无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 1466-1474.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230215
所属专题: 【能源环境】锂离子电池(202312)
收稿日期:2023-05-05
修回日期:2023-06-25
出版日期:2023-07-28
网络出版日期:2023-07-28
通讯作者:
万 勇, 教授. E-mail: wanyongqd@hotmail.com;作者简介:谭淑雨(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: tsy1576362772@163.com
TAN Shuyu( ), LIU Xiaoning, BI Zhijie, WAN Yong(
), LIU Xiaoning, BI Zhijie, WAN Yong( ), GUO Xiangxin(
), GUO Xiangxin( )
)
Received:2023-05-05
Revised:2023-06-25
Published:2023-07-28
Online:2023-07-28
Contact:
WAN Yong, professor. E-mail: wanyongqd@hotmail.com;About author:TAN Shuyu (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: tsy1576362772@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
聚氧化乙烯(PEO)基固体电解质具有成本低、对锂稳定、易于大规模生产等优点, 是固态锂电池最有前途的固体电解质。然而, PEO对高压正极不稳定, 严重限制了其在高能量密度领域的应用。本研究在LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 (NCM)正极颗粒上部分包覆环化聚丙烯腈(cPAN)纳米层作为电子导电层, 在NCM/PEO界面上引入离子液体作为离子导电通道, 用以提高PEO与高压NCM正极的相容性。其中, cPAN层不仅在物理上隔离了PEO电解质与NCM正极的直接接触, 而且cPAN中具有非局域的sp2 π键, 有助于正极内部的电子传输。同时, 高离子电导率的离子液体的流动性较高, 可以充分润湿正极侧界面, 并在循环过程中分解为富LiF和Li3N的CEI层, 进一步限制PEO电解质的氧化分解。基于上述复合策略的固态NCM/Li电池可在0.1C (1C=0.18 A·g-1), 4.30 V截止电压下稳定循环100次, 且容量保持率可达85.3%。本研究通过表面包覆和界面修饰, 为提高PEO基电解质对高压正极的稳定性提供了可行方案。
中图分类号:
