无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 634-646.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230530
王伟明1( ), 王为得1,2(
), 王为得1,2( ), 粟毅1, 马青松1, 姚冬旭3, 曾宇平3(
), 粟毅1, 马青松1, 姚冬旭3, 曾宇平3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-14
修回日期:2024-01-15
出版日期:2024-06-20
网络出版日期:2024-01-22
通讯作者:
王为得, 助理研究员. E-mail: nudtwwd@163.com;作者简介:王伟明(1995-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: wangweiming1207@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Weiming1( ), WANG Weide1,2(
), WANG Weide1,2( ), SU Yi1, MA Qingsong1, YAO Dongxu3, ZENG Yuping3(
), SU Yi1, MA Qingsong1, YAO Dongxu3, ZENG Yuping3( )
)
Received:2023-11-14
Revised:2024-01-15
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-01-22
Contact:
WANG Weide, associate professor. E-mail: nudtwwd@163.com;About author:WANG Weiming (1995-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: wangweiming1207@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
功率半导体器件高电压、大电流、高功率密度的发展趋势, 对器件中陶瓷基板的散热能力和可靠性提出了更高的要求, 兼具高热导率和优异力学性能的氮化硅陶瓷作为功率半导体器件的首选散热基板材料受到了广泛关注。目前氮化硅陶瓷热导率的实验值与理论值存在较大差距, 高温、长时间保温的制备条件不仅会使晶粒过分长大,削弱其力学性能, 而且会造成成本高企, 限制了其规模化应用。晶格氧缺陷是影响氮化硅陶瓷热导率的主要因素, 通过筛选非氧化物烧结助剂降低体系中的氧含量, 调节液相的组成和性质并构建“富氮-缺氧”的液相, 调控液相中的溶解析出过程, 促进氮化硅陶瓷晶格氧的移除及双峰形貌的充分发育, 从而实现氮化硅陶瓷热导率-力学性能的协同优化是目前研究的热点。本文基于元素分类综述了当前国内外开发的非氧化物烧结助剂体系, 着重从液相调节和微观形貌调控的角度介绍了非氧化物烧结助剂改善氮化硅陶瓷热导率的作用机理, 分析了晶粒发育、形貌演变规律和晶格氧移除机制, 并展望了高导热氮化硅陶瓷的未来发展前景。
中图分类号:
王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646.
WANG Weiming, WANG Weide, SU Yi, MA Qingsong, YAO Dongxu, ZENG Yuping. Research Progress of High Thermal Conductivity Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared by Non-oxide Sintering Additives[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 634-646.
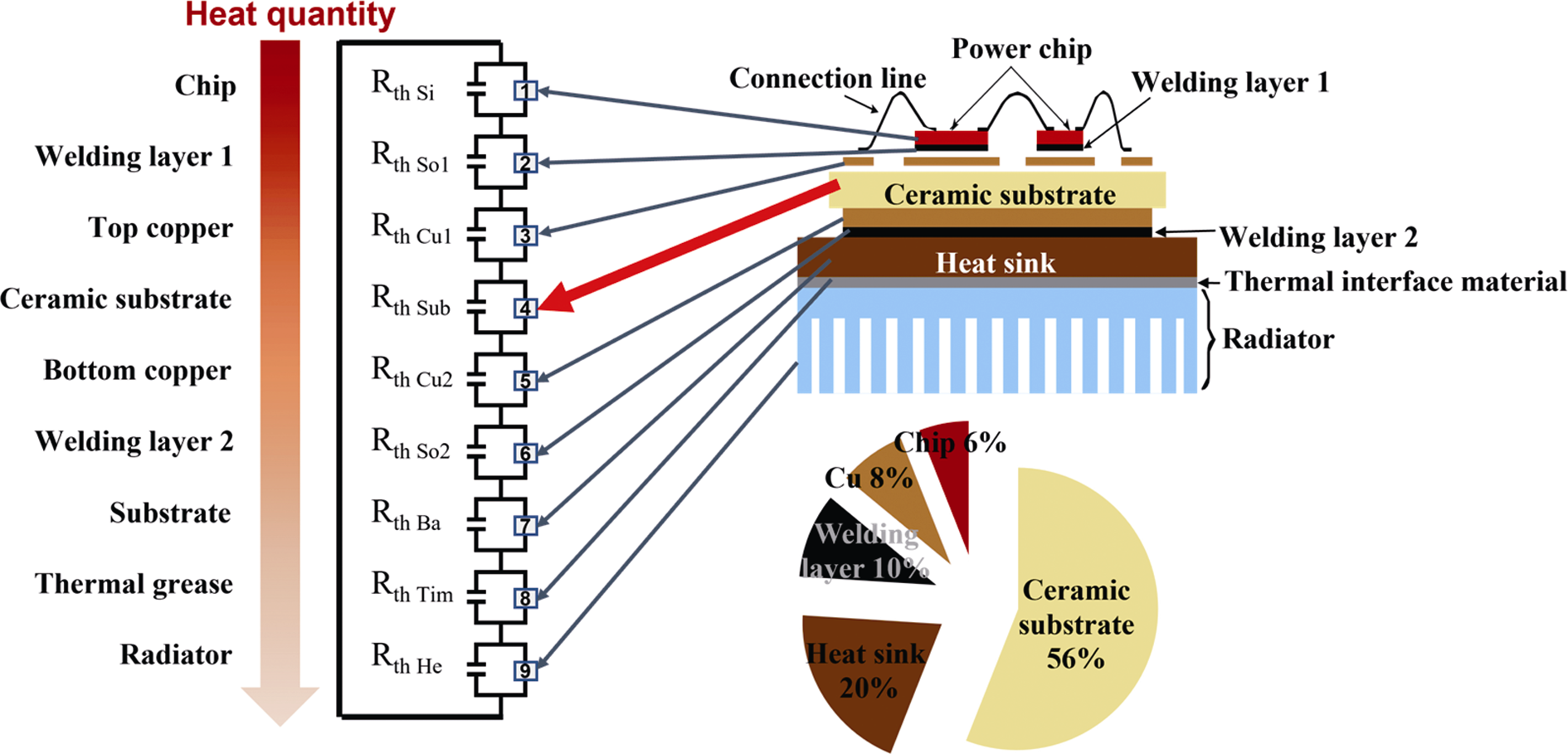
图1 功率半导体器件封装示意图[1]
Fig. 1 Schematic of typical packaging of power semiconductor device[1] (1200 V, chip area 9 mm×9 mm, encapsulated with Al2O3 DCB substrate)
| Material | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Fracture toughness/ (MPa·m1/2) | Bending strength/ MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 18-24 | 3.5-4.0 | 300-400 |
| AlN | 150-270 | 3.0-3.5 | 220-310 |
| ZTA | 28 | 4.5 | 650 |
| Si3N4 | 80-177 | 6.5-7.5 | 600-800 |
表1 常用陶瓷基板材料特性[2]
Table 1 Properties of ceramic substrate materials[2]
