无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 681-690.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230546
收稿日期:2023-11-29
修回日期:2023-12-29
出版日期:2024-06-20
网络出版日期:2024-01-08
通讯作者:
孙佳, 副教授. E-mail: j.sun@nwpu.edu.cn;作者简介:张育育(1997-), 女, 博士研究生. E-mail: Zhangyuyu@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Yuyu( ), WU Yicheng, SUN Jia(
), WU Yicheng, SUN Jia( ), FU Qiangang(
), FU Qiangang( )
)
Received:2023-11-29
Revised:2023-12-29
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-01-08
Contact:
SUN Jia, associate professor. E-mail: j.sun@nwpu.edu.cn;About author:ZHANG Yuyu (1997-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: Zhangyuyu@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
聚合物转化SiCN陶瓷得益于质量轻和热膨胀系数低等优势, 在电磁波吸收领域受到广泛关注。由于电磁损耗机制单一及耐温性不足, SiCN陶瓷的吸波性能有待进一步提高, 借助多组元协同作用增强吸波性能是可行的途径之一。本工作对聚氮硅烷结合不同化合物进行单源化改性得到SiHfCN、SiHfCN-C、SiHfCN-B和SiHfCN-N等四种纳米陶瓷。结果表明:SiHfCN中由于Hf源的含氧量高达13.5%(质量分数), 生成HfO2和SiO2, 使其最低反射损耗(Reflection loss, RLmin)仅为-13.8 dB, 有效吸收带宽(Effective absorption bandwidth, EAB)仅为0.42 GHz。相比于SiHfCN, 含Hf聚合物分别与C源、B源和N源共改性增加了聚合物转化陶瓷的界面和导电相, SiHfCN-C、SiHfCN-B和SiHfCN-N的介电常数实部和虚部分别提高了1.4~1.8和2.7~3.9倍, RLmin分别为-50.6、-57.3和-63.5 dB, EAB分别为3.53、3.99和4.01 GHz, 吸波性能得到了显著改善。SiHfCN-C中大量的自由碳抑制了HfO2的生成, 增强了电导损耗。SiHfCN-B中生成了B-N和B-C键, 且析出的纳米棒状HfSiO4提供了更多的异质界面, 增强了极化损耗。SiHfCN-N中因引入大量N使N-C键数量增加, 强化了偶极子极化损耗, 同时生成纳米碳片, 不仅可以增强电导损耗, 而且提供大量界面, 改善了阻抗匹配并增强了界面极化, 因而SiHfCN-N具有最佳的吸波性能。
中图分类号:
张育育, 吴轶城, 孙佳, 付前刚. 聚合物转化SiHfCN陶瓷的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 681-690.
ZHANG Yuyu, WU Yicheng, SUN Jia, FU Qiangang. Preparation and Wave-absorbing Properties of Polymer-derived SiHfCN Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 681-690.
| SSPs | PDCs | PSN | Hf isopropoxide isopropanol complex | DVB | Melamine | Dimethylamino borane |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P7Hf3 | SiHfCN | 7 | 3 | - | - | - |
| P7Hf3-C | SiHfCN-C | 7 | 3 | 6 | - | - |
| P7Hf3-N | SiHfCN-N | 7 | 3 | - | 6 | - |
| P7Hf3-B | SiHfCN-B | 7 | 3 | - | - | 6 |
表1 不同样品的原料比例(%, 质量分数)
Table 1 Raw material proportions (%, in mass) of different samples
