无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1323-1330.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230169
王烨1,3( ), 焦忆楠3, 郭军霞2, 刘欢3, 李睿3, 尚子璇1, 张士东4, 王永浩4, 耿海川4, 侯登录2, 赵晋津1(
), 焦忆楠3, 郭军霞2, 刘欢3, 李睿3, 尚子璇1, 张士东4, 王永浩4, 耿海川4, 侯登录2, 赵晋津1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-06
修回日期:2023-06-30
出版日期:2023-07-28
网络出版日期:2023-07-28
通讯作者:
赵晋津, 教授. E-mail: jinjinzhao2012@163.com作者简介:王 烨(1995-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: yestruggle20@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Ye1,3( ), JIAO Yinan3, GUO Junxia2, LIU Huan3, LI Rui3, SHANG Zixuan1, ZHANG Shidong4, WANG Yonghao4, GENG Haichuan4, HOU Denglu2, ZHAO Jinjin1(
), JIAO Yinan3, GUO Junxia2, LIU Huan3, LI Rui3, SHANG Zixuan1, ZHANG Shidong4, WANG Yonghao4, GENG Haichuan4, HOU Denglu2, ZHAO Jinjin1( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Revised:2023-06-30
Published:2023-07-28
Online:2023-07-28
Contact:
ZHAO Jinjin, professor. E-mail: jinjinzhao2012@163.comAbout author:About author: WANG Ye (1995-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: yestruggle20@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
有机-无机杂化钙钛矿太阳能电池(PSCs)具有高能量转换效率、低能耗和低成本等优点, 但PSCs界面缺陷引起的非辐射复合严重阻碍了其光电转换性能提升。本研究通过降低氧化镍空穴传输层的粒径尺寸, 提高粒径均匀性, 实现了光生空穴在电池界面的高效传输; 并通过优化钙钛矿薄膜的反溶剂作用时间提升结晶质量, 降低界面非辐射复合, 改善空穴传输层和钙钛矿的界面问题, 使钙钛矿太阳能电池的能量转换效率(PCE)从10.11%提高到18.37%。开尔文探针力显微镜(KPFM)研究表明, 界面优化后的钙钛矿薄膜在亮态下的表面接触电位差相比于暗态下增加了120.39 mV。采用压电力原子力显微镜(PFM)分析钙钛矿薄膜明暗态铁电性能, 发现界面优化后的钙钛矿铁电极化变化微弱, 说明优化界面有效降低了电池界面缺陷和迟滞效应。该研究结果表明, 优化氧化镍空穴传输层, 提高钙钛矿薄膜质量, 减少了界面缺陷, 降低了非辐射复合和电池迟滞效应, 提高了钙钛矿太阳能电池的能量转换效率。
中图分类号:
王烨, 焦忆楠, 郭军霞, 刘欢, 李睿, 尚子璇, 张士东, 王永浩, 耿海川, 侯登录, 赵晋津. 钙钛矿太阳能电池界面工程优化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1323-1330.
WANG Ye, JIAO Yinan, GUO Junxia, LIU Huan, LI Rui, SHANG Zixuan, ZHANG Shidong, WANG Yonghao, GENG Haichuan, HOU Denglu, ZHAO Jinjin. Optimization of Interfacial Engineering of Perovskite Solar Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1323-1330.