| Material | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Fracture toughness/ (MPa·m1/2) | Bending strength/ MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 18-24 | 3.5-4.0 | 300-400 |
| AlN | 150-270 | 3.0-3.5 | 220-310 |
| ZTA | 28 | 4.5 | 650 |
| Si3N4 | 80-177 | 6.5-7.5 | 600-800 |
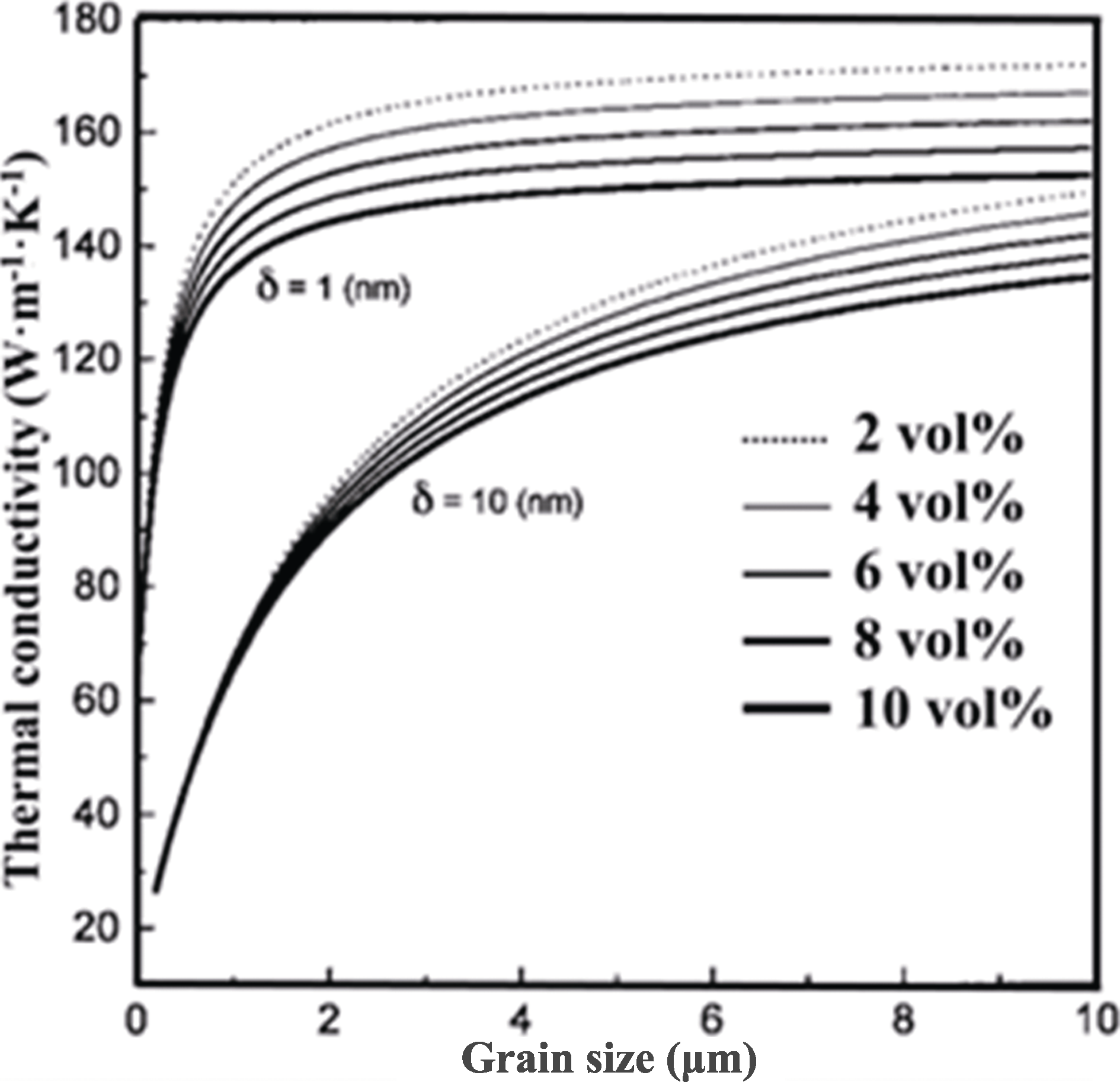
图3 玻璃相体积分数、晶界膜厚度(δ)、晶粒尺寸对β-Si3N4热导率的影响[13]
Fig. 3 Effects of volume fraction of glassy phase, grain- boundary film thickness(δ), and grain size on the thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4[13]
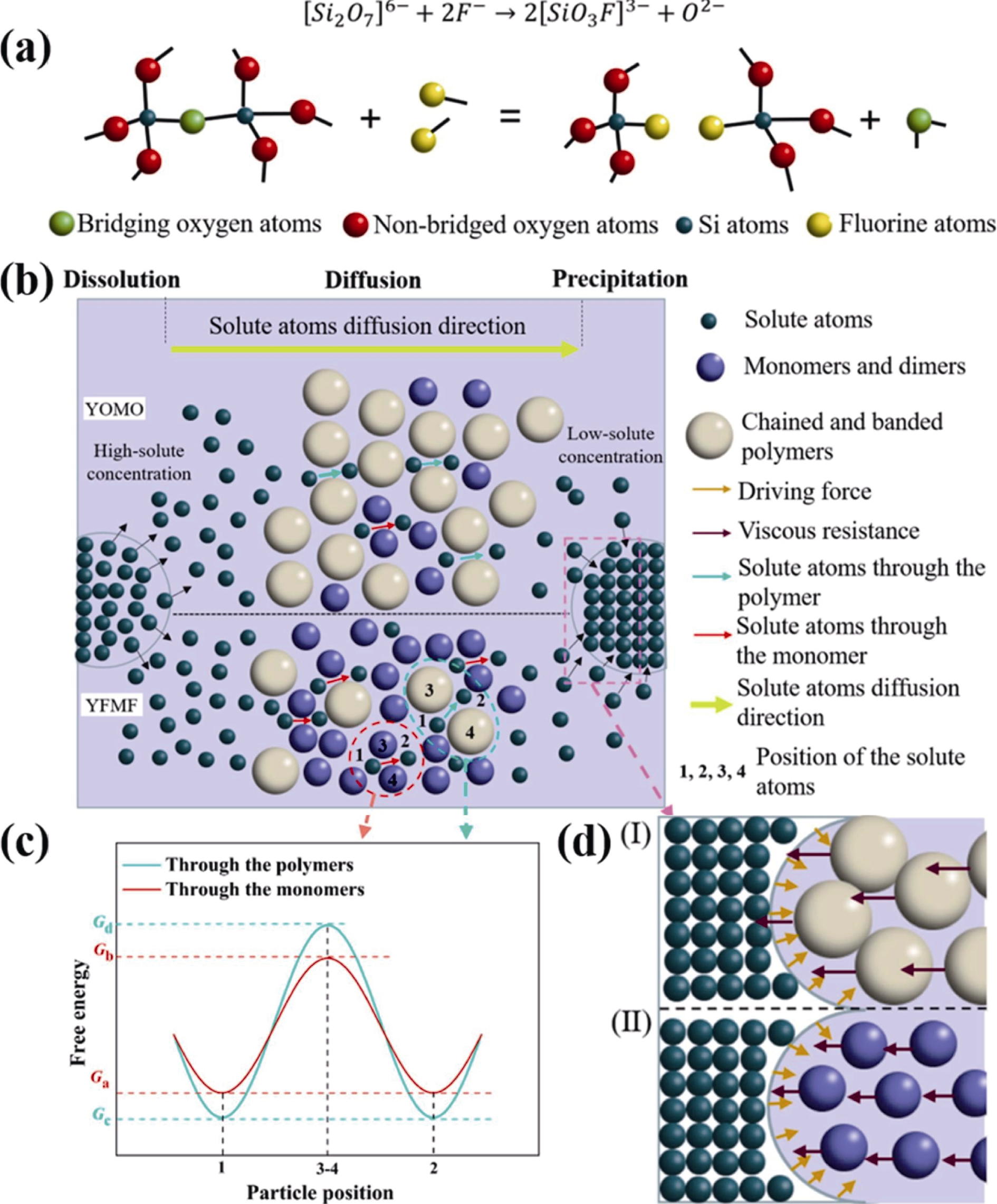
图7 硅酸盐液相中氟原子的解聚机理[22]
Fig. 7 Depolymerization mechanism of F atom in silicate melts[22] (a) F atom breaks the network structure by replacing the bridging oxygen atoms; (b) Solute atom solution-diffusion-precipitation mechanism during liquid-phase sintering in samples YOMO and YFMF; (c) Free energy barriers overcome by solute atoms in melts Y-Si-O-N and Y-Si-O-N-F; (d) Mechanism of solute drag effect on grain boundary migration
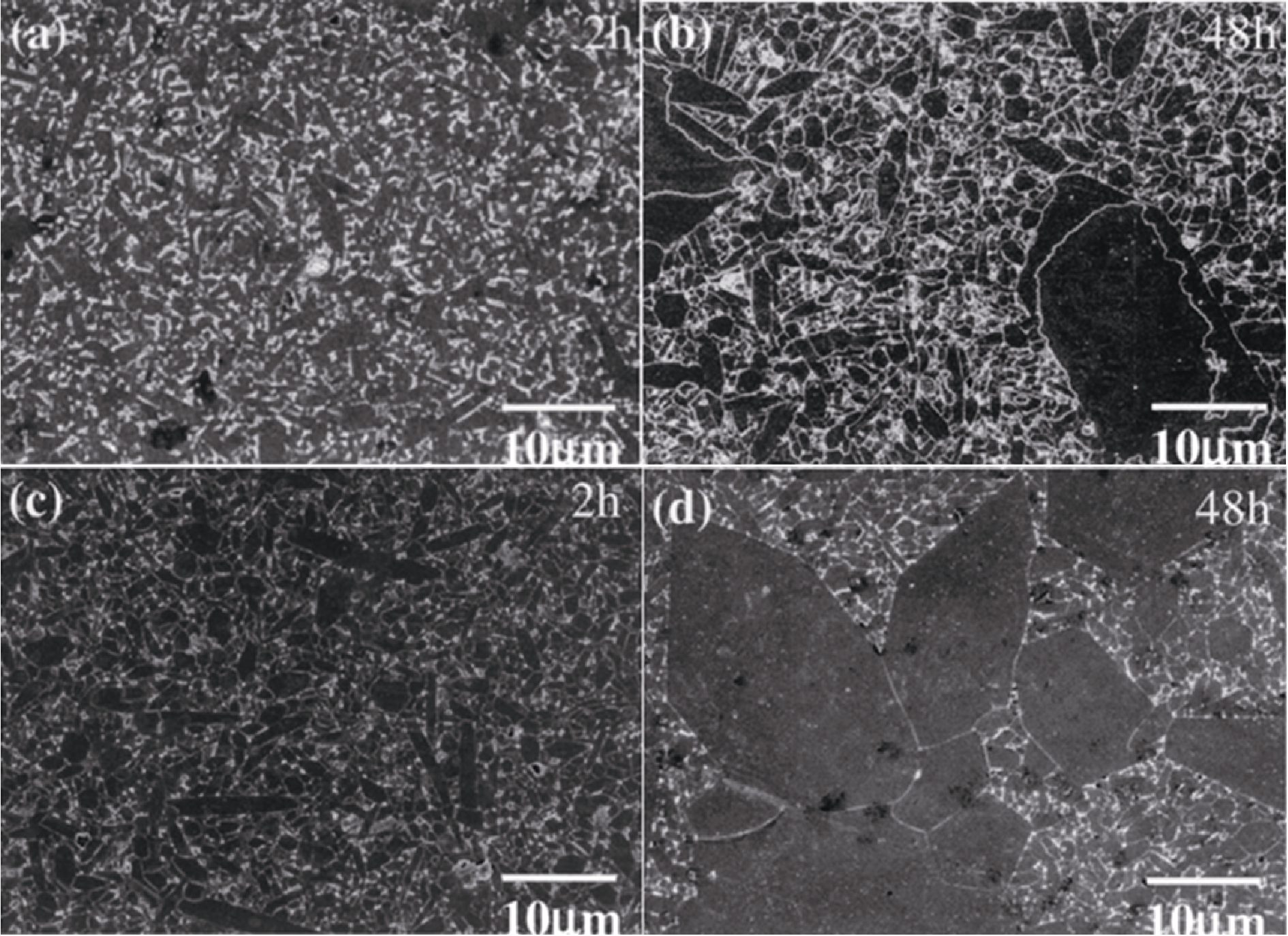
图8 添加不同助剂的氮化硅陶瓷气压烧结(GPS)后的SEM形貌[24]
Fig. 8 SEM morphologies of the polished surfaces of Si3N4 ceramics after gas pressure sintering (GPS) with different additives added[24] (a) MgO-doped for 2 h; (b) MgO-doped for 48 h; (c) MgSiN2-doped for 2 h; (d) MgSiN2-doped for 48 h
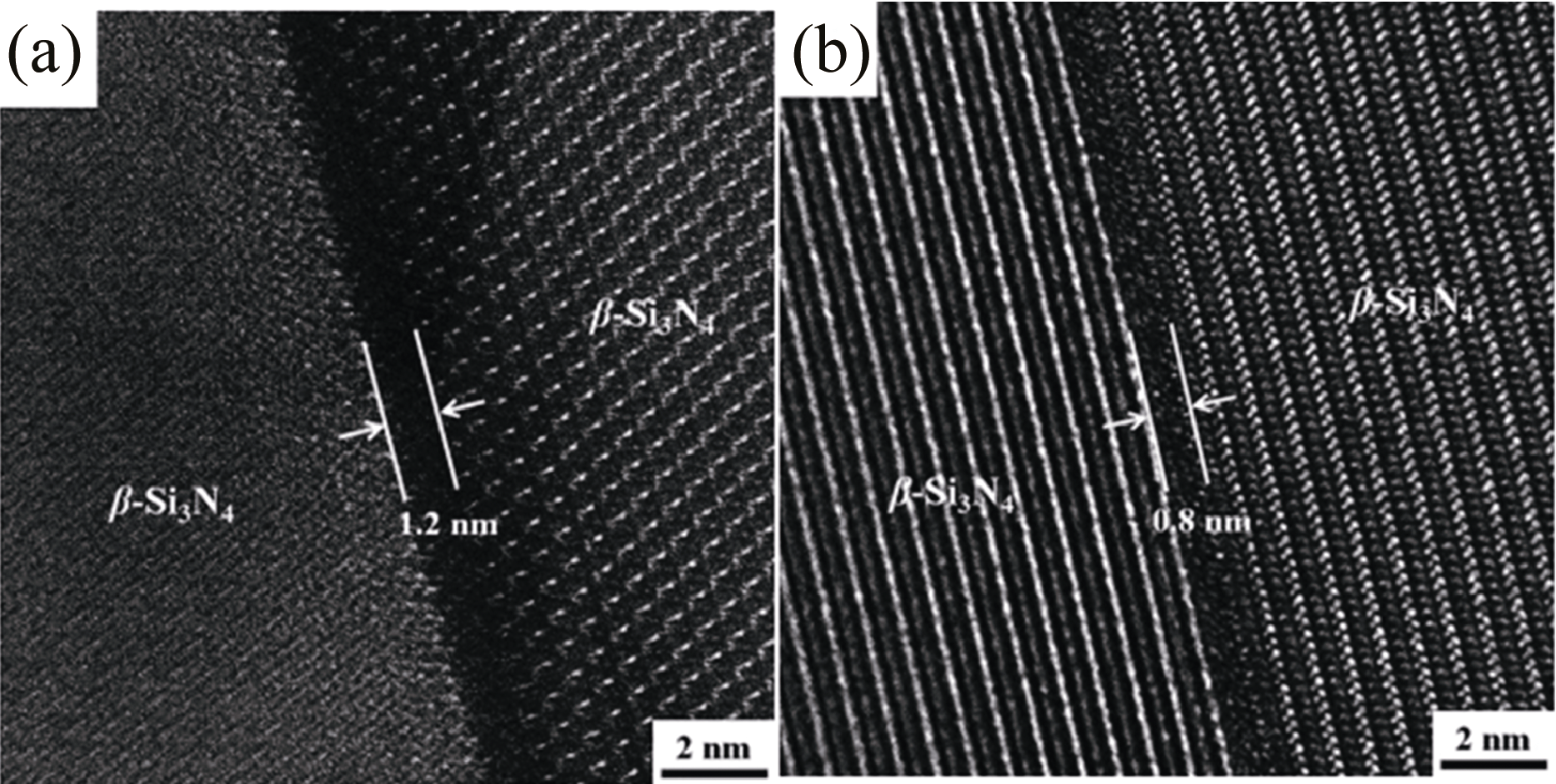
图9 添加Y2O3 (a)和Y2Si4N6C (b)烧结助剂的氮化硅陶瓷样品的HRTEM照片[31]
Fig. 9 Typical HRTEM images of Si3N4 ceramics added with Y2O3 (a) and Y2Si4N6C (b) as additives[31]
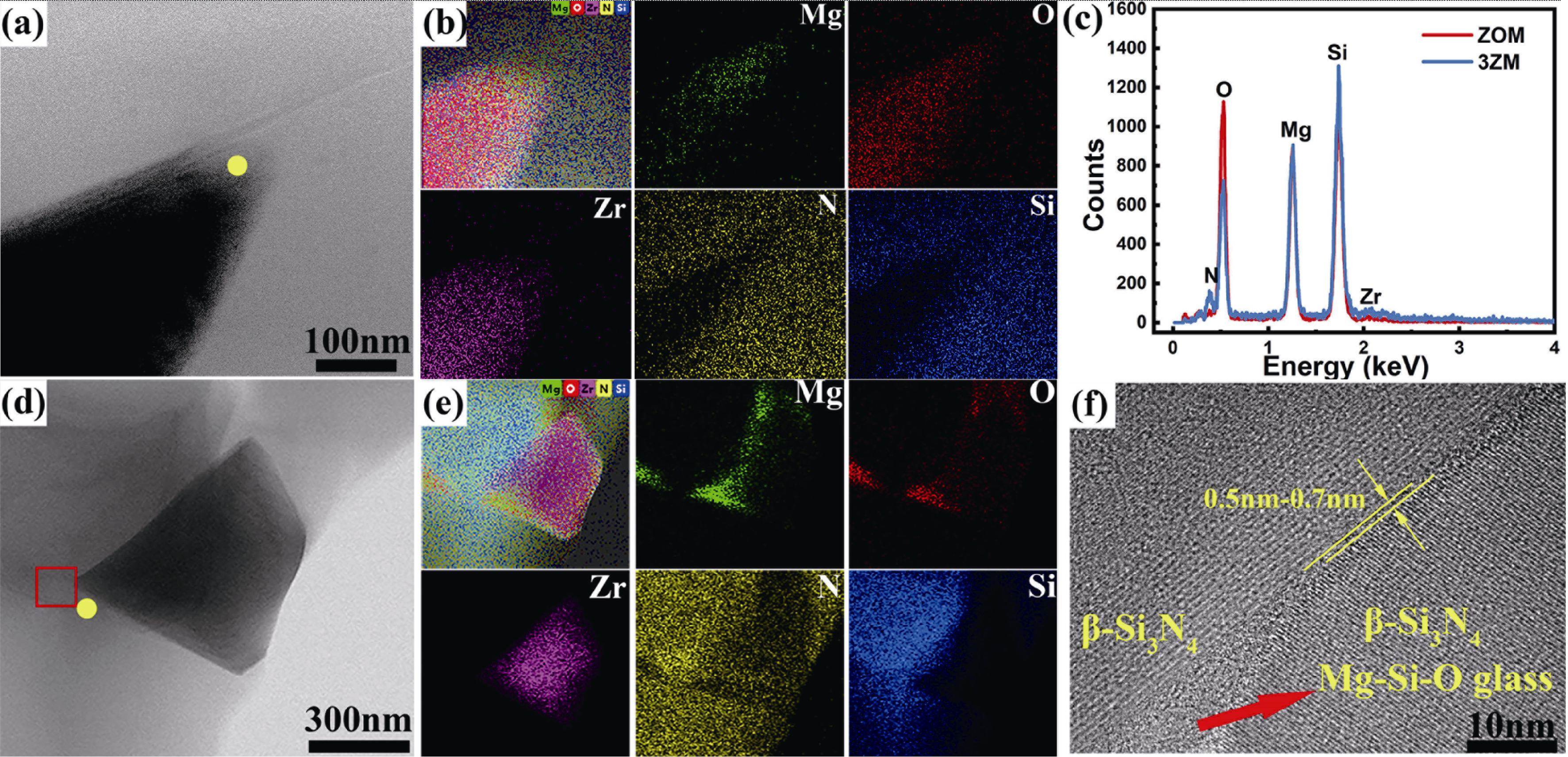
图14 添加ZrO2、ZrH2的氮化硅陶瓷STEM-EDS表征[47]
Fig. 14 STEM-EDS characterizations of Si3N4 ceramics with the addition of ZrO2 and ZrH2[47] (a, d) Bright-field TEM images for Si3N4 ceramics with the addition of (a) ZrO2 and (d) ZrH2; (b, e) Elements distribution for Si3N4 ceramics with the addition of (b) ZrO2 and (e) ZrH2; (c) EDS analysis of the marked points in (a, d) images; (f) HRTEM image presenting the grain boundary film marked by the red rectangle in (d) image
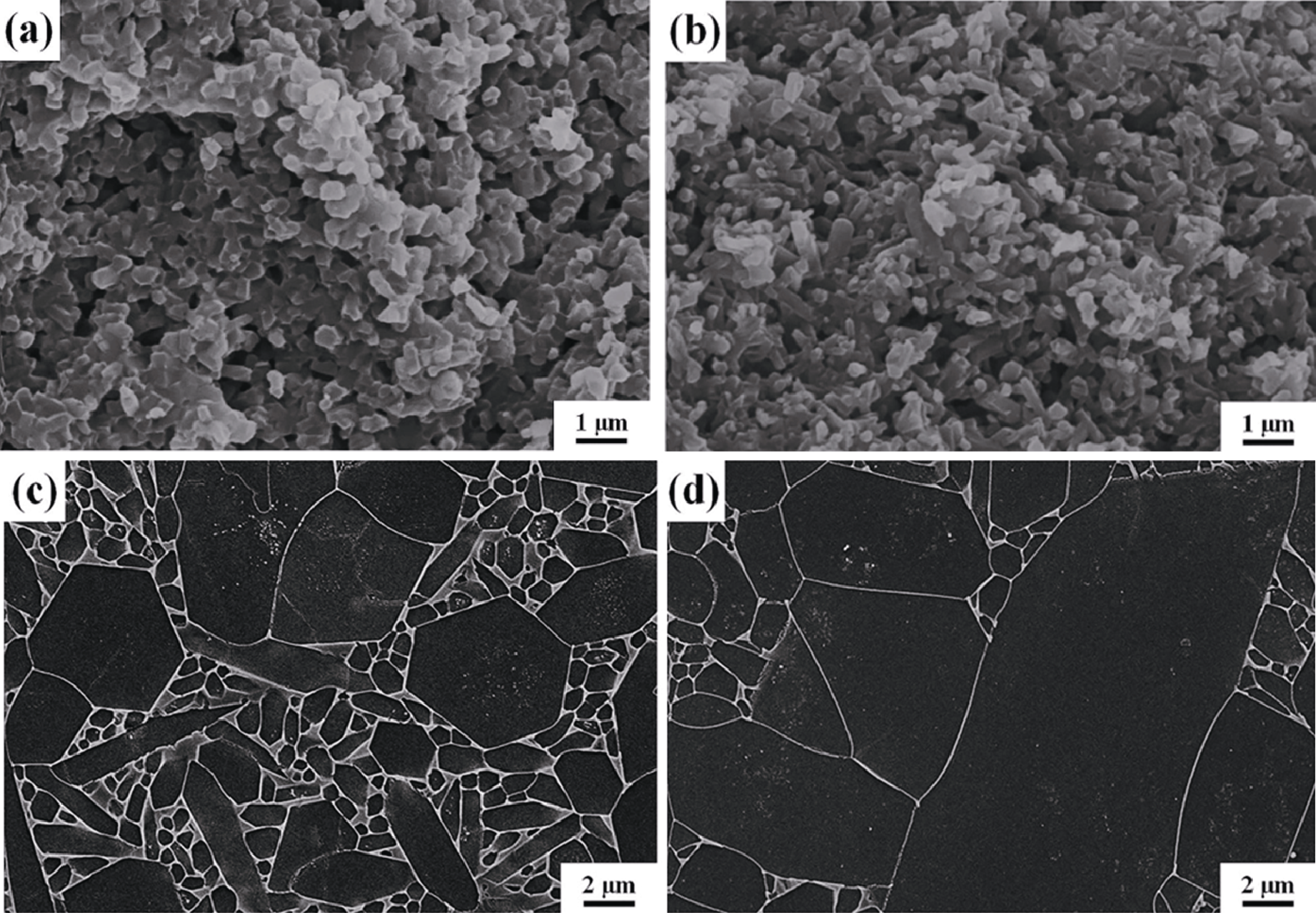
图15 未添加(a, c)和添加(b, d)含C埋粉的氮化后样品微观形貌(a, b)和气压烧结后氮化硅微观形貌(c, d)[57]
Fig. 15 SEM images on the fracture surfaces of nitrided samples (a, b) and post-sintered samples (c, d) without (a, c) and with (b, d) graphite powder bed addition[57]
