无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1355-1363.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230118
陈长( ), 赵若伊, 韩少杰, 王焕燃, 杨群, 高彦峰(
), 赵若伊, 韩少杰, 王焕燃, 杨群, 高彦峰( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-08
修回日期:2023-04-04
出版日期:2023-08-31
网络出版日期:2023-08-31
通讯作者:
高彦峰, 教授. E-mail: yfgao@shu.edu.cn作者简介:陈 长(1985-), 男, 博士, 副教授. E-mail: chenzhang@shu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Zhang( ), ZHAO Ruoyi, HAN Shaojie, WANG Huanran, YANG Qun, GAO Yanfeng(
), ZHAO Ruoyi, HAN Shaojie, WANG Huanran, YANG Qun, GAO Yanfeng( )
)
Received:2023-03-08
Revised:2023-04-04
Published:2023-08-31
Online:2023-08-31
Contact:
GAO Yanfeng, professor. E-mail: yfgao@shu.edu.cnAbout author:CHEN Zhang (1985-), male, PhD, associate professor. E-mail: chenzhang@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
电致变色材料应用于节能建筑、智能显示等领域, 是最具研究前景的智能材料之一。液相法制备WO3电致变色薄膜可以构建复杂多元变色结构, 在光调制幅值、响应时间, 特别是大面积低成本制备方面显现出巨大的潜力。本研究旨在开发一种低成本、易于规模化的WO3纳米晶液相镀膜工艺, 改善液相法常见的循环稳定性差和制备工艺复杂的问题。通过该方法制备了光调制幅度高、响应迅速和抗疲劳性能好的WO3电致变色薄膜。本工作对退火工艺进行优化, 成功合成出低聚集度、高结晶性的WO3纳米粉体。通过球磨分散制备WO3纳米晶镀膜液, 探究球磨对WO3纳米粒子的性能影响, 针对薄膜微结构和镀膜液结晶性对其电致变色性能进行工艺优化。获得了高光学调制幅度(82%), 短响应时间(tc/tb: 8 s/4.2 s), 高着色效率(81.5 cm2·C-1)和高循环稳定性(>1000次)的WO3电致变色薄膜。本工作通过改性WO3纳米粉体结晶和分散性能, 全面提升了纳米晶液相镀膜技术制备的WO3电致变色薄膜性能, 表明采用液相法制备WO3电致变色薄膜在变色性能和循环稳定性上有望突破可实用水平。
中图分类号:
陈长, 赵若伊, 韩少杰, 王焕燃, 杨群, 高彦峰. 纳米晶液相镀膜制备WO3电致变色薄膜研究和性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1355-1363.
CHEN Zhang, ZHAO Ruoyi, HAN Shaojie, WANG Huanran, YANG Qun, GAO Yanfeng. Electrochromic WO3 Thin Films: Preparation by Nanocrystalloid Liquid Phase Coating and Performance Optimization[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1355-1363.
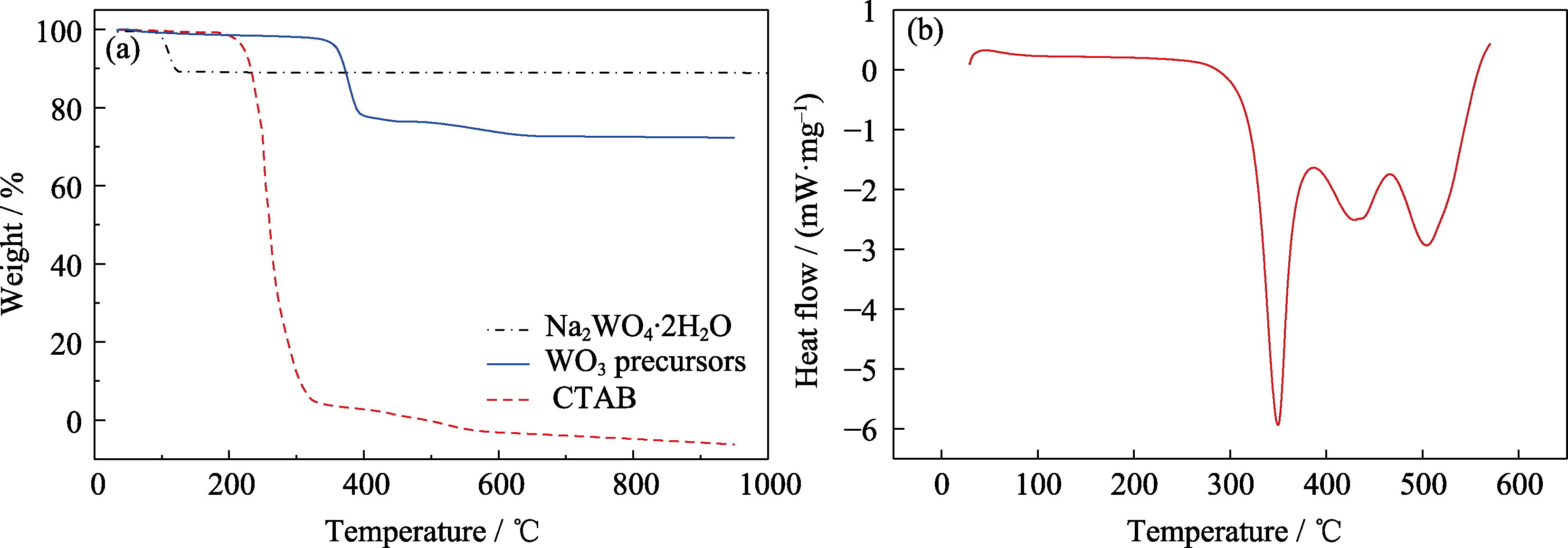
图1 不同样品的热重分析结果
Fig. 1 Thermogravimetric analyses of different samples (a) Thermogravimetric analysis curves of samples; (b) DSC curve of WO3 precursors
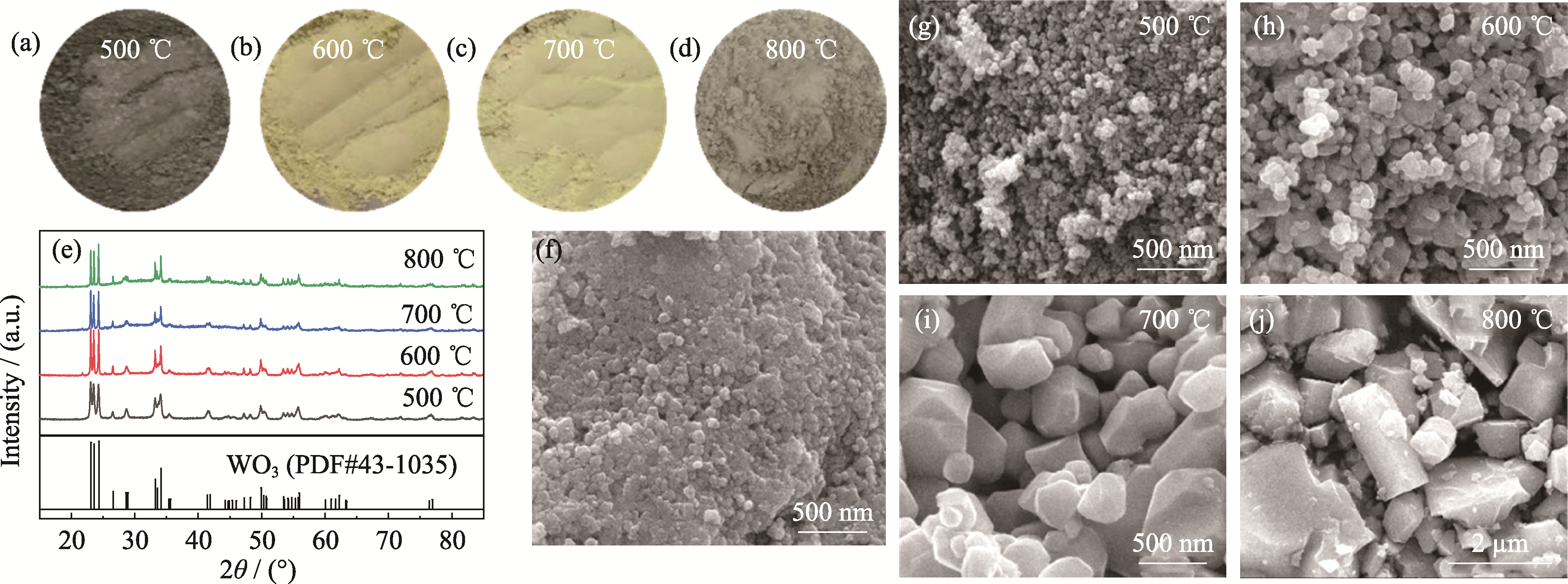
图2 不同温度退火WO3粉体的形貌分析及XRD图谱
Fig. 2 Morphology analyses and XRD patterns of WO3 powders after annealed at different temperatures (a-d) Digital photographs; (e) XRD patterns and (g-j) SEM images of WO3 powders; (f) SEM image of WO3 powders without CTAB