| SSPs | PDCs | PSN | Hf isopropoxide isopropanol complex | DVB | Melamine | Dimethylamino borane |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P7Hf3 | SiHfCN | 7 | 3 | - | - | - |
| P7Hf3-C | SiHfCN-C | 7 | 3 | 6 | - | - |
| P7Hf3-N | SiHfCN-N | 7 | 3 | - | 6 | - |
| P7Hf3-B | SiHfCN-B | 7 | 3 | - | - | 6 |
| Element | SiHfCN | SiHfCN-C | SiHfCN-N | SiHfCN-B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 35.5 | 42.3 | 40.8 | 33.8 |
| Hf | 22.5 | 18.6 | 20.4 | 13.5 |
| C | 13.6 | 24 | 8.2 | 13.3 |
| N | 22.8 | 9.4 | 55.5 | 29.8 |
| O | 5.6 | 5.7 | 7.1 | 5.3 |
| Empirical formula | SiHf0.10C0.90N1.29O0.28 | SiHf0.07C1.33N0.45O0.24 | SiHf0.08C0.47N2.73O0.31 | SiHf0.06C0.92N1.77O0.28B0.33 |
表2 PDCs的元素含量(%, 质量分数)和经验化学式
Table 2 Elemental contents (%, in mass) and empirical chemical compositions of the PDCs
| Element | SiHfCN | SiHfCN-C | SiHfCN-N | SiHfCN-B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 35.5 | 42.3 | 40.8 | 33.8 |
| Hf | 22.5 | 18.6 | 20.4 | 13.5 |
| C | 13.6 | 24 | 8.2 | 13.3 |
| N | 22.8 | 9.4 | 55.5 | 29.8 |
| O | 5.6 | 5.7 | 7.1 | 5.3 |
| Empirical formula | SiHf0.10C0.90N1.29O0.28 | SiHf0.07C1.33N0.45O0.24 | SiHf0.08C0.47N2.73O0.31 | SiHf0.06C0.92N1.77O0.28B0.33 |
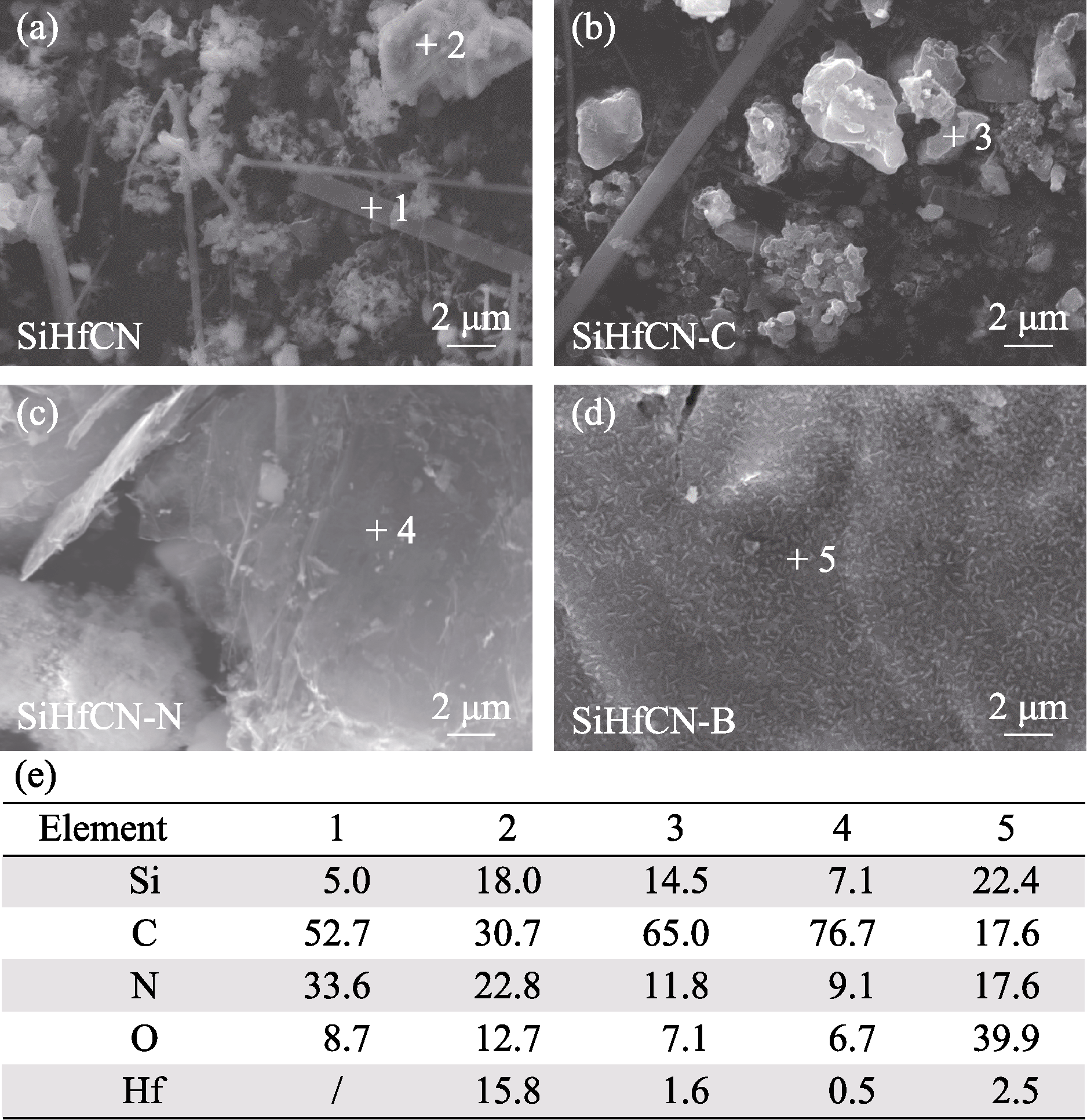

图5 PDCs的SEM照片及EDS分析
Fig. 5 SEM images and EDS analyses of the PDCs (a) SiHfCN; (b) SiHfCN-C; (c) SiHfCN-N; (d) SiHfCN-B; (e) Elemental contents (%, in atom) of spots in (a-d)

图6 SiHfCN和SiHfCN-C的TEM照片
Fig. 6 TEM images of SiHfCN and SiHfCN-C (a-d) SiHfCN; (e-h) SiHfCN-C; (a, e) Bright field images; (b, c, f, g) HRTEM images with corresponding SAED inserted; (d, h) EDS mappings

图7 SiHfCN-N和SiHfCN-B的TEM照片
Fig. 7 TEM images of SiHfCN-N and SiHfCN-B (a-d) SiHfCN-N; (e-h) SiHfCN-B; (a, e) Bright field images; (b, c, f, g) HRTEM images with corresponding SAED inserted; (d, h) EDS mappings
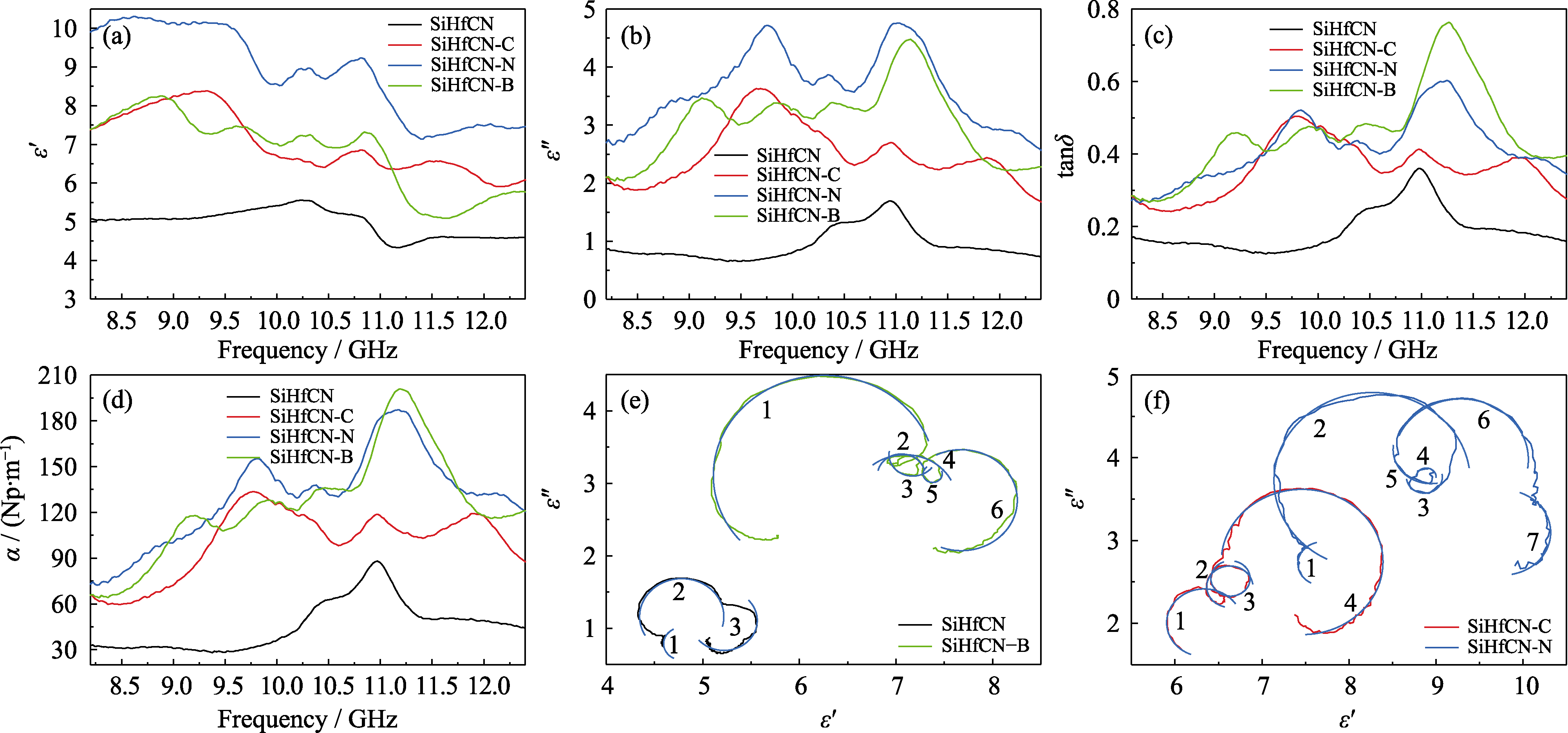
图8 PDCs的电磁参数
Fig. 8 Electromagnetic parameters of the PDCs (a) Real part; (b) Imaginary part; (c) Loss tangent; (d) Attenuation coefficient; (e, f) Cole-Cole curves; Colorful figures are available on website
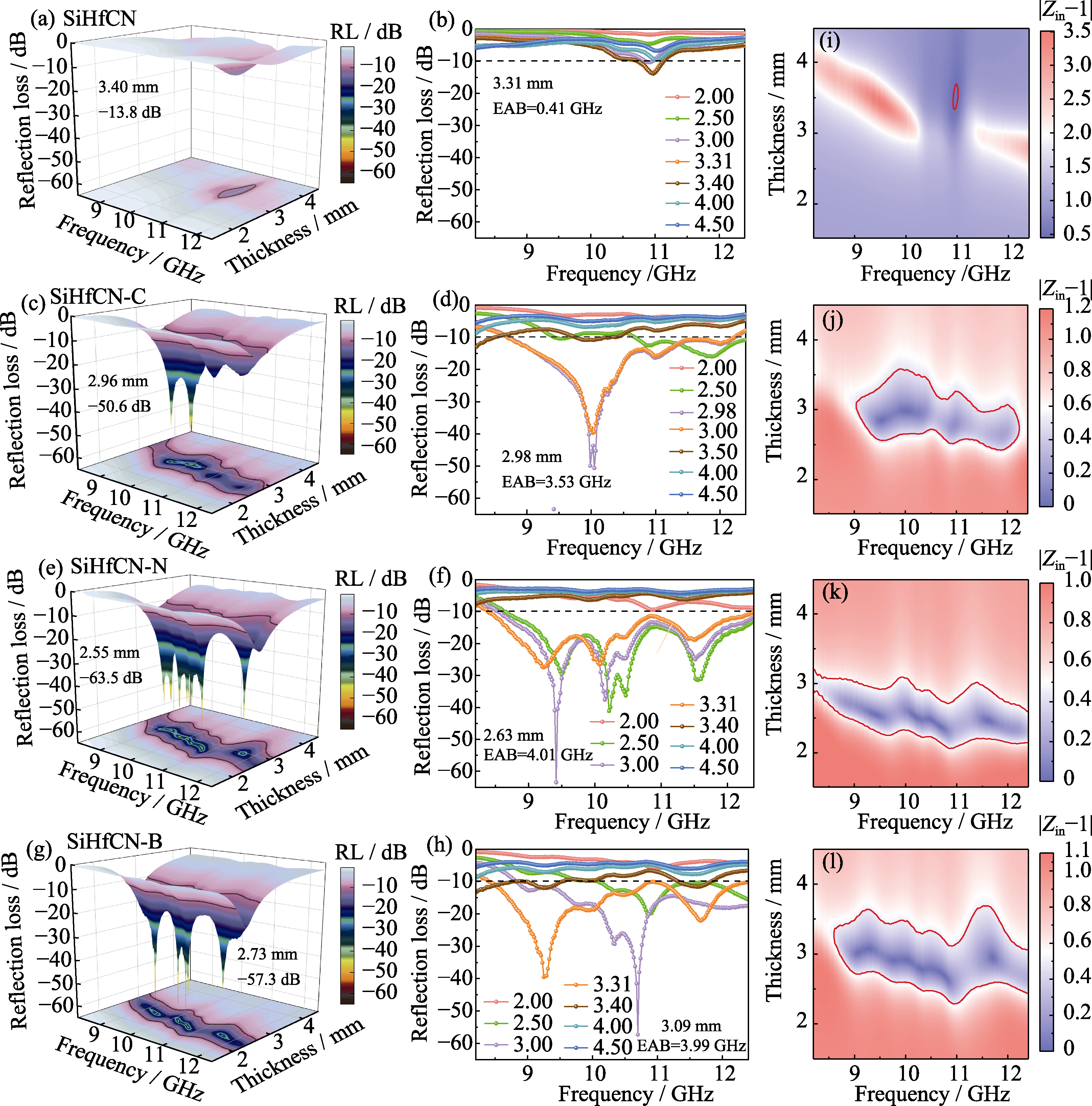
图9 PDCs的RL图和阻抗匹配图