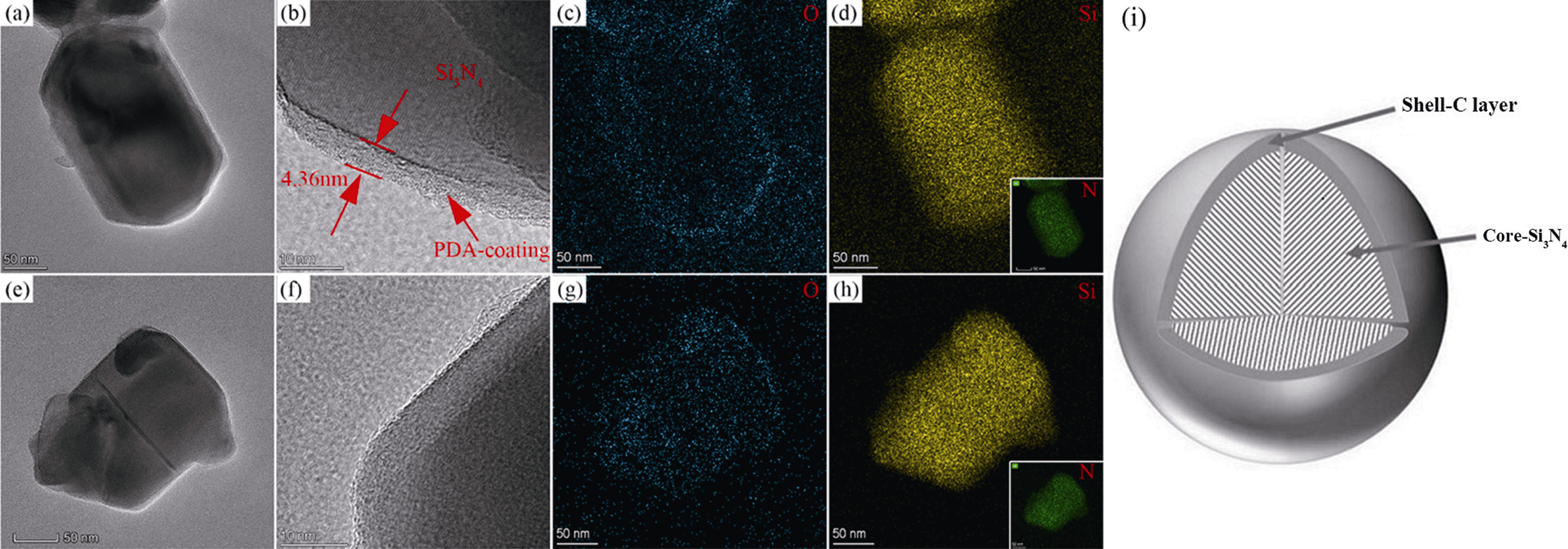
图16 PDA涂层的TEM照片及碳-氮化硅核壳结构示意图[59-60]
Fig. 16 TEM images of PDA-coated powder and schematic of Si3N4-C core-shell structure[59-60] (a, e) Overall morphologies of PDA-coated (a) and PDA-free (e) powder; (b, f) Partial magnified images of (a, e), respectively; (c, g) O distributions of PDA-coated (c) and PDA-free (g) powder; (d, h) Si and N distributions of PDA-coated (d) and PDA-free (h) powder; (i) Schematic of Si3N4-C core-shell structure
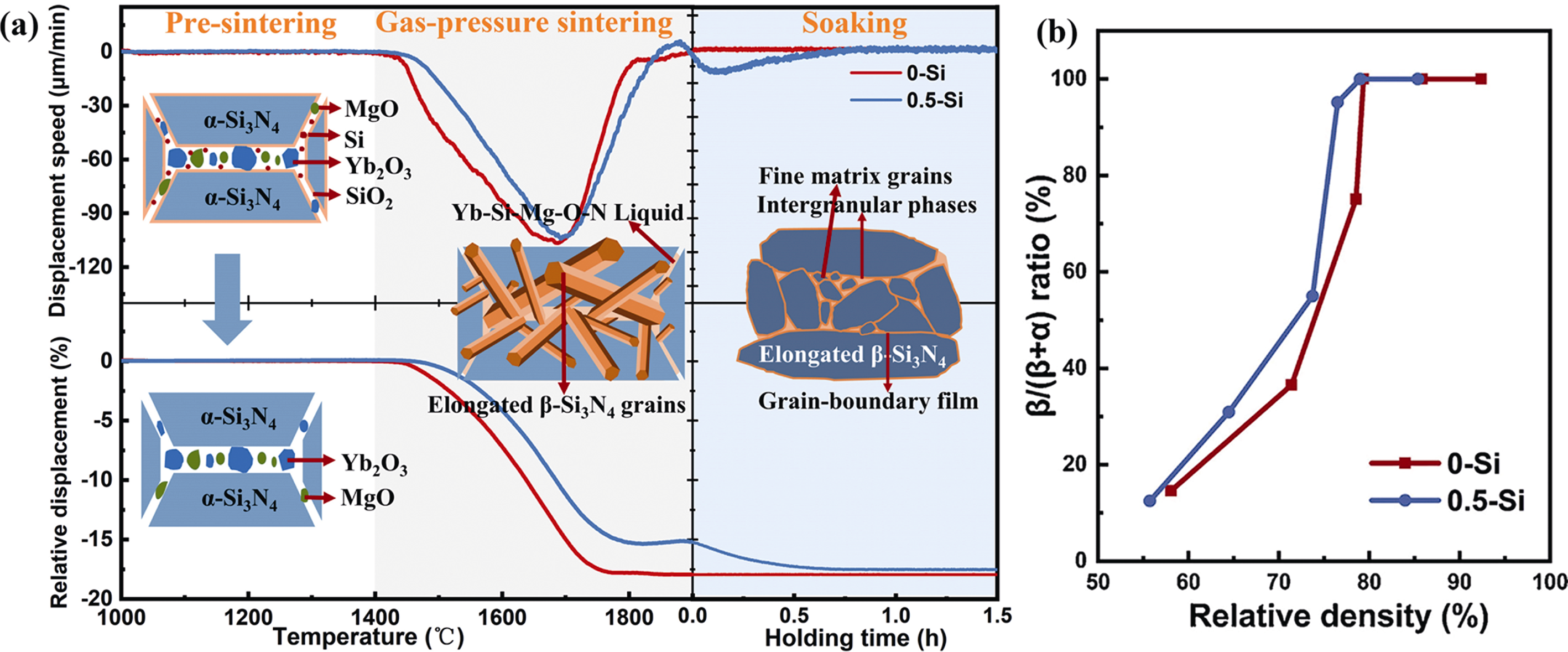
图17 氮化硅陶瓷烧结过程的(a)收缩行为和致密化机理, 以及(b)β相比例与相对密度的关系[62]
Fig. 17 (a) Shrinkage behaviors and densification mechanism of Si3N4 ceramics during sintering, and (b) relationship between β phase ratio and relative density[62]
| [1] | Tobiasreimann U N, 李毅, 魏宇浩. 现代功率模块及器件应用技术(3). 电源技术应用, 2005, 8(3):59. |
| [2] | UTSCHIG T, DESCHER P, RAUER M, et al. Metal ceramic substrates for highly reliable power modules-not only in electric vehicles. Interceram-International Ceramic Review, 2020, 69(2):20. |
| [3] | 张兆生, 卢振亚, 陈志武. 电子封装用陶瓷基片材料的研究进展. 材料导报, 2008, 22(11):16. |
| [4] | YAMAGIWA M. Packaging technologies of power modules for hybrid electric vehicles and electric vehicles. Bulletin of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2010, 45(6):432. |
| [5] | HAGGERTY J S, LIGHTFOOT A. Opportunities for enhancing the thermal conductivities of SiC and Si3N4 ceramics through improved processing. Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, 1995, 16: 475. |
| [6] | HIROSAKI N, OGATA S, KOCER C, et al. Molecular dynamics calculation of the ideal thermal conductivity of single-crystal α- and β-Si3N4. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(13):134110. |
| [7] | ZHOU H, FENG T. Theoretical upper limits of the thermal conductivity of Si3N4. Applied Physics Letters, 2023, 122(18):182203. |
| [8] | WATARI K, HIRAO K, BRITO M E, et al. Hot isostatic pressing to increase thermal conductivity of Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of Materials Research, 1999, 14(4):1538. |
| [9] |
ZHOU Y, HYUGA H, KUSANO D, et al. A tough silicon nitride ceramic with high thermal conductivity. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(39):4563.
DOI |
| [10] | 王为得. 基于液相组成和显微结构调控的高热导率氮化硅陶瓷的研究. 上海: 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所博士论文, 2021. |
