无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 1396-1404.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230288
所属专题: 【能源环境】热电材料(202312)
李建波1( ), 田震1, 蒋全伟1, 于砺锋1, 康慧君1,2(
), 田震1, 蒋全伟1, 于砺锋1, 康慧君1,2( ), 曹志强1,2, 王同敏1,2
), 曹志强1,2, 王同敏1,2
收稿日期:2023-06-19
修回日期:2023-07-25
出版日期:2023-08-21
网络出版日期:2023-08-21
通讯作者:
康慧君, 教授. E-mail: kanghuijun@dlut.edu.cn作者简介:李建波(1991-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: lijianbo0408@mail.dlut.eud.cn
基金资助:
LI Jianbo1( ), TIAN Zhen1, JIANG Quanwei1, YU Lifeng1, KANG Huijun1,2(
), TIAN Zhen1, JIANG Quanwei1, YU Lifeng1, KANG Huijun1,2( ), CAO Zhiqiang1,2, WANG Tongmin1,2
), CAO Zhiqiang1,2, WANG Tongmin1,2
Received:2023-06-19
Revised:2023-07-25
Published:2023-08-21
Online:2023-08-21
Contact:
KANG Huijun, professor. E-mail: kanghuijun@dlut.edu.cnAbout author:LI Jianbo (1991-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: lijianbo0408@mail.dlut.eud.cn
Supported by:摘要:
CaTiO3是一种新兴的高温氧化物热电材料, 但多种元素掺杂对其微观结构与热电性能的影响规律尚不清晰。本研究采用水热法结合真空热压烧结分别制备了Cr、Nb、Eu、Dy、Ce与La六种不同元素掺杂的CaTiO3多晶块体样品。Cr掺杂导致大量纳米级Cr相析出, 由于基体中施主元素含量过低, 功率因子严重损失, 其ZT仅为0.012(983 K)。Eu掺杂并未为基体提供施主载流子, 导致ZT提升不明显, 仅为0.141(1031 K)。Nb掺杂导致高热导的微米级Nb相析出, 热导率上升, 但基体中Nb含量较多为基体提供了载流子, 使其ZT有明显改善, 达到0.263(1013 K)。Dy、Ce与La掺杂则既提供载流子又作为点缺陷散射声子, 既提高了功率因子又降低了晶格热导率, 极大地提升了热电性能, ZT在1031 K分别达到0.357、0.398、0.329, 比纯CaTiO3(0.096)分别提升了296%、342%、265%。其中, Dy掺杂的样品在整个温度测试范围内具有最低的晶格热导率和较高的功率因子, 通过调控Dy含量与晶界处富集第二相的含量, 可以解耦电和热传输性能, 有望刷新目前CaTiO3的ZT记录。本研究揭示了多种元素掺杂条件下CaTiO3的成分-结构-性能联系, 为其在高温热电领域的应用提供了理论支撑。
中图分类号:
李建波, 田震, 蒋全伟, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 曹志强, 王同敏. 不同元素掺杂对CaTiO3微观结构及热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404.
LI Jianbo, TIAN Zhen, JIANG Quanwei, YU Lifeng, KANG Huijun, CAO Zhiqiang, WANG Tongmin. Effects of Different Element Doping on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of CaTiO3[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404.