Fig. 9 RL patterns and impedance matching maps of the PDCs (a-h) RL patterns; (i-l) Impedance matching maps; (a, b, i) SiHfCN; (c, d, j) SiHfCN-C; (e, f, k) SiHfCN-N; (g, h, l) SiHfCN-B
| [1] | XIA Y, GAO W, GAO C. A review on graphene-based electromagnetic functional materials: electromagnetic wave shielding and absorption. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(42):2204591. |
| [2] | ZHOU R, WANG Y, LIU Z, et al. Digital light processing 3D-printed ceramic metamaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14: 122. |
| [3] | ZOU Z, NING M, LEI Z, et al. 0D/1D/2D architectural Co@C/MXene composite for boosting microwave attenuation performance in 2-18 GHz. Carbon, 2022, 193: 182. |
| [4] | QIAO M, QI J, WANG J, et al. Recent progress on 3D graphene aerogel based microwave absorbing materials. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(2):550. |
| [5] | SONG Y, LIU P, ZHOU R, et al. SiBNCx ceramics derived from single source polymeric precursor with controllable carbon structures for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption at high temperature. Carbon, 2022, 188: 12. |
| [6] | SONG Y, JIN S, HU K, et al. Adjustable iron-containing SiBCN ceramics with high temperature microwave absorption and anti-oxidation properties. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104: 5244. |
| [7] | CHEN P, CHEN J, WANG C, et al. The heterointerface of graphene in-situ growth for enhanced microwave attenuation properties in La-doped SiBCN ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(16):26642. |
| [8] | ANAND R, LU K, NAYAK B B, et al. Structural evolution and oxidation resistance of polysilazane-derived SiCN-HfO2 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(3):1657. |
| [9] | XIA Q, HAN Z, ZHANG Z, et al. High temperature microwave absorbing materials. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(14):4552. |
| [10] | JIAO X, HE Q, QING M, et al. Ablation behavior of C/C-Zr1-xHfxC-SiC composites under an oxyacetylene flame at above 2500 ℃. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 24: 3235. |
| [11] | REN B, DENG Y, JIA Y, et al. Achieving broadband electromagnetic absorption at a wide temperature range up to 1273 K by metamaterial design on polymer-derived SiC-BN@CNT ceramic composites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 478: 147251. |
