无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 99-106.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230278
戴乐1( ), 刘洋1, 高轩1, 王书豪1, 宋雅婷1, 唐明猛1, 刘丽莎1(
), 刘洋1, 高轩1, 王书豪1, 宋雅婷1, 唐明猛1, 刘丽莎1( ), 汪尧进1(
), 汪尧进1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-12
修回日期:2023-08-07
出版日期:2024-01-20
网络出版日期:2023-10-07
通讯作者:
汪尧进, 教授. E-mail: yjwang@njust.edu.cn;作者简介:戴 乐(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: DL_2323@163.com
DAI Le1( ), LIU Yang1, GAO Xuan1, WANG Shuhao1, SONG Yating1, TANG Mingmeng1, DMITRY V Karpinsky2, LIU Lisha1(
), LIU Yang1, GAO Xuan1, WANG Shuhao1, SONG Yating1, TANG Mingmeng1, DMITRY V Karpinsky2, LIU Lisha1( ), WANG Yaojin1(
), WANG Yaojin1( )
)
Received:2023-06-12
Revised:2023-08-07
Published:2024-01-20
Online:2023-10-07
Contact:
WANG Yaojin, professor. E-mail: yjwang@njust.edu.cn;About author:DAI Le (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: DL_2323@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
BiFeO3是一种非常有前途的无铅铁电材料, 与大多数传统铁电材料相比, 它具有更大的极化和更高的居里温度, 为高温应用提供了可能。受到衬底强烈的夹持效应、较大的矫顽场和漏电流的影响, BiFeO3薄膜难以被极化。自极化是解决这一问题的可行方法。本研究采用溶胶-凝胶法在Pt(111)/Ti/SiO2/Si衬底上生长了BiFeO3薄膜, 向上梯度薄膜(从衬底BiFeO3过渡到薄膜表面Bi0.80Ca0.20FeO2.90)以及向下梯度薄膜(从衬底Bi0.80Ca0.20FeO2.90过渡到薄膜表面BiFeO3)。通过细致地调控薄膜内部缺陷的定向分布形成内置电场,从而导致薄膜具有自极化特性。压电力显微镜结果表明:在BiFeO3薄膜中, Ca的梯度方向可以调控自极化的方向。此外, 类似二极管的单向导通特性验证了薄膜的自极化是由Ca的浓度梯度掺杂导致。X射线光电子能谱结果表明, 氧空位的梯度分布导致的内置电场可能是造成自极化现象的原因。本研究为实现铁电薄膜的自极化提供了一种新的策略, 并在以自极化的内置电场为驱动, 提高光伏或光敏器件性能方面具有潜在的应用前景。
中图分类号:
戴乐, 刘洋, 高轩, 王书豪, 宋雅婷, 唐明猛, 刘丽莎, 汪尧进. 浓度梯度掺杂实现BiFeO3薄膜自极化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 99-106.
DAI Le, LIU Yang, GAO Xuan, WANG Shuhao, SONG Yating, TANG Mingmeng, DMITRY V Karpinsky, LIU Lisha, WANG Yaojin. Self-polarization Achieved by Compositionally Gradient Doping in BiFeO3 Thin Films[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 99-106.

