无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 741-753.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230560
• 综述 • 下一篇
陈乾1( ), 苏海军1,2(
), 苏海军1,2( ), 姜浩1, 申仲琳1, 余明辉1, 张卓1(
), 姜浩1, 申仲琳1, 余明辉1, 张卓1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-05
修回日期:2024-01-04
出版日期:2024-07-20
网络出版日期:2024-01-31
通讯作者:
苏海军, 教授. E-mail: shjnpu@nwpu.edu.cn;作者简介:陈 乾(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: cq12138@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Qian1( ), SU Haijun1,2(
), SU Haijun1,2( ), JIANG Hao1, SHEN Zhonglin1, YU Minghui1, ZHANG Zhuo1(
), JIANG Hao1, SHEN Zhonglin1, YU Minghui1, ZHANG Zhuo1( )
)
Received:2023-12-05
Revised:2024-01-04
Published:2024-07-20
Online:2024-01-31
Contact:
SU Haijun, professor. E-mail: shjnpu@nwpu.edu.cn;About author:CHEN Qian (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: cq12138@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
氧化物陶瓷具有高硬度、高强度以及优异的抗氧化和抗腐蚀性能, 是高性能发动机极端高温、燃气腐蚀、氧化服役环境用重要的候选高温结构材料, 在航空航天用高端装备领域具有广阔的应用前景。与传统陶瓷制备技术相比, 激光增材制造技术能够一步实现从原材料粉末到高性能结构件的一体化高致密成型, 具有柔性度好、成型效率高的特点, 可以快速制备高性能、高精度、大尺寸复杂结构部件。近年来, 基于液固相变发展的熔体生长氧化物陶瓷激光增材制造技术已成为高温结构材料制备技术领域的前沿研究热点之一。本文首先概述了激光增材制造技术的基本原理, 着重介绍了选区激光熔化与激光定向能量沉积两种典型激光增材制造技术的工艺特点。在此基础上, 重点阐述了利用激光增材制造技术制备不同氧化物陶瓷的组织特征及工艺参数对微观组织的影响规律, 并总结比较了不同体系氧化物陶瓷力学性能的差异。最后, 对该领域存在的问题进行了梳理和分析, 并对未来的发展趋势进行了展望。
中图分类号:
陈乾, 苏海军, 姜浩, 申仲琳, 余明辉, 张卓. 超高温氧化物陶瓷激光增材制造及组织性能调控研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 741-753.
CHEN Qian, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, SHEN Zhonglin, YU Minghui, ZHANG Zhuo. Progress of Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics: Laser Additive Manufacturing and Microstructure Evolution[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 741-753.
| Laser type | CO2 laser | Nd: YAG laser | Yb-fiber laser |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength/μm | 10.6 | 1.06 | 1.07 |
| Efficiency/% | 5-20 | 1-3 | 10-30 |
| Output power/kW | ~20 | ~16 | ~10 |
| Beam quality factor | 3-5 | 0.4-20 | 0.3-4 |
| Preferred material | Ceramic/polymer | Metal | Metal |
表1 LAM常用激光器及其特点[19]
Table 1 Lasers for LAM and their characteristics[19]
| Laser type | CO2 laser | Nd: YAG laser | Yb-fiber laser |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength/μm | 10.6 | 1.06 | 1.07 |
| Efficiency/% | 5-20 | 1-3 | 10-30 |
| Output power/kW | ~20 | ~16 | ~10 |
| Beam quality factor | 3-5 | 0.4-20 | 0.3-4 |
| Preferred material | Ceramic/polymer | Metal | Metal |
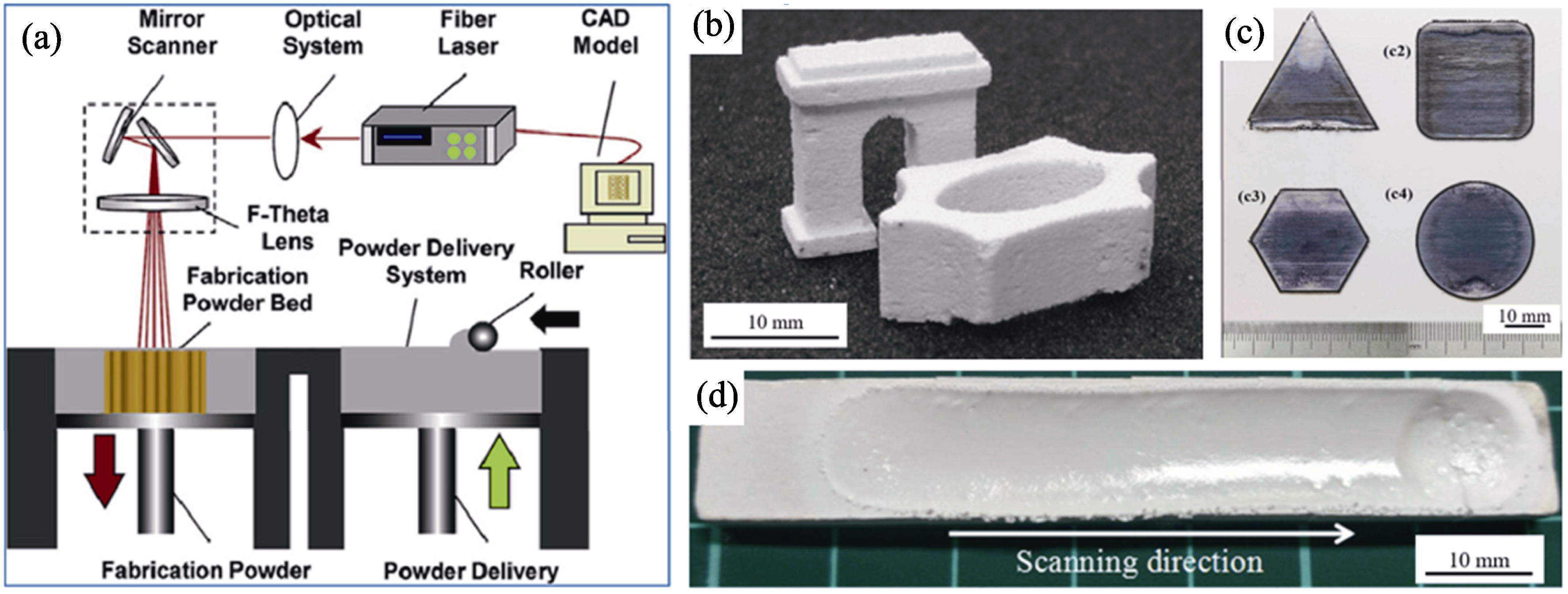
图1 选区激光熔化(SLM)技术原理及其制备的氧化物陶瓷样件
Fig. 1 Principle of selective laser melting (SLM) and as-prepared oxide ceramic samples (a) Schematic diagram[22]; (b) ZrO2 ceramic[23]; (c) Al2O3/GAP eutectic ceramic[24]; (d) Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic[25]
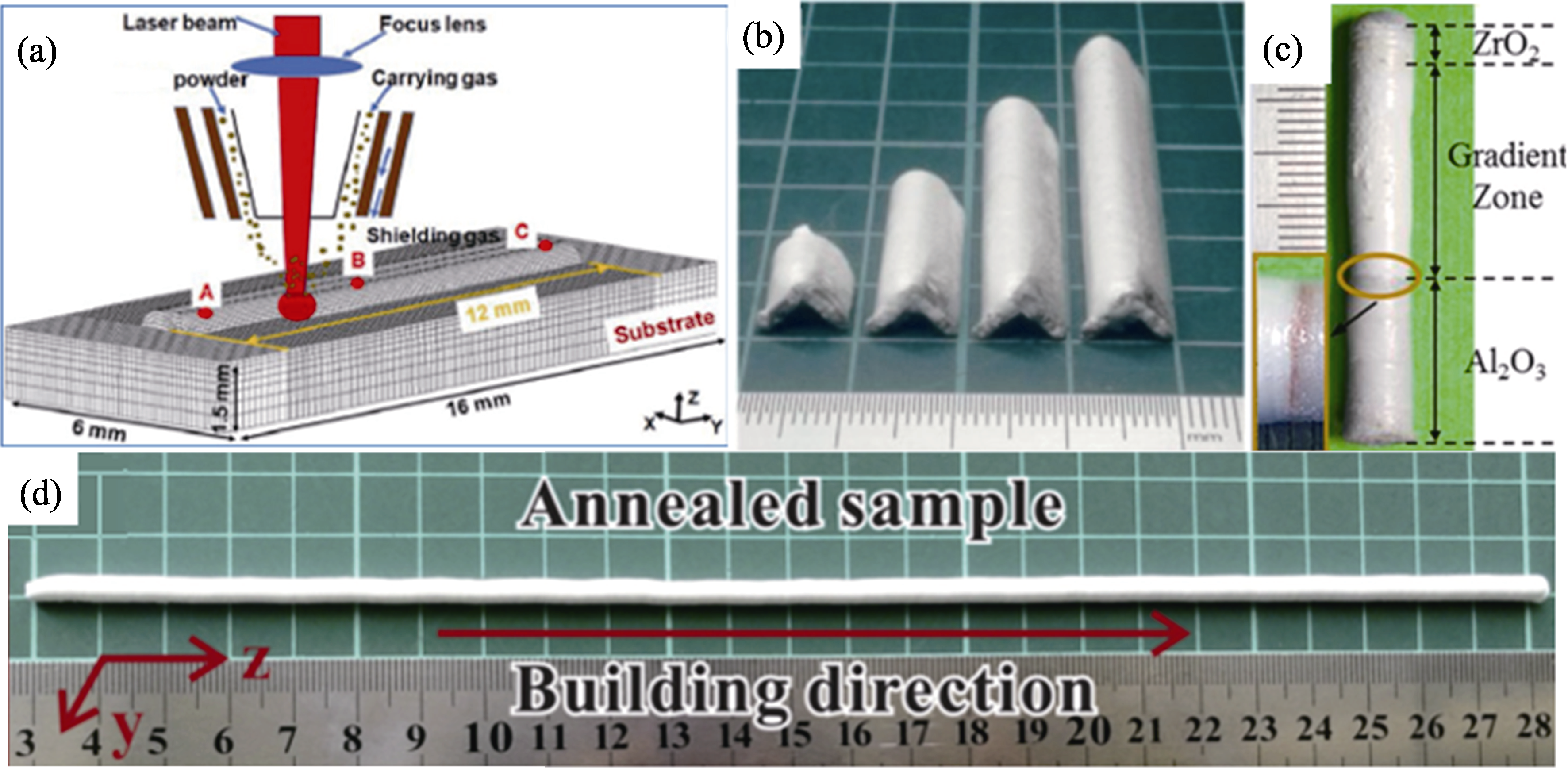
图2 激光定向能量沉积(LDED)技术原理及其制备的氧化物陶瓷样件
Fig. 2 Principle of laser directed energy deposition (LDED) and as-prepared oxide ceramic samples (a) Schematic diagram[26]; (b) Al2O3/ GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic with complex structure[29]; (c) Graded Al2O3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic[31]; (d) Rod-like Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic[30]
| Process | Preferred laser | Power/W | Building rate / (cm3·min-1) | Dimensional accuracy/mm | Surface roughness/μm | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLM | Nd: YAG laser/fiber laser | 50-1000 | 1.3 | 0.04-0.2 | 7-20 | High precision and small scale component |