| [12] | SHEN J, TANG Z, TUSIIME R, et al. Effects of hafnium sources and hafnium content on the structures and properties of SiBNC-Hf ceramic precursors. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(5):3239. |
| [13] | SONG Y, LIU Z, ZHANG X, et al. Single source precursor derived SiBCNHf ceramic with enhanced high-temperature microwave absorption and antioxidation. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 126: 215. |
| [14] | SUN C, WANG H, ZHOU X. Research progress on ultra-high temperature ceramics powder prepared by precursor-derived method. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 42(8):2865. |
| [15] | ZHAO Z, HAN C, WANG X, et al. Synthesis and pyrolysis of Hf-N-B backbone polymer precursor for HfC/HfB2 composite ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(5):3424. |
| [16] | ZHANG X, SUN J, ZHANG Y, et al. Microstructure and phase evolution of polymer-derived SiHfOC ceramic microspheres. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(12):7726. |
| [17] | ZHANG M, FAN X, YE F, et al. Synthesis, microstructure and electromagnetic properties of Hf-based SiBCN ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(12):19664. |
| [18] | SONG L, WU C, ZHI Q, et al. Multifunctional SiC aerogel reinforced with nanofibers and nanowires for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 467: 143518. |
| [19] | LIU X, YU Z, ISHIKAWA R, et al. Single-source-precursor synthesis and electromagnetic properties of novel RGO-SiCN ceramic nanocomposites. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(31):7950. |
| [20] | CHEN Q, LI D, YANG Z, et al. SiBCN-reduced graphene oxide (rGO) ceramic composites derived from single-source-precursor with enhanced and tunable microwave absorption performance. Carbon, 2021, 179: 180. |
| [21] | HOU Y, XIAO B, YANG G, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of novel carbon-coated Fe3Si nanoparticles in an amorphous SiCO ceramic matrix. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(28):7661. |