| [11] | ZHU X, ZHOU Y, HIRAO K, et al. Potential use of only Yb2O3 in producing dense Si3N4 ceramics with high thermal conductivity by gas pressure sintering. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials. 2010, 11(6):065001. |
| [12] | KITAYAMA M, HIRAO K, WATARI K, et al. Thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4: III, effect of rare earth (RE = La, Nd, Cd, Y, Yb, and Sc) oxide additives. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(2):353. |
| [13] | KITAYAMA M, HIRAO K, TORIYAMA M, et al. Thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4: I, effects of various microstructural factors. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1999, 82(11):3105. |
| [14] | KITAYAMA M, HIRAO K, TSUGE A, et al. Thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4: II, effect of lattice oxygen. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 2000, 83(8): 1985. |
| [15] | KITAYAMA M, HIRAO K, TSUGE A, et al. Oxygen content in β-Si3N4 crystal lattice. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 1999, 82(11):3263. |
| [16] | FU S, YANG Z C, LI J T. Progress of high strength and high thermal conductivity Si3N4 ceramics for power module packaging. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10):1117. |
| [17] | ZHOU Y, HYUGA H, KUSANO D, et al. Development of high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramics. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 2015, 3(3):221. |
| [18] | ÇALIŞKAN F, TATLI Z, GENSON A, et al. Pressureless sintering of β-SiAlON ceramic compositions using fluorine and oxide additive system. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(7):1337. |
| [19] | HU F, ZHAO L, XIE Z. Silicon nitride ceramics with high thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical properties fabricated with MgF2 sintering aid and post-sintering heat treatment. Journal of Ceramic Science and Technology, 2016, 7(4):423. |
| [20] | LUO C, ZHANG Y, DENG T. Pressureless sintering of high performance silicon nitride ceramics at 1620 ℃. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(20):29371. |
| [21] | BAI B, FU T, NING X. Thermal conductivity and mechanical property of Si3N4 ceramics sintered with CeF3/LaF3 additives. Advanced Materials Research, 2010, 105-106: 171. |
