无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1271-1280.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230143
所属专题: 【结构材料】热障与环境障涂层(202312)
蔡佳1,2( ), 赵芳霞1(
), 赵芳霞1( ), 范栋1,2, 黄利平2, 牛亚然2(
), 范栋1,2, 黄利平2, 牛亚然2( ), 郑学斌2, 张振忠1
), 郑学斌2, 张振忠1
收稿日期:2023-03-21
修回日期:2023-06-07
出版日期:2023-07-17
网络出版日期:2023-07-17
通讯作者:
赵芳霞, 教授. E-mail: fangxiazhao@126.com;作者简介:蔡 佳(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: cj15850730899@163.com
基金资助:
CAI Jia1,2( ), ZHAO Fangxia1(
), ZHAO Fangxia1( ), FAN Dong1,2, HUANG Liping2, NIU Yaran2(
), FAN Dong1,2, HUANG Liping2, NIU Yaran2( ), ZHENG Xuebin2, ZHANG Zhenzhong1
), ZHENG Xuebin2, ZHANG Zhenzhong1
Received:2023-03-21
Revised:2023-06-07
Published:2023-07-17
Online:2023-07-17
Contact:
ZHAO Fangxia, professor. E-mail: fangxiazhao@126.com;About author:CAI Jia(1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: cj15850730899@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
针对高性能激光防护涂层的开发问题, 根据聚碳硅烷(PCS)裂解时会消耗大量激光能量, 并产生高温陶瓷保护相的特点, 本研究创新性地提出在传统氧化钇稳定氧化锆(YSZ)隔热涂层表面再复合PCS烧蚀型涂层的防护思路, 采用料浆法结合大气等离子喷涂技术(APS)在Ni基合金表面分别制备了NiCrAlY/YSZ/PCS-TiO2(YPT)和NiCrAlY/YSZ/PCS-Y2O3(YPY)涂层。在研究TiO2和Y2O3添加相对PCS裂解行为影响的基础上, 系统研究了YPT和YPY复合涂层对10.6 μm CO2激光器的抗激光烧蚀性能, 并与单层YSZ涂层进行比较。结果表明, YPY和YPT复合涂层比传统YSZ涂层的激光防护效果更好, 这是因为在激光烧蚀初期, 涂层表面的PCS裂解会消耗激光能量, 且烧蚀后残余的Y2SiO5、SiC和SiO2相会沉积在YSZ涂层上, 形成致密的保护层, 继续对YSZ涂层进行激光防护。YPY比YPT涂层激光防护性能更好, 这是因为Y2O3具有高热导率和低热膨胀系数, YPY涂层产生的温度梯度更小, 从而缓解热应力, 且Y2O3参与PCS的裂解生成了Y2SiO5相, 比TiO2更能抑制PCS裂解引起的体积膨胀。此外YPY涂层中心烧蚀温度更高, 生成PCS裂解产物SiC和SiO2相的速度更快, 能及时保护下方涂层, 表现出更好的抗激光烧蚀性能。该研究有望为新型抗激光复合涂层的设计提供研究思路。
中图分类号:
蔡佳, 赵芳霞, 范栋, 黄利平, 牛亚然, 郑学斌, 张振忠. 聚碳硅烷基复合涂层PCS裂解行为及其抗激光烧蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1271-1280.
CAI Jia, ZHAO Fangxia, FAN Dong, HUANG Liping, NIU Yaran, ZHENG Xuebin, ZHANG Zhenzhong. Pyrolysis Behavior and Laser Ablation Resistance of PCS in Polycarbosilane Composite Coatings[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1271-1280.
| Coatings | YSZ | NiCrAlY |
|---|---|---|
| Ar/slpm | 30−40 | 30−40 |
| H2/slpm | 5−15 | 5−15 |
| Spray distance/mm | 90−130 | 200−300 |
| Feed rate/(r·min-1) | 15−30 | 15−30 |
| Power/kW | 38−48 | 30−40 |
表1 YSZ和NiCrAlY涂层喷涂参数[18]
Table 1 Spray parameters of YSZ and NiCrAlY coatings[18]
| Coatings | YSZ | NiCrAlY |
|---|---|---|
| Ar/slpm | 30−40 | 30−40 |
| H2/slpm | 5−15 | 5−15 |
| Spray distance/mm | 90−130 | 200−300 |
| Feed rate/(r·min-1) | 15−30 | 15−30 |
| Power/kW | 38−48 | 30−40 |

图7 YPT (a)和YPY (b)涂层经425 W/cm2激光烧蚀不同时间的温度曲线
Fig. 7 Temperature curves of YPT (a) and YPY (b) coatings ablated by 425 W/cm2 laser for different periods

图9 YPT和YPY涂层经425 W/cm2激光烧蚀5 s的SEM表面形貌
Fig. 9 Surface SEM morphologies of YPT and YPY coatings after 425 W/cm2, 5 s laser ablation (a, d) Original morphologies; (b, e) Central ablative zone; (c, f) Transition zone; (g) EDS results of A1, A2 and P1 points