| LDED | CO2 laser | 100-3000 | 11.5 | 0.5-1.0 | 4-10 | Large scale component |
表2 SLM与LDED的工艺特点对比[32]
Table 2 Comparison of process characteristics of SLM and LDED[32]
| Process | Preferred laser | Power/W | Building rate / (cm3·min-1) | Dimensional accuracy/mm | Surface roughness/μm | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLM | Nd: YAG laser/fiber laser | 50-1000 | 1.3 | 0.04-0.2 | 7-20 | High precision and small scale component |
| LDED | CO2 laser | 100-3000 | 11.5 | 0.5-1.0 | 4-10 | Large scale component |
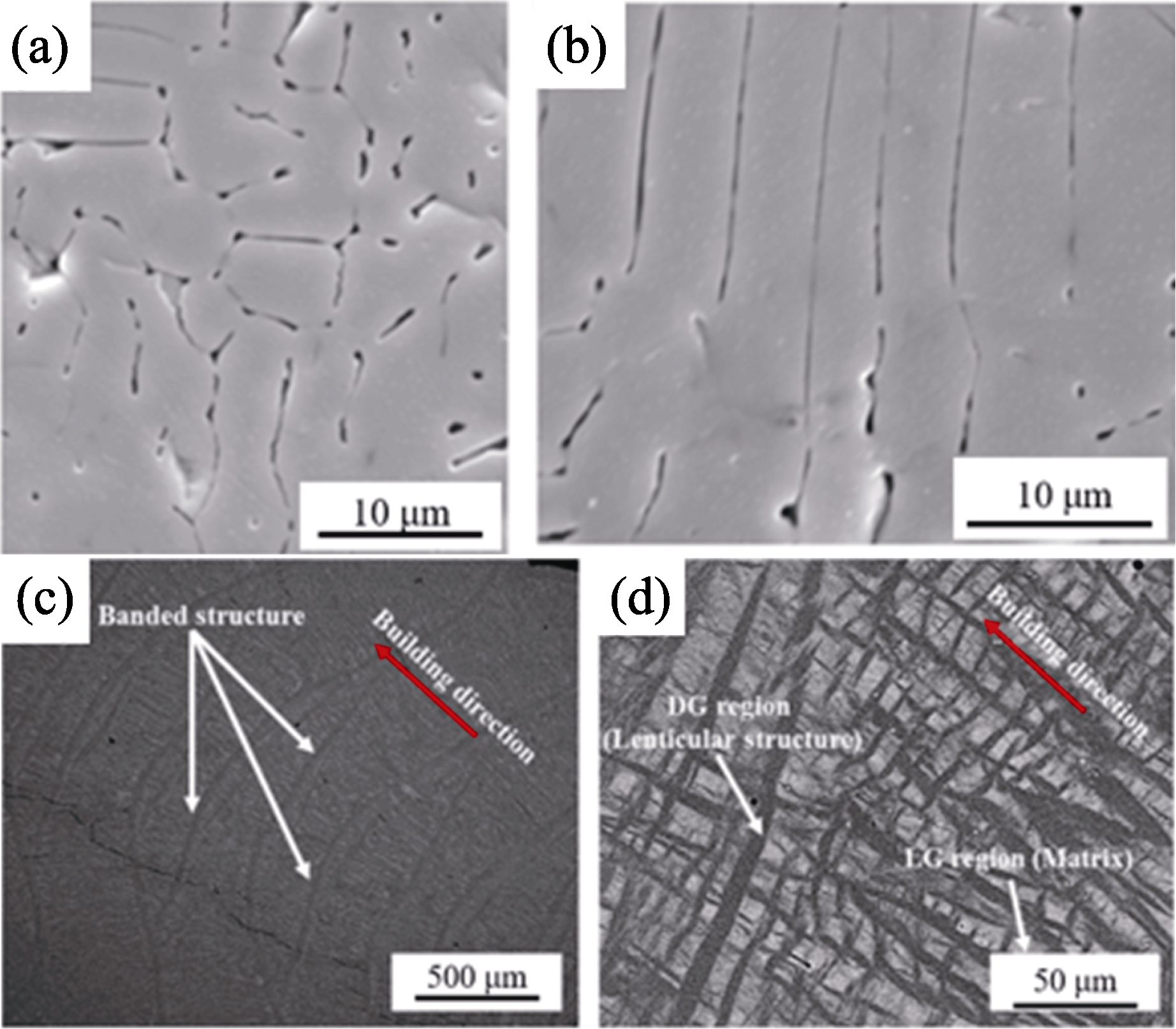
图3 LDED制备的单相氧化物陶瓷微观组织
Fig. 3 Microstructures of single-phase oxide ceramics prepared by LDED (a, b) Cross section (a) and longitudinal section (b) of Al2O3 ceramic[33]; (c, d) Longitudinal section of ZrO2 ceramic (c) and its magnified image (d)[34]
| Phase | Entropy/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | Jackson factor | Growth manner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 48 | 5.74 | Faceted |
| GAP | 16.5 | 1.9 | Non-faceted |
| YAG | 122 | 14.72 | Faceted |
| ZrO2 | 30 | 3.55 | Weak faceted |
表3 共晶生长中各相熔化熵及对应生长方式[35-36]
Table 3 Entropy of different phases in eutectic and corresponding growth manner[35-36]
| Phase | Entropy/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | Jackson factor | Growth manner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 48 | 5.74 | Faceted |
| GAP | 16.5 | 1.9 | Non-faceted |
| YAG | 122 | 14.72 | Faceted |
| ZrO2 | 30 | 3.55 | Weak faceted |
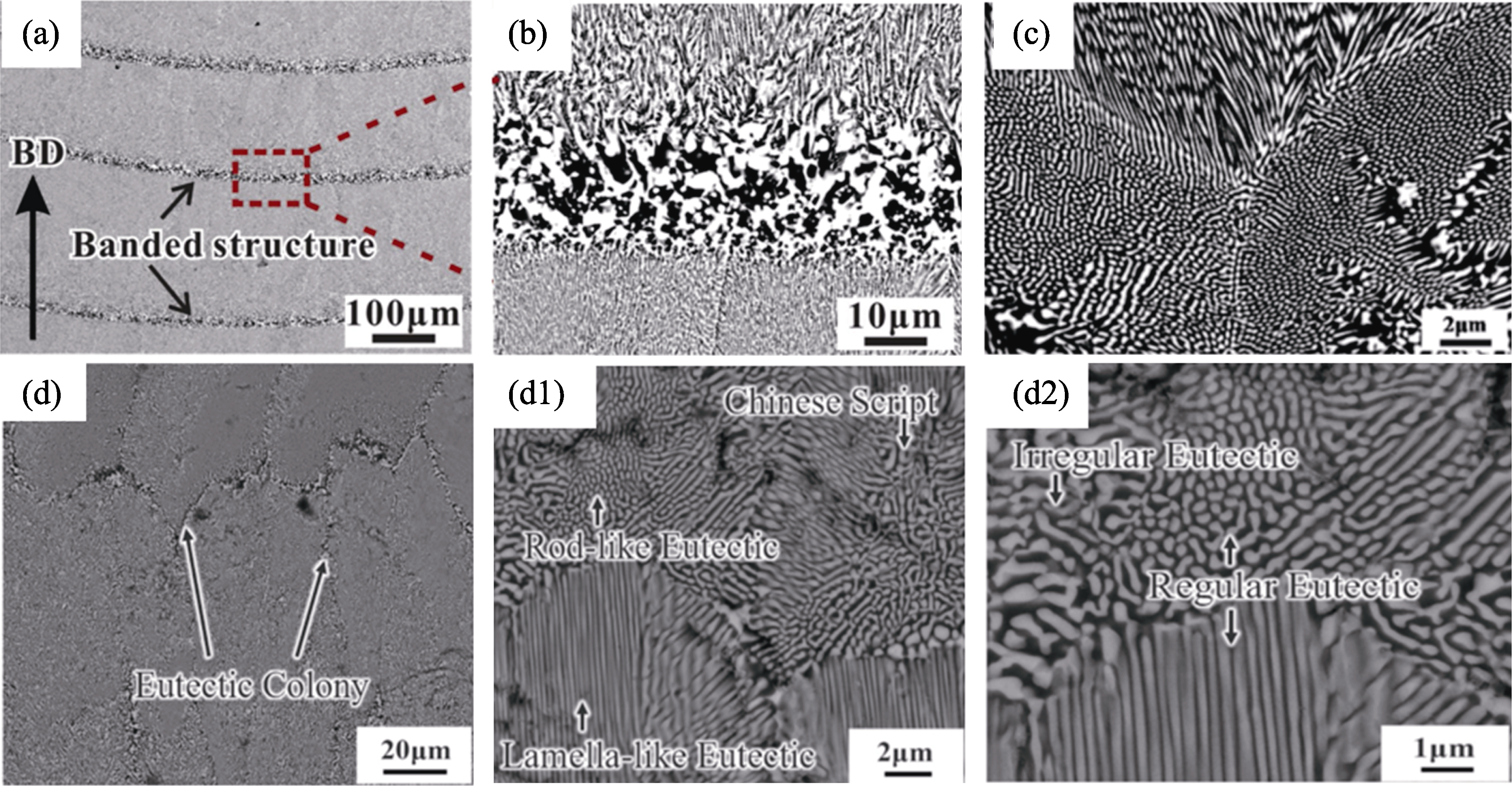
图4 LAM制备的氧化物共晶陶瓷的横、纵截面典型微观组织形貌
Fig. 4 Typical microstructure morphologies of cross/longitudinal sections of LAM fabricated oxide eutectic ceramics (a) Periodic banded structure and (b) magnified image[42]; (c) Three ways of intersectional dispersion microstructure[36]; (d) Colony structure and (d1, d2) magnified images[36]
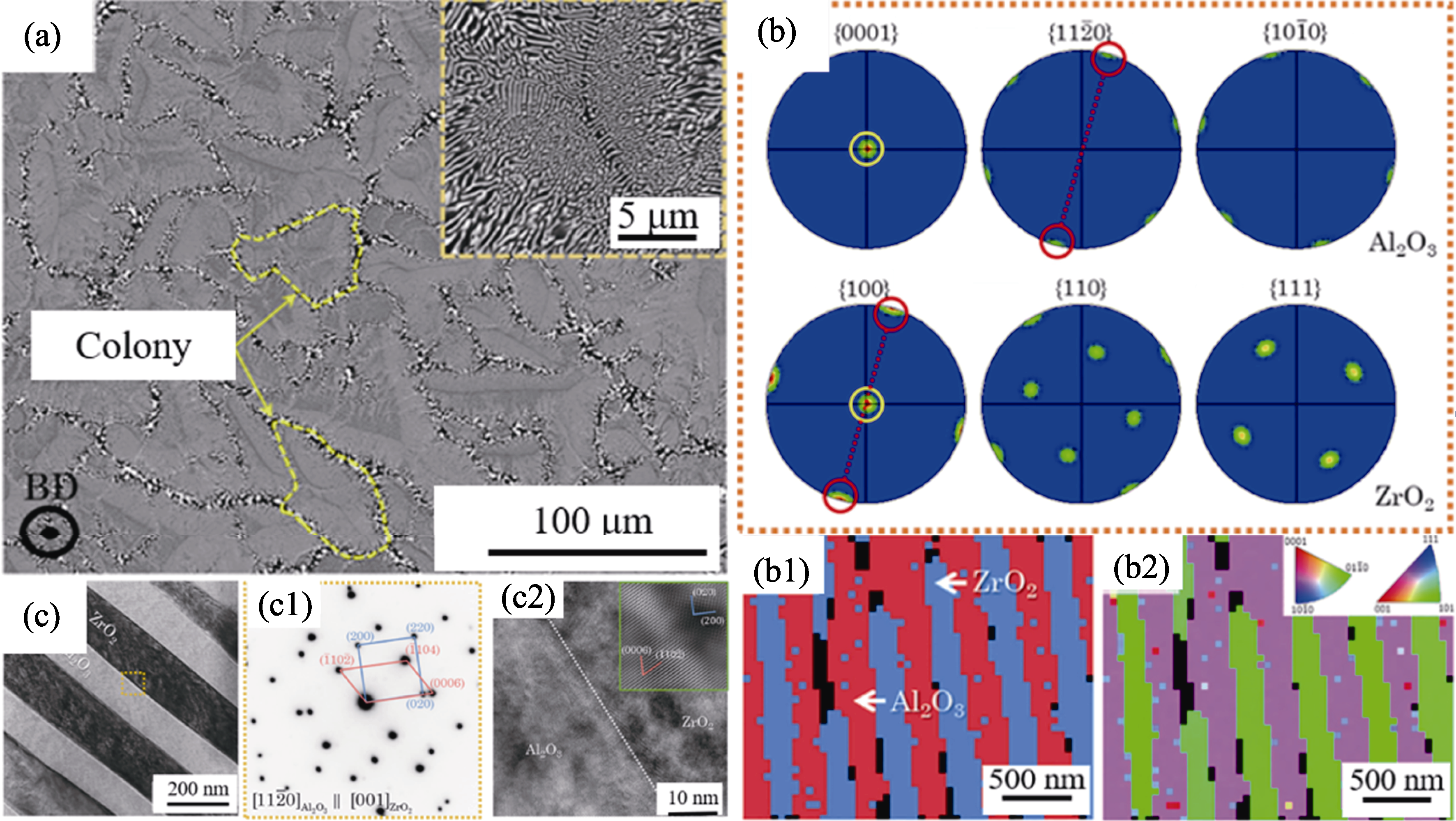
图5 Al2O3/ZrO2共晶陶瓷的微观组织及其晶体取向[43]
Fig. 5 Microstructure of Al2O3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic and corresponding crystallographic orientation[43] (a) Transversal section; (b) Corresponding EBSD pole figures of Al2O3 and ZrO2 with (b1) EBSD phases and (b2) IPF (inverse pole figure); (c) Transverse sectional TEM (transmission electron microscope) image with (c1) SAED (selected area electron diffraction) and (c2) HRTEM (high-resolution TEM) at Al2O3/ZrO2 interface
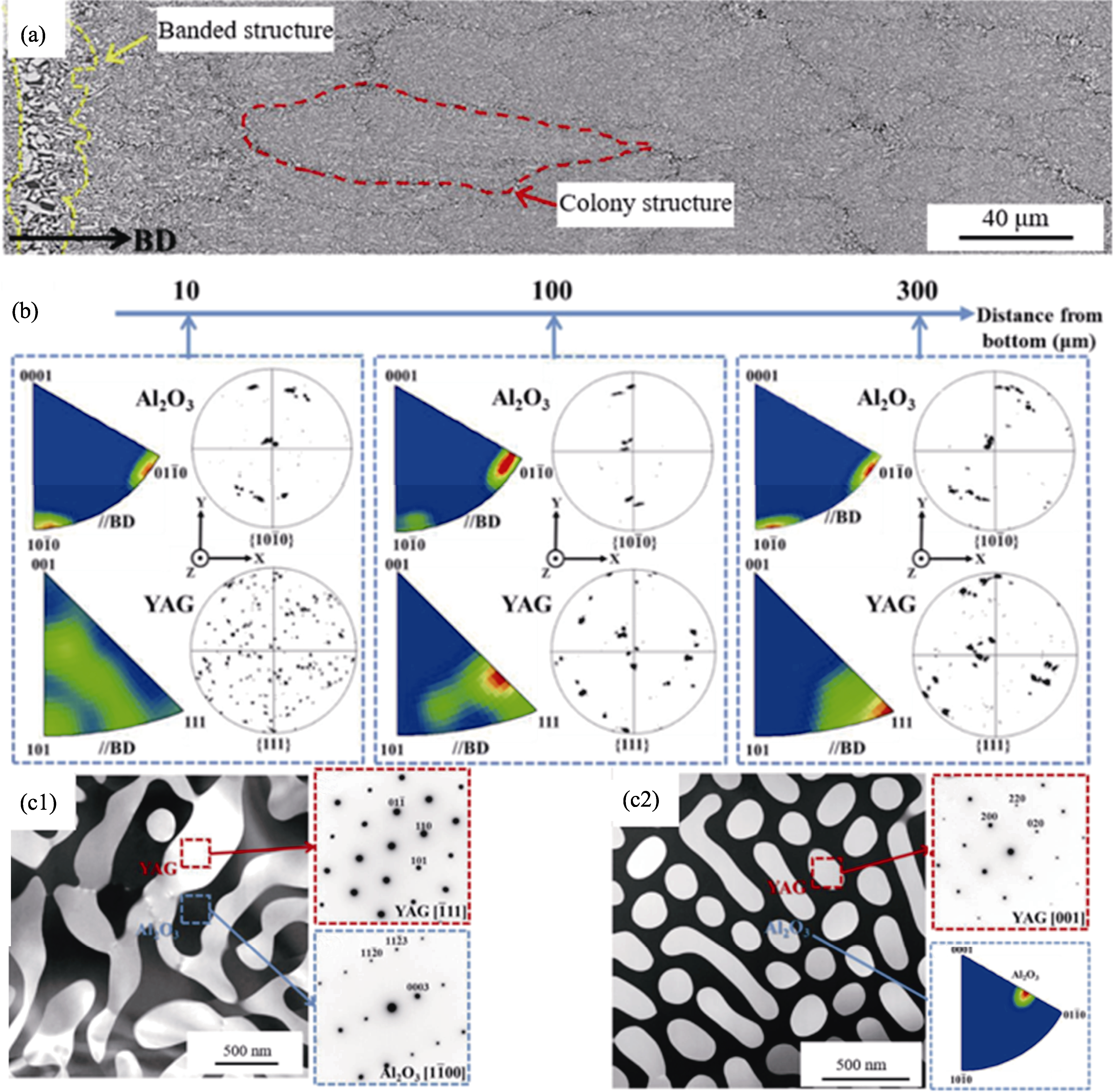
图6 Al2O3/YAG共晶陶瓷沿沉积方向的微观组织及晶体取向演变[37]
Fig. 6 Microstructure and orientation evolution of Al2O3/YAG eutectic ceramic along deposition direction[37] (a) Longitudinal section; (b) Orientation variations of Al2O3 and YAG along the height; (c1, c2) TEM images and SAED patterns of (c1) irregular and (c2) regular eutectic inverse pole figures
| Eutectic system | Preparation method | Crystal orientation relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | Laser directed energy deposition[ Optical floating zone method[ | [0001]Al2O3∥[001]YAG∥[001]ZrO2 <11¯00>Al2O3∥<001>YAG∥<001>ZrO2 |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | Laser directed energy deposition[ Laser floating zone method[ | [112¯0]Al2O3∥[001]ZrO2 [022¯1]Al2O3∥[111]ZrO2 |
| Al2O3/YAG | Bridgman[ Laser directed energy deposition[ | [101¯0]Al2O3∥[101]YAG [101¯0]Al2O3∥[111]YAG |
表4 不同制备工艺下氧化物共晶陶瓷的晶体取向关系
Table 4 Crystal orientation relationship of the oxide eutectic ceramics by different preparation methods