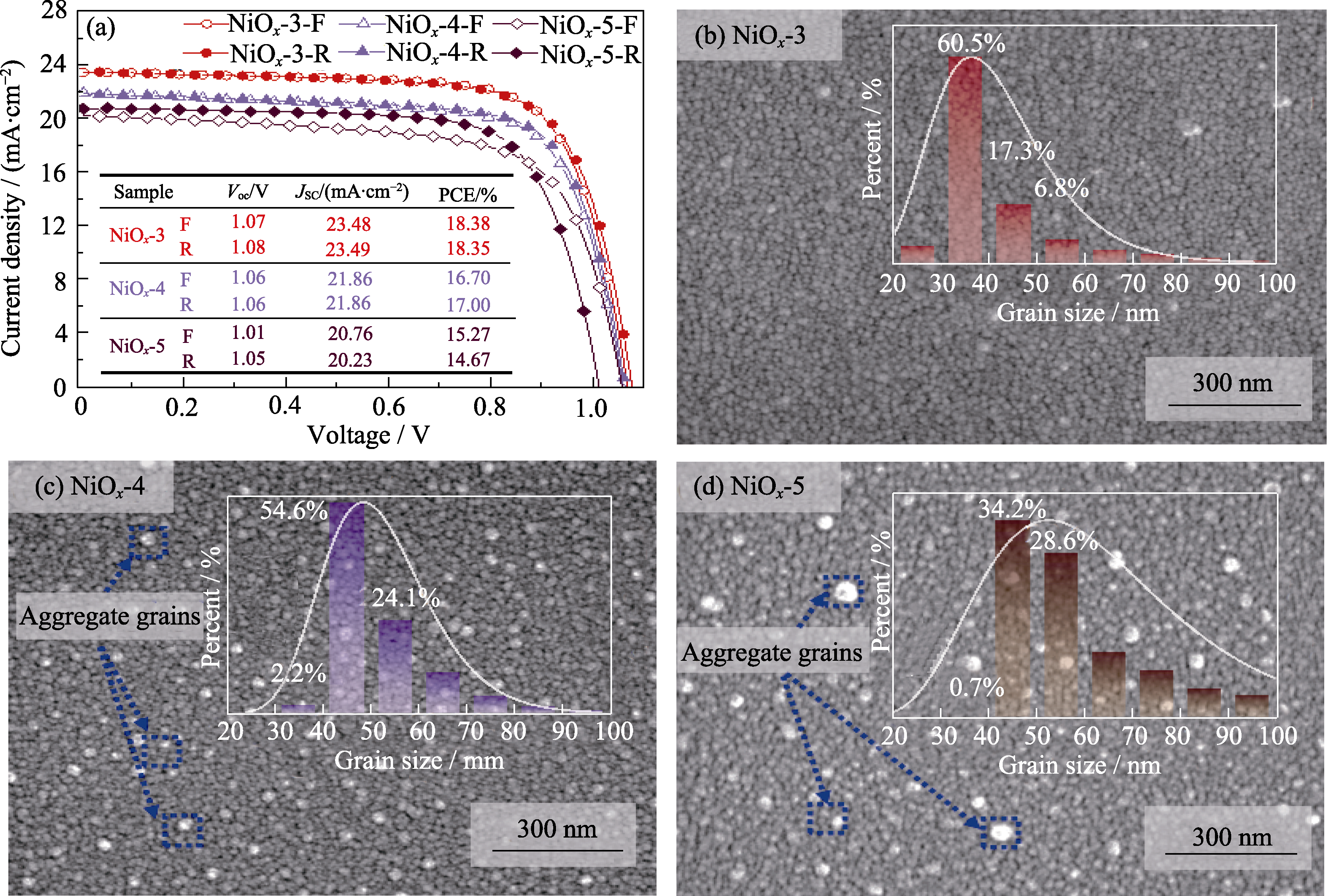
图1 NiOx-3、NiOx-4、NiOx-5钙钛矿太阳能电池的(a) J-V曲线和(b~d)相应钙钛矿薄膜的SEM形貌
Fig. 1 (a) J-V curves of PSCs and (b-d) SEM morphologies for NiOx-3, NiOx-4 and NiOx-5 “F” and “R” refer to forward scanning and reverse scanning, respectively
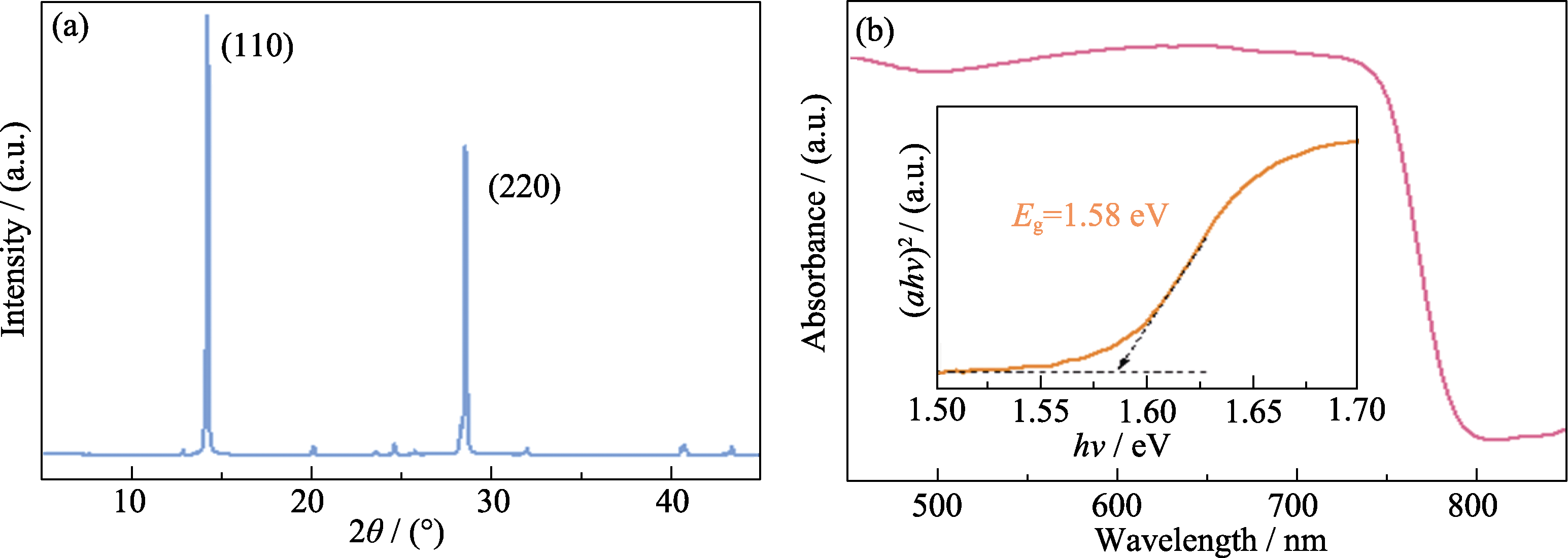
图3 钙钛矿薄膜的晶体结构和光学性能
Fig. 3 Crystal structure and absorbance characterization of perovskite film (a)XRD pattern of MAPbI3 film; (b) UV-Vis absorption spectrum and Tauc plot of MAPbI3 film
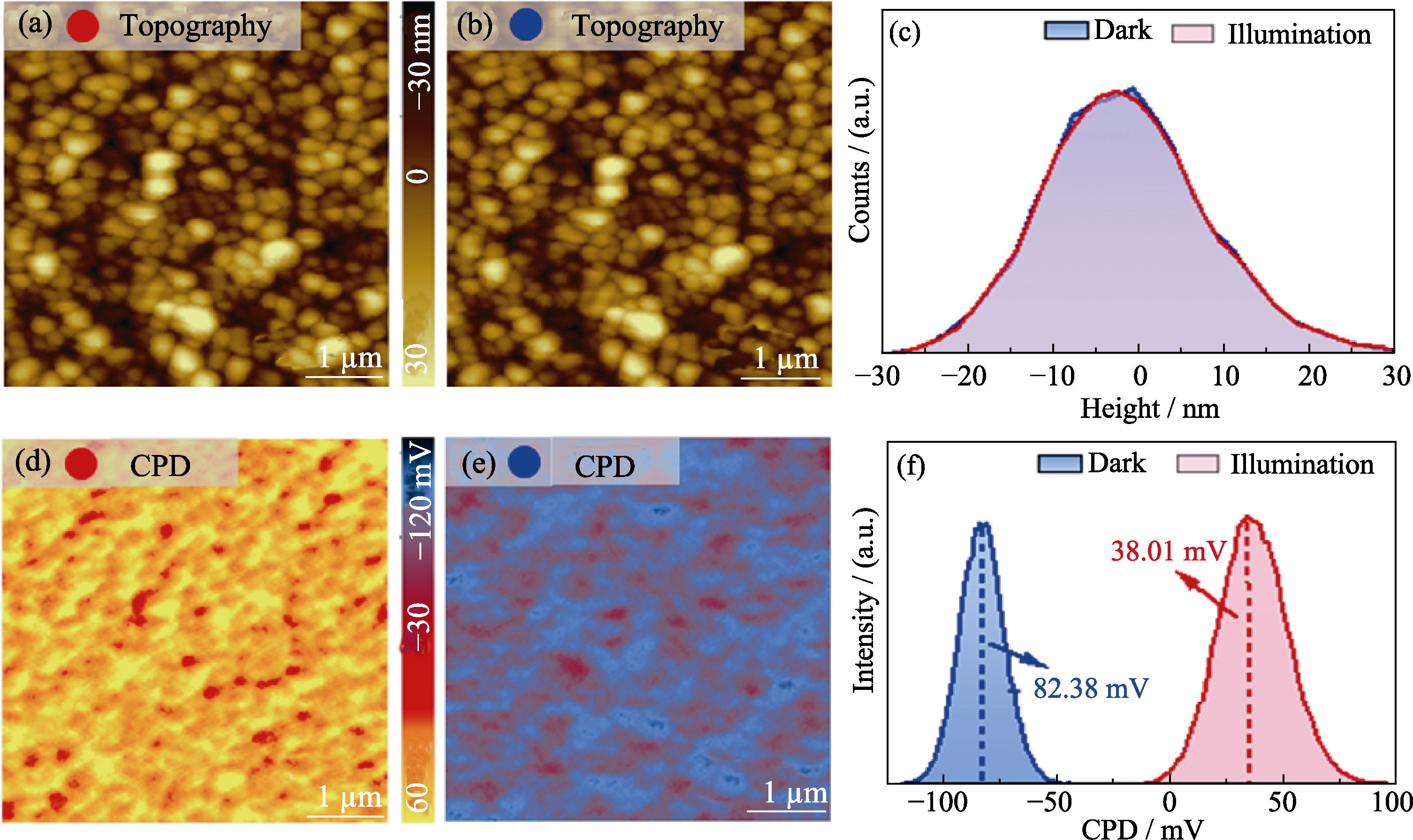