谭淑雨, 刘晓宁, 毕志杰, 万勇, 郭向欣. 正极包覆与界面修饰: 双策略改善聚氧化乙烯固态电解质对高电压正极稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1466-1474.
TAN Shuyu, LIU Xiaoning, BI Zhijie, WAN Yong, GUO Xiangxin. Jointing of Cathode Coating and Interface Modification for Stabilizing Poly(ethylene oxide) Electrolytes Against High-voltage Cathodes[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1466-1474.

Fig. 1 (a) Preparation process of NCM@cPAN powder, (b) schematic representation of as-prepared NCM@cPAN particle, and (c) schematic diagram of the solid-state NCM@cPAN+IL/PEO/Li cell

Fig. 2 (a) FT-IR spectra of pristine PAN and PAN treated at 400 ℃, (b) schematic diagrams of pristine PAN and cPAN, and (c) Raman spectra of PAN, cPAN, NCM, and NCM@cPAN
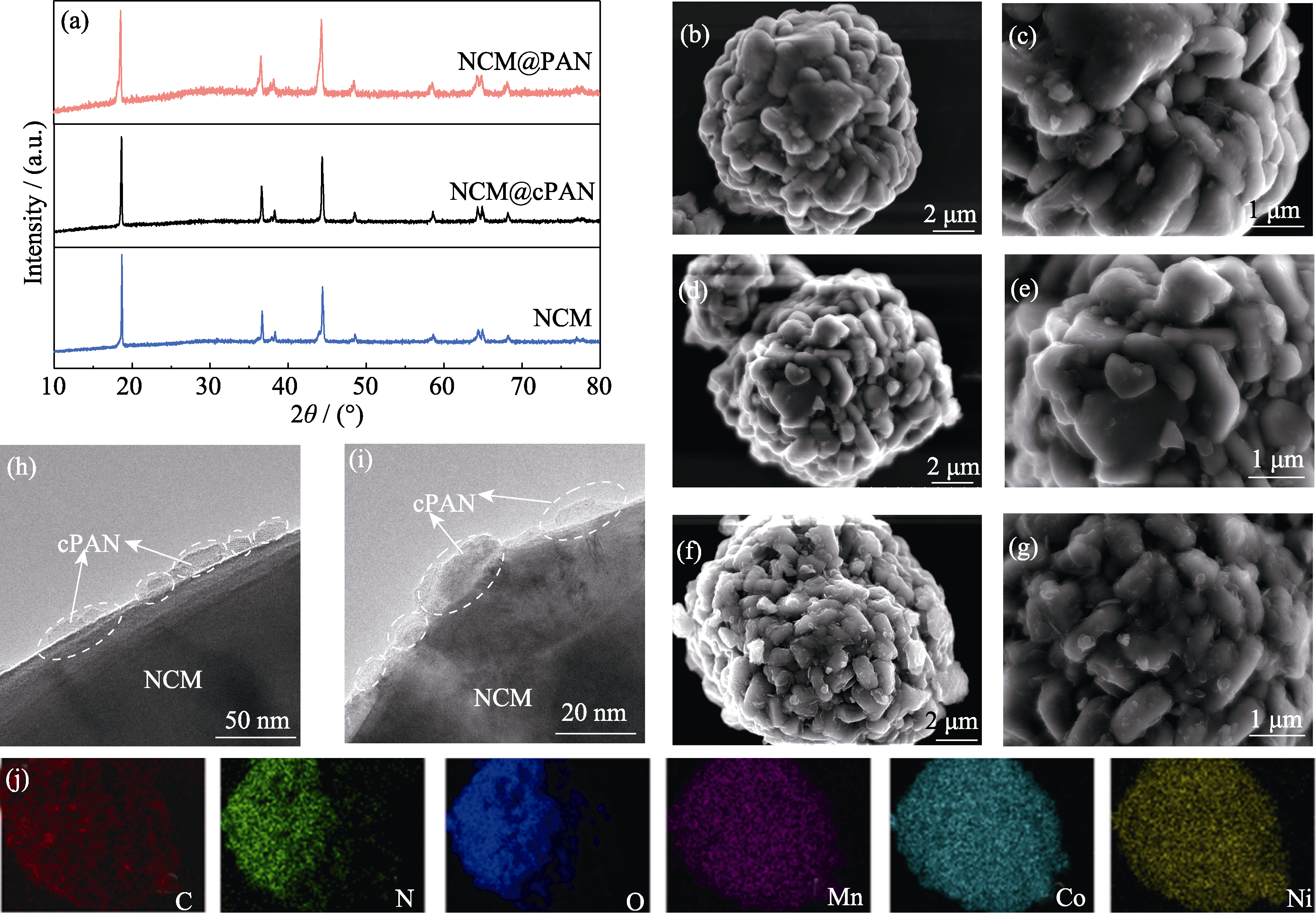
Fig. 3 (a) XRD patterns of NCM, NCM@PAN, and NCM@cPAN powders; SEM images of (b, c) NCM, (d, e) NCM@PAN, and (f, g) NCM@cPAN powders; (h, i) TEM images of NCM@cPAN; (j) EDS mappings of C, N, O, Mn, Co and Ni elements of the region in (f)

Fig. 4 Cycling performance of solid-state NCM@cPAN+IL/PEO/Li batteries Typical charge-discharge curves and the corresponding specific capacities with cutoff voltages of (a, d) 4.20 V, (b, e) 4.25 V, and (c, f) 4.30 V

