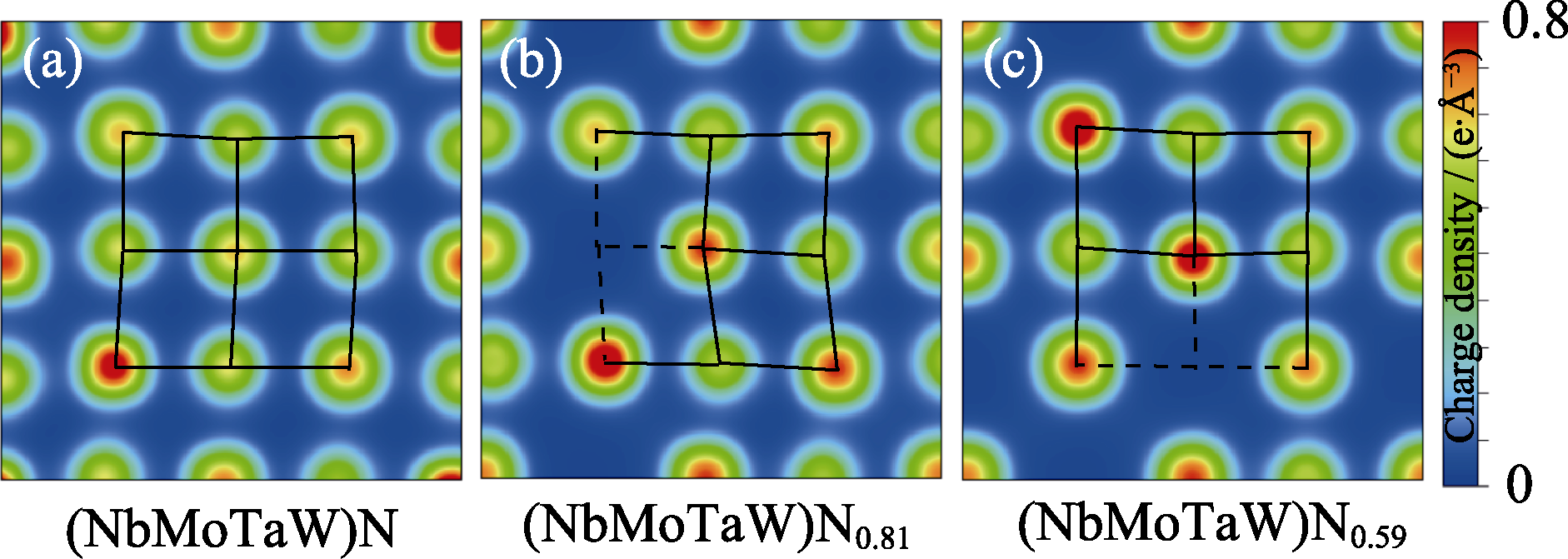
图4 x = (a) 1.00, (b) 0.81, (c) 0.59时, (NbMoTaW)Nx化合物(001)晶面的电荷密度分布示意图
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of charge density on the (001) plane of (NbMoTaW)Nx compounds when x = (a) 1.00, (b) 0.81, (c) 0.59 Black lines indicating atomic lattice, while dashed lines indicating empty lattice points
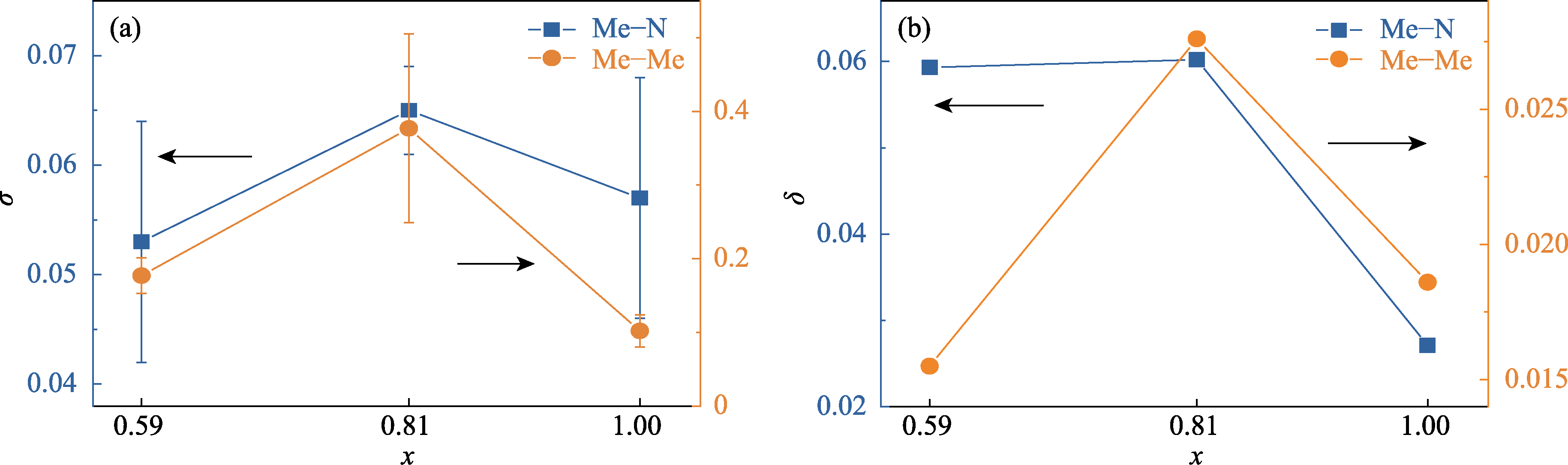
图5 基于两种方法评估(NbMoTaW)Nx (x = 0.59, 0.81, 1.00)中氮原子亚晶格和金属原子亚晶格畸变度随氮含量x的变化趋势
Fig. 5 Trends in lattice distortions of nitrogen and metal sublattices in (NbMoTaW)Nx (x = 0.59, 0.81, 1.00) as function of nitrogen content x evaluated by two methods (a) Method one: lattice distortions σ obtained from the peak width of Gaussian fitting results as described in Fig. 3; (b) Method two: lattice distortions δ calculated using equations
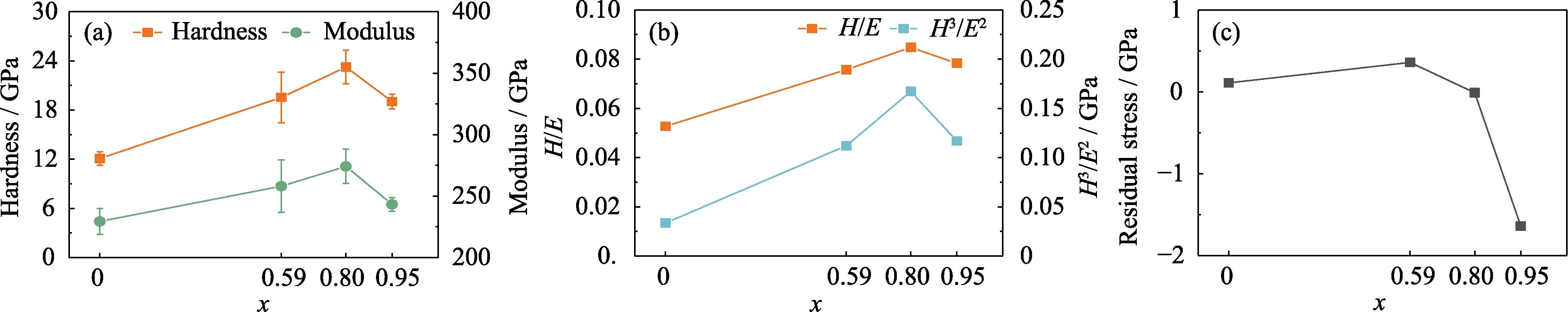
图6 (NbMoTaW)Nx薄膜的(a) H及E, (b) H/E和H3/E2, 以及(c)相应的残余应力
Fig. 6 (a) H and E values, (b) H/E and H3/E2 ratio values, and (c) corresponding residual stress values for (NbMoTaW)Nx thin films

图7 (a) NbMoTaW, (b) (NbMoTaW)N0.59, (c) (NbMoTaW)N0.80和(d) (NbMoTaW)N0.95薄膜的10000圈磨损轨迹的SEM照片和相应的EDS元素分析
Fig. 7 SEM images of wear tracks at 10000 laps and corresponding EDS mappings for (a) NbMoTaW, (b) (NbMoTaW)N0.59, (c) (NbMoTaW)N0.80, and (d) (NbMoTaW)N0.95 thin films
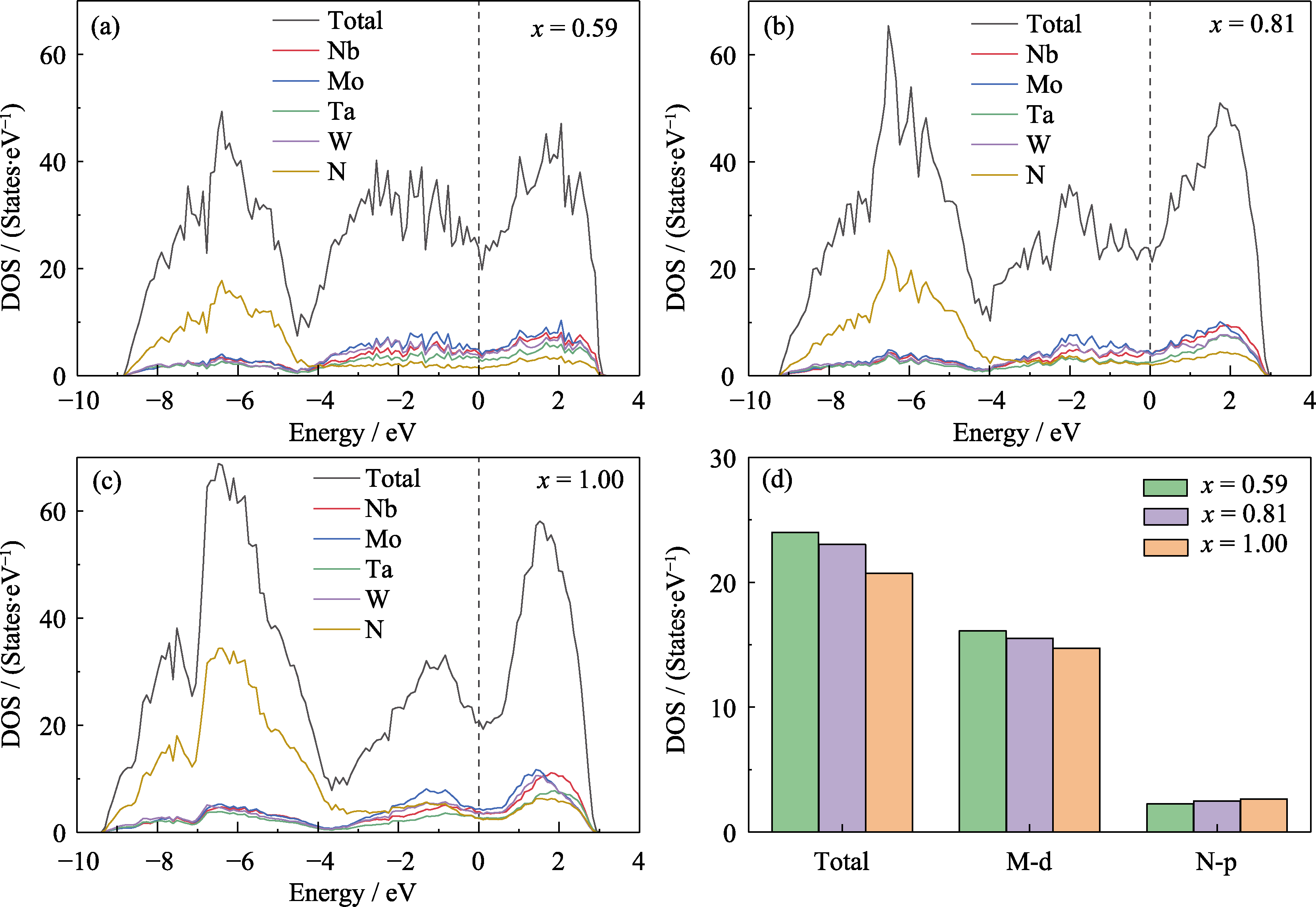
图8 (a) (NbMoTaW)N0.59, (b) (NbMoTaW)N0.81和(c) (NbMoTaW)N的态密度(DOS)和分波态密度(PDOS), 以及(d)三种薄膜在费米能级的DOS
Fig. 8 Density of states (DOS) and partial density of states (PDOS) for (a) (NbMoTaW)N0.59, (b) (NbMoTaW)N0.81 and (c) (NbMoTaW)N, and (d) DOS at the Fermi level for the three thin films The position of the Fermi surface is indicated by dotted lines; Colorful figures are available on website
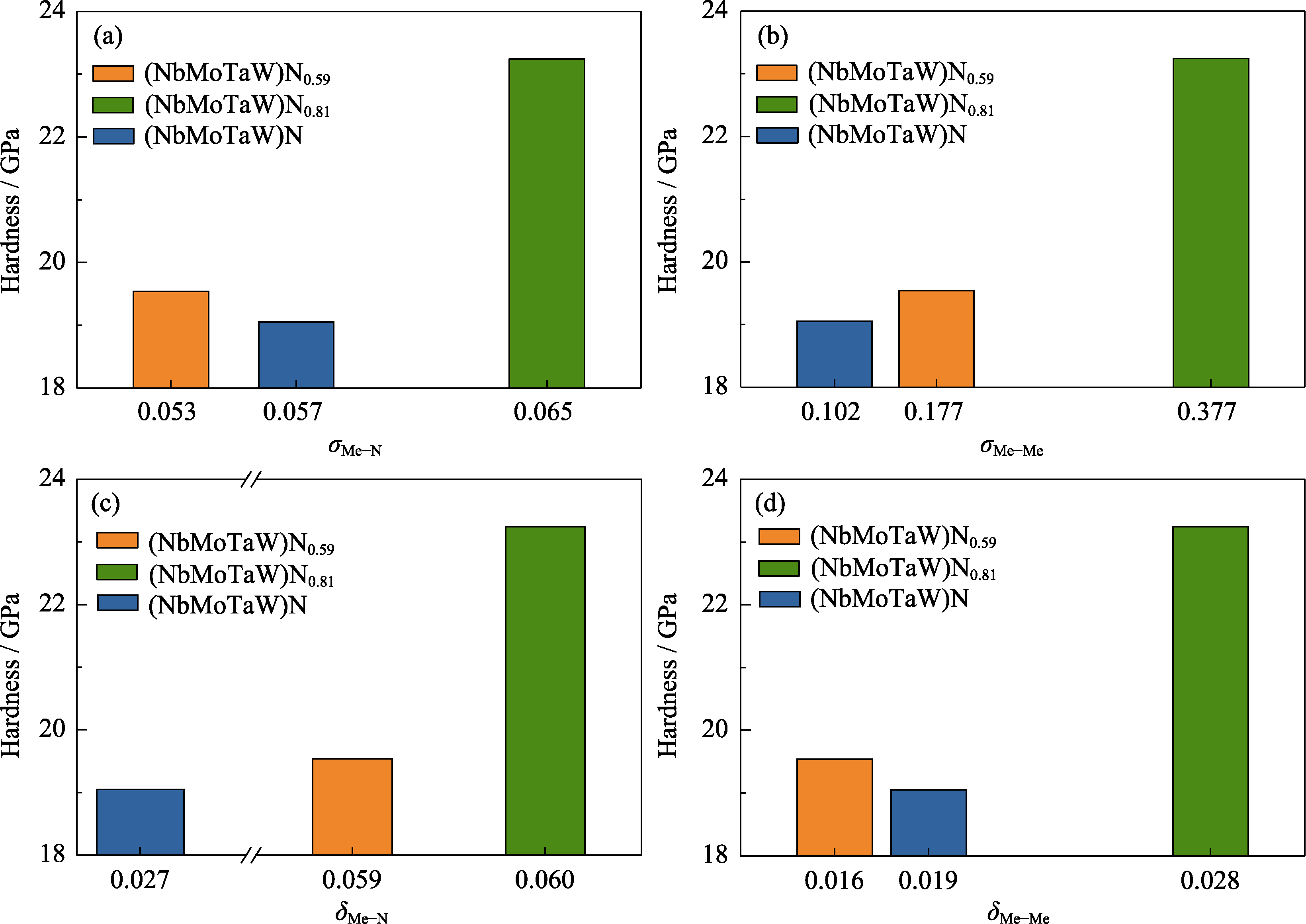
图9 (NbMoTaW)Nx (x = 0.59, 0.81, 1.00)的硬度随晶格畸变度变化的趋势