图4 PTF-15 MAPbI3薄膜在亮态和暗态条件下的形貌和接触电位差
Fig. 4 Morphologies and contact potential difference of PTF-15 MAPbI3 films under illumination and dark conditions. (a, b) Morphologies of MAPbI3 film under (a) illumination and (b) dark conditions; (c) Height distributions of MAPbI3 morphology under illumination and dark conditions; (d, e) CPD maps of MAPbI3 morphologies under (d) illumination and (e) dark; (f) Potential statistical diagram of CPD. Colorful figures are available on website
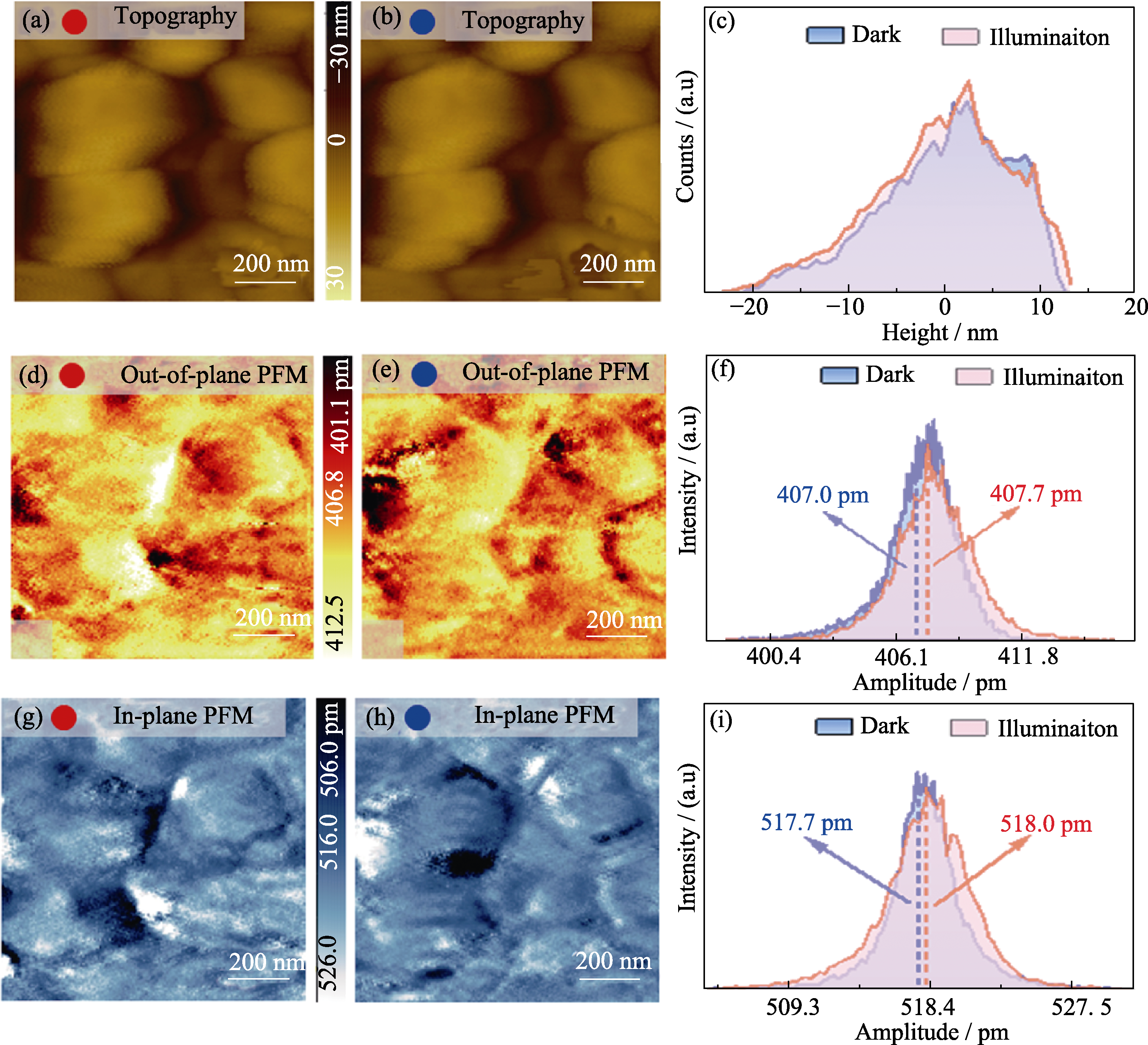
图5 PTF-15 MAPbI3薄膜在亮态和暗态条件下原位的形貌和面外、面内铁电极性
Fig. 5 In-situ characterization of the out-of-plane and in-plane ferroelectric polarization of PTF-15 MAPbI3 films under illumination and dark conditions (a, b) Morphologies of MAPbI3 film under (a) illumination and (b) dark conditions; (c) Height distributions of MAPbI3 morphologies under illumination and dark conditions; (d, e) Out-of-plane ferroelectric polarization images under (d) illumination and (e) dark conditions; (f) Out-of-plane ferroelectric polarization distributions of the topography under illumination and dark conditions; (g, h) In-plane ferroelectric polarization images under (g) illumination and (h) dark conditions; (i) In-plane ferroelectric polarization distributions of MAPbI3 film under illumination and dark conditions. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] |
HE C L, MENG Z Q, REN S X, et al. Water-ultrastable perovskite CsPbBr3 nanocrystals for fluorescence-enhanced cellular imaging. Rare Metals, 2023, 42: 1624.