Fig. 1 (a-c) Schematic drawings of structures; Ferroelectric domains illustrating (d) up-graded film, (e) down-graded film and (f) BFO thin film; Schematic diagrams of crystal structures of BFO films (g) before and (h, i) after doping
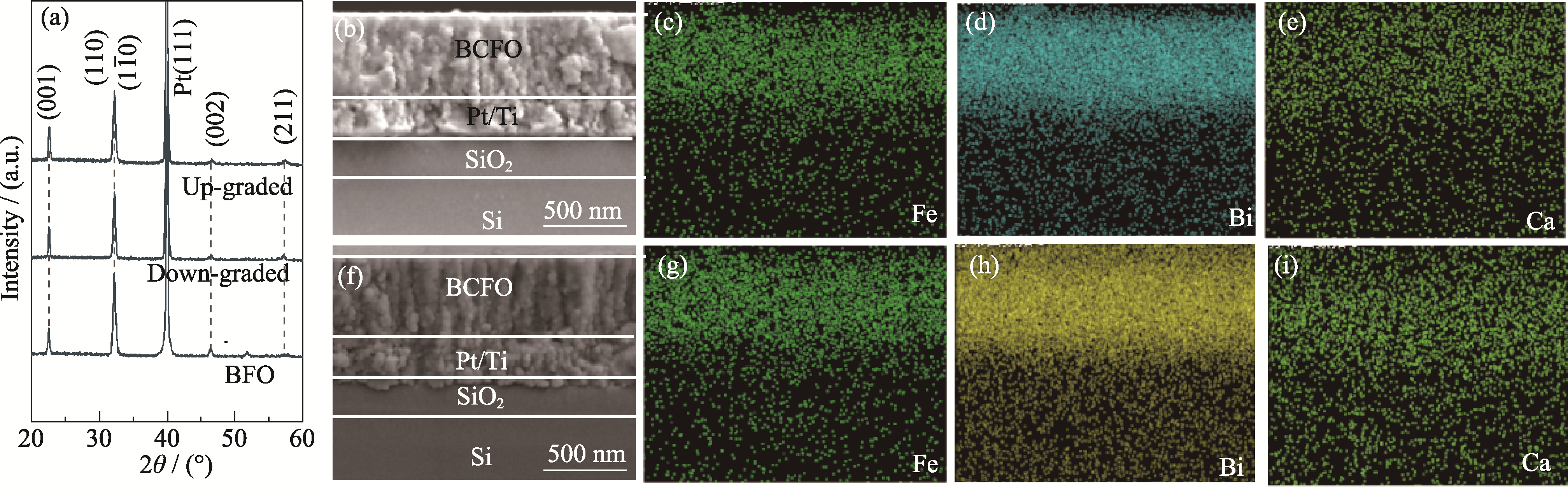
Fig. 2 Structures and cross section morphologies of thin films (a) XRD patterns and SEM images of (b) up-graded films and (f) down-graded films. Bismuth, iron and calcium mappings of (c-e) up-graded BFO films and (g-i) down-graded BFO films
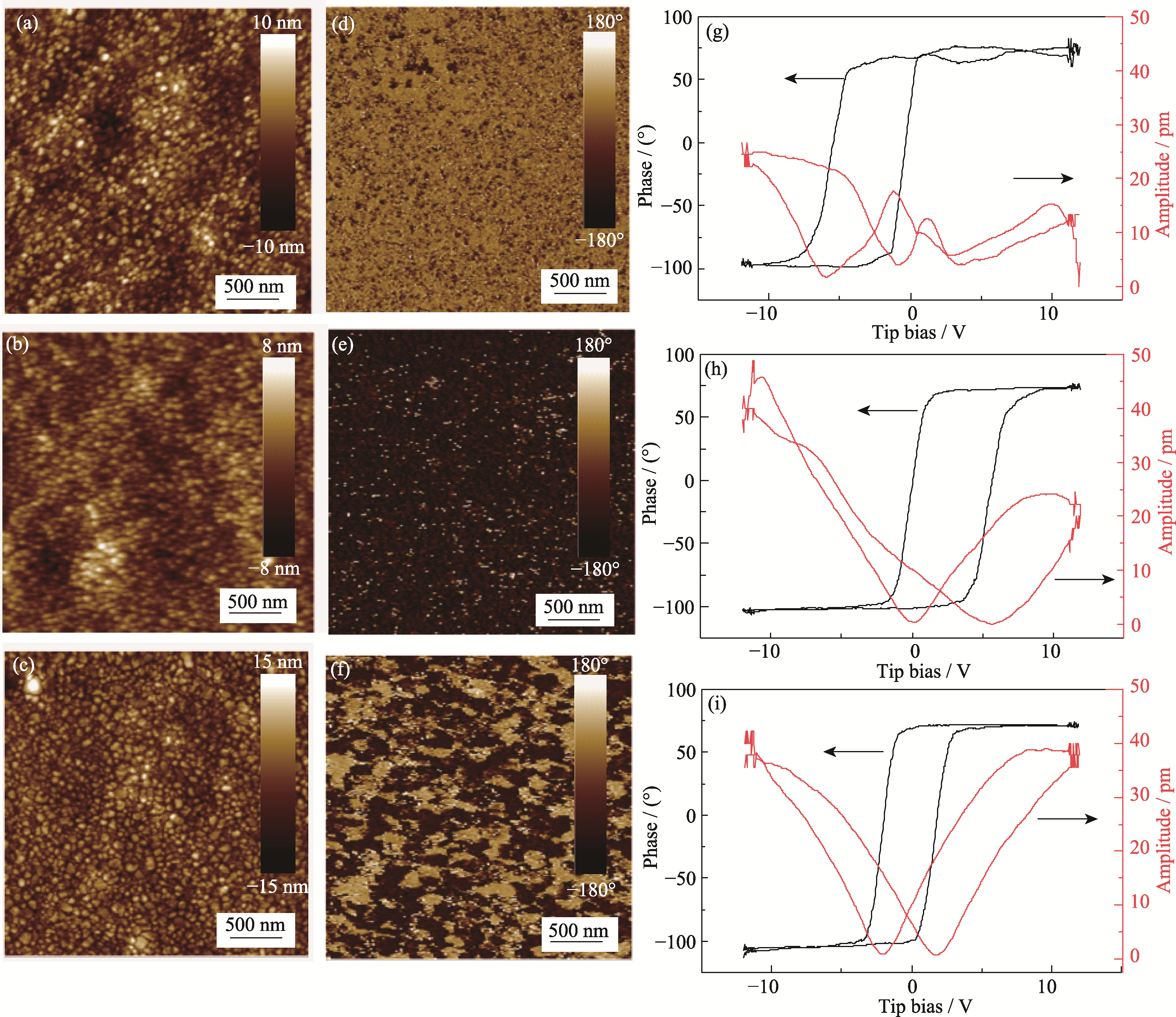
Fig. 3 Surface morphologies and domain structures of thin films (a-c) AFM images, (d-f) out-of-plane PFM images, (g-i) accordingly asymmetric phase and amplitude loops versus tip bias voltage of (a, d, g) up-graded films, (b, e, h) down-graded films and (c, f, i) BFO films