| [22] | ZHANG Y, SUN J, WANG Y, et al. SiCN ceramics with controllable carbon nanomaterials for electromagnetic absorption performance. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(7):4220. |
| [23] | ZENG G, XU P, ZENG C, et al. Preparation of HfCxN1-x nanoparticles derived from a multifunction precursor with Hf-O and Hf-N bonds. Materials, 2023, 16(12):4426. |
| [24] | SUN J, WEN Q, LI T, et al. Phase evolution of SiOC-based ceramic nanocomposites derived from a polymethylsiloxane modified by Hf- and Ti-alkoxides. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(2):1436. |
| [25] | NADAR S S, RATHOD V K. One pot synthesis of α-amylase metal organic framework (MOF)-sponge via dip-coating technique. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 138: 1035. |
| [26] | NOROUZI M, ELHAMIFAR D, MIRBAGHERI R. Phenylene- based periodic mesoporous organosilica supported melamine: an efficient, durable and reusable organocatalyst. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 278: 251. |
| [27] | WANG H, ZHU W, SUN X, et al. Preparation of aerogel-like SiOC ceramic with honeycomb structure and its high-temperature performance. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 937: 168438. |
| [28] | WU C, WANG B, WU N, et al. Molecular-scale understanding on the structure evolution from melamine diborate supramolecule to boron nitride fibers. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(1):1083. |
| [29] | TAVAKOLI A H, GERSTEL P, GOLCZEWSKI J A, et al. Kinetic effect of boron on the thermal stability of Si-(B-)C-N polymer- derived ceramics. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(18):6002. |
| [30] | CHENG Y, HU L, ZHANG K, et al. Facile synthesis of hollow SiC/C nanospheres for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon, 2023, 215: 118391. |
| [31] | FERRARI A C, ROBERTSON J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Physical Review B, 2000, 61(20):14095. |
| [32] |
WANG K, MA B, LI X, et al. Structural evolutions in polymer-derived carbon-rich amorphous silicon carbide. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2015, 119(4):552.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | ZHONG C, HOU Y, YANG W, et al. Carbon rich SiOC fibres derived from ceramic precursor for microwave absorption. Journal of Ceramics, 2023, 44(4):703. |
