无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 697-706.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230544
收稿日期:2023-11-28
修回日期:2024-01-27
出版日期:2024-06-20
网络出版日期:2024-01-31
通讯作者:
王海龙, 教授. E-mail: 119whl@zzu.edu.cn;作者简介:刘国昂(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: liuguoang2022@163.com
基金资助:
LIU Guoang( ), WANG Hailong(
), WANG Hailong( ), FANG Cheng(
), FANG Cheng( ), HUANG Feilong, YANG Huan
), HUANG Feilong, YANG Huan
Received:2023-11-28
Revised:2024-01-27
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-01-31
Contact:
WANG Hailong, professor. E-mail: 119whl@zzu.edu.cn;About author:LIU Guoang (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: liuguoang2022@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
新型高熵硼化物陶瓷具有优异的高温稳定性、低热导率等优点, 在高温热防护领域具有广阔的应用前景。本研究采用硼/碳热还原法结合热压烧结技术在1900 ℃下制备了(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C高熵硼化物陶瓷, 并研究了B4C第二相含量对其力学及抗氧化性能的影响规律。结果表明, B4C均匀分布在高熵基体中, 有效改善了高熵陶瓷的相对密度和力学性能。当B4C体积分数为20%时, 复相陶瓷的抗弯强度、断裂韧性以及维氏硬度均达到最高, 分别为(570.0±27.6) MPa、(5.58±0.36) MPa·m1/2和(24.6±1.1) GPa。微观结构分析表明, B4C能够钉扎晶界、细化晶粒, 并能够引入裂纹偏转、分支等增韧机制, 最终实现复相陶瓷的强化及韧化。此外, 利用静态氧化实验, 揭示了B4C含量对复相陶瓷800~1400 ℃抗氧化性能的影响。当B4C体积分数不小于20%时, 其氧化生成的玻璃相B2O3能够均匀包裹(Zr, Hf)O2、TiOx及Ta2O5等高熵基体对应的氧化物, 从而在陶瓷表面形成均匀致密的氧化层, 抑制氧向基体内部扩散, 降低氧化层厚度并提升复相陶瓷的抗氧化性能。本工作能够为高熵硼化物陶瓷的力学及抗氧化性能研究提供实验依据和数据支撑。
中图分类号:
刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706.
LIU Guoang, WANG Hailong, FANG Cheng, HUANG Feilong, YANG Huan. Effect of B4C Content on Mechanical Properties and Oxidation Resistance of (Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 697-706.
| Crystalline | HBC-0 | HBC-1 | HBC-2 | HBC-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (2θ)/(°) | (101) | 0.187±0.002 | 0.186±0.002 | 0.194±0.002 | 0.199±0.002 |
| (100) | 0.119±0.001 | 0.118±0.002 | 0.131±0.002 | 0.126±0.002 | |
| (001) | 0.153±0.002 | 0.151±0.003 | 0.163±0.004 | 0.184±0.003 | |
| Crystallinity/% | (101) | 68.51±0.55 | 70.30±0.80 | 70.75±0.85 | 68.93±0.81 |
| (100) | 81.77±0.85 | 81.85±1.26 | 82.78±1.31 | 81.92±1.14 | |
| (001) | 88.85±1.04 | 89.39±1.67 | 89.34±1.86 | 90.85±1.61 |
表1 不同陶瓷样品对应衍射峰的半峰宽(FWHM)和结晶度
Table 1 FWHM and crystallinity of the corresponding diffraction peaks of different ceramic samples
| Crystalline | HBC-0 | HBC-1 | HBC-2 | HBC-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (2θ)/(°) | (101) | 0.187±0.002 | 0.186±0.002 | 0.194±0.002 | 0.199±0.002 |
| (100) | 0.119±0.001 | 0.118±0.002 | 0.131±0.002 | 0.126±0.002 | |
| (001) | 0.153±0.002 | 0.151±0.003 | 0.163±0.004 | 0.184±0.003 | |
| Crystallinity/% | (101) | 68.51±0.55 | 70.30±0.80 | 70.75±0.85 | 68.93±0.81 |
| (100) | 81.77±0.85 | 81.85±1.26 | 82.78±1.31 | 81.92±1.14 | |
| (001) | 88.85±1.04 | 89.39±1.67 | 89.34±1.86 | 90.85±1.61 |