图3 不同元素掺杂的CaTiO3(a, b)粉体与(c, d)块体的XRD图谱; (e)纯CaTiO3粉体的SEM照片与(f)块体的EPMA背散图片
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of CaTiO3 (a, b) powders and (c, d) bulks doped with different elements; (e) SEM image of powder and (f) BES image of bulk for the pristine CaTiO3 sample
| Atom | Atomic radius/pm | Ionic radius/pm |
|---|---|---|
| Ca | 174 | 99 (M2+) |
| Ti | 132 | 68 (M4+) |
| Cr | 118 | 84 (M3+) |
| Nb | 134 | 70 (M5+) |
| Dy | 177.3 | 90.8 (M3+) |
| Ce | 182.4 | 103.4 (M3+) |
| La | 187.7 | 106 (M3+) |
表1 不同原子的原子半径与离子半径
Table 1 Atomic radii and ionic radii of different atoms
| Atom | Atomic radius/pm | Ionic radius/pm |
|---|---|---|
| Ca | 174 | 99 (M2+) |
| Ti | 132 | 68 (M4+) |
| Cr | 118 | 84 (M3+) |
| Nb | 134 | 70 (M5+) |
| Dy | 177.3 | 90.8 (M3+) |
| Ce | 182.4 | 103.4 (M3+) |
| La | 187.7 | 106 (M3+) |

图4 (a)Cr20、(b)Nb20、(c)Eu20、(d)Dy20、(e)Ce20与(f)La20粉体的SEM照片以及对应的元素分布图与EDS能谱图
Fig. 4 SEM images, element mappings, and corresponding EDS spectra of (a) Cr20, (b) Nb20, (c) Eu20, (d) Dy20, (e) Ce20, and (f) La20 powders
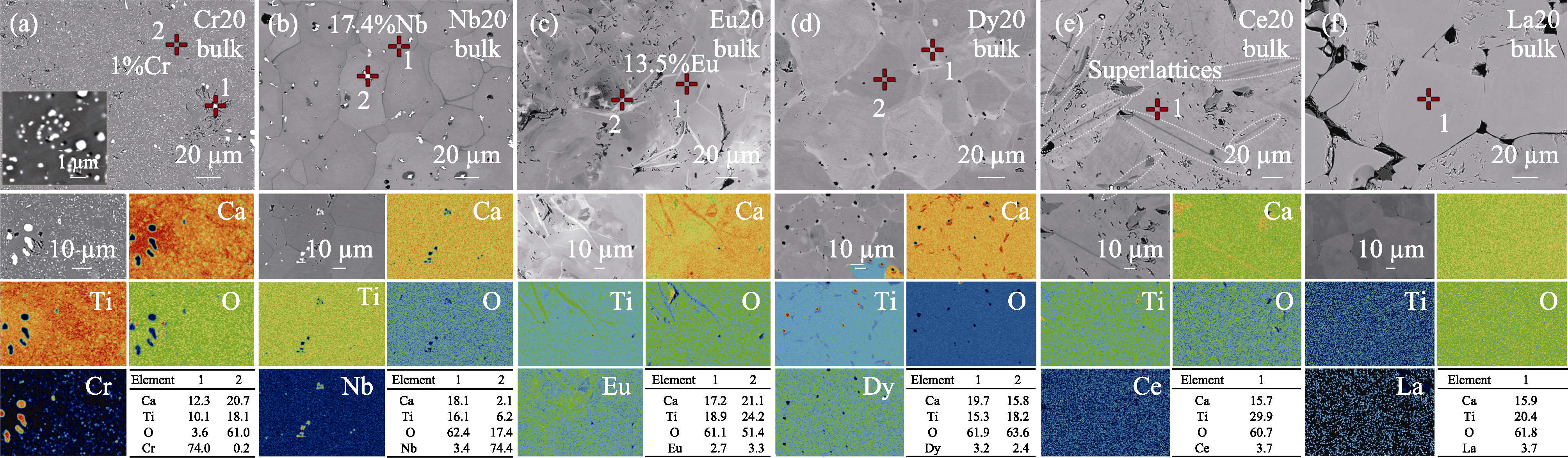
图5 (a)Cr20、(b)Nb20、(c)Eu20、(d)Dy20、(e)Ce20与(f)La20块体的EPMA分析图以及对应元素分布图与点分析结果
Fig. 5 EPMA images, element mappings, and corresponding chemical compositions of (a) Cr20, (b) Nb20, (c) Eu20, (d) Dy20, (e) Ce20, and (f) La20 bulks Unit in tables: % (in atom)
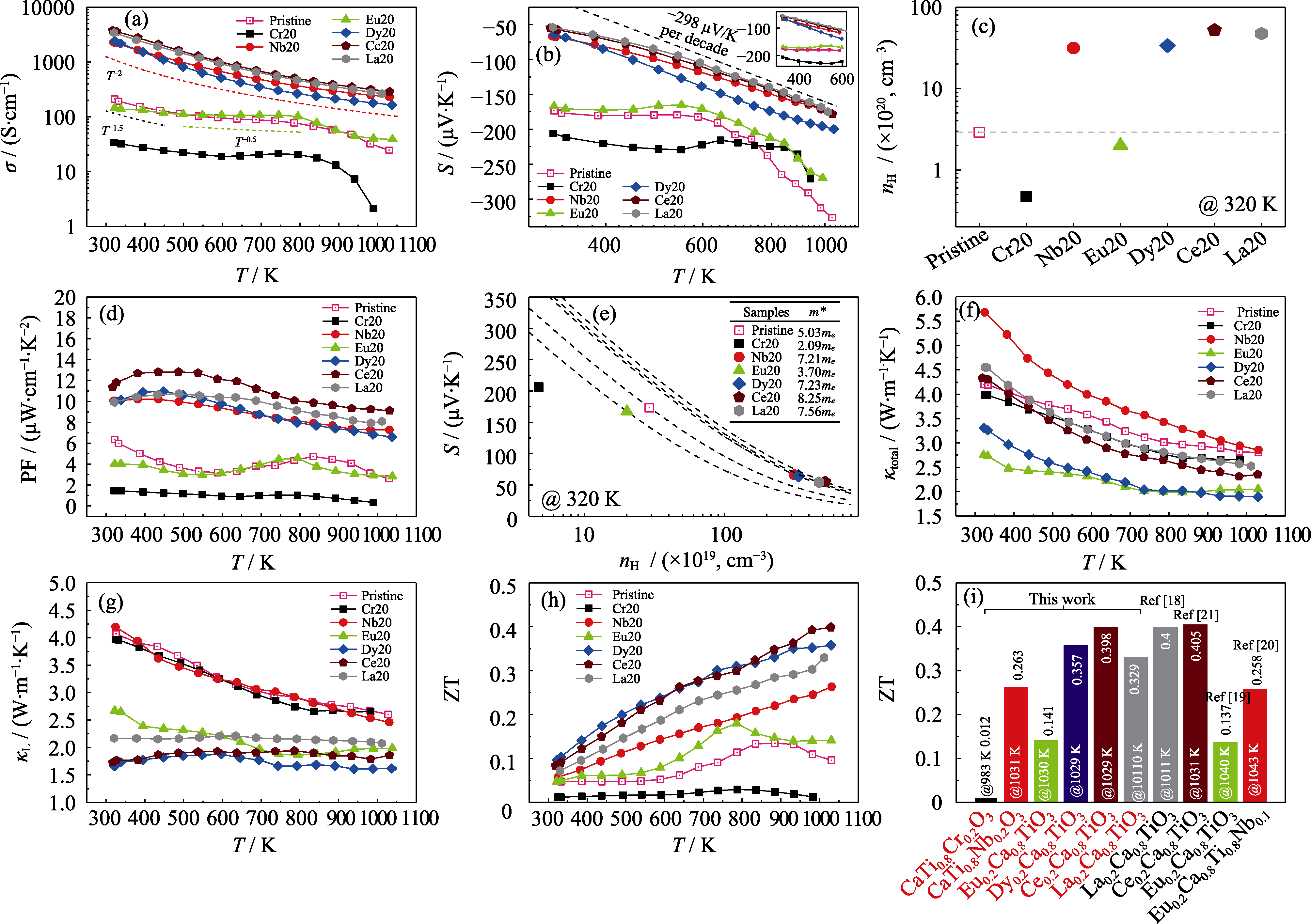
图6 Cr20、Nb20、Eu20、Dy20、Ce20、La20等块体的(a)电导率、(b)塞贝克系数(插图为在300~600 K范围内的放大图)、(d)功率因子、(f) 总热导率、(g) 晶格热导率、(h)热电优值随温度的变化曲线; Cr20、Nb20、Eu20、Dy20、Ce20、La20等块体在320 K的(c)载流子浓度、(e)Pisarenko曲线及(i)与文献[18⇓⇓-21]报道的ZT性能比较
Fig. 6 Temperature-dependence of (a) electrical conductivity, (b) Seebeck coefficient with inset showing enlarged plots in temperature range of 300-600 K, (d) power factor, (f) total thermal conductivity, (g) lattice thermal conductivity, and (h) ZT of Cr20, Nb20, Eu20, Dy20, Ce20, and La20 bulks, and their (c) carrier concentration at 320 K, (e) Pisarenko curves and (i) ZT compared to literature[18⇓⇓-21]