| [34] | PANG L, LUO H, FAN X, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorbing performance of multiphase (SiC/HfC/C)/SiO2 nanocomposites with an unique microstructure. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(4):2425. |
| [35] | LUO C, MIAO P, TANG Y, et al. Excellent electromagnetic wave absorption of MOF/SiBCN nanomaterials at high temperature. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2020, 34(11):277. |
| [36] | PAN R, CHEN G, YU X, et al. Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of Ta4HfC5-based ceramics obtained from synthesized nanoscale powder. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(4):2247. |
| [37] | JIA Y, AJAYI T D, RAMAKRISHNAN K R, et al. A skin layer made of cured polysilazane and yttria stabilized zirconia for enhanced thermal protection of carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRPs). Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 404: 126481. |
| [38] | ZENG G, LI X, WEI Y, et al. Significantly toughened SiC foams with enhanced microwave absorption via in situ growth of Si3N4 nanowires. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 131745. |
| [39] | WANG C, CHEN P, LI X, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption for Y2O3-doped SiBCN ceramics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13: 55440. |
| [40] | ZHOU X, HAN H, WANG Y, et al. Silicon-coated fibrous network of carbon nanotube/iron towards stable and wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 121: 199. |
| [41] | ZHI D, LI T, QI Z, et al. Core-shell heterogeneous graphene-based aerogel microspheres for high-performance broadband microwave absorption via resonance loss and sequential attenuation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 134496. |
| [42] | YAO L, YANG W, ZHOU S, et al. Design paradigm for strong-lightweight perfect microwave absorbers: the case of 3D printed gyroid shellular SiOC-based metamaterials. Carbon, 2022, 196: 961. |