| Sample | Theoretical density/(g·cm-3) | Bulk density/(g·cm-3) | Relative density/% | Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBC-0 | 8.59 | 8.07 | 94.0 | 6.0 |
| HBC-1 | 8.03 | 7.66 | 95.4 | 4.6 |
| HBC-2 | 7.78 | 7.50 | 96.4 | 3.6 |
| HBC-3 | 7.54 | 7.40 | 98.1 | 1.9 |
表2 不同陶瓷样品的相对密度及孔隙率
Table 2 Relative density and porosity of different ceramic samples
| Sample | Theoretical density/(g·cm-3) | Bulk density/(g·cm-3) | Relative density/% | Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBC-0 | 8.59 | 8.07 | 94.0 | 6.0 |
| HBC-1 | 8.03 | 7.66 | 95.4 | 4.6 |
| HBC-2 | 7.78 | 7.50 | 96.4 | 3.6 |
| HBC-3 | 7.54 | 7.40 | 98.1 | 1.9 |
| Sample | Flexural strength/MPa | Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | Vickers hardness/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBC-0 | 409.0±37.4 | 3.22±0.13 | 21.5±0.5 |
| HBC-1 | 273.0±11.2 | 4.85±0.16 | 22.2±0.3 |
| HBC-2 | 570.0±27.6 | 5.58±0.36 | 24.6±1.1 |
| HBC-3 | 418.0±8.3 | 5.14±0.45 | 23.3±0.8 |
表3 不同陶瓷样品的抗弯强度、断裂韧性和硬度
Table 3 Flexural strength, fracture toughness and hardness of different ceramic samples
| Sample | Flexural strength/MPa | Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | Vickers hardness/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBC-0 | 409.0±37.4 | 3.22±0.13 | 21.5±0.5 |
| HBC-1 | 273.0±11.2 | 4.85±0.16 | 22.2±0.3 |