| Chemical composition | Purity | Production factories |
|---|---|---|
| CaCl2 | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| DyCl3·6H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| EuCl3·6H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| La(NO3)3·6H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| CeCl3·7H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| CrCl3 | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| NbCl5 | ≥ 99.9% | Aladdin |
| C16H36O4Ti | ≥ 99% | Aladdin |
| NbCl5 | ≥ 99.9% | Aladdin |
| NaOH | ≥ 99% | Aladdin |
| C2H6O2 | ≥ 95% | Aladdin |
表S1 实验试剂一览表
Table S1 Summary of the raw materials used for experiments
| Chemical composition | Purity | Production factories |
|---|---|---|
| CaCl2 | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| DyCl3·6H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| EuCl3·6H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| La(NO3)3·6H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| CeCl3·7H2O | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| CrCl3 | ≥ 99.99% | Aladdin |
| NbCl5 | ≥ 99.9% | Aladdin |
| C16H36O4Ti | ≥ 99% | Aladdin |
| NbCl5 | ≥ 99.9% | Aladdin |
| NaOH | ≥ 99% | Aladdin |
| C2H6O2 | ≥ 95% | Aladdin |

图S2 纯CaTiO3、Cr20、Nb20、Eu20、Dy20、Ce20与La20样品的(a)扩散系数、(b)比热容、(c) 电子热导率和(d) 洛伦兹常数随温度的变化曲线
Fig. S2 Temperature-dependent (a) thermal diffusion, (b) specific heat, (c) electrical thermal conductivity, and (d) Lorenz constant for pristine for Pristine CaTiO3, Cr20, Nb20, Eu20, Dy20, Ce20, and La20 samples

图S3 CaTi0.8Nb0.2O3(Nb20)经过(a)1400、(b)1450、(c)1500 ℃温度烧结后块体的EPMA背散射图
Fig. S3 EPMA backscattering images of the CaTi0.8Nb0.2O3 (Nb20) bulk sintered at (a) 1400, (b) 1450, and (c) 1500 ℃, respectively

图S4 经过1400、1450、1500 ℃温度烧结后块体的(a)电导率、(b)塞贝克系数、(c)功率因子随温度的变化曲线
Fig. S4 Temperature-dependence of the (a) electrical conductivity, (b) Seebeck coefficient, and (c) power factor of CaTi0.8Nb0.2O3 (Nb20) sintered at (a) 1400, (b) 1450, and (c) 1500 ℃, respectively
