无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 81-89.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230229
收稿日期:2023-05-11
修回日期:2023-08-02
出版日期:2024-01-20
网络出版日期:2023-10-15
作者简介:王艳莉(1975-), 女, 博士, 副教授. E-mail: ylwang@ecust.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Yanli( ), QIAN Xinyi, SHEN Chunyin, ZHAN Liang
), QIAN Xinyi, SHEN Chunyin, ZHAN Liang
Received:2023-05-11
Revised:2023-08-02
Published:2024-01-20
Online:2023-10-15
About author:WANG Yanli (1975-), female, PhD, associate professor. E-mail: ylwang@ecust.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
锰铈氧化物由于较强的氧化还原活性、优良的低温脱硝性能, 已被广泛用于选择性催化还原(SCR)脱硝反应, 但是锰铈氧化物存在活性组分易团聚、比表面积较低等问题, 限制其催化剂活性的提高。本研究以介孔结构的石墨烯基SiO2(G@SiO2)纳米材料为模板, 采用水热法制备了系列石墨烯基介孔锰铈氧化物(G@MnOx-CeO2)催化剂, 并考察了该催化剂在低温下(100~300 ℃)的SCR脱硝性能。结果表明, 与石墨烯基铈氧化物(G@CeO2)相比, G@MnOx-CeO2催化剂具有较高脱硝活性。当Mn、Ce与模板G@SiO2质量比分别为0.35、0.90时, G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9)催化剂的脱硝活性最佳, 220 ℃下NO转化率达到最高(80%)。添加适量MnOx, 提高了G@MnOx-CeO2催化剂的比表面积、孔容, 降低了催化剂的结晶度; 并且MnOx-CeO2以纳米尺度(2~3 nm)较为均匀地分散于石墨烯片层表面。此外, 由于MnOx与CeO2之间存在协同作用, Mn原子可以部分替代Ce原子掺杂于CeO2的晶体结构中形成MnOx-CeO2固溶体, 使G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9)催化剂表面存在较高含量的高价态Mn3+和Mn4+、Ce4+以及较高的化学吸附氧浓度, 从而展现出较高的脱硝性能。该工作为MnOx-CeO2基催化剂在低温NH3-SCR中的实际应用提供了基础数据。
中图分类号:
王艳莉, 钱心怡, 沈春银, 詹亮. 石墨烯基介孔锰铈氧化物催化剂: 制备和低温催化还原NO[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 81-89.
WANG Yanli, QIAN Xinyi, SHEN Chunyin, ZHAN Liang. Graphene Based Mesoporous Manganese-Cerium Oxides Catalysts: Preparation and Low-temperature Catalytic Reduction of NO[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 81-89.
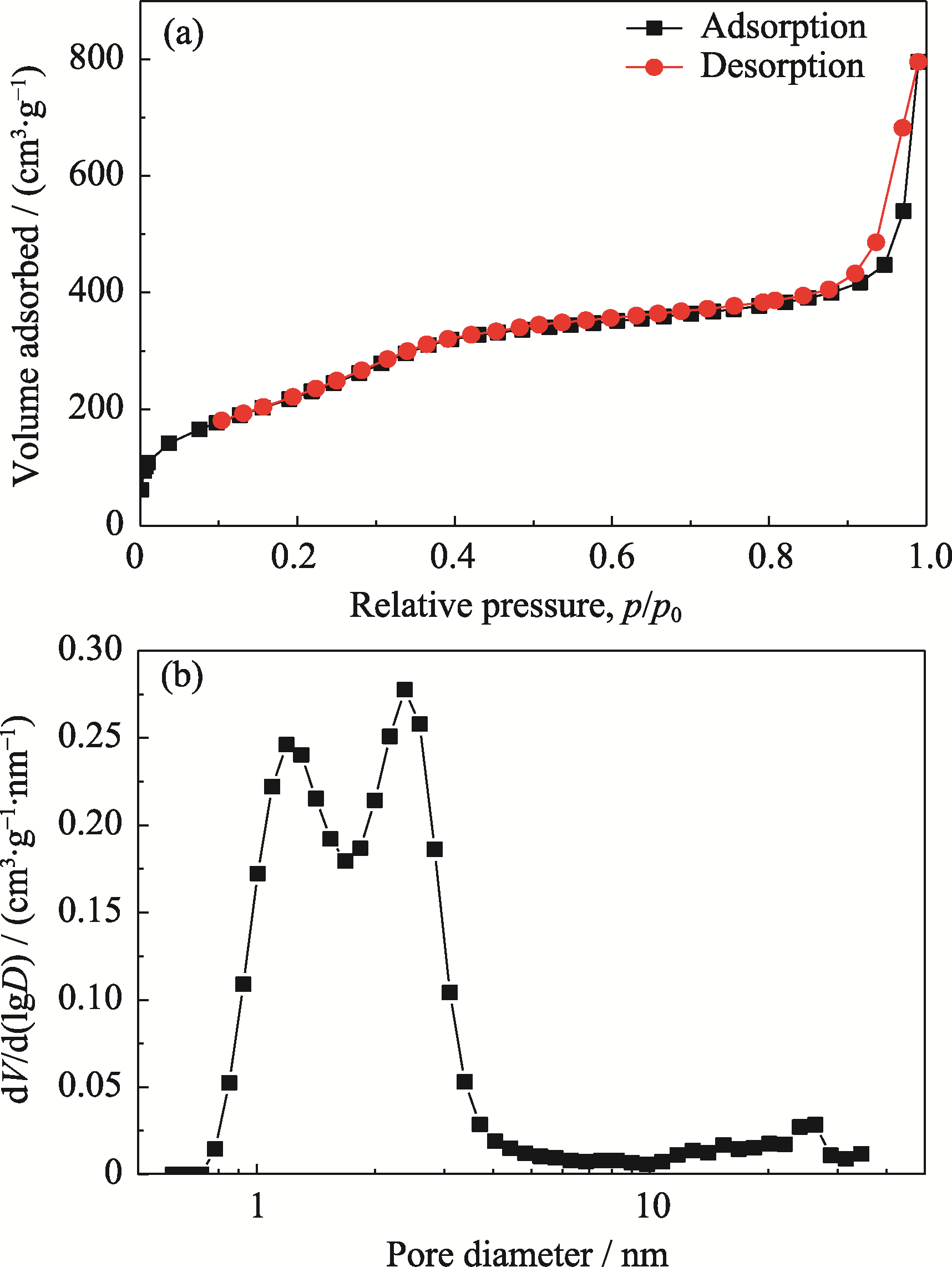
图4 G@SiO2介孔模板的(a) N2吸附-脱附等温线和(b)孔径分布曲线
Fig. 4 (a) Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm and (b) corresponding pore size distribution curve of G@SiO2 template
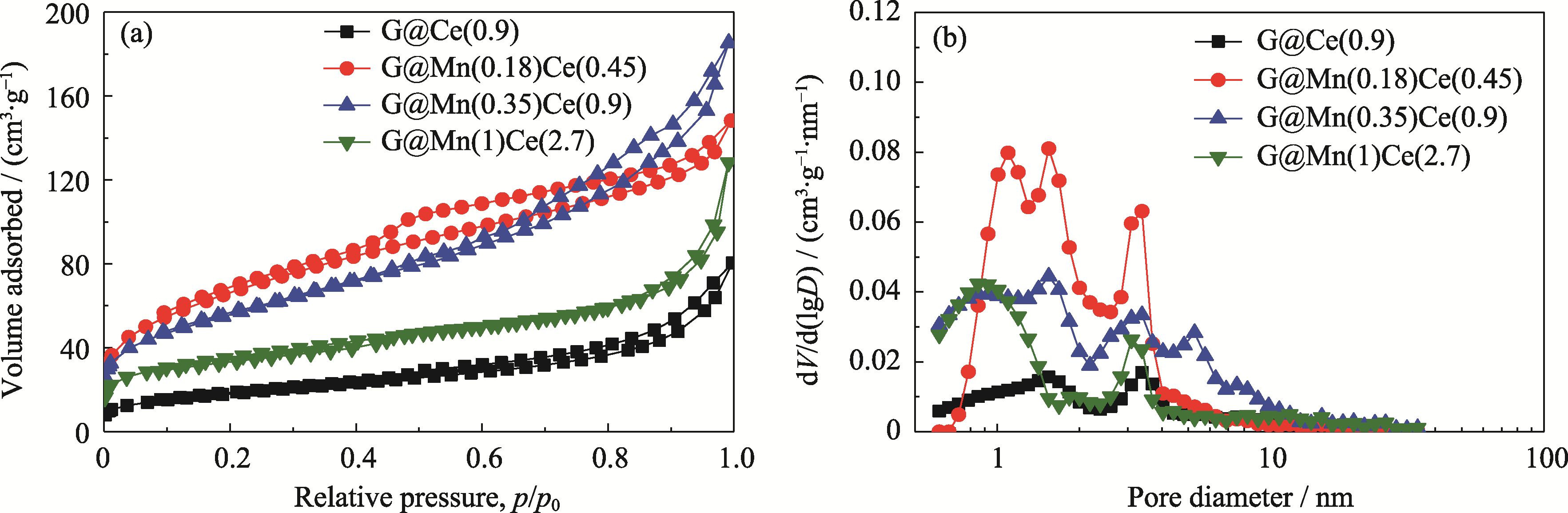
图5 不同金属担载量时G@MnOx-CeO2催化剂的(a)N2吸附-脱附等温线和(b)孔径分布曲线