Fig. 9 Trend in hardness of (NbMoTaW)Nx (x = 0.59, 0.81, 1.00) with respect to lattice distortion (a, b) Lattice distortions obtained through the peak width of Gaussian fitting results of (a) nitrogen sublattice (σMe-N) and (b) metal sublattice (σMe-Me); (c, d) Calculated lattice distortions using equations of (c) nitrogen sublattice (δMe-N) and (d) metal sublattice (δMe-Me); Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | MAMUN M A, FARHA A H, ER A O, et al. Nanomechanical properties of NbN films prepared by pulsed laser deposition using nanoindendation. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258: 4308. |
| [2] | ZHANG K, BALASUBRAMANIAN K, OZSDOLAY B D, et al. Growth and mechanical properties of epitaxial NbN(001) films on MgO(001). Surface and Coatings Technology, 2016, 288: 105. |
| [3] | TANG Z, WEN Z, LIU Y, et al. Rapid experimental screening of high-entropy diborides for superior oxidation resistance. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(12):2312239. |
| [4] | YEH J W, CHEN S K, LIN S J, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6: 299. |
| [5] | CANTOR B, CHANG I T H, KNIGHT P, et al. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 375-377: 213. |
| [6] | SENKOV O N, WILKS G B, MIRACLE D B, et al. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2010, 18: 1758. |
| [7] | YEH J W. Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys. JOM, 2013, 65: 1759. |
| [8] |
ZHANG G J, WANG Y J. Non-order is the new order: high-entropy ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4):337.
DOI |
| [9] | ROST C M, SACHET E, BORMAN T, et al. Entropy-stabilized oxides. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8485. |
| [10] | GILD J, ZHANG Y, HARRINGTON T, et al. High-entropy metal diborides: a new class of high-entropy materials and a new type of ultrahigh temperature ceramics. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 37946. |
| [11] | ALPER J S. The Gibbs phase rule revisited: interrelationships between components and phases. Journal of Chemical Education, 1999, 76: 1567. |
| [12] | FRACCHIA M, CODURI M, GHIGNA P, et al. Phase stability of high entropy oxides: a critical review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44: 585. |