图10 YPT和YPY原始涂层(a, d)和经425 W/cm2激光烧蚀5 s的SEM截面形貌(b, c, e, f)及EDS结果(g, h)
Fig. 10 Cross-sectional original SEM morphologies (a, d), cross-sectional morphologies (b, c, e, f) and EDS results (g, h) of YPT and YPY coatings after 425 W/cm2, 5 s laser ablation
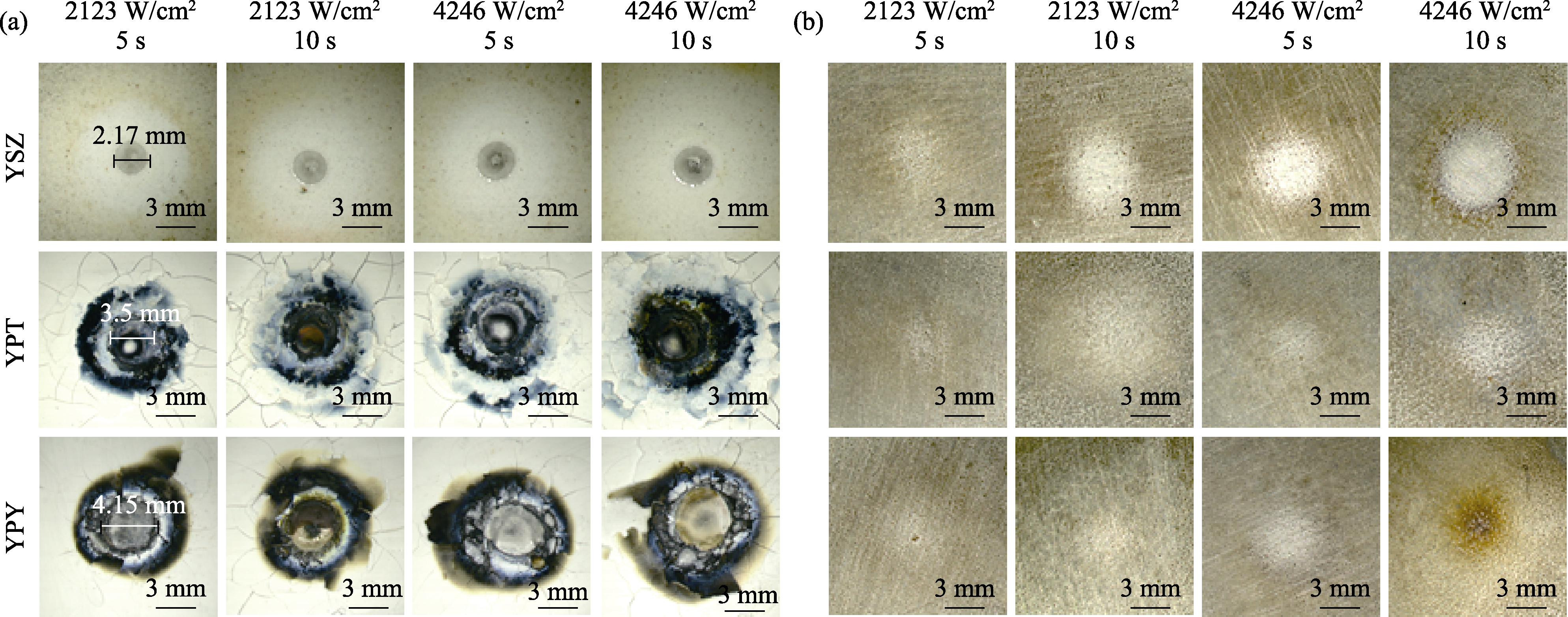
图11 YSZ、YPT和YPY涂层经2123和4246 W/cm2激光分别烧蚀5和10 s的(a)表面形貌和(b)背面形貌
Fig. 11 Surface morphologies (a) and back surface morphologies (b) of YSZ, YPT and YPY coatings ablated by 2123 and 4246 W/cm2 laser for 5 and 10 s, respectively

图13 YSZ、YPT和YPY原始涂层经4246 W/cm2激光烧蚀10 s的SEM表面形貌和EDS分析结果
Fig. 13 SEM surface morphologies and EDS analyses of YSZ, YPT and YPY coatingsafter 4246 W/cm2, 10 s laser ablation (a, e, i) Original coatings; (b, f, j) High magnification of central ablation areas; (c, g, k) Low magnification of central ablation areas; (d, h, l) Transition areas; (m) EDS results; (n) YPT element mappings ; (o) YPY element mappings