| Nominal chemical composition | Composition sample code | Measured density/ (g·cm-3) | Theoretical density/(g·cm-3) | Relative density/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaTiO3 | Pristine | 3.85 | 4.04 | 95.2 |
| CaTi0.8Cr0.2O3 | Cr20 | 3.89 | 4.06 | 95.8 |
| CaTi0.8Nb0.2O3 | Nb20 | 4.07 | 4.30 | 94.6 |
| Eu0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | Eu20 | 4.39 | 4.70 | 93.4 |
| Dy0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | Dy20 | 4.48 | 4.76 | 94.1 |
| Ce0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | Ce20 | 4.40 | 4.63 | 95.0 |
| La0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | La20 | 4.19 | 4.62 | 90.7 |
表S2 所有块体的化学成分、简称、测量密度、理论密度以及致密度
Table S2 Nominal chemical compositions, sample codes, measured densities, theoretical densities, and relative densities of the prepared bulk samples
| Nominal chemical composition | Composition sample code | Measured density/ (g·cm-3) | Theoretical density/(g·cm-3) | Relative density/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaTiO3 | Pristine | 3.85 | 4.04 | 95.2 |
| CaTi0.8Cr0.2O3 | Cr20 | 3.89 | 4.06 | 95.8 |
| CaTi0.8Nb0.2O3 | Nb20 | 4.07 | 4.30 | 94.6 |
| Eu0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | Eu20 | 4.39 | 4.70 | 93.4 |
| Dy0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | Dy20 | 4.48 | 4.76 | 94.1 |
| Ce0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | Ce20 | 4.40 | 4.63 | 95.0 |
| La0.2Ca0.8TiO3 | La20 | 4.19 | 4.62 | 90.7 |
| [1] |
BRENDAN J K, CHRISTOPHER J H, BRYAN C C. Phase transitions in perovskite at elevated temperatures: a powder neutron diffraction study. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 1999, 11(6): 1479.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
SHI J, GUO L. ABO3-based photocatalysts for water splitting. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2012, 22(6): 592.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MANAN A, NAWAZ A, AHMAD A S, et al. Preparation and microwave dielectric properties of CaTiO3added Mg0.95Ni0.05-Ti0.98Zr0.02O3 composite ceramics for high frequency applications. Materials Science-Poland, 37(4): 639.