图5 不同温度退火的WO3粉体的照片
Fig. 5 Pictures of WO3 annealed at different temperatures (a-d) Digital photographs of WO3 dispersions and (e-g) TEM images at (a, g) 500, (b, f) 600, (c, e) 700, and (d) 800 ℃

图6 WO3分散液中WO3的吸收光谱分析
Fig. 6 UV-Vis absorbance spectrum of the WO3 dispersion held in a quartz cell Inset: plot of (ahv)1/2 against hv to achieve the bandgap
| WO3 thin film | ΔT/% | (tc/tb)/s | CE/(cm2·C-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| W500 | 72.8 | 11/12 | 52.6 |
| W600 | 75.3 | 8/10 | 54.3 |
| W700 | 78.6 | 7/6 | 64.8 |
| W800 | 75.2 | 13/12 | 61.2 |
表1 不同温度退火所得WO3薄膜的电致变色性能
Table 1 Electrochromic properties of tungsten oxide films annealed at different temperatures
| WO3 thin film | ΔT/% | (tc/tb)/s | CE/(cm2·C-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| W500 | 72.8 | 11/12 | 52.6 |
| W600 | 75.3 | 8/10 | 54.3 |
| W700 | 78.6 | 7/6 | 64.8 |
| W800 | 75.2 | 13/12 | 61.2 |

图8 薄膜W700的电化学性能
Fig. 8 Electrochemical performances of thin film W700 (a) Transmittance spectra; (b) Coloring efficiency plot; (c) Cyclic transmittance curves; (d) Chronograph current curve

图10 分散液水热处理前(a, b)和后(c, d)旋涂薄膜的光学性能
Fig. 10 Optical performance of thin films made from dispersions before (a, b) and after (c, d) hydrothermal treatment (a, c) Cyclic transmittance curves ; (b, d) Coloring efficiency plots
| [1] | GRANQVIST C G. Solar energy materials. Advanced Materials, 2003, 15(21): 1248. |
| [2] |
BEAUJUGE P M, REYNOLD J R. Color control in pi-conjugated organic polymers for use in electrochromic devices. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(1): 268.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
MCEVOY T M, STEVENSON K J, HUPP J T, et al. Electrochemical preparation of molybdenum trioxide thin films: effect of sintering on electrochromic and electroinsertion properties. Langmuir, 2016, 19(10): 4316.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GRANQVIST C G. Progress in electrochromics: tungsten oxide revisited. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 44(18): 3005.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GRANQVIST C G. Electrochromic materials: out of a niche. Nature Materials, 2006, 5(2): 89.