| Eutectic system | Preparation method | Crystal orientation relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | Laser directed energy deposition[ Optical floating zone method[ | [0001]Al2O3∥[001]YAG∥[001]ZrO2 <11¯00>Al2O3∥<001>YAG∥<001>ZrO2 |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | Laser directed energy deposition[ Laser floating zone method[ | [112¯0]Al2O3∥[001]ZrO2 [022¯1]Al2O3∥[111]ZrO2 |
| Al2O3/YAG | Bridgman[ Laser directed energy deposition[ | [101¯0]Al2O3∥[101]YAG [101¯0]Al2O3∥[111]YAG |
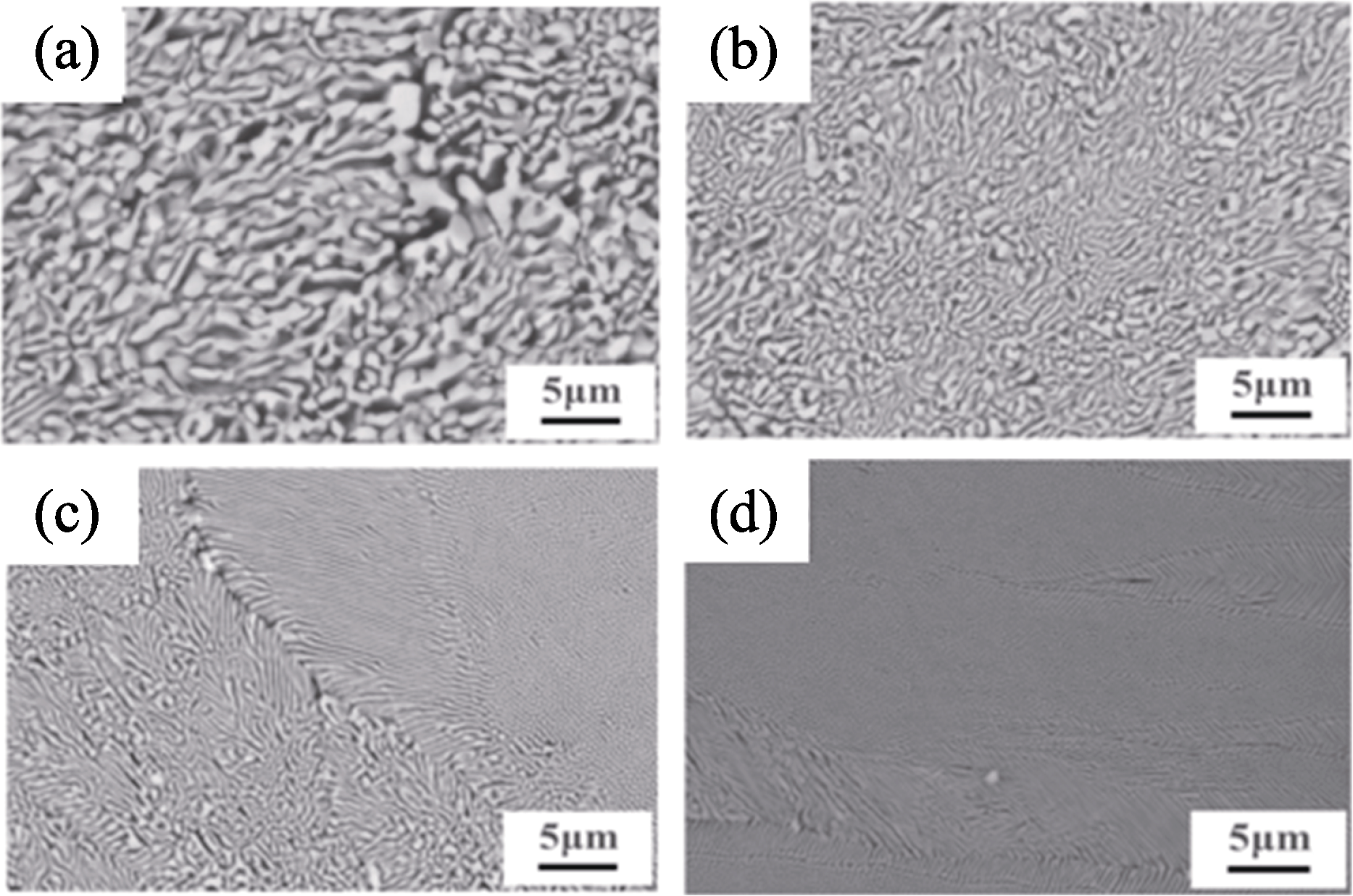
图8 不同扫描速率下Al2O3/GAP共晶陶瓷的顶部微观组织[36]
Fig. 8 Microstructures at top region of the Al2O3/GAP eutectic ceramics under different scanning rates[36] (a) 4 mm/min; (b) 8 mm/min; (c) 16 mm/min; (d) 30 mm/min
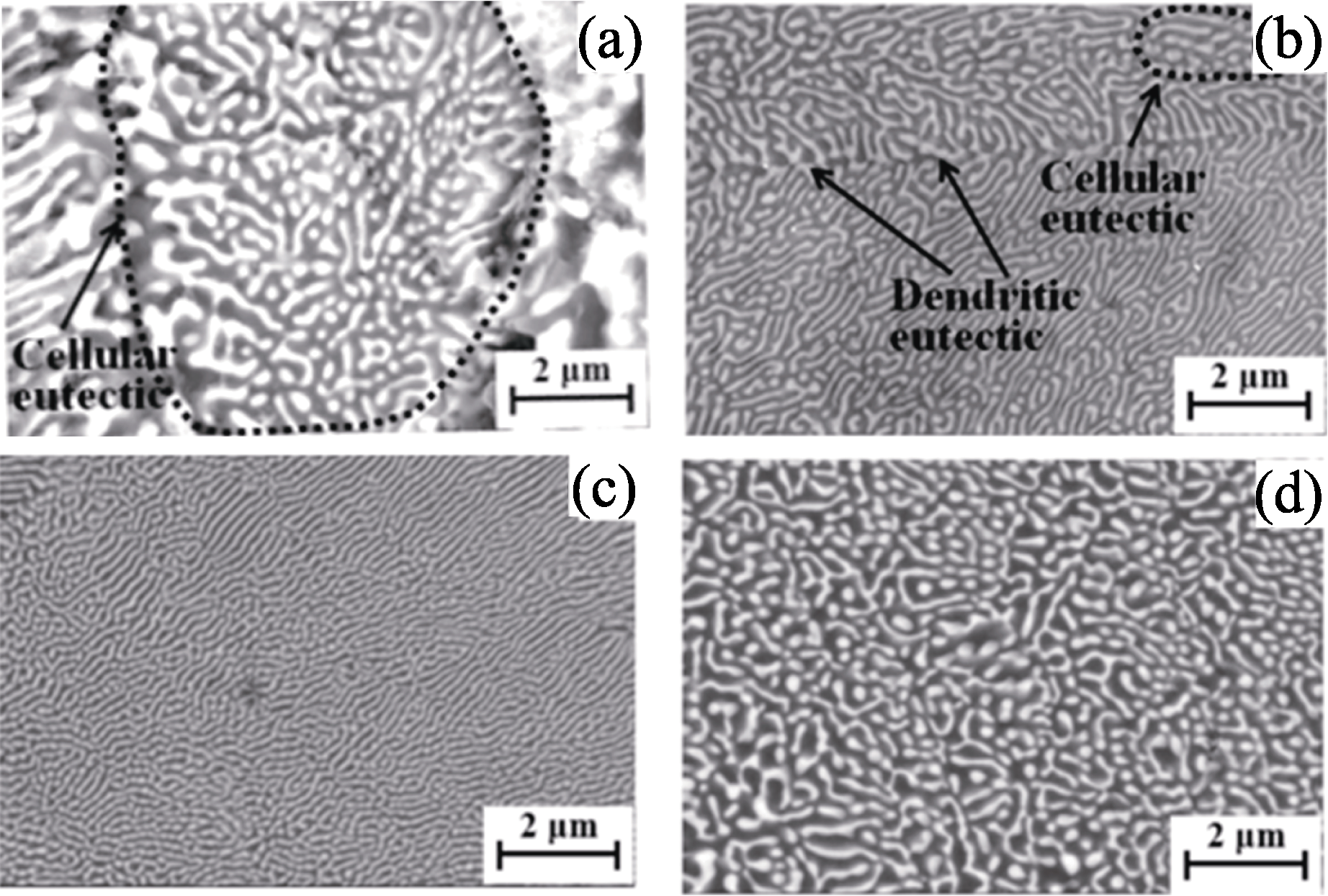
图9 不同超声功率下Al2O3/ZrO2共晶陶瓷的微观组织形貌[57]
Fig. 9 Micro-morphologies of the Al2O3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics with different ultrasonic powers[57] (a) 20-50 W; (b) 110 W; (c) 120-150 W; (d) 160 W
| Material | Hardness/GPa | Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | Flexural strength/MPa | Preparation method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 16 18.91 | / 3.55 | / 350 | Sintering[ LDED[ |
| ZrO2(Y2O3) | 19.80 | / | / | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | / 15.3 / 18.59 / | 6.03 7.8 / 6.52 7.67/8.70 | 525 / 538 / / | Sintering[ DS[ SLM[ LDED[ LDED (ultrasonic assisted/C fiber)[ |
| Al2O3/GAP | 23.36 17.1 15.16 | 3.12 4.5 4.3 | / / / | DS[ SLM[ LDED[ |
| Al2O3/TiO2 | 16.38 | 3.75 | 212 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/SiO2 | 11.10 18.39 18.64 | 2.54 3.07 3.54 | 350 310 504 | Sintering[ LDED[ LDED (heat treatment)[ |
| Al2O3/YAG | 17.50 17.35 21.50 | 3.60 3.14 5.86 | / / / | DS[ LDED[ LDED (water cooling)[ |
| Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 | 17.50 17.90 15.30 | 6.50 8.50 7.80 | 485 / / | Sintering[ DS[ SLM[ |
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | 15.80 18.90 | 3.90 3.84 | / / | DS[ LDED[ |
表5 不同LAM技术制备的氧化物陶瓷材料的力学性能对比
Table 5 Comparison of mechanical properties among different oxide ceramics prepared by different LAM technologies
| Material | Hardness/GPa | Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | Flexural strength/MPa | Preparation method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 16 18.91 | / 3.55 | / 350 | Sintering[ LDED[ |
| ZrO2(Y2O3) | 19.80 | / | / | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | / 15.3 / 18.59 / | 6.03 7.8 / 6.52 7.67/8.70 | 525 / 538 / / | Sintering[ DS[ SLM[ LDED[ LDED (ultrasonic assisted/C fiber)[ |
| Al2O3/GAP | 23.36 17.1 15.16 | 3.12 4.5 4.3 | / / / | DS[ SLM[ LDED[ |
| Al2O3/TiO2 | 16.38 | 3.75 | 212 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/SiO2 | 11.10 18.39 18.64 | 2.54 3.07 3.54 | 350 310 504 | Sintering[ LDED[ LDED (heat treatment)[ |
| Al2O3/YAG | 17.50 17.35 21.50 | 3.60 3.14 5.86 | / / / | DS[ LDED[ LDED (water cooling)[ |
| Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 | 17.50 17.90 15.30 | 6.50 8.50 7.80 | 485 / / | Sintering[ DS[ SLM[ |
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | 15.80 18.90 | 3.90 3.84 | / / | DS[ LDED[ |
| [1] | 傅恒志. 航空航天材料定向凝固. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 1. |
| [2] | 宋希文. “热障涂层新材料、制备技术及性能评价”专题序言. 装备环境工程, 2019, 16(1): 10. |
| [3] | JAMES C W, EDGAR A S. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(19): 5775. |