| [13] | EVANS D, CHEN J, BOKAS G, et al. Visualizing temperature- dependent phase stability in high entropy alloys. npj Computational Materials, 2021, 7: 151. |
| [14] | YE Y F, WANG Q, LU J, et al. High-entropy alloy: challenges and prospects. Materials Today, 2016, 19: 349. |
| [15] | ZHANG Y, ZUO T T, TANG Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Progress in Materials Science, 2014, 61: 1. |
| [16] | MIRACLE D B, SENKOV O N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Materialia, 2017, 122: 448. |
| [17] | CHEN T K, SHUN T T, YEH J W, et al. Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 188/189: 193. |
| [18] | CHEN T K, WONG M S, SHUN T T, et al. Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2005, 200: 1361. |
| [19] | LAI C H, LIN S J, YEH J W, et al. Preparation and characterization of AlCrTaTiZr multi-element nitride coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 201: 3275. |
| [20] | LEWIN E. Multi-component and high-entropy nitride coatings—a promising field in need of a novel approach. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 127: 160901. |
| [21] | YAN X H, LI J S, ZHANG W R, et al. A brief review of high- entropy films. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 210: 12. |
| [22] | YUAN M, GAO X, GU X, et al. Simultaneous enhancement of hardness and wear and corrosion resistance of high-entropy transition-metal nitride. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 106: 1356. |
| [23] | LO W L, HSU S Y, LIN Y C, et al. Improvement of high entropy alloy nitride coatings (AlCrNbSiTiMo)N on mechanical and high temperature tribological properties by tuning substrate bias. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 401: 126247. |
| [24] | WANG Y, YANG Y, YANG H, et al. Microstructure and wear properties of nitrided AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 210: 233. |
| [25] | JHI S H, IHM J, LOUIE S G, et al. Electronic mechanism of hardness enhancement in transition-metal carbonitrides. Nature, 1999, 399: 132. |