| [43] | YU H, KOU X, ZUO X, et al. Optimization of multiple attenuation mechanisms by cation substitution in imidazolic MOFs-derived porous composites for superior broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 176: 176. |
| [44] | YANG S, TANG L, WEI H, et al. In-situ construction of volcanic rock-like structures in Yb2O3 modified reduced graphene oxide and their boosted electromagnetic wave absorbing properties. Carbon, 2023, 215: 118445. |
| [1] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [2] | 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590. |
| [3] | 武志红, 邓悦, 蒙真真, 张国丽, 张路平, 王宇斌. 含SiC阵列改性涂层的新型SiC/Cf复合材料吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 306-312. |
| [4] | 张兆甫,沙建军,祖宇飞,代吉祥. 晶粒互锁结构与短切碳纤维增韧ZrB2-SiC复合材料的制备与力学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 918-924. |
| [5] | 郑海亚, 孟晨曦, 胡冬力, 顾辉, 刘海涛, 张国军. 织构化ZrB2-SiC超高温陶瓷中取向关系的EBSD研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 380-384. |
| [6] | 穆阳, 邓佳欣, 李皓, 周万城. 两种连续SiC纤维的高温介电及吸波性能对比[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 427-433. |
| [7] | 康越, 原博, 马天, 楚增勇, 张政军. 基于石墨烯的电磁波损耗材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1259-1273. |
| [8] | 刘 克, 王际童, 龙东辉, 凌立成. 低密度Fe3O4/中孔炭微球复合材料的可规模制备及吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(10): 1023-1028. |
| [9] | 周 伟, 肖 鹏, 李 杨, 罗 衡, 洪 文. BN/SiC复合涂层改性炭纤维的吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1093-1098. |
| [10] | 胡冬力, 邢娟娟, 郑 强, 顾 辉, 倪德伟, 张国军. HfB2-SiC-HfC陶瓷相组成与相成分定量分析的对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1105-1109. |
| [11] | 周 伟, 肖 鹏, 李 杨, 罗 衡, 周 亮. 热解炭(PyC)/BN复合粉的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(5): 479-484. |
| [12] | 郑 强, 王贤浩, 邢娟娟, 顾 辉, 张国军. ZrB2-SiC-ZrC复相超高温陶瓷相组成的定量分析[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(4): 358-362. |
| [13] | 周海军, 张翔宇, 高 乐, 胡建宝, 吴 斌, 董绍明. ZrB2-SiC超高温陶瓷涂层的抗烧蚀性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(3): 256-260. |
| [14] | 刘 渊, 刘祥萱, 陈 鑫, 王煊军. 碳纤维表面α-Fe的MOCVD生长制备及吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(12): 1328-1332. |
| [15] | 刘保荣, 黄智斌, 罗 发, 钱七虎. 碳/氧化铝/二氧化硅涂层的介电和吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(8): 817-821. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||