DOI |
| [6] |
GRANQVIST C G. Oxide electrochromics: an introduction to devices and materials. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2012, 99(4): 1.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WEN R T, GRANQVIST C G, NIKLASSON G A. Eliminating degradation and uncovering ion-trapping dynamics in electrochromic WO3 thin films. Nature Materials, 2015, 14(10): 996.
DOI |
| [8] |
XIA X, CHAO D, QI X, et al. Controllable growth of conducting polymers shell for constructing high-quality organic/inorganic core/shell nanostructures and their optical-electrochemical properties. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(9): 4562.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
MORTIMER R J, DYER A L, REYNOLDS J R. Electrochromic organic and polymeric materials for display applications. Displays, 2006, 27(1): 2.
DOI URL |
| [10] | MA D, WANG J, ENGINEERING E M, et al. Inorganic electrochromic materials based on tungsten oxide and nickel oxide nanostructures. Science China (Chemistry), 2017, 60(1): 9. |
| [11] | GILLASPIE D T, TENENT R C, DILLON A C. Metal-oxide films for electrochromic applications: present technology and future directions. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2010, 20(1): 168. |
| [12] | CHEN G X, MIYAUCHI M, SHIMIZU H. UV-induced surface electrical conductivity jump of polymer nanocomposites. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(20): 787. |
| [13] | ZHU W, LIU J, YU S, et al. Ag loaded WO3 nanoplates for efficient photocatalytic degradation of sulfanilamide and their bactericidal effect under visible light irradiation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 2016(1): 407. |
| [14] |
LI Y, LI X, YANG C, et al. Controlled synthesis of CdS nanorods and hexagonal nanocrystals. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2003, 13(10): 2641.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DEEPA M, SINGH D P, SHIVAPRASAD S M, et al. A comparison of electrochromic properties of Sol-Gel derived amorphous and nanocrystalline tungsten oxide films. Current Applied Physics, 2007, 7(2): 220.