| [22] | LIAO S J, ZHOU L, JIANG C, et al. Thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of Si3N4 ceramics with binary fluoride sintering additives. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(14):6971. |
| [23] | HILLINGER G, HLAVACEK V. Direct synthesis and sintering of silicon nitridenitanium nitride composite. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1995, 78(2):495. |
| [24] | HAYASHI H, HIRAO K, TORIYAMA M, et al. MgSiN2 addition as a means of increasing the thermal conductivity of β-silicon nitride. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(12):3060. |
| [25] | PENG G, LIANG M, LIANG Z, et al. Spark plasma sintered silicon nitride ceramics with high thermal conductivity using MgSiN2 as additives. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2009, 92(9): 2122. |
| [26] | FU S, YANG Z C, LI H H, et al. Mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of Si3N4 ceramics with composite sintering additives. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9):947. |
| [27] | HU F, ZHU T, XIE Z, et al. Effect of composite sintering additives containing non-oxide on mechanical, thermal and dielectric properties of silicon nitride ceramics substrate. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(10):13635. |
| [28] | ZHANG J, CUI W, LI F, et al. Effects of MgSiN2 addition and post-annealing on mechanical and thermal properties of Si3N4 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10):15719. |
| [29] | 李聪, 张博, 胡加斌, 等. MgSiN2-Y2O3复合烧结助剂对Si3N4陶瓷力学及导热性能的影响. 硅酸盐学报, 2021, 49(12):2556. |
| [30] | 杨建辉, 陈义祥, 刘光华, 等. 自蔓延高温合成制备单相氮化硅镁粉体. 硅酸盐学报, 2011, 39(2):177. |
| [31] | LI Y, KIM H, WU H, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in Si3N4 ceramic with the addition of Y2Si4N6C. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(9):4128. |
| [32] | LIANG H, WANG W, ZUO K, et al. Effect of LaB6 addition on mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(11):17776. |
| [33] | BOYER S M, MOULSON A J. A mechanism for the nitridation of Fe-contaminated silicon. Journal of Materials Science, 1978, 13(8):1637. |
| [34] | MUKERJI J, BISWAS S K. Effect of iron, titanium, and hafnium on second-stage nitriding of silicon. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1981, 64(9):549. |