| [26] | GU X, LIU C, GUO H, et al. Sorting transition-metal diborides: new descriptor for mechanical properties. Acta Materialia, 2021, 207: 116685. |
| [27] | GU X, LIU C, GAO X, et al. Solving strength-toughness dilemma in superhard transition-metal diborides via a distinct chemically tuned solid solution approach. Research, 2023, 6: 0035. |
| [28] | ZHANG R, GU X, ZHANG K, et al. Core electron count as a versatile and accurate new descriptor for sorting mechanical properties of diverse transition metal compounds. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35: 2304729. |
| [29] | IVANOVSKII A L. Ternary carbides and nitrides based on transition metals and subgroup ⅢB, ⅣB elements: electronic structure and chemical bonding. Russian Chemical Reviews, 1996, 65: 461. |
| [30] | ABADIAS G, KANOUN M B, GOUMRI-SAID S, et al. Electronic structure and mechanical properties of ternary ZrTaN alloys studied by ab initio calculations and thin-film growth experiments. Physical Review B, 2014, 90: 144107. |
| [31] | LIU C, GAO X, ZHANG K, et al. Exceptional strain strengthening and tuning of mechanical properties of TiN. Physical Review B, 2022, 106: 054112. |
| [32] | XU Y, LI G, XIA Y. Synthesis and characterization of super-hard AlCrTiVZr high-entropy alloy nitride films deposited by hipims. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 523: 146529. |
| [33] | MA C H, HUANG J H, CHEN H. Nanohardness of nanocrystalline tin thin films. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 200: 3868. |
| [34] | LIU C, GU X, ZHANG K, et al. Superhard metallic compound TaB2 via crystal orientation resolved strain stiffening. Physical Review B, 2022, 105: 024105. |
| [35] | ZHAO S. Effects of local elemental ordering on defect-grain boundary interactions in high-entropy alloys. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 887: 161314. |
| [36] | ZHAO S. Role of chemical disorder and local ordering on defect evolution in high-entropy alloys. Physical Review Materials, 2021, 5: 103604. |
| [37] | GLUDOVATZ B, HOHENWARTER A, CATOOR D, et al. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science, 2014, 345: 1153. |