DOI |
| [2] | 杨帅, 徐瑜歆, 郝子坤, 等. 高效医学传感钙钛矿材料研究进展. 物理化学学报, 2023, 39(5): 2211025. |
| [3] | 任书霞, 杨铮, 安帅领, 等. 高效光电调控钙钛矿量子点阻变存储性能. 物理化学学报, 2023, 39(12): 2301033. |
| [4] |
LIU X, REN S, LI Z, et al. Flexible transparent high-efficiency photoelectric perovskite resistive switching memory. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(38): 2202951.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
JIA C, ZHAO X, LAI Y, et al. Highly flexible, robust, stable and high efficiency perovskite solar cells enabled by van der Waals epitaxy on mica substrate. Nano Energy, 2019, 60: 476.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG P, ZHAO J, LIU J, et al. Stabilization of organometal halide perovskite films by SnO2 coating with inactive surface hydroxyl groups on ZnO nanorods. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 339: 51.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
REN S, SUN G, ZHAO J, et al. Electric field-induced magnetic switching in Mn: ZnO film. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(23): 232406.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHAO J, SALLARD S, SMARSLY B M, et al. Photocatalytic performances of mesoporous TiO2 films doped with gold clusters. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2010, 20(14): 2831.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHAO J, SU X, MI Z, et al. Trivalent Ni oxidation controlled through regulating lithium content to minimize perovskite interfacial recombination. Rare Metals, 2022, 41(1): 96.
DOI |
| [10] |
KIM M, JEONG J, LU H, et al. Conformal quantum dot-SnO2 layers as electron transporters for efficient perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 375(6578): 302.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
BURSCHKA A J, PELLET N, MOON S J, et al. Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature, 2013, 499(7458): 316.
DOI |
| [12] |
CHEN W, WU Y, YUE Y, et al. Efficient and stable large-area perovskite solar cells with inorganic charge extraction layers. Science, 2015, 350(6263): 944.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 查吴送, 张连萍, 文龙, 等. 溶剂工程调控钙钛矿薄膜中PbI2和PbI2(DMSO)的形成. 物理化学学报, 2022, 38(2): 2003022. |
| [14] |
DONG Q, FANG Y, SHAO Y, et al. Electron-hole diffusion lengths>175 μm in solution-grown CH3NH3PbI3 single crystals. Science, 2015, 347(6225): 967.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
XING G, MATHEWS N, SUN S, et al. Long-range balanced electron-and hole-transport lengths in organic-inorganic CH3NH3PbI3. Science, 2013, 342(6156): 344.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHAO J, KONG G, CHEN S, et al. Single crystalline CH3NH3PbI3 self-grown on FTO/TiO2 substrate for high efficiency perovskite solar cells. Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(17): 1173.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DE QUILETTES D W, VORPAHL S M, STRANKS S D, et al. Impact of microstructure on local carrier lifetime in perovskite solar cells. Science, 2015, 348(6235): 683.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEHRENFENNIG C, EPERON G E, JOHNSTON M B, et al. High charge carrier mobilities and lifetimes in organolead trihalide perovskites. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(10): 1584.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YUAN Y, HUANG J. Ion migration in organometal trihalide perovskite and its impact on photovoltaic efficiency and stability. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016, 49(2): 286.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
STOUMAPOS C C, MALLOAKAS C D, KANATZIDIS M. Semiconducting tin and lead iodide perovskites with organic cations: phase transitions, high mobilities, and near-infrared photoluminescent properties. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(15): 9019.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
JIANG Y, WANG X, PAN A. Properties of excitons and photogenerated charge carriers in metal halide perovskites. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(47): 1806671.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
JIAO Y, YI S, WANG H, et al. Strain engineering of metal halide perovskites on coupling anisotropic behaviors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(4): 2006243.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
QIN S, YI S, XU Y, et al. Ferroic alternation in methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite. EcoMat, 2021, 3(5): e12131.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHAO J, WEI L, JIA C, et al. Metallic tin substitution of organic lead perovskite films for efficient solar cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(41): 20224.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHOI J, HAN J S, HONG K, et al. Organic-inorganic hybrid halide perovskites for memories, transistors, and artificial synapses. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(42): 1704002.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PARK J, KIM J, YUN H S, et al. Controlled growth of perovskite layers with volatile alkylammonium chlorides. Nature, 2023, 616(7958): 724.