| [35] | WANG L, QI Q, CAI P, et al. New route to improve the fracture toughness and flexural strength of Si3N4 ceramics by adding FeSi2. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 126: 11. |
| [36] | WANG W D, YAO D, CHEN H, et al. ZrSi2-MgO as novel additives for high thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(3): 2090. |
| [37] | SAJGALIK P, DUSZA J, HOFFMANN M J. Relationship between microstructure, toughening mechanisms, and fracture-toughness of reinforced silicon-nitride ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1995, 78(10):2619. |
| [38] | PARK H, KIM H E, NIIHARA K. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Si3N4 with Yb2O3 as a sintering additive. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1997, 80(3):750. |
| [39] | WANG W D, YAO D, LIANG H Q, et al. Effect of the binary nonoxide additives on the densification behavior and thermal conductivity of Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(10):5891. |
| [40] | YAN M, LIU Y, LIU Y, et al. Simultaneous gettering of oxygen and chlorine and homogenization of the β phase by rare earth hydride additions to a powder metallurgy Ti-2.25Mo-1.5Fe alloy. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 67(5):491. |
| [41] | HAMPSHIRE S. Oxynitride glasses. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2008, 28(7):1475. |
| [42] | LEMERCIER H, ROUXEL T, FARGEOT D, et al. Yttrium SiAlON glasses: structure and mechanical properties-elasticity and viscosity. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1996, 201(1/2):128 |
| [43] | HAKEEM A S, DAUC R, LEONOVA E, et al. Silicate glasses with unprecedented high nitrogen and electropositive metal contents obtained by using metals as precursors. Advanced Materials, 2005, 17(18): 2214. |
| [44] | WANG W D, YAO D, LIANG H Q, et al. Effect of in-situ formed Y2O3 by metal hydride reduction reaction on thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15):5316. |
| [45] | WANG W D, CHEN H B, LI S H, et al. Preparation of silicon nitride with high thermal conductivity and high flexural strength using YbH2-MgO as sintering additive. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9):959. |