| [38] | PSHYK A V, VASYLENKO A, BAKHIT B, et al. High-entropy transition metal nitride thin films alloyed with Al: microstructure, phase composition and mechanical properties. Materials Design, 2022, 219: 110789. |
| [39] | CUI P, LI W, LIU P, et al. Effects of nitrogen content on microstructures and mechanical properties of (AlCrTiZrHf)N high-entropy alloy nitride films. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 834: 155063. |
| [40] | TUCK J R, KORSUNSKY A M, BULL S J, et al. On the application of the work-of-indentation approach to depth-sensing indentation experiments in coated systems. Surface Coatings Technology, 2001, 137: 217. |
| [41] | KRESSE G, HAFNER J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Physical Review B-Condensed Matter, 1993, 47: 558. |
| [42] | KRESSE G, FURTHMULLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Physical Review B, 1996, 54: 11169. |
| [43] | BLOCHL P E. Projector augmented-wave method. Physical Review B-Condensed Matter, 1994, 50: 17953. |
| [44] | PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77: 3865. |
| [45] | ZUNGER A, WEI S, FERREIRA L G, et al. Special quasirandom structures. Physical Review Letters, 1990, 65: 353. |
| [46] | MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for brillouin-zone integrations. Physical Review B, 1976, 13: 5188. |
| [47] | PACK J D, MONKHORST H J. "Special points for brillouin-zone integrations"—a reply. Physical Review B, 1977, 16: 1748. |
| [48] | ZOU Y, MA H, SPOLENAK R. Ultrastrong ductile and stable high-entropy alloys at small scales. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7748. |
| [49] | FRITZE S, HANS M, RIEKEHR L, et al. Influence of carbon on microstructure and mechanical properties of magnetron sputtered taw coatings. Materials & Design, 2020, 196: 109070. |
| [50] | CHENG K H, LAI C H, LIN S J, et al. Structural and mechanical properties of multi-element (AlCrMoTaTiZr)Nx coatings by reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519: 3185. |