Fig. 4 J-V characteristics of thin films (a) Up-graded BFO films and down-graded BFO films; (b) BCFO (x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20) films; Colorful figures are available on website
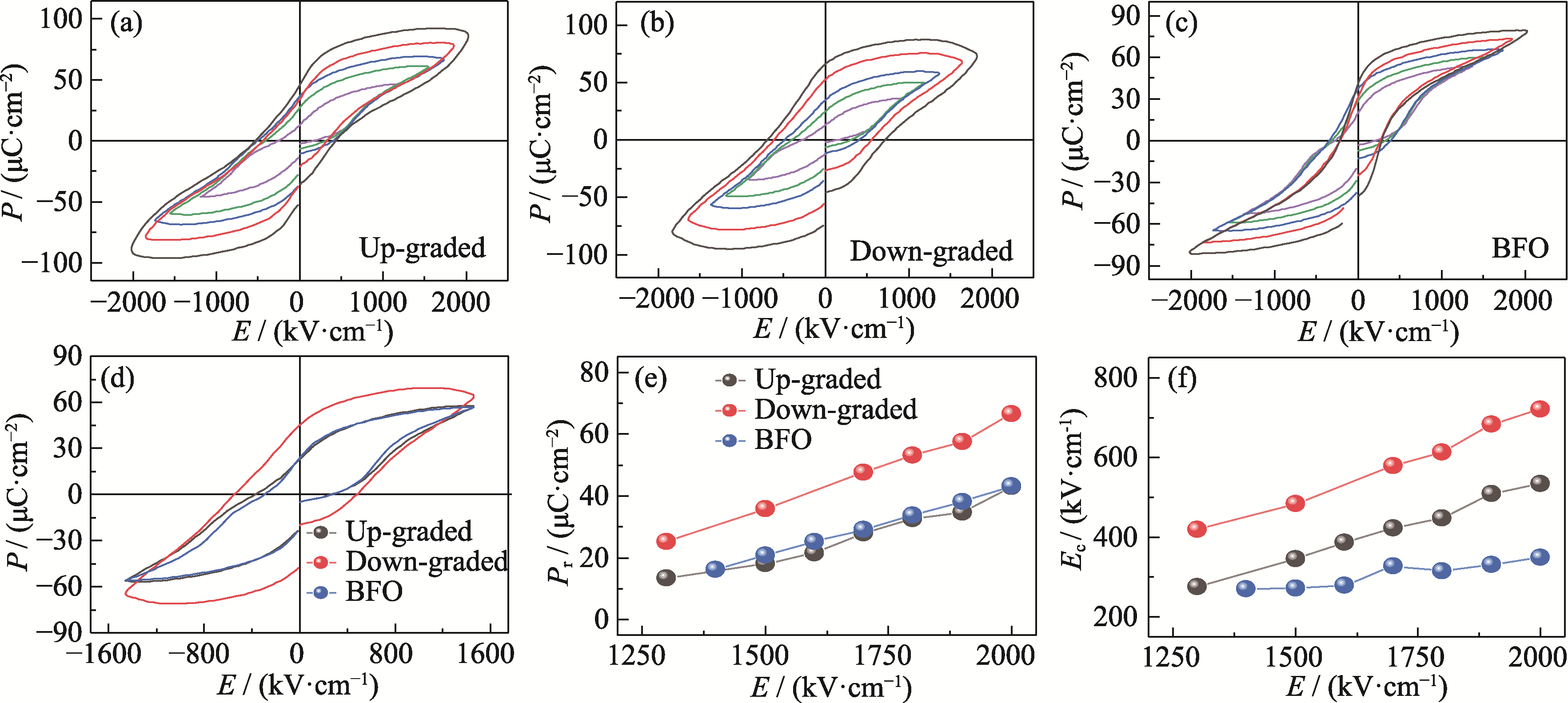
Fig. 5 Ferroelectric properties of BFO compositionally graded films (a) Up-graded films; (b) Down-graded films; (c) BFO thin films; (d) Three kinds of films at the electric field intensity of 1500 kV/cm; (e) Remanent polarization, Pr and (f) coercive field, Ec changed with applied voltage; Colorful figures are available on website
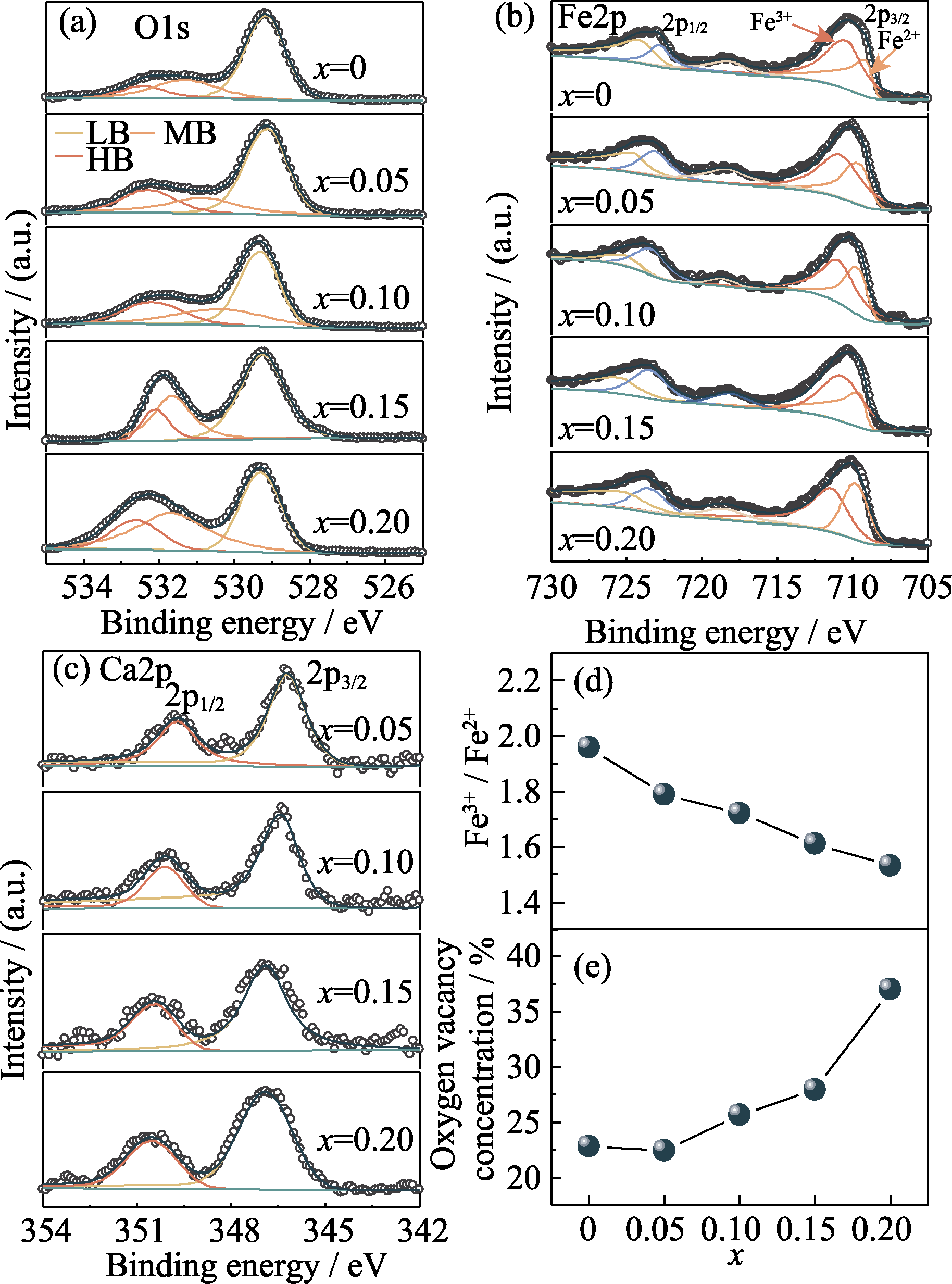