| [46] | WANG W D, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Improved thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics through the modification of the liquid phase by using GdH2 as a sintering additive. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(4):5631. |
| [47] | WANG W D, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in Si3N4ceramics prepared by using ZrH2 as an oxygen getter. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 855: 157451. |
| [48] | DUAN Y, ZHANG J, LI X, et al. High thermal conductivity silicon nitride ceramics prepared by pressureless sintering with ternary sintering additives. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2019, 16(4):1399. |
| [49] | 李勇霞.高热导Si3N4基复合材料的制备与性能研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士学位论文, 2018. |
| [50] | LUO H, LI C, DENG L, et al. C0.3N0.7Ti-SiC toughed silicon nitride hybrids with non-oxide additives Ti3SiC2. Materials, 2020, 13(6):1428. |
| [51] | LEE B, LEE D, LEE J H. Enhancement of toughness and wear resistance in boron nitride nanoplatelet (BNNP) reinforced Si3N4 nanocomposites. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27609. |
| [52] | LIANG H, WANG W, ZUO K, et al. YB2C2: a new additive for fabricating Si3N4 ceramics with superior mechanical properties and medium thermal conductivity. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(4):5239. |
| [53] | HUANG M, HUANG Y, OU J, et al. Effect of a new nonoxide additive, Y3Si2C2, on the thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of Si3N4 ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2022, 19(6):3403. |
| [54] | WATARI K, KAWAMOTO M, ISHIZAKI K. Carbon behavior in sintered silicon nitride grain boundaries. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1989, 109: 89. |
| [55] | HNATKO M, SAJGALIK P, LENČÉŠ Z, et al. Carbon reduction reaction in the Y2O3-SiO2 glass system at high temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001, 21(16):2797. |
| [56] | KIM H D, HAN B D, PARK D S, et al. Novel two-step sintering process to obtain a bimodal microstructure in silicon nitride. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2002, 85(1):245. |
| [57] | LI Y, KIM H, WU H, et al. Improved thermal conductivity of sintered reaction-bonded silicon nitride using a BN/graphite powder bed. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(15):4483. |