Fig. 5 (a) Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms and (b) corresponding pore size distribution curves of G@MnOx-CeO2 catalysts with different metal loadings
| Sample | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Vtotal/ (cm3·g-1) | Average pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| G@Ce(0.9) | 65.0 | 0.125 | 7.67 |
| G@Mn(0.18)Ce(0.45) | 241.2 | 0.230 | 3.81 |
| G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9) | 197.5 | 0.287 | 5.82 |
| G@Mn(1)Ce(2.7) | 126.6 | 0.199 | 6.29 |
表1 不同催化剂的孔结构参数
Table 1 Pore parameters of various catalysts
| Sample | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Vtotal/ (cm3·g-1) | Average pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| G@Ce(0.9) | 65.0 | 0.125 | 7.67 |
| G@Mn(0.18)Ce(0.45) | 241.2 | 0.230 | 3.81 |
| G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9) | 197.5 | 0.287 | 5.82 |
| G@Mn(1)Ce(2.7) | 126.6 | 0.199 | 6.29 |
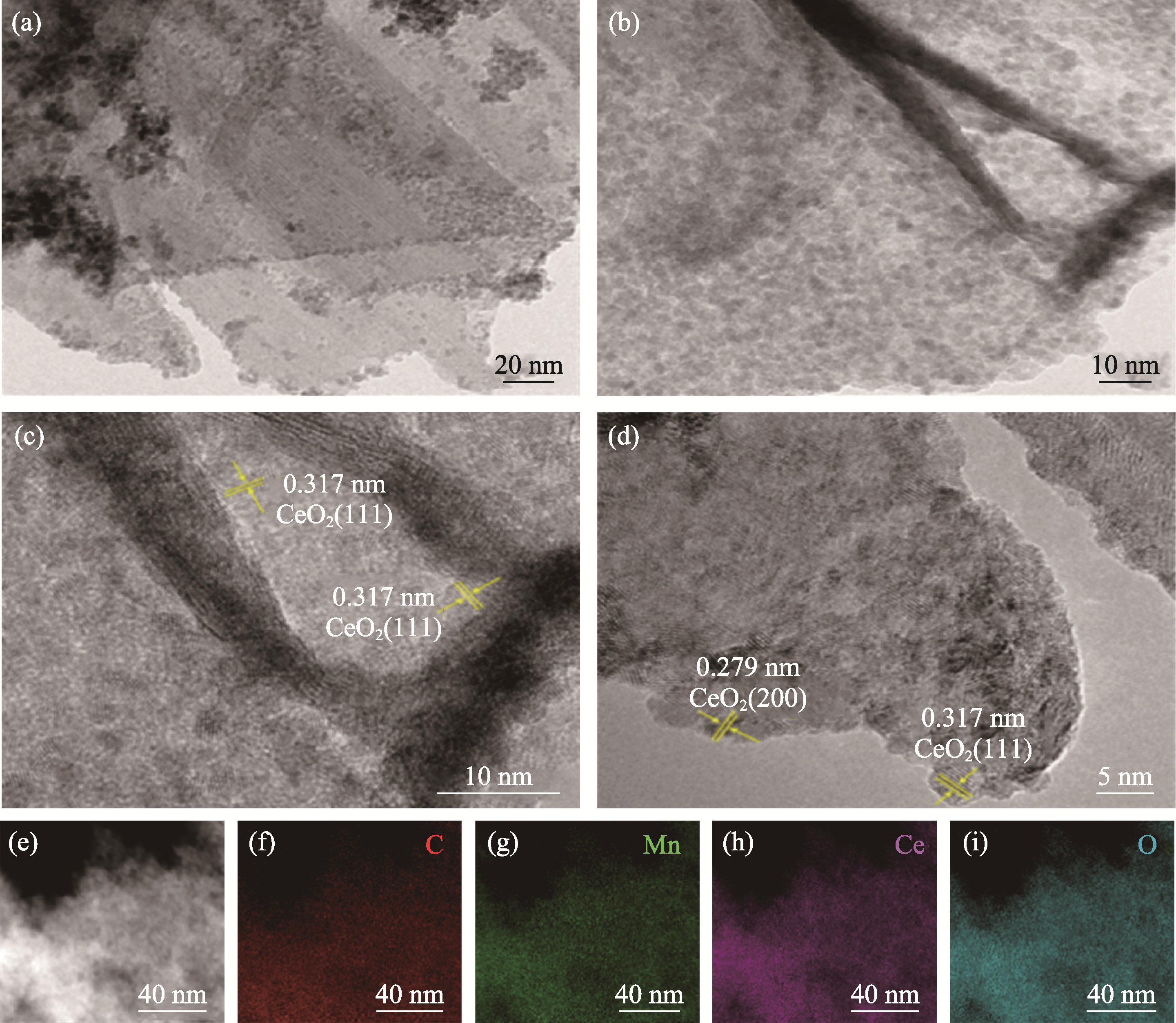
图7 G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9)催化剂的(a-d)TEM照片, (e-i)选定区域TEM照片及其对应的C、Mn、Ce、O元素分布图
Fig. 7 (a-d) TEM images, (e-i) TEM image and corresponding C, Mn, Ce, O element mappings for selected area of G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9) catalyst
| Sample | Surface atomic concentration/% | Relative atomic ratio/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Mn | Ce | Oβ/O | (Mn3++Mn4+)/Mn | |
| G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9) | 18.10 | 65.72 | 8.26 | 7.92 | 45.2 | 80.1 |
表2 G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9)催化剂的表面元素浓度
Table 2 Surface atomic concentrations of G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9) catalyst
| Sample | Surface atomic concentration/% | Relative atomic ratio/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Mn | Ce | Oβ/O | (Mn3++Mn4+)/Mn | |
| G@Mn(0.35)Ce(0.9) | 18.10 | 65.72 | 8.26 | 7.92 | 45.2 | 80.1 |