| [51] | CHANG C C, HSIAO Y T, CHEN Y L, et al. Lattice distortion or cocktail effect dominates the performance of tantalum-based high- entropy nitride coatings. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 577: 151894. |
| [52] | SHULUMBA N, ALLING B, HELLMAN O, et al. Vibrational free energy and phase stability of paramagnetic and antiferromagnetic crn fromab initiomolecular dynamics. Physical Review B, 2014, 89: 174108. |
| [53] | BALASUBRAMANIAN K, KHARE S, GALL D. Vacancy-induced mechanical stabilization of cubic tungsten nitride. Physical Review B, 2016, 94: 174111. |
| [54] | ISAEV E I, SIMASK S I, ABRIKOSOV I A, et al. Phonon related properties of transition metals, their carbides, and nitrides: a first- principles study. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101: 123519. |
| [55] | 谷鑫磊, 张侃, 文懋, 等. 过渡族金属轻元素化合物薄膜强韧化的研究进展. 中国材料进展, 2021, 40(3):167. |
| [56] | MORGAN W L. Universal resputtering curve. Applied Physics Letters, 1989, 55: 106. |
| [57] | SENKOV O N, WILKS G B, SCOTT J M, et al. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2011, 19: 698. |
| [58] | ZAID H, TANAKA K, LIAO M, et al. Self-organized growth of 111-oriented (VNbTaMoW)N nanorods on MgO(001). Nano Letters, 2020, 21: 577. |
| [59] | ZAID H, TANAKA K, CIOBANU C V, et al. Growth of elastically- stiff, nanostructured, high-entropy alloy nitride, (VNbTaMoW) N/Al2O3(0001) thin film. Scripta Materialia, 2021, 197: 113813. |
| [60] | SHIN C S, GALL D, HELLGREN N, et al. Vacancy hardening in single-crystal TiNx(001) layers. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 93: 6025. |
| [61] | GU Z, HU C, HUANG H, et al. Identification and thermodynamic mechanism of the phase transition in hafnium nitride films. Acta Materialia, 2015, 90: 59. |
| [62] | BALASUBRAMANIAN K, HUANG L, GALL D. Phase stability and mechanical properties of Mo1-xNx with 0≤x≤1. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122: 195101. |
| [63] | QI Z, WU Z, ZHANG D, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and oxidation behaviors of magnetron sputtered NbNx coatings. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 675: 22. |