| [58] | LI Y, KIM H, WU H, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in Si3N4 ceramic by addition of a small amount of carbon. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2/3):157. |
| [59] | LU D, YANG P, HUANG Y, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in Si3N4 ceramics by carbonizing polydopamine coatings. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(13):18615. |
| [60] | 伍尚华, 杨平, 李建斌. 一种用碳包覆制备低氧含量、高热导的氮化硅陶瓷的方法及其应用: CN202010588120. 3. 2020-11-03. |
| [61] | LINDLEY M, PITMAN K, JONES B, et al. The influence of hydrogen in the nitriding gas on the strength, structure and composition of reaction-sintered silicon nitride. Journal of Materials Science, 1979, 14(1):70. |
| [62] | WANG W D, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Novel silicothermic reduction method to obtain Si3N4 ceramics with enhanced thermal conductivity and fracture toughness. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(2):1735. |
| [1] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [2] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [3] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [4] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [5] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [6] | 赵日达, 汤素芳. 多孔碳陶瓷化改进反应熔渗法制备陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 623-633. |
| [7] | 方光武, 谢浩元, 张华军, 高希光, 宋迎东. CMC-EBC损伤耦合机理及一体化设计研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 647-661. |
| [8] | 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590. |
| [9] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [10] | 吕朝阳, 徐勇, 杨久延, 涂广升, 涂兵田, 王皓. MgF2助剂对MgAl1.9Ga0.1O4透明陶瓷的制备与光学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 531-538. |
| [11] | 金敏, 马玉鹏, 魏天然, 林思琪, 白旭东, 史迅, 刘学超. 非化学计量溶液区熔法生长大尺寸InSe晶体及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 554-560. |
| [12] | 李宗晓, 胡令祥, 王敬蕊, 诸葛飞. 氧化物神经元器件及其神经网络应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 345-358. |
| [13] | 鲍可, 李西军. 化学气相沉积法制备智能窗用热致变色VO2薄膜的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 233-258. |
| [14] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| [15] | 刘艳艳, 谢曦, 刘增乾, 张哲峰. MAX相陶瓷增强金属基复合材料: 制备、性能与仿生设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 145-152. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||