| [1] |
QI G, YANG R T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over iron and manganese oxides supported on titania. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2003, 44(3):217.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
KOMPIO P G, BRUCKNER A, HIPLER F, et al. A new view on the relations between tungsten and vanadium in V2O5-WO3/TiO2catalysts for the selective reduction of NO with NH3. Journal of Catalysis, 2012, 286(1):237.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LEE I Y, KIM D W, LEE J B, et al. A practical scale evaluation of sulfated V2O5/TiO2 catalyst from metatitanic acid for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2002, 90(3):267.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
KANG M, PARK E D, KIM J M, et al. Manganese oxide catalysts for NOx reduction with NH3 at low temperatures. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2007, 327(2):261.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
QI G, YANG R T. Performance and kinetics study for low- temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over MnOx-CeO2 catalyst. Journal of Catalysis, 2003, 217(2):434.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WU Z B, JIN R B, LIU Y, et al. Ceria modified MnOx/TiO2 as a superior catalyst for NO reduction with NH3 at low-temperature. Catalysis Communications, 2008, 9(13): 2217.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LIU Z M, YANG Y, ZHANG S X, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over Mn-Ce mixed oxide catalyst at low temperatures. Catalysis Today, 2013, 216: 76. |
| [8] | LI Yi, LI Y P, WANG P F, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over MnFeOx nanorods. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 330: 213. |
| [9] | DENG S S, LI Y H, A R T, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over manganese and tin oxides supported on titania. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2013, 32(10):2403. |