| HBC-2 | 570.0±27.6 | 5.58±0.36 | 24.6±1.1 |
| HBC-3 | 418.0±8.3 | 5.14±0.45 | 23.3±0.8 |
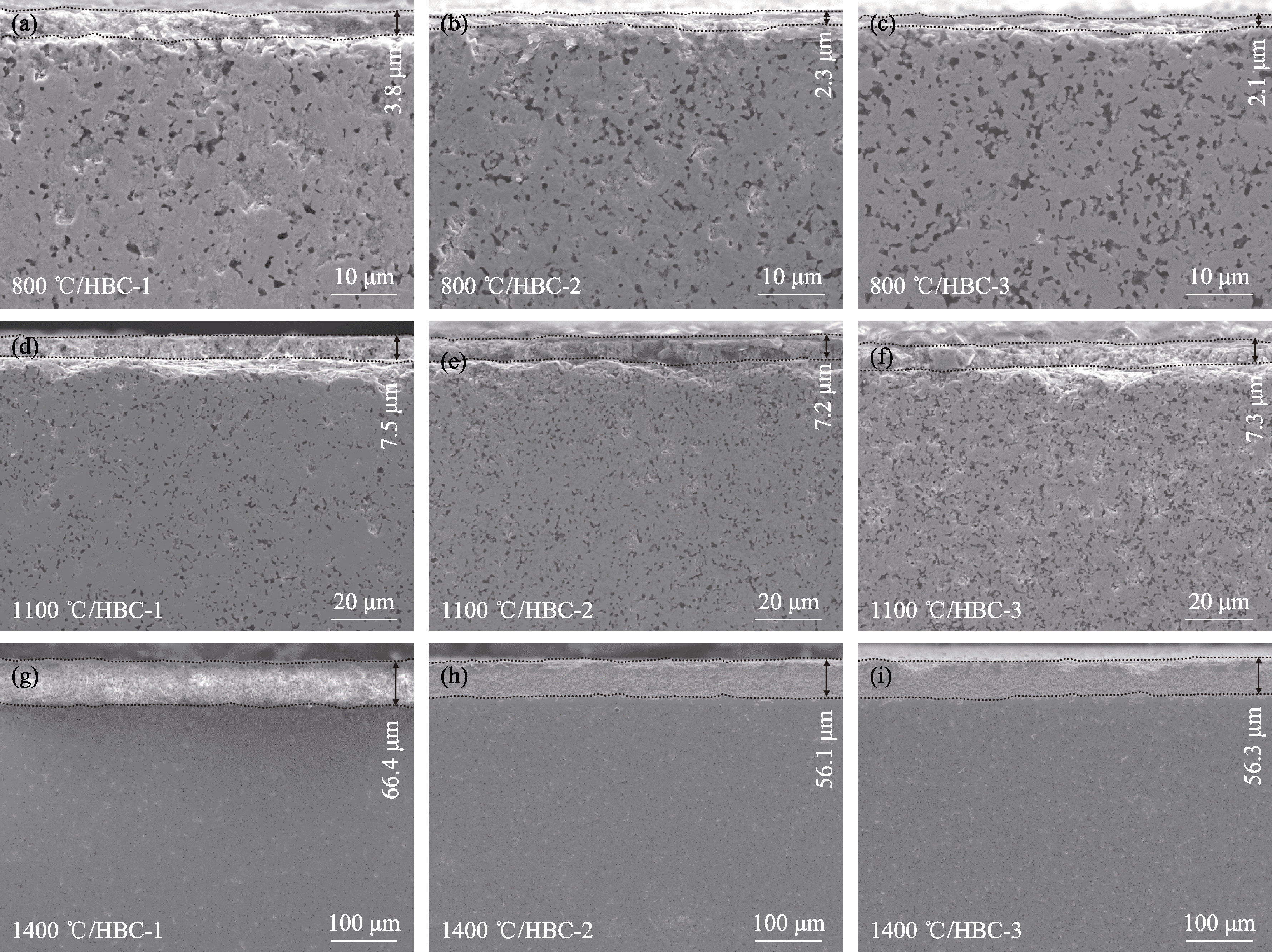
图7 不同陶瓷样品在不同温度静态氧化1 h后的截面微观形貌
Fig. 7 Cross-sectional morphologies of different ceramic samples after static oxidation at different temperatures for 1 h
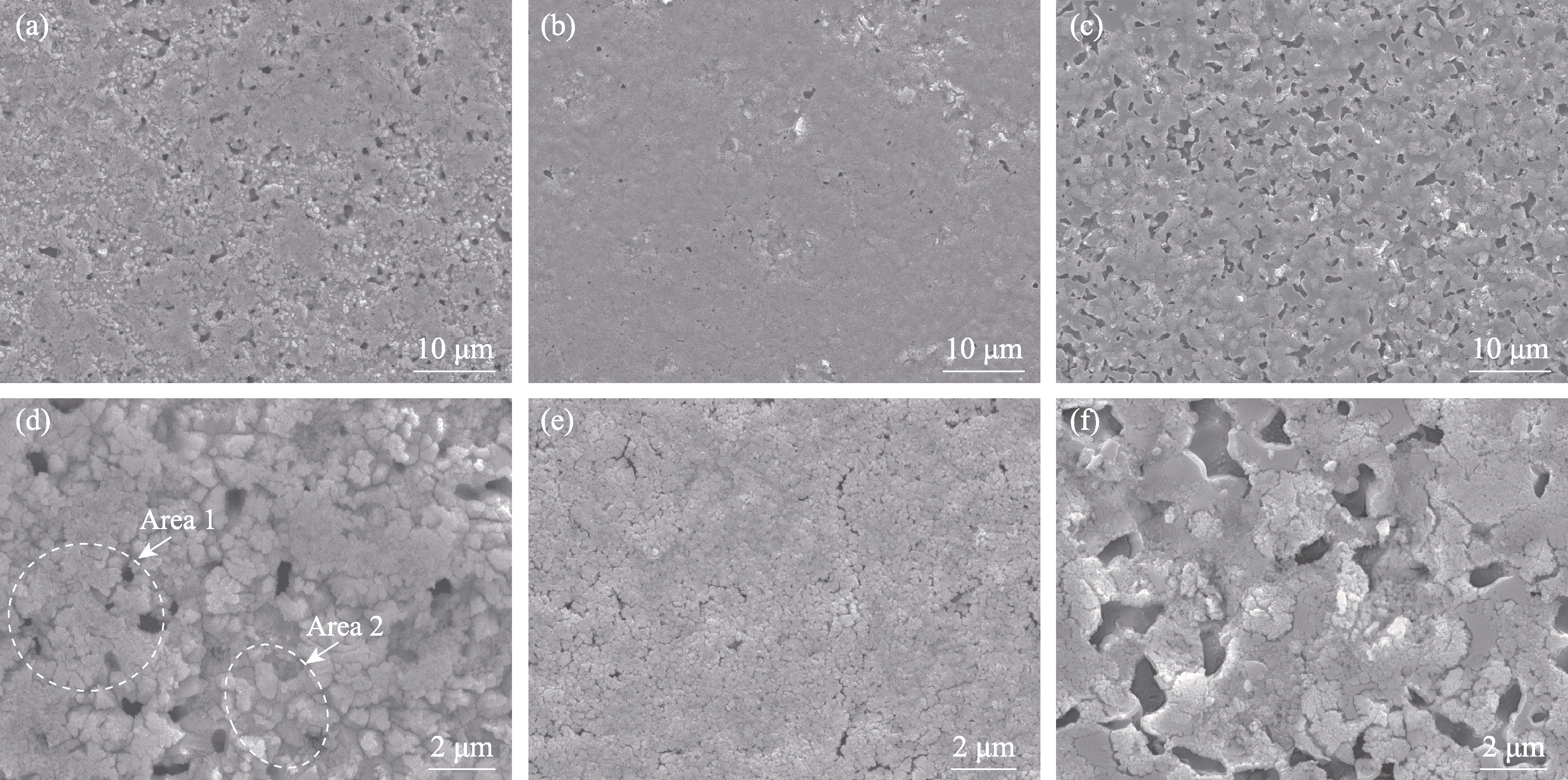
图8 不同陶瓷样品800 ℃静态氧化后的表面形貌
Fig. 8 Surface morphologies of different ceramic samples after static oxidation at 800 ℃ (a, d) HBC-1; (b, e) HBC-2; (c, f) HBC-3
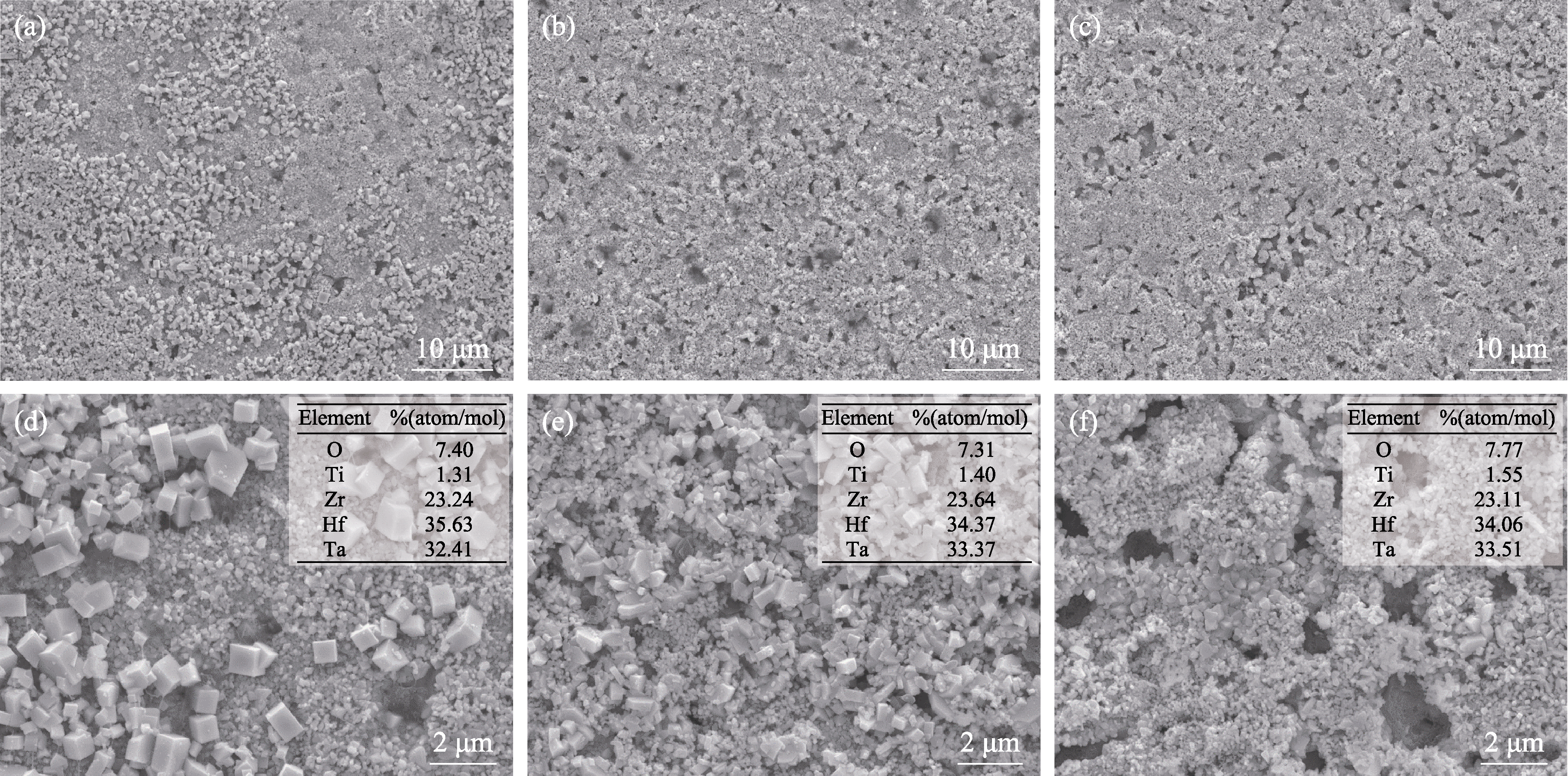
图10 不同陶瓷样品1100 ℃静态氧化后的表面形貌
Fig. 10 Surface morphologies of different ceramic samples after static oxidation at 1100 ℃ (a, d) HBC-1; (b, e) HBC-2; (c, f) HBC-3
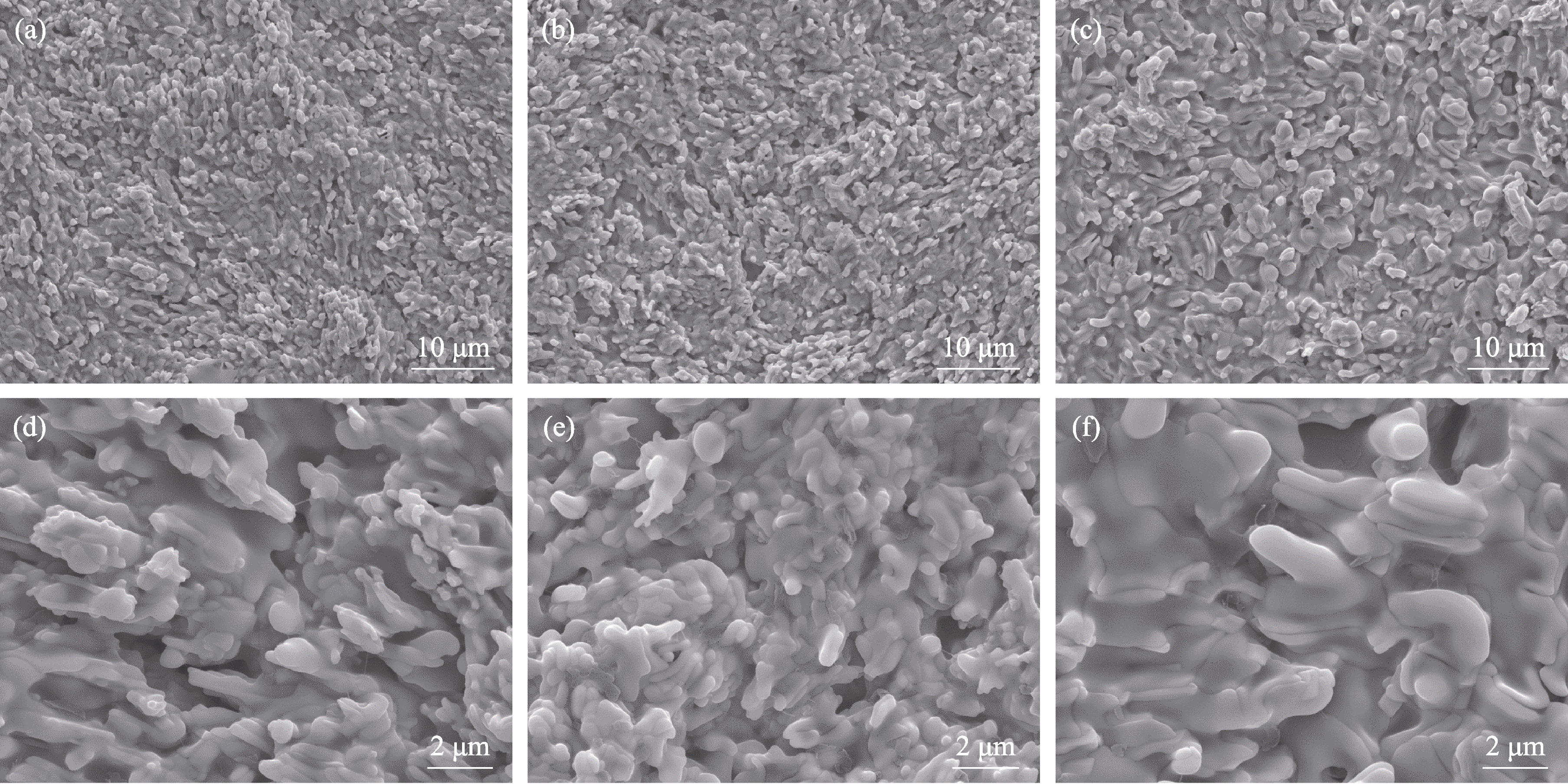
图11 不同陶瓷样品1400 ℃静态氧化后的表面形貌
Fig. 11 Surface morphologies of different ceramic samples after static oxidation at 1400 ℃ (a, d) HBC-1; (b, e) HBC-2; (c, f) HBC-3
| [1] | FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, et al. Processing of dense high-entropy boride ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(12):3815. |
| [2] | MAYRHOFER P H, KIRNBAUER K, ERTELTHALER P, et al. High-entropy ceramic thin films; A case study on transition metal diborides. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 149: 93. |
| [3] | XIANG H M, XING Y, DAI F Z, et al. High-entropy ceramics: present status, challenges, and a look forward. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(3):385. |