Fig. 5 (a) Charge-discharge curves, and (b) corresponding specific capacities for solid-state NCM@cPAN+IL/PEO/Li batteries at various current densities; (c) Typical charge-discharge curves and (d) corresponding specific capacities and Coulombic efficiency for solid-state NCM@cPAN+IL/PEO/Li batteries with high cathode loading of ~6.2 mg·cm-2
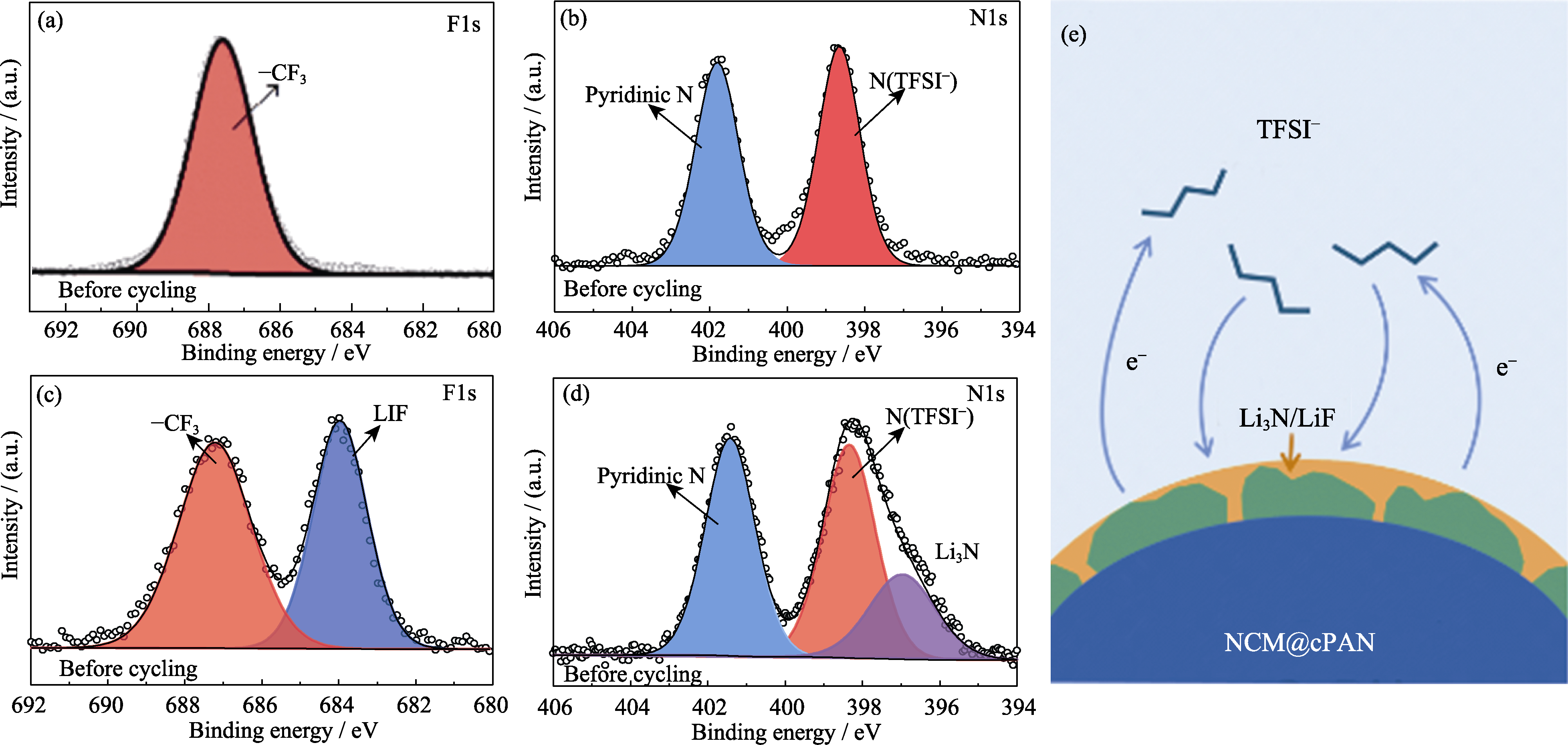
Fig. 6 (a, c) F1s and (b, d) N1s XPS spectra of PP13-TFSI (a, b) before and (c, d) after cycling; (e) Schematic diagram of TFSI− decomposition during cycling

Fig. 7 (a) FT-IR spectra of PEO electrolyte before and after cycling; SEM images of NCM@cPAN cathodes (b) before and (c) after cycling; (d) Ni2p XPS spectra of NCM@cPAN cathode before and after cycling

Fig. S4 Rate performance of solid NCM@cPAN+IL/PEO/Li batteries at various current densities (a, c) Typical charge-discharge curves and (b, d) corresponding specific capacities with the cutoff voltages of (a, b) 4.25 V, and (c, d) 4.30 V
| [1] |
CHENG X B, ZHANG R, ZHAO C Z, et al. Toward safe lithium metal anode in rechargeable batteries: a review. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(15): 10403.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LIU J, BAO Z, CUI Y, et al. Pathways for practical high-energy long-cycling lithium metal batteries. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(3): 180.