| [10] | CHANG H Z, LI J H, CHEN X Y, et al. Effect of Sn on MnOx-CeO2 catalyst for SCR of NOx by ammonia: Enhancement of activity and remarkable resistance to SO2. Catalysis Communications, 2012, 27: 54. |
| [11] | YAO X J, CHEN L, CAO J, et al. Enhancing the deNOx performance of MnOx/CeO2-ZrO2 nanorod catalyst for low- temperature NH3-SCR by TiO2 modification. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 46. |
| [12] |
TANG X L, WANG C Z, GAO F Y, et al. Effect of hierarchical element doping on the low-temperature activity of manganese- based catalysts for NH3-SCR. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5):104399.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WANG Y L, LI X X, ZHAN L, et al. Effect of SO2 on activated carbon honeycomb supported CeO2-MnOx catalyst for NO removal at low temperature. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(8):2274.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SHEN B X, LIU T. Deactivation of MnOx-CeOx/ACF catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR in the presence of SO2. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2010, 26(11):3009.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG D S, ZHANG L, SHI L Y, et al. In situ supported MnOx-CeOx on carbon nanotubes for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(3):1127.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JIAO J Z, LI S H, HUANG B C. Preparation of manganese oxides supported on graphene catalysts and their activity in low-temperature NH3-SCR. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2015, 31(7):1383.
DOI URL |
| [17] | XU H M, QU Z, ZONG C X, et al. MnOx/graphene for the catalytic oxidation and adsorption of elemental mercury. Environmental Science and Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6823. |
| [18] |