| [4] | ZHAO P B, ZHU J B, LI M L, et al. Theoretical and experimental investigations on the phase stability and fabrication of high-entropy monoborides. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(6):2320. |
| [5] | ZHANG W M, DAI F Z, XIANG H M, et al. Enabling highly efficient and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption by tuning impedance match in high-entropy transition metal diborides (HE TMB2). Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(6):1299. |
| [6] | BACKMAN L, GILD J, LUO J, et al. Part I: theoretical predictions of preferential oxidation in refractory high entropy materials. Acta Materialia, 2020, 197: 20. |
| [7] | FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, BRENNER D W, et al. High- entropy ultra-high-temperature borides and carbides: a new class of materials for extreme environments. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2021, 51(1):165. |
| [8] | STORR B, MOORE L, CHAKRABARTY K, et al. Properties of high entropy borides synthesized via microwave-induced plasma. APL Materials, 2022, 10(6):061109. |
| [9] | ZHAO P B, ZHU J B, YANG K J, et al. Outstanding wear resistance of plasma sprayed high-entropy monoboride composite coating by inducing phase structural cooperative mechanism. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 616: 156516. |
| [10] | GILD J, ZHANG Y, HARRINGTON T, et al. High-entropy metal diborides: a new class of high-entropy materials and a new type of ultrahigh temperature ceramics. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 37946. |
| [11] | QIAO L J, LIU Y, GAO Y, et al. First-principles prediction, fabrication and characterization of (Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Zr0.2)B2 high- entropy borides. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(12):17234. |
| [12] | TALLARITA G, LICHERI R, GARRONI S, et al. High-entropy transition metal diborides by reactive and non-reactive spark plasma sintering: a comparative investigation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 40(4):842. |
| [13] | WUCHINA E, OPILA E, OPEKA M, et al. UHTCs: ultra-high temperature ceramic materials for extreme environment applications. The Electrochemical Society Interface, 2007, 16(4):30. |
| [14] | FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, TALMY I, et al. Refractory diborides of zirconium and hafnium. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(5):1347. |
| [15] |
FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, et al. Two-step synthesis process for high-entropy diboride powders. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(2):724.