Fig. 6 Valence analysis of thin films Narrow scan spectra of thin films: (a) O1s, (b) Fe2p, and (c) Ca2p of Bi1-xCaxFeO3 samples with x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15 and 0.20; (d) Ratio of Fe3+/Fe2+ and (e) percentage of the oxygen vacancy concentration of BFCO with the increase of x
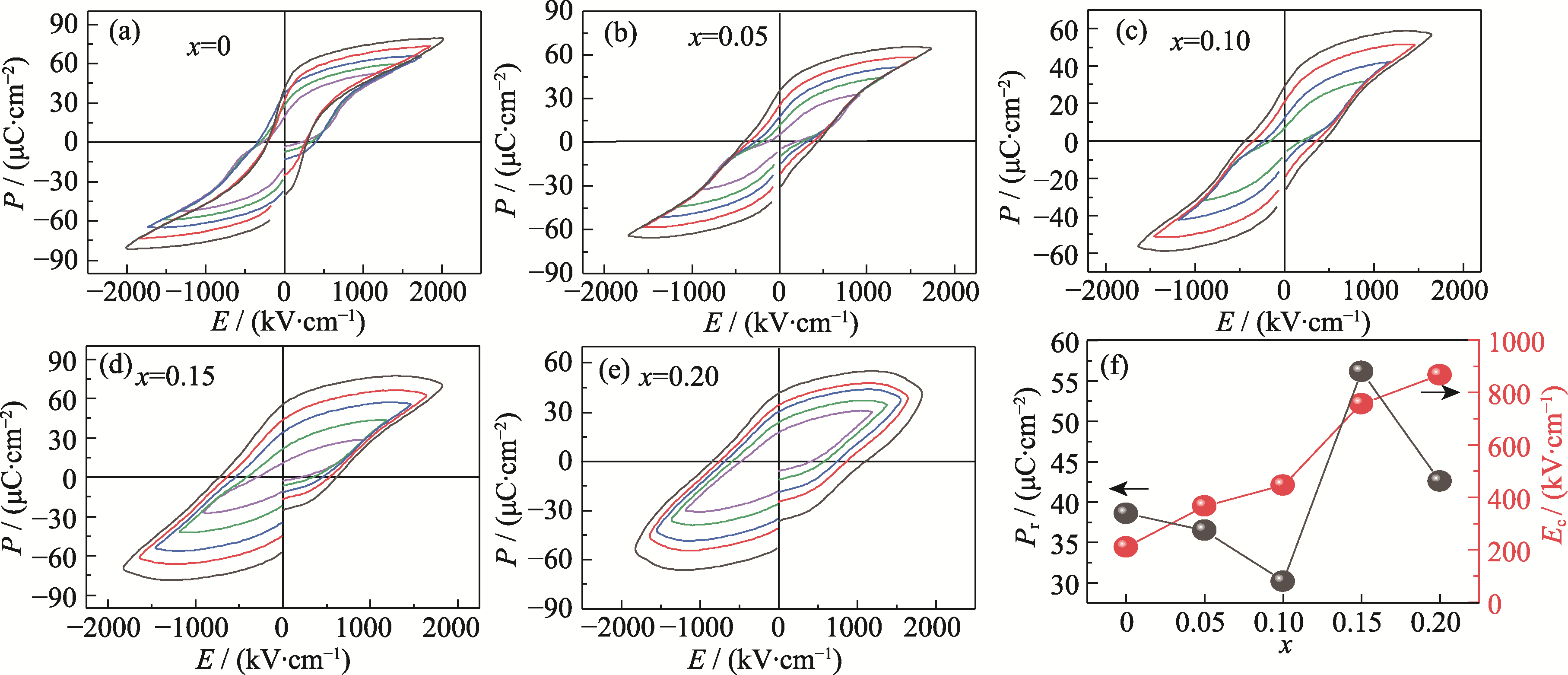
Fig. S2 Ferroelectric properties of Bi1-xCaxFeO3 films (a) x=0; (b) x=0.05; (c) x=0.10; (d) x=0.15; (e) x=0.20; (f) The remanent polarization Pr, the coercive field Ec measured under the electric field intensity of 1800 kV·cm-1
| [1] |
JIN L, TANG X, SONG D, et al. Annealing temperature effects on (111)-oriented BiFeO3 thin films deposited on Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si by chemical solution deposition. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(41):10742.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
XIAO M, LI S, LEI Z. Study of (111)-oriented PZT thin films prepared by a modified Sol-Gel method. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(6):4031.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LI Z, ZHAO Y, LI W L, et al. Photovoltaic effect induced by self- polarization in BiFeO3 films. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(17):9411.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHANG Y, ZHENG H, WANG X, et al. Enhanced photovoltaic properties of gradient calcium-doped BiFeO3 films. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8):10083.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LI Y, CUI X, TIAN M, et al. Stable photovoltaic output and optically tunable resistive switching in all-inorganic flexible ferroelectric thin film with self-polarization characteristic. Acta Materialia, 2021, 217(15):117173.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HOU Y, HAN R, LIU Y, et al. Enhanced piezoelectric properties in LixBi1-xNbxFe1-xO3 films contributed by low-symmetry phase and self-polarization. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(3):3723.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIU Y, DING L, DAI L, et al. All-ceramic flexible piezoelectric energy harvester. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(52):2209297.