DOI URL |
| [4] | OLIVEIRA R, SILVA R, DE MORAIS J, et al. Effects of CaTiO3 addition on the microwave dielectric properties and antenna properties of BiVO4 ceramics. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 175: 107122. |
| [5] | SAHOO S, DASH U, PARASHAR S, et al. Frequency and temperature dependent electrical characteristics of CaTiO3nano-ceramic prepared by high-energy ball milling. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2013, 2: 291. |
| [6] |
CAI J, CAO A, HUANG J, et al. Understanding oxygen vacancies in disorder-engineered surface and subsurface of CaTiO3 nanosheets on photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 267: 118378.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MANJUNATH K, G THIMMANNA C. Studies on synthesis, characterization and applications of nano CaTiO3powder. Current Nanomaterials, 2016, 1(2): 145.
DOI URL |
| [8] | PASSI M, PAL B. A review on CaTiO3 photocatalyst: activity enhancement methods and photocatalytic applications. Powder Technology, 2021, 388: 274. |
| [9] | SINGH B K, HAFEEZ M A, KIM H, et al. Inorganic waste forms for efficient immobilization of radionuclides. ACS ES&T Engineering, 2021, 1(8): 1149. |
| [10] |
CHEN Y, LIN Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Dielectric and MLCC property of modified (Sr,Ca)TiO3based energy storage ceramic. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 976.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHOU W M, CHEN Q H, KE M Z, et al. Preparation and properties of CaTiO3:Pr3+/TiO2-mica fluorescent pearlescent pigments. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(12): 1275.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TIAN B Z, JIANG X P, CHEN J, et al. Low lattice thermal conductivity and enhanced thermoelectric performance of SnTe via chemical electroless plating of Ag. Rare Metals, 2022, 41(1): 86.