DOI |
| [16] | ZHANG Y, GUO W M, JIANG Z B, et al. Dense high-entropy boride ceramics with ultra-high hardness. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 164: 135. |
| [17] | ZHANG Y, JIANG Z B, SUN S K, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high-entropy borides derived from boro/ carbothermal reduction. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2021, 39(13):3920. |
| [18] | MA H B, LIU H L, ZHAO J, et al. Pressureless sintering, mechanical properties and oxidation behavior of ZrB2 ceramics doped with B4C. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(10):2699. |
| [19] | MEUMAN E W, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G. Processing, microstructure, and mechanical properties of zirconium diboride- boron carbide ceramics. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(9):6942. |
| [20] | ZHAO J, LI Q G, CAO W X, et al. Influences of B4C content and particle size on the mechanical properties of hot pressed TiB2-B4C composites. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 2021, 9(3):1239. |
| [21] | HAO J J, LI J Y, ZOU B L, et al. Effect of phase composition on the oxidation resistance of ZrB2-SiC coatings. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(5): 2097. |
| [22] | MA M D, YE B L, HAN Y J, et al. High-pressure sintering of ultrafine-grained high-entropy diboride ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(12):6655. |
| [23] | MONTEVERDE F, SARAGA F, GABOARDI M. Compositional disorder and sintering of entropy stabilized (Hf, Nb, Ta, Ti, Zr)B2 solid solution powders. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(12):3807. |
| [24] | MOSHTAGHIOUN B M, GOMEA-ARCIA D, DOMING- RODRIGUEZ A, et al. Grain size dependence of hardness and fracture toughness in pure near fully-dense boron carbide ceramics. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(7): 1829. |
| [25] | ZHANG Y, SUN S K, GUO W M, et al. Optimal preparation of high-entropy boride-silicon carbide ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(1):173. |
| [26] | LIU J X, SHEN X Q, WU Y, et al. Mechanical properties of hot-pressed high-entropy diboride-based ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(4):503. |
| [27] | SONG Q, ZHANG Z H, HU Z Y, et al. Influences of the pre-oxidation time on the microstructure and flexural strength of monolithic B4C ceramic and TiB2-SiC/B4C composite ceramic. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 831: 154852. |
| [28] | FAHRENHOLTZ W G. Thermodynamic analysis of ZrB2-SiC oxidation: formation of a SiC-depleted region. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(1):143. |
| [29] | YE B L, WEN T Q, CHU Y H. High-emperature oxidation behavior of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics in air. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(1):500. |
| [30] | ZENG L Y, LIU Q Y, SUN S K. Microstructure evolution of MeB2 (Me=Zr, Ti) powders prepared by borothermal reduction during heat treatment at 1000 ℃-1800 ℃. Ceramics International, 2020, 45(17):23794. |
| [1] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [2] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [3] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [4] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [5] | 郑斌, 康凯, 张青, 叶昉, 解静, 贾研, 孙国栋, 成来飞. 前驱体转化陶瓷法制备Ti3SiC2陶瓷及其热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 733-740. |
| [6] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| [7] | 刘艳艳, 谢曦, 刘增乾, 张哲峰. MAX相陶瓷增强金属基复合材料: 制备、性能与仿生设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 145-152. |
| [8] | 倪晓诗, 林子扬, 秦沐严, 叶松, 王德平. 硅烷化介孔硼硅酸盐生物玻璃微球对PMMA骨水泥生物活性和力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 971-977. |
| [9] | 付师, 杨增朝, 李江涛. 功率模块封装用高强度高热导率Si3N4陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1117-1132. |
| [10] | 吴东江, 赵紫渊, 于学鑫, 马广义, 由竹琳, 任冠辉, 牛方勇. Al2O3-TiCp复相陶瓷激光定向能量沉积直接增材制造[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192. |
| [11] | 安文然, 黄晶琪, 卢祥荣, 蒋佳宁, 邓龙辉, 曹学强. 热处理温度对LaMgAl11O19涂层热/力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 925-932. |
| [12] | 张叶, 曾宇平. 自蔓延高温合成氮化硅多孔陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [13] | 夏乾, 孙是昊, 赵义亮, 张翠萍, 茹红强, 王伟, 岳新艳. 碳化硼颗粒级配对硅反应结合碳化硼复合材料结构与性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 636-642. |
| [14] | 洪督, 牛亚然, 李红, 钟鑫, 郑学斌. 等离子喷涂TiC-Graphite复合涂层摩擦磨损性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [15] | 徐谱昊, 张相召, 刘桂武, 张明芬, 桂新易, 乔冠军. Al-Ti合金钎焊SiC陶瓷接头界面微观结构与力学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 683-690. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||