DOI URL |
| [8] | ZOU D, LIU S, ZHANG C, et al. Flexible and translucent PZT films enhanced by the compositionally graded heterostructure for human body monitoring. Nano Energy, 2021, 85: 105984. |
| [9] |
CHEN X, ZOU Y, YUAN G, et al. Temperature gradient introduced ferroelectric self-poling in BiFeO3 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(12):3788.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LICHTENSTEIGER C, WEYMANN C, FERNANDEZ-PENA S, et al. Built-in voltage in thin ferroelectric PbTiO3 films: the effect of electrostatic boundary conditions. New Journal of Physics, 2016, 18(4):043030.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FONG D, KOLPAK A, EASTMAN J, et al. Stabilization of monodomain polarization in ultrathin PbTiO3 films. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(12):127601.
DOI URL |
| [12] | PANTEL D, GOETZE S, HESSE D, et al. Room-temperature ferroelectric resistive switching in ultrathin Pb(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 films. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(7):6032. |
| [13] |
GUO R, SHEN L, WANG H, et al. Tailoring self-polarization of BaTiO3 thin films by interface engineering and flexoelectric effect. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2016, 3(23):1600737.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HOU Y F, ZHANG T D, LI W L, et al. Self-polarization induced by lattice mismatch and defect dipole alignment in (001) BaTiO3/LaNiO3 polycrystalline film prepared by magnetron sputtering at low temperature. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(76):61821.
DOI URL |
| [15] | ZHAO J, REN W, NIU G, et al. Recoverable self-polarization in lead-free bismuth sodium titanate piezoelectric thin films. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(34):28716. |
| [16] | ZHAO J, NIU G, REN W, et al. Self-polarization in epitaxial fully matched lead-free bismuth sodium titanate based ferroelectric thin films. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(28):23945. |
| [17] |
ZHAO J, NIU G, REN W, et al. Polarization behavior of` lead-free 0.94(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-0.06BaTiO3 thin films with enhanced ferroelectric properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(12):3928.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
JEON B C, LEE D, LEE M H, et al. Flexoelectric effect in the reversal of self-polarization and associated changes in the electronic functional properties of BiFeO3 thin films. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(39):5643.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HOU Y, LI W, ZHANG T, et al. Large piezoelectric response induced by the coexistence of low-symmetry and self-polarization in Li+-Nb5+-doped BiFeO3 polycrystalline films. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(11):6246.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
CHISHOLM M F, LUO W, OXLEY M P, et al. Atomic-scale compensation phenomena at polar interfaces. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 105(19):197602.
DOI URL |
| [21] | LIU C, LIU Y, ZHANG B, et al. Ferroelectric self-polarization controlled magnetic stratification and magnetic coupling in ultrathin La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 films. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(25):30137. |
| [22] |
CHU Y H, CRUZ M P, YANG C H, et al. Domain control in multiferroic bifeo3 through substrate vicinality. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(18):2662.
DOI URL |
| [23] | BAEK S H, JANG H W, FOLKMAN C M, et al.Ferroelastic switching for nanoscale non-volatile magnetoelectric devices: 4. Nature Materials, 2010, 9(4):309. |
| [24] |
CHEN J, LUO Y, OU X, et al. Upward ferroelectric self-polarization induced by compressive epitaxial strain in (001) BaTiO3 films. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(20):204105.