LU X N, SONG C Y, JIA S H, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over cerium and manganese oxides supported on TiO2-graphene. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 260(12):776.
DOI URL |
| [19] | XIAO X, SHENG Z Y, YANG L, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over a manganese and cerium oxide/graphene composite prepared by a hydrothermal method. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(5):1507. |
| [20] | YAO W Q, WU S B, ZHAN L, et al. Two-dimensional porous carbon-coated sandwich-like mesoporous SnO2/graphene/mesoporous SnO2 nanosheets towards high-rate and long cycle life lithium-ion batteries. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 329. |
| [21] |
YANG S B, ZHAN L, XU X Y, et al. Graphene-based porous silica sheets impregnated with polyethyleneimine for superior CO2 capture. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(15): 2130.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
YAO W Q, CUI Y S, ZHAN L, et al. Two-dimensional sandwich-like Ag coated silicon-graphene-silicon nanostructures for superior lithium storage. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 425(1):614.
DOI URL |
| [23] | LV L, SHEN Y Q. Selective catalytic reduction with NH3 at low temperature. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2011, 17(2):103. |
| [24] | LIU Chang, GAO G, SHI J W, et al. MnOx-CeO2 shell-in-shell microspheres for NH3-SCR de-NOx at low temperature. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 86: 36. |
| [25] | KONG Z K, LI Y, WANG Y L, et al. Monodispersed MnOx-CeO2 solid solution as superior electrocatalyst for Li2S precipitation and conversion. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123697. |
| [26] |
DENG D Y, CHEN N, XIAO X C, et al. Electrochemical performance of CeO2 nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide as an electrode material for supercapacitor. Ionics, 2017, 23(1):121.