| [4] | 孔祥灿, 张子卿, 朱俊强, 等. 航空发动机气冷涡轮叶片冷却结构研究进展. 推进技术, 2022, 43(5): 6. |
| [5] | LIU L, WANG S Z, ZHANG B Q, et al. Present status and prospects of nanostructured thermal barrier coatings and their performance improvement strategies: a review. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 97: 12. |
| [6] | 耿广仁, 周明星, 周长灵, 等. 高温陶瓷纤维/高温陶瓷基复合材料研究进展. 佛山陶瓷, 2019, 29(11): 9. |
| [7] | LIU Y, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. Effect of seed orientations on crystallographic texture control in faceted Al2O3/YAG eutectic ceramic during directional solidification. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 146: 86. |
| [8] | DUAN B H, MAO L, LV M R, et al. Interface interaction during the preparation of TiAl-(Nb, V) quaternary intermetallic single crystals by directional solidification based on Y2O3 doped BaZrO3/Al2O3 composite ceramic mold. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(11): 5032. |
| [9] | LIU Y, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. High temperature calcium- magnesium-alumina-silicate (CMAS) corrosion behavior of directionally solidified Al2O3/YAG eutectic ceramic. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 165: 66. |
| [10] | SUN H F, SUN L C, REN X M, et al. Outstanding molten calcium- magnesium-aluminosilicate (CMAS) corrosion resistance of directionally solidified Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 eutectic ceramic at 1500 °C. Corrosion Science, 2023, 220: 111289. |
| [11] | WAKU Y, NAKAGAWA N, WAKAMOTO T, et al. A ductile ceramic eutectic composite with high strength at 1873 K. Nature, 1997, 389: 49. |
| [12] | NAKAGAWA N, OHTSUBO H, MITANI A, et al. High temperature strength and thermal stability for melt growth composite. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25: 1251. |
| [13] | ARMSTRONG M, MEHRABI H, NAVEED N. An overview of modern metal additive manufacturing technology. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 84: 1001. |
| [14] | LIU J K, HUANG J Q, ZHENG Y F, et al. Challenges in topology optimization for hybrid additive-subtractive manufacturing: a review. Computer-Aided Design, 2023, 161: 103531. |
| [15] | KIM Y S, CHANG W, JEONG H J, et al. High performance of protonic ceramic fuel cells with 1-μm-thick electrolytes fabricated by inkjet printing. Additive Manufacturing, 2023, 71: 103590. |
| [16] | LI J G, AN X L, LIANG J J, et al. Recent advances in the stereolithographic three-dimensional printing of ceramic cores: challenges and prospects. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 117: 79. |
| [17] | ZHANG H, ZHAI Q, CAO Y, et al. Design and facile manufacturing of tri-layer laminated polyolefin microfibrous fabrics with tailoring pore size for enhancing waterproof breathable performance. Materials & Design, 2023, 228: 111829. |
| [18] | PFEIFFERP S, FLORIO K, PUCCIO D, et al. Direct laser additive manufacturing of high performance oxide ceramics: a state-of-the-art review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(13): 6087. |
| [19] | LEE H, LIM C H J, LOW M J, et al. Lasers in additive manufacturing: a review. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 2017, 4: 307. |
| [20] | GLARDON R, KARAPATIS N, ROMANO V, et al. Influence of Nd: YAG parameters on the selective laser sintering of metallic powders. CIRP Annals, 2001, 50(1): 133. |
| [21] | KRUTH J P, WANG X, LAOUI T, et al. Laser and materials in selective laser sintering. Assembly Automation, 2003, 23(4): 357. |