DOI |
| [3] |
MA G, GUO L, DING X, et al. Effect of dual-functional electrolyte additive on high temperature and high voltage performance of Li-ion battery. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 710.
DOI |
| [4] | XU H, SHI J, HU G, et al. Hybrid electrolytes incorporated with dandelion-like silane-Al2O3 nanoparticles for high-safety high- voltage lithium ion batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 391: 113. |
| [5] | COMMARIEU B, PAOLELLA A, DAIGLE J C, et al. Toward high lithium conduction in solid polymer and polymer-ceramic batteries. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2018, 9: 56. |
| [6] |
LI Y, MAO J, WEI C, et al. In-situ modification of carbon nanotubes with metallic bismuth nanoparticles for uniform lithium deposition. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1337.
DOI URL |
| [7] | WANG J, GE B, LI H, et al. Challenges and progresses of lithium-metal batteries. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 129739. |
| [8] | ZHANG H, DAI R, ZHU S, et al. Bimetallic nitride modified separator constructs internal electric field for high-performance lithium-sulfur battery. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132454. |
| [9] |
WEN Z, LIANG F. MOF/poly(ethylene oxide) composite polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium battery. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 332.
DOI |
| [10] |
FAN L, WEI S, LI S, et al. Recent progress of the solid-state electrolytes for high-energy metal-based batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(11): 1702657.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LIN D, YUEN P Y, LIU Y, et al. A silica-aerogel-reinforced composite polymer electrolyte with high ionic conductivity and high modulus. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(32): 1802661.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHAO Y, ZHENG K, SUN X. Addressing interfacial issues in liquid-based and solid-state batteries by atomic and molecular layer deposition. Joule, 2018, 2(12): 2583.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WU J, RAO Z, CHENG Z, et al. Ultrathin, flexible polymer electrolyte for cost-effective fabrication of all-solid-state lithium metal batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(46): 1902767.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CHEN R, LI Q, YU X, et al. Approaching practically accessible solid-state batteries: stability issues related to solid electrolytes and interfaces. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(14): 6820.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
WAN Z, LEI D, YANG W, et al. Low resistance-integrated all- solid-state battery achieved by Li7La3Zr2O12 nanowire upgrading polyethylene oxide (PEO) composite electrolyte and PEO cathode binder. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(1): 1805301.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
BALAISH M, GONZALEZ-ROSILLO J C, KIM K J, et al. Processing thin but robust electrolytes for solid-state batteries. Nature Energy, 2021, 6(3): 227.
DOI |
| [17] |
LIU X Y, LIU B D, JIANG Y N, et al. In-situ synthesis of perovskite SrTiO3 nanostructures with modified morphology and tunable optical absorption property. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 65.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
NIE K, WANG X, QIU J, et al. Increasing poly(ethylene oxide) stability to 4.5 V by surface coating of the cathode. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(3): 826.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HUO H, CHEN Y, LUO J, et al. Rational design of hierarchical “ceramic-in-polymer” and “polymer-in-ceramic” electrolytes for dendrite-free solid-state batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(17): 1804004.
DOI URL |
| [20] | YANG X, JIANG M, GAO X, et al. Determining the limiting factor of the electrochemical stability window for PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes: main chain or terminal -OH group? Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(5): 1318. |
| [21] | YANG Q, HUANG J, LI Y, et al. Surface-protected LiCoO2 with ultrathin solid oxide electrolyte film for high-voltage lithium ion batteries and lithium polymer batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 388: 65. |
| [22] |
LIANG J, SUN Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Engineering the conductive carbon/PEO interface to stabilize solid polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state high voltage LiCoO2 batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(5): 2769.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
XU H, CHIEN P H, SHI J, et al. High-performance all-solid-state batteries enabled by salt bonding to perovskite in poly(ethylene oxide). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(38): 18815.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
WANG Y, LIU B N, ZHOU G, et al. Improved electrochemical performance of Li(Ni0.6Co0.2Mn0.2)O2 at high charging cut-off voltage with Li1.4Al0.4Ti1.6(PO4)3 surface coating. Chinese Physics B, 2019, 28(6): 068202.