DOI |
| [13] |
LIU K J, ZHANG Z W, CHEN C, et al. Entropy engineering in CaZn2Sb2-YbMg2Sb2 Zintl alloys for enhanced thermoelectric performance. Rare Metals, 2022, 41(9): 2998.
DOI |
| [14] |
ZHANG R Z, HU X Y, GUO P, et al. Thermoelectric transport coefficients of n-doped CaTiO3, SrTiO3 and BaTiO3: a theoretical study. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2012, 407(7): 1114.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
NOOR N A, ALAY-E-ABBAS S M, HASSAN M, et al. The under-pressure behaviour of mechanical, electronic and optical properties of calcium titanate and its ground state thermoelectric response. Philosophical Magazine, 2017, 97(22): 1884.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHOU H Y, LIU X Q, ZHU X L, et al. CaTiO3 linear dielectric ceramics with greatly enhanced dielectric strength and energy storage density. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(5): 1999.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CAVALCANTE L S, MARQUES V S, SCZANCOSKI J C, et al. Synthesis, structural refinement and optical behavior of CaTiO3 powders: a comparative study of processing in different furnaces. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 143(1): 299.
DOI URL |
| [18] | LI J, WANG Y, YANG X, et al. Processing bulk insulating CaTiO3 into a high-performance thermoelectric material. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131121. |
| [19] | XIAO X, WIDENMEYER M, MUELLER K, et al. A squeeze on the perovskite structure improves the thermoelectric performance of europium calcium titanates. Materials Today Physics, 2018, 7: 96. |
| [20] | XIAO X, XIE W, WIDENMEYER M, et al. Synergistic effects of Eu and Nb dual substitution on improving the thermoelectric performance of the natural perovskite CaTiO3. Materials Today Physics, 2022, 26: 100741. |
| [21] |
LI J, WANG Y, JIANG X, et al. Emerging homogeneous superlattices in CaTiO3bulk thermoelectric materials. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(2): 454.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHI F, QIN Y, ZHOU S, et al. Eu3+-site occupation in CaTiO3 perovskite material at low temperature. Current Applied Physics, 2017, 17(1): 24.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ITO M, MATSUDA T. Thermoelectric properties of non-doped and Y-doped SrTiO3 polycrystals synthesized by polymerized complex process and hot pressing. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 477(1): 473.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG Y, FAN H J. Sr1-xLaxTiO3 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and enhanced thermoelectric response. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65(3): 190.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SHANG P P, ZHANG B P, LI J F, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on thermoelectric properties of La-doped SrTiO3ceramics prepared by Sol-Gel process and spark plasma sintering. Solid State Sciences, 2010, 12(8): 1341.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
KIKUCHI A, OKINAKA N, AKIYAMA T. A large thermoelectric figure of merit of La-doped SrTiO3 prepared by combustion synthesis with post-spark plasma sintering. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63(4): 407.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LI J B, WANG J, LI J F, et al. Broadening the temperature range for high thermoelectric performance of bulk polycrystalline strontium titanate by controlling the electronic transport properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(28): 7594.
DOI URL |
| [28] | WANG J, ZHANG B Y, KANG H J, et al. Record high thermoelectric performance in bulk SrTiO3 via nano-scale modulation doping. Nano Energy, 2017, 35: 387. |
| [29] |
LU Z, ZHANG H, LEI W, et al. High-figure-of-merit thermoelectric La-doped A-site-deficient SrTiO3 ceramics. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(3): 925.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
KIMIJIMA T, KANIE K, NAKAYA M, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of size- and shape-controlled CaTiO3 fine particles and their photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm, 2014, 16(25): 5591.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
FU B G, YANG J C, GAO Z K, et al. Hot pressing sintering process and sintering mechanism of W-La2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2. Rare Metals, 2021, 40(7): 1949.