| [22] | HU K M, LIN K J, GU D D, et al. Mechanical properties and deformation behavior under compressive loading of selective laser melting processed bio-inspired sandwich structures. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 762: 138089. |
| [23] | SHISHKOVSKY I, YADROITSEV I, BERTRAND P, et al. Alumina-zirconium ceramics synthesis by selective laser sintering/ melting. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 254(4): 966. |
| [24] | SHEN Z L, SU H J, YU M H, et al. Large-size complex-structure ternary eutectic ceramic fabricated using laser powder bed fusion assisted with finite element analysis. Additive Manufacturing, 2023, 72: 103627. |
| [25] | LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. Direct formation of Al2O3/ GdAlO3/ZrO2 ternary eutectic ceramics by selective laser melting: microstructure evolutions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(15): 5144. |
| [26] | GU D D, DU L, DAI D H, et al. Influence of thermal behavior along deposition direction on microstructure and microhardness of laser melting deposited metallic parts. Applied Physics A, 2019, 125(7): 455. |
| [27] | GU D D, SHI X Y, POPRAWE R, et al. Material-structure- performance integrated laser-metal additive manufacturing. Science, 2021, 372(6545): 932. |
| [28] | KOKARE S, OLIVEIRA J P, GODINA R. A LCA and LCC analysis of pure subtractive manufacturing, wire arc additive manufacturing, and selective laser melting approaches. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 101: 67. |
| [29] | SU H J, LIU H F, JIANG H, et al. One-step preparation of melt-grown Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics with large size and irregular shape by directed energy deposition. Additive Manufacturing, 2023, 70: 103563. |
| [30] | WU D J, SHI J, NIU F Y, et al. Direct additive manufacturing of melt growth Al2O3-ZrO2 functionally graded ceramics by laser directed energy deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(6): 2957. |
| [31] | LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. Preparation of large-size Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2ternary eutectic ceramic rod by laser directed energy deposition and its microstructure homogenization mechanism. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 85: 218. |
| [32] | DEBROY T, WEI L H, ZUBACK J S, et al. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—process, structure and properties. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 92: 112. |
| [33] | BALLA V K, BOSE S, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Processing of bulk alumina ceramics using laser engineered net shaping. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2008, 5(3): 234. |
| [34] | FAN Z Q, ZHAO Y T, LU M Y, et al. Yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) thin wall structures fabricated using laser engineered net shaping (LENS). International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 105: 4491. |
| [35] | FAN Z Q, ZHAO Y T, TAN Q Y, et al. Nanostructured Al2O3-YAG-ZrO2 ternary eutectic components prepared by laser engineered net shaping. Acta Materialia, 2019, 170: 24. |
| [36] | SHEN Z L, SU H J, LIU H F, et al. Directly fabricated Al2O3/ GdAlO3 eutectic ceramic with large smooth surface by selective laser melting: rapid solidification behavior and thermal field simulation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(3): 1088. |