DOI URL |
| [25] | WU J, FAN Z, XIAO D, et al. Multiferroic bismuth ferrite-based materials for multifunctional applications: ceramic bulks, thin films and nanostructures. Progress in Materials Science, 2016, 84: 335. |
| [26] |
LI X, ZHANG L, LUO N, et al. Enhanced H2S sensing performance of BiFeO3 based MEMS gas sensor with corona poling. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2022, 358(1):131477.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
CAMPANINI M, ERNI R, YANG C, et al. Periodic giant polarization gradients in doped BiFeO3 thin films. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(2):717.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
CHAUHAN S, KUMAR M, CHHOKER S, et al. Substitution driven structural and magnetic transformation in Ca-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(49):43080.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
JIN L, TANG X, WEI R, et al. BiFeO3(00l)/LaNiO3/Si thin films with enhanced polarization: an all-solution approach. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(82):78629.
DOI URL |
| [30] | KHOMYAKOVA E, SADL M, URSIC H, et al. Self-poling of BiFeO3 thick films. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(30):19626. |
| [1] | 贾玉娜, 曹旭, 焦秀玲, 陈代荣. 无机酸铝体系氧化铝连续纤维的制备技术研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1257-1264. |
| [2] | 满鑫, 吴南, 张牧, 贺红亮, 孙旭东, 李晓东. Lu2O3-MgO纳米粉体合成及其复相红外透明陶瓷制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1263-1269. |
| [3] | 杨丛纲, 米乐, 冯爱虎, 于洋, 孙大志, 于云. KH-560改性SiO2绝缘薄膜的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1343-1348. |
| [4] | 朱本必,张旺,张志坚,章建忠,IMRAN Zada,张荻. 光热增强光催化性能二氧化钛(B)/玻纤布复合研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 961-966. |
| [5] | 张少丹, 包维维, 马海萍. Cu 2+、Tb 3+共掺杂BaZrO3高近红外反射颜料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 599-604. |
| [6] | 宋建民, 代秀红, 梁杰通, 赵磊, 周阳, 葛大勇, 孟旭东, 刘保亭. 偏轴磁控溅射法外延BiFeO3薄膜的介电性能与阻变效应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(9): 1017-1021. |
| [7] | 何 飞, 李 亚, 骆 金, 方旻翰, 赫晓东. 具有气凝胶结构特征的C/SiO2和C/SiC复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(5): 449-458. |
| [8] | 陈婷, 查剑锐, 张筱君, 江伟辉, 江莞, 刘健敏, 吴倩. 硅烷偶联剂对制备硅酸锆薄膜及其抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(11): 1154-1158. |
| [9] | 胡亚华, 顾 牡, 张致远, 刘小林, 黄世明, 刘 波, 张娟楠. Lu2O3纳米线阵列的超声辅助溶胶-凝胶模板法制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(8): 807-811. |
| [10] | 尹月锋, 梁桂杰, 张 强, 潘 峥, 李望南, 李在房. 基于Pechini溶胶-凝胶法的染料敏化太阳能电池的优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(7): 739-744. |
| [11] | 张晓欣, 谢建军, 范灵聪, 林德宝, 陈 旭, 施 鹰. Ce、Pr共掺LSO多晶薄膜的溶胶-凝胶法制备及其发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(6): 647-651. |
| [12] | 吴 霜, 刘 波, 邱志澈, 陈士伟, 张娟楠, 刘小林, 顾 牡, 黄世明, 倪 晨. LuTaO4:Ln3+(Ln=Eu,Tb)透明薄膜制备改进与其发光性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(4): 372-376. |
| [13] | 张媛媛, 唐晓东, 陈莹, 王根水, 董显林. La0.7Ca0.3-xSrxMnO3薄膜的电输运特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(3): 274-278. |
| [14] | 徐家跃, 王 杰, 陈 炜, 肖学峰, 杨波波, 王占勇, 李 飞, 谢会东. 大尺寸硅酸铋晶体的原料合成、晶体生长及闪烁性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(10): 1147-1150. |
| [15] | 刘阳龙, 郑玉婴, 尚鹏博. 铕掺杂的TiO2空心微球的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(7): 699-705. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||