DOI URL |
| [27] | YAO W Y, LIU Y, WU Z B. The promoting effect of CeO2@Ce-O-P multi-core@shell structure on SO2 tolerance for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 442: 156. |
| [28] |
MACHIDA M, UTO M, KUROGI D, et al. Solid-gas interaction of nitrogen oxide adsorbed on MnOx-CeO2: a DRIFTS study. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2001, 11(3):900.
DOI URL |
| [29] | ZHANG X M, DENG Y Q, TIAN P, et al. Dynamic active sites over binary oxide catalysts: In situ/operando spectroscopic study of low-temperature CO oxidation over MnOx-CeO2 catalysts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 191: 179. |
| [30] | YOU X C, SHENG Z Y, YU D Q, et al. Influence of Mn/Ce ratio on the physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of graphene supported MnOx-CeO2 oxides for NH3-SCR at low temperature. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 423: 845. |
| [31] | WU Y Z, LIU S Q, WANG H Y, et al. A novel solvothermal synthesis of Mn3O4/graphene composites for supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 90: 210. |
| [32] |
WANG Y L, KANG Y, GE M, et al. Cerium and tin oxides anchored onto reduced graphene oxide for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(63):36383.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LU X N, SONG C Y, CHANG C C, et al. Manganese oxides supported on TiO2-graphene nanocomposite catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(29):11601.
DOI URL |
| [34] | WANG X, ZHENG Y Y, XU Z, et al. Low-temperature NO reduction with NH3 over Mn-CeOx/CNT catalysts prepared by a liquid-phase method. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2014, 4(6):1738. |
| [35] | FAN Z Y, SHI J W, GAO C, et al. Rationally designed porous MnOx-FeOx nanoneedles for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(19):16117. |
| [36] |
SUN M T, HUANG B C, MA J W, et al. Morphological effects of manganese dioxide on catalytic reactions for low-temperature NH3-SCR. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2016, 32(6):1501.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杨平军, 李铁虎, 李昊, 党阿磊. 石墨烯对环氧树脂泡沫炭石墨化、电导率和力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 107-112. |
| [2] | 董怡曼, 谭占鳌. 宽带隙钙钛矿基二端叠层太阳电池复合层的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1031-1043. |
| [3] | 陈赛赛, 庞雅莉, 王娇娜, 龚䶮, 王锐, 栾筱婉, 李昕. 绿-黄可逆电热致变色织物的制备及其性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 954-960. |
| [4] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [5] | 王虹力, 王男, 王丽莹, 宋二红, 赵占奎. 功能化石墨烯担载型AuPd纳米催化剂增强甲酸制氢反应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 547-553. |
| [6] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [7] | 董淑蕊, 赵笛, 赵静, 金万勤. 离子化氨基酸对氧化石墨烯膜渗透汽化过程中水选择性渗透的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 387-394. |
| [8] | 蒋丽丽, 徐帅帅, 夏宝凯, 陈胜, 朱俊武. 缺陷调控石墨烯复合催化剂在氧还原反应中的作用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 215-222. |
| [9] | 吴静, 余立兵, 刘帅帅, 黄秋艳, 姜姗姗, ANTON Matveev, 王连莉, 宋二红, 肖蓓蓓. NiN4/Cr修饰的石墨烯电化学固氮电极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1141-1148. |
| [10] | 李铁, 李玥, 王颖异, 张珽. 石墨烯-铁酸铋纳米晶复合材料的制备及其催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 725-732. |
| [11] | 向晖, 全慧, 胡艺媛, 赵炜骞, 徐波, 殷江. 类石墨烯单层结构ZnO和GaN的压电特性对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 492-496. |
| [12] | 王艳香, 高培养, 范学运, 李家科, 郭平春, 黄丽群, 孙健. SnO2退火温度对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 168-174. |
| [13] | 李豪, 唐志红, 卓尚军, 钱荣. 基于ZIF8/rGO的高性能NO2室温传感器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1277-1282. |
| [14] | 张清明, 朱敏, 周晓霞. CuO/ZnO复合电催化剂的制备及其还原CO2制合成气[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1145-1153. |
| [15] | 何俊龙, 宋二红, 王连军, 江莞. DFT方法研究一氧化氮在铬掺杂石墨烯上的吸附行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1047-1052. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||