| [37] | FAN Z Q, ZHAO Y T, TAN Q Y, et al. New insights into the growth mechanism of 3D-printed Al2O3-Y3Al5O12 binary eutectic composites. Scripta Materialia, 2020, 178: 274. |
| [38] | PENA J I, MERINO R I, HARLAN N R, et al. Microstructure of Y2O3 doped Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectics grown by the laser floating zone method. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(14/15): 2595. |
| [39] | SU H J, ZHANG J, YU J C, et al. Directional solidification and microstructural development of Al2O3/GdAlO3 eutectic ceramic in situ composite under rapid growth conditions. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(12): 4420. |
| [40] | SONG K, ZHANG J, LIN X, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12/ZrO2 hypereutectic directionally solidified ceramic prepared by laser floating zone. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(12): 3051. |
| [41] | SU H J, ZHANG J, TIAN J J, et al. Preparation and characterization of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12/ZrO2 ternary hypoeutectic in situ composites by laser rapid solidification. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(2): 023511. |
| [42] | LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. One-step additive manufacturing and microstructure evolution of melt-grown Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics by laser directed energy deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3547. |
| [43] | FAN Z Q, YIN Y, TAN Q Y, et al. Unveiling solidification mode transition and crystallographic characteristics in laser 3D-printed Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramics. Scripta Materialia, 2022, 210: 114433. |
| [44] | WANG X, ZHONG Y J, SUN Q, et al. Crystallography and interfacial structure in a directionally solidified Al2O3/Y3Al5O12/ ZrO2 eutectic crystal. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 145: 23. |
| [45] | LARREA A, FUENTE G F, MERINO R I, et al. ZrO2-Al2O3 eutectic plates produced by laser zone melting. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(2): 191. |
| [46] | WAKU Y, NAKAGAWA N, WAKAMOTO T, et al. High- temperature strength and thermal stability of a unidirectionally solidified Al2O3/YAG eutectic composite. Journal of Materials Science, 1998, 33: 1217. |
| [47] | HUANG Y F, WU D J, ZHAO D K, et al. Process optimization of melt growth alumina/aluminum titanate composites directed energy deposition: effects of scanning speed. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 35: 101210. |
| [48] | ZHAO D K, WU D J, NIU F Y, et al. Heat treatment of melt- grown alumina ceramics with trace glass fabricated by laser directed energy deposition. Materials Characterization, 2023, 196: 112639. |
| [49] | WU D J, SAN J D, NIU F Y, et al. Directed laser deposition of Al2O3-ZrO2 melt-grown composite ceramics with multiple composition ratios. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55: 6794. |
| [50] | HU Y B, WANG H, CONG W L, et al. Directed energy deposition of zirconia-toughened alumina ceramic: novel microstructure formation and mechanical performance. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2019, 142: 021005. |
| [51] | WU D J, NIU F Y, HUANG Y F, et al. Effects of TiO2 doping on microstructure and properties of directed laser deposition alumina/ aluminum titanate composites. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2019, 14(4): 371. |