DOI |
| [27] |
WANG Y, WU T, BARBAUD J, et al. Stabilizing heterostructures of soft perovskite semiconductors. Science, 2019, 365(6454): 687.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
WANG B, ZHANG M, CUI X, et al. Unconventional route to oxygen-vacancy-enabled highly efficient electron extraction and transport in perovskite solar cells. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(4): 1611.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHANG C, WANG Z, YUAN S, et al. Polarized ferroelectric polymers for high-performance perovskite solar cells. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(30): 1902222.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LIU C, CHENG Y B, GE Z. Understanding of perovskite crystal growth and film formation in scalable deposition processes. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(6): 1653.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
ARISTIDOU N, EAMES C, SANCHEZ MOLINA I, et al. Fast oxygen diffusion and iodide defects mediate oxygen-induced degradation of perovskite solar cells. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15218.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
LIU Z, CAO F, WANG M, et al. Observing defect passivation of the grain boundary with 2-aminoterephthalic acid for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(10): 4161.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHENG X, CHEN B, DAI J, et al. Defect passivation in hybrid perovskite solar cells using quaternary ammonium halide anions and cations. Nature Energy, 2017, 2(7): 17102.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHAO J, WANG P, LIU Z, et al. Controlled reaction for improved CH3NH3PbI3 transition in perovskite solar cells. Dalton Transactions, 2015, 44(40): 17841.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WANG W, ZHOU J, TANG W. Passivation strategies of perovskite film defects for solar cells. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 129.
DOI |
| [36] |
WANG Y, GAO P, FAN X, et al. Effect of SnO2 annealing temperature on the performance of perovskite solar cells. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 168.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHOU Q, CAI C, XIONG Q, et al. Surface polarity regulation by relieving Fermi-level pinning with naphthalocyanine tetraimides toward efficient perovskite solar cells with improved photostability. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(27): 2201243.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
WU T, WANG Y, LI X, et al. Efficient defect passivation for perovskite solar cells by controlling the electron density distribution of donor-π-acceptor molecules. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(17): 1803766.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHANG S, WANG H, DUAN X, et al. Printable and homogeneous NiOx hole transport layers prepared by a polymer-network gel method for large-area and flexible perovskite solar cells. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(47): 2106495.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
LI Y, ZHENG J, CHEN X, et al. Realize larger grain size of CH3NH3PbI3 film with reduced non-radiative recombination for high performance perovskite solar cells via precursor colloidal size engineering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 886: 161300.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LUO D, SU R, ZHANG W, et al. Minimizing non-radiative recombination losses in perovskite solar cells. Nature Reviews Materials, 2020, 5(1): 44.
DOI |
| [42] |
BAIKIE I, ESTRUP P. Low cost PC based scanning Kelvin probe. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1998, 69(11): 3902.