DOI |
| [25] |
QIU J, YANG L, SUN G, et al. A stabilized PEO-based solid electrolyte via a facile interfacial engineering method for a high voltage solid-state lithium metal battery. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(42): 5633.
DOI URL |
| [26] | FENG W, LI J, LIU H, et al. In-situ modification of ultrathin and uniform layer on LiCoO2 particles for 4.2 V polyethylene oxide based solid-state lithium batteries with excellent cycle performance. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 421: 140473. |
| [27] | LI Z, LI A, ZHANG H, et al. Interfacial engineering for stabilizing polymer electrolytes with 4 V cathodes in lithium metal batteries at elevated temperature. Nano Energy, 2020, 72: 104655. |
| [28] | FU F, ZHENG Y, JIANG N, et al. A dual-salt PEO-based polymer electrolyte with cross-linked polymer network for high-voltage lithium metal batteries. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 137776. |
| [29] |
ZHOU W, WANG Z, PU Y, et al. Double-layer polymer electrolyte for high-voltage all-solid-state rechargeable batteries. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(4): 1805574.
DOI URL |
| [30] | SUN Y, DONG H, XU Y, et al. Incorporating cyclized- polyacrylonitrile with Li4Ti5O12 nanosheet for high performance lithium ion battery anode material. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 246: 106. |
| [31] | SUN X L, LIU Z, CHENG Z L. Design and fabrication of in-situ N-doped paper-like carbon nanofiber film for thiophene removal from a liquid model fuel. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 121879. |
| [32] | HONG Y, HU Q, DONG H, et al. N-doped carbon coated porous hierarchical MnO microspheres as superior additive-free anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Scripta Materialia, 2022, 211: 114495. |
| [33] | HAMEDANI A A, OW-YANG C W, HAYAT SOYTAS S. Silicon nanocrystals-embedded carbon nanofibers from hybrid polyacrylonitrile-TEOS precursor as high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 909: 164734. |
| [34] | FENG W, LIU H, ZHAO M, et al. Improving interfacial stability by in situ protective layer formation in 4.2 V poly(ethylene oxide) based solid state lithium batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 523: 231062. |
| [35] | XIE Z, WU Z, AN X, et al. 2-Fluoropyridine: a novel electrolyte additive for lithium metal batteries with high areal capacity as well as high cycling stability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 393: 124789. |
| [36] | CHEN K, SUN Y, ZHAO C, et al. A semi-interpenetrating network polymer electrolyte membrane prepared from non-self- polymerized precursors for ambient temperature all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2021, 296: 121958. |
| [37] |
YAN C, YAO Y X, CHEN X, et al. Lithium nitrate solvation chemistry in carbonate electrolyte sustains high-voltage lithium metal batteries. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(43): 14055.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
LI T, ZHANG X Q, SHI P, et al. Fluorinated solid-electrolyte interphase in high-voltage lithium metal batteries. Joule, 2019, 3(11): 2647.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
POLU A R, RHEE H W. Ionic liquid doped PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion polymer batteries. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(10): 7212.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
SONG G, ZHONG H, WANG Z, et al. Interfacial film Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7PO4-coated LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 for the long cycle stability of lithium-ion batteries. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(11): 7923.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 夏求应, 孙硕, 昝峰, 徐璟, 夏晖. 非晶LiSiON薄膜电解质的全固态薄膜锂电池性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 230-236. |
| [2] | 梁凤青, 温兆银. 固态锂电池用MOF/聚氧化乙烯复合聚合物电解质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 332-336. |
| [3] | 柯剑煌, 谢凯, 韩喻, 孙巍巍, 罗世强, 刘锦锋. 基于不同共溶剂体系对于高电压正极材料LiCoPO4的形貌控制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 618-624. |
| [4] | 杜付明, 赵宁, 方锐, 崔忠慧, 李忆秋, 郭向欣. 电子导电剂对石榴石基固态锂电池循环性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 462-468. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||