| [52] | ZHAO D K, WU D J, SHI J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of melt-grown alumina-mullite/glass composites fabricated by directed laser deposition. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(1): 75. |
| [53] | PAPPAS J M, DONG X Y. Effects of processing conditions on laser direct deposited alumina ceramics. ASME 2020 15th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, New York, 2020: 8260. |
| [54] | LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. Effect of scanning speed on the solidification process of Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics in a single track by selective laser melting. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14): 17252. |
| [55] | FAN Z Q, LU M Y, HUANG H. Selective laser melting of alumina: a single track study. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(8): 9484. |
| [56] | WU D J, ZHAO D K, HUANG Y F, et al. Shaping quality, microstructure, and mechanical properties of melt-grown mullite ceramics by directed laser deposition. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 871: 159609. |
| [57] | YAN S, WU D J, NIU F Y, et al. Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic via ultrasonic-assisted laser engineered net shaping. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 15905. |
| [58] | YAN S, WU D J, NIU F Y, et al. Effect of ultrasonic power on forming quality of nano-sized Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic via laser engineered net shaping (LENS). Ceramics International, 2018, 44(1): 1120. |
| [59] | MOHANTY P, MAHAPATRA R, PADHI P, et al. Ultrasonic cavitation: an approach to synthesize uniformly dispersed metal matrix nanocomposites—a review. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects, 2020, 23: 100475. |
| [60] | WU D J, LIU H C, LU F, et al. Al2O3-YAG eutectic ceramic prepared by laser additive manufacturing with water-cooled substrate. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(3): 4119. |
| [61] | YAN S, WU D J, HUANG Y F, et al. C fiber toughening Al2O3- ZrO2 eutectic via ultrasonic-assisted directed laser deposition. Materials Letters, 2019, 235: 228. |
| [62] | WU D J, LU F, ZHAO D K, et al. Effect of doping SiC particles on cracks and pores of Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramics fabricated by directed laser deposition. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54: 9321. |
| [63] | YAN S, WU D J, MA G Y, et al. Formation mechanism and process optimization of nano Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic via laser engineered net shaping (LENS). Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 14742. |
| [64] | CHEN X T, GUO W, WANG H M, et al. Highly transparent cubic γ-Al2O3 ceramic prepared by high-pressure sintering of home- made nanopowders. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(9): 4219. |
| [65] | NIU F Y, WU D J, LU F, et al. Microstructure and macro properties of Al2O3 ceramics prepared by laser engineered net shaping. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14303. |
| [66] | LIU X D, YUAN Y C, WANG R J, et al. Pressureless sintering behaviour of Al2O3/ZrO2 amorphous/solid solution powder with ultra-fine ZrO2 nanoparticle precipitation. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(24): 39886. |