DOI URL |
| [16] | CHEN X C, LI Y G, WANG H Z, et al. Morphology regulation and photoelectric performance of hole transport layer WO3 for QLED. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2014, 33(5): 1141. |
| [17] |
GUO Y, MURATA N, ONO K, et al. Production of ultrafine particles of high-temperature tetragonal WO3 by dc arc discharge in Ar-O2 gases. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2005, 7(1): 101.
DOI URL |
| [18] | JIAO Z H, SUN X W. Hydrothermally grown nanostructured tungsten trioxide (hydrate) films and their photocatalytic properties. MRS Proceedings, 2012, 1406: mrsf11-1406-z18-16. |
| [19] | CAI W L, SU X T, WANG J D. Surfactant-assisted ultrasonic synthesis of nano-tungsten oxide powder. China Tungsten Industry, 2008, 14(6): 26. |
| [20] | ZHOU D, SHI F, XIE D, et al. Bi-functional Mo-doped WO3 nanowire array electrochromism-plus electrochemical energy storage. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 465(112): 120. |
| [21] |
CAI G F, TU J P, ZHOU D, et al. The direct growth of a WO3 nanosheet array on a transparent conducting substrate for highly efficient electrochromic and electrocatalytic applications. CrystEngComm, 2014, 16(30): 6866.
DOI URL |
| [22] | MORALES A E, MORA E S, PAL U. Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Sociedad Mexicana de Física A.C, 2007, 53(5): 18. |
| [23] | LEE Y, LEE T, JANG W, et al. Unraveling the intercalation chemistry of hexagonal tungsten bronze and its optical responses. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(13): 286. |
| [24] | YAO Y, ZHAO Q, WEI W, et al. WO3 quantum-dots electrochromism. Nano Energy, 2019, 68(10): 43. |
| [25] | ZHAO Q, FANG Y, QIAO K, et al. Printing of WO3/ITO nanocomposite electrochromic smart windows. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2019, 2(2): 95. |
| [26] | PAIK T, CARGNELLO M, GORDON T R, et al. Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from substoichiometric colloidal WO3-x nanowires. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(8): 19. |
| [1] | 吐尔洪·木尼热, 赵红刚, 马玉花, 齐献慧, 李钰宸, 闫沉香, 李佳文, 陈平. 单晶WO3/红磷S型异质结的构建及光催化活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 701-707. |
| [2] | 张家强, 邹馨蕾, 王能泽, 贾春阳. 两步电沉积法制备Zn-Fe PBA薄膜及其在电致变色器件中的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 961-968. |
| [3] | 张笑宇, 刘永盛, 李然, 李耀刚, 张青红, 侯成义, 李克睿, 王宏志. 基于Cu3(HHTP)2薄膜的离子液体电致变色电极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 883-890. |
| [4] | 黄郅航, 滕官宏伟, 铁鹏, 范德松. 钙钛矿陶瓷薄膜的电致变色特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 611-616. |
| [5] | 王金敏, 后丽君, 马董云. 氧化钼电致变色材料与器件[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 461-470. |
| [6] | 张翔, 李文杰, 王乐滨, 陈曦, 赵九蓬, 李垚. 无机电致变色材料反射特性研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 451-460. |
| [7] | 武琦, 丛杉, 赵志刚. 多彩氧化钨薄膜的红外电致变色性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 485-491. |
| [8] | 王天悦, 王梦颖, 黄庆姣, 杨佳明, 王顺花, 刁训刚. 溶胶-凝胶旋涂法制备电致变色智能窗用钛酸锂薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 471-478. |
| [9] | 贾汉祥, 邵泽伟, 黄爱彬, 金平实, 曹逊. 光学设计用于全固态电致变色器件的高溅射效率三明治结构电解质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 479-484. |
| [10] | 熊金艳, 罗强, 赵凯, 张梦梦, 韩朝, 程刚. 界面电荷快速转移提升铜修饰氧化钨光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [11] | 周开岭, 汪浩, 张倩倩, 刘晶冰, 严辉. WO3电致变色薄膜离子传输动力过程及其循环稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 152-160. |
| [12] | 赵起, 乔科, 姚勇吉, 陈长, 陈东初, 高彦峰. 基于高电导率的疏水气相SiO2复合凝胶电解质的高性能电致变色器件[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 161-167. |
| [13] | 范宏伟, 李克睿, 侯成义, 张青红, 李耀刚, 王宏志. 多功能电致变色器件:从多器件到单器件集成[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 115-127. |
| [14] | 钟晓岚, 刘雪晴, 刁训刚. 基于氧化钨和氧化镍的电致变色器件研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 128-139. |
| [15] | 方华靖, 赵泽天, 武文婷, 汪宏. 柔性电致变色器件研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 140-151. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||