| [64] | LEE C, CHOU Y, KIM G, et al. Lattice-distortion-enhanced yield strength in a refractory high-entropy alloy. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32: e2004029. |
| [65] | GUO Z, YUAN W, SUN Y, et al. Thermodynamic assessment of the Si-Ta and Si-W systems. Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion, 2009, 30: 564. |
| [66] | LEYLAND A, MATTHEWS A. On the significance of the H/E ratio in wear control: a nanocomposite coating approach to optimised tribological behaviour. Wear, 2000, 246: 1. |
| [67] | DAHLQVIST M, JANSSON U, ROSEN J. Influence of boron vacancies on phase stability, bonding and structure of MB2 (M = Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W) with AlB2 type structure. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2015, 27: 435702. |
| [68] | LU K, LEI Z, DENG S, et al. Synergistic effects of grain sizes on the corrosion behavior and mechanical properties in a metastable high-entropy alloy. Corrosion Science, 2023, 225: 111588. |
| [69] | NIE J, LIU Y, WANG F, et al. Key roles of particles in grain refinement and material strengthening for an aluminum matrix composite. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 801: 140414. |
| [70] | MA M D, HAN Y J, ZHAO A S, et al. Ultrafine-grained high-entropy zirconates with superior mechanical and thermal properties. Journal of Materiomics, 2023, 9: 370. |
| [71] | LEE C, SONG G, GAO M C, et al. Lattice distortion in a strong and ductile refractory high-entropy alloy. Acta Materialia, 2018, 160: 158. |
| [72] | WANG P, WU Y, LIU J, et al. Impacts of atomic scale lattice distortion on dislocation activity in high-entropy alloys. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2017, 17: 38. |
| [1] | 乔振杰, 高乐, 冯倩, 胡建宝, 董绍明, 马良来. 硼含量对碳硼化合物结构、力学影响行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(11): 1228-1232. |
| [2] | 杨 晓, 刘学建, 黄政仁, 刘桂玲, 姚秀敏. 维氏压痕对常压固相烧结碳化硅陶瓷材料力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(9): 965-969. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||