| [67] | PASTOR J, POZA P, LLORCA J, et al. Mechanical properties of directionally solidified Al2O3-ZrO2(Y2O3) eutectics. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2001, 308(1/2): 241. |
| [68] | WILKES J, HAGEDORN Y C, WILHELM M, et al. Additive manufacturing of ZrO2-Al2O3ceramic components by selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2013, 19(1): 51. |
| [69] | WANG S H, CHU Z F, LIU J C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of directionally solidified Al2O3/GdAlO3 eutectic ceramic prepared with horizontal high-frequency zone melting. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(8): 10279. |
| [70] | SHEN Z L, SU H J, LIU Y, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of melt-grown Al2O3/GdAlO3 eutectic ceramic composite: powder designs and crack analysis with thermo-mechanical simulation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(14): 6583. |
| [71] | MEDVEDOVSKI E. Alumina-mullite ceramics for structural applications. Ceramics International, 2006, 32: 369. |
| [72] | SU H J, ZHANG J, CUI C J, et al. Rapid solidification behaviour of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 (YAG) binary eutectic ceramic in situ composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 479(1/2): 380. |
| [73] | NIU F Y, WU D J, MA G Y, et al. Rapid fabrication of eutectic ceramic structures by laser engineered net shaping. Procedia CIRP, 2016, 42: 91. |
| [74] | HENNICHE A, OUYANG J, MA Y, et al. Microstructure, mechanical and thermo-physical properties of hot-pressed Al2O3- GdAlO3-ZrO2 ceramics with eutectic composition. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2017, 27(4): 491. |
| [75] | MAZEROLLES L, PIQUET N, TRICHET M, et al. New microstructures in ceramic materials from the melt for high temperature applications. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2008, 12(7): 499. |
| [76] | SU H J, ZHANG J, YU J Z, et al. Rapid solidification and fracture behavior of ternary metastable eutectic Al2O3/YAG/YSZ in situ composite ceramic. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(4/5): 1967. |
| [1] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [2] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [3] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [4] | 赵日达, 汤素芳. 多孔碳陶瓷化改进反应熔渗法制备陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 623-633. |
| [5] | 方光武, 谢浩元, 张华军, 高希光, 宋迎东. CMC-EBC损伤耦合机理及一体化设计研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 647-661. |
| [6] | 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590. |
| [7] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [8] | 李宗晓, 胡令祥, 王敬蕊, 诸葛飞. 氧化物神经元器件及其神经网络应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 345-358. |
| [9] | 鲍可, 李西军. 化学气相沉积法制备智能窗用热致变色VO2薄膜的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 233-258. |
| [10] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [11] | 柯鑫, 谢炳卿, 王忠, 张敬国, 王建伟, 李占荣, 贺会军, 汪礼敏. 第三代半导体互连材料与低温烧结纳米铜材的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 17-31. |
| [12] | 董思吟, 帖舒婕, 袁瑞涵, 郑霄家. 低维卤化物钙钛矿直接型X射线探测器研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1017-1030. |
| [13] | 张伦, 吕梅, 朱俊. Cs2AgBiBr6钙钛矿太阳能电池研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1044-1054. |
| [14] | 陈雨, 林埔安, 蔡冰, 张文华. 钙钛矿太阳能电池无机空穴传输材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 991-1004. |
| [15] | 董怡曼, 谭占鳌. 宽带隙钙钛矿基二端叠层太阳电池复合层的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1031-1043. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||