DOI URL |
| [43] | HE X, WANG M, CAO F, et al. Hydrophobic long alkyl chain organic cations induced 2D/3D heterojunction for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 124: 243. |
| [44] |
KIM D, YUN J H, LYM M, et al. Probing facet-dependent surface defects in MAPbI3 perovskite single crystals. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(23): 14144.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
LEE D S, YUN J S, KIM J, et al. Passivation of grain boundaries by phenethylammonium in formamidinium-methylammonium lead halide perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(3): 647.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
NGUYEN B P, JUNG H R, KIM J, et al. Enhanced carrier transport over grain boundaries in lead-free CH3NH3Sn(I1-xBrx)3(0≤x≤1) perovskite solar cells. Nanotechnology, 2019, 30(31): 314005.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
WANG P, ZHAO J, WEI L, et al. Photo-induced ferroelectric switching in perovskite CH3NH3PbI3 films. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(11): 3806.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
XIA G, HUANG B, ZHANG Y, et al. Nanoscale insights into photovoltaic hysteresis in triple-cation mixed-halide perovskite: resolving the role of polarization and ionic migration. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(36): 1902870.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 韩旭, 姚恒大, 吕梅, 陆红波, 朱俊. 单分子液晶添加剂在甲脒铅碘钙钛矿太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1097-1102. |
| [2] | 方万丽, 沈黎丽, 李海艳, 陈薪羽, 陈宗琦, 寿春晖, 赵斌, 杨松旺. NiOx介孔层的成膜过程对碳电极钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1103-1109. |
| [3] | 丁统顺, 丰平, 孙学文, 单沪生, 李琪, 宋健. Fmoc-FF-OH钝化钙钛矿薄膜及其太阳能电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1076-1082. |
| [4] | 陈雨, 林埔安, 蔡冰, 张文华. 钙钛矿太阳能电池无机空穴传输材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 991-1004. |
| [5] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [6] | 张万文, 罗建强, 刘淑娟, 马建国, 张小平, 杨松旺. 氧化锆间隔层的低温喷涂制备及其三层结构钙钛矿太阳能电池应用性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 213-218. |
| [7] | 杨新月, 董庆顺, 赵伟冬, 史彦涛. 基于对氯苄胺的2D/3D钙钛矿太阳能电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 72-78. |
| [8] | 王艳香, 高培养, 范学运, 李家科, 郭平春, 黄丽群, 孙健. SnO2退火温度对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 168-174. |
| [9] | 于守武, 赵泽文, 赵晋津, 肖淑娟, 师岩, 高存法, 苏晓, 胡宇翔, 赵智胜, 王婕, 王连洲. 新型光伏储电原位集成电池研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 623-632. |
| [10] | 熊浩, 张渤昕, 贾巍, 张青红, 谢华清. 高分子PVP添加剂对钙钛矿太阳电池稳定性的提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(1): 96-102. |
| [11] | 王舒玮, 胡和丰, 王德宇, 沈 彩. 钠离子电池HOPG负极固体电解质界面膜的AFM研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 596-602. |
| [12] | 刘 畅, 苑 帅, 张海良, 曹丙强, 吴莉莉, 尹龙卫. 铜膜碘化法制备p型CuI薄膜及其用作空穴传输层的反型钙钛矿电池性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(4): 358-364. |
| [13] | 王晓媛, 闫亚宾, 嶋田隆広, 北村隆行. 纳米铁电材料铁电性及其力电耦合特性的原子尺度模拟研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(6): 561-570. |
| [14] | 钱清华,柏扬,周雪锋,刘畅,冯新,陆小华. 溶胶-凝胶法制备纳米平整度的四钛酸钾薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(4): 749-753. |
| [15] | 左霞,王智民1,刘静波,张艳熹,韦永德. 锂修饰钙掺杂钛酸铅纳米薄膜的显微结构与湿敏机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(1): 158-162. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||