DOI |
| [32] | KIM Y J, ZHAO L D, KANATZIDIS M G, et al. Analysis of nanoprecipitates in a Na-doped PbTe-SrTe thermoelectric material with a high figure of merit. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(26): 21791. |
| [33] |
MOOS R, GNUDI A, HÄRDTL K H. Thermopower of Sr1-xLaxTiO3 ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 1995, 78(8): 5042.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
KIM H S, GIBBS Z M, TANG Y, et al. Characterization of Lorenz number with Seebeck coefficient measurement. APL Materials, 2015, 3(4): 041506.
DOI URL |
| [35] | SINGARAVELU S, KLOPF J, KRAFFT G, et al. Laser nitriding of niobium for application to superconducting radio-frequency accelerator cavities. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 2011, 29(6): 061803. |
| [36] |
COOK B A, KRAMER M J, HARRINGA J L, et al. Analysis of nanostructuring in high figure-of-merit Ag1-xPbmSbTe2+m thermoelectric materials. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(8): 1254.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 吴爽, 苟燕子, 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德. 高温热处理对国产KD-SA型SiC纤维组成结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [2] | 吴东江, 赵紫渊, 于学鑫, 马广义, 由竹琳, 任冠辉, 牛方勇. Al2O3-TiCp复相陶瓷激光定向能量沉积直接增材制造[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192. |
| [3] | 吴西士, 朱云洲, 黄庆, 黄政仁. 树脂基多孔碳孔结构对Cf/SiC复合材料连接性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280. |
| [4] | 黄新友, 刘玉敏, 刘洋, 李晓英, 冯亚刚, 陈肖朴, 陈鹏辉, 刘欣, 谢腾飞, 李江. 醇水共沉淀法制备Yb:YAG透明陶瓷及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 217-224. |
| [5] | 宋可可, 黄浩, 鲁梦婕, 杨安春, 翁杰, 段可. 水热制备锌、硅、镁、铁等元素掺杂羟基磷灰石及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [6] | 张俊敏, 陈小武, 廖春景, 郭斐宇, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. SiCf/SiC复合材料的RMI制备方法以及微观结构和性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1103-1110. |
| [7] | 朱丹阳, 钱康, 陈肖朴, 胡泽望, 刘欣, 李晓英, 潘裕柏, MIHÓKOVÁ Eva, NIKL Martin, 李江. 热等静压烧结制备细晶粒Ce,Y:SrHfO3闪烁陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1118-1124. |
| [8] | 康慧君,张校影,王燕遐,李建波,杨雄,刘达权,杨泽荣,王同敏. 变价稀土元素Eu掺杂BiCuSeO热电性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1041-1046. |
| [9] | 董少杰,王旭东,沈国芳,王晓虹,林开利. 生物陶瓷支架的功能改性及应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 867-881. |
| [10] | 吴小军,杨杰,郑蕊,张兆甫,杨毅. 烧蚀型面结构对CVI+HPIC工艺制备针刺C/C喉衬等离子烧蚀性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 654-660. |
| [11] | 董丽佳, 郭筱洁, 李雪, 陈朝贵, 金阳, AHMED Alsaedi, TASAWAr Hayat, 赵轻舟, 盛国栋. 不同pH条件下硫化钼纳米片吸附Cd(II)的微观机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 293-300. |
| [12] | 徐维民, 李世波, 胡树郡, 姜吉鹏, 于文波, 周洋. ZrC/Cr2AlC复合材料的微观结构及力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 61-64. |
| [13] | 焦思怡, 葛万银, 殷立雄, 徐美美, 常哲, 张荔. 新型二维TiSe2纳米片的可控合成及其生长机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 834-838. |
| [14] | 吴青青, 王震, 丁奇, 倪德伟, 阚艳梅, 董绍明. 基于固体聚硅氧烷的前驱体浸渍裂解法(PIP)制备C/SiOC复合材料及其微结构与力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(12): 1349-1356. |
| [15] | 刘大锐. 非金属S掺杂对NaTaO3可见光下光催化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 409-415. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||