图14 YSZ (a)、YPT (b)和YPY (c)涂层经4246 W/cm2激光烧蚀10 s中心烧蚀区域的SEM截面形貌及其对应的元素分布图
Fig. 14 Cross-sectional SEM morphologies and corresponding elements mapping of the central ablation area of YSZ (a), YPT (b) and YPY (c) coatings after 4246 W/cm2, 10 s laser ablation
| [1] | 郑佳艺, 马壮, 高丽红, 等. 智能化高能激光防护材料新进展. 现代技术陶瓷, 2020, 41(3): 121. |
| [2] | Hambling D. US Army laser weapon to be most powerful ever. The New Scientist, 2021, 249(3323): 12. |
| [3] | 杨剑波, 宗思光, 陈利斐, 等. 高功率激光武器进展与启示. 激光与红外, 2021, 51(6): 695. |
| [4] |
XIONG Y, YAN K, YU H Y, et al. Comparative investigation on the hot corrosion failure of YSZ and GdYb-YSZ double-ceramic- layer thermal barrier coatings under Na2SO4+V2O5 molten salts. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(11): 18678.
DOI URL |
| [5] | SHAO J, JITSUNO T, RUDOLPH W, et al. Study on high power CW laser's irradiation effect on yttria-stabilized zirconia coating. Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, 2017, 10339: 1. |
| [6] |
ZOU Y, ZHAO L L, YOU L J, et al. Preparation and numerical simulation investigation of high reflectance anti-laser-ablation coating. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 869.
DOI |
| [7] |
CHEN Y, PING C, HONG C, et al. Improved ablation resistance of carbon-phenolic composites by introducing zirconium diboride particles. Composites Part B, 2013, 47: 320.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN S, ZHANG C, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of polymer derived SiC interphase on the properties of C/ZrC composites. Materials and Design, 2014, 58: 102.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HORCHER A, TANGERMANN-GERK K, BARROSO G, et al. Laser and furnace pyrolyzed organosilazane-based glass/ZrO2 composite coating system-a comparison. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 40(7): 2642.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU R, LIU X Y, WANG Y F, et al. Laser ablation behavior and mechanism of Cf/SiC-ZrC ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composite prepared by PIP method. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(16): 23610.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Kiyohito, Okamura, Tadao, et al. Application of radiation curing in the preparation of polycarbosilane-derived SiC fibers. Journal of Inorganic & Organometallic Polymers, 1992, 2(1): 171. |
| [12] | FEI Y W, YU X F, TANG W H, et al. Study on SiC fine ceramic anti-laser reinforcement material. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2001, 24(1): 39. |
| [13] |
NIU J H, MENG S H, JIN H, et al. Thermal stability and nanostructure evolution of amorphous SiCN ceramics during laser ablation in an argon atmosphere. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(15): 4535.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 李静, 郑轶, 罗晋, 等. 航空复合涂层材料的激光烧蚀效应. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26(2): 029003. |
| [15] | XIE Z F, CHEN Z H, LI Y Q, et al. Application of active fillers in the preparation of polycarbosilane derived ceramics. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2000, 4: 27. |
| [16] |
TINGA C C, CHENA S Y, LIUB D M, et al. Preferential growth of thin rutile TiO2 films upon thermal oxidation of sputtered Ti films. Thin Solid Films, 2002, 402: 290.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
PAN Y Y, LIANG B, HONG D, et al. High temperature long-term service performance of TiAlCrY/YSZ coating on TiAl alloy. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 105.
DOI |
| [18] | PAN Y Y, LIANG B, NIU Y R, et al. Thermal shock behaviors of plasma sprayed YSZ/TiAlCrY system on TiAl alloy. Ceramics International, 2022, 5: 6199. |
| [19] |
LY H Q, TAYLOR R, DAY R J, et al. Conversion of polycarbosilane (PCS) to SiC-based ceramic Part 1. Characterisation of PCS and curing products. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 36(16): 4037.
DOI URL |
| [20] | YUAN Q, SONG Y C, LI Y Q, et al. Synthesis and properties of a high ceramic yield thermosetting polycarbosilane. Silicone Material, 2011, 25(6): 380. |
| [21] |
FANG Y H, HUANG M H, YU Z Y, et al. Synthesis, characterization and pyrolytic conversion of a novel liquid polycarbosilane. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(10): 3298.
DOI URL |
| [22] | CABEZAS-RODRIGUEZ R, CIRIA D, MARTINEZ-FERNANDEZ J, et al. High temperature mechanical properties of polycrystalline Y2SiO5. Journal of the Spanish Ceramic and Glass Society, 2022, 61(S1): 60. |
| [23] | 王扬, 袁哲俊, 胡广义, 等. 陶瓷表面激光加热温度场的分析. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 1999, (3):71. |
| [24] | 孙承纬. 激光辐照效应. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2002. |
| [1] | 洪督, 牛亚然, 李红, 钟鑫, 郑学斌. 等离子喷涂TiC-Graphite复合涂层摩擦磨损性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [2] | 冯清影, 刘东, 张莹, 冯浩, 李强. 太阳能驱动的两步热化学循环二氧化碳裂解反应活性材料的热力学与第一性原理评价[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 223-229. |
| [3] | 罗艺, 夏书海, 牛波, 张亚运, 龙东辉. 柔性有机硅气凝胶的制备及其高温无机化转变研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1281-1288. |
| [4] | 王袁杰, 裴学良, 李好义, 徐鑫, 何流, 黄政仁, 黄庆. 自由基引发活性聚碳硅烷交联及其在制备SiC纤维中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 967-973. |
| [5] | 张冰玉,王岭,王晓猛,邱海鹏. 不同先驱体制备C/SiC复合材料及其浸渍行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1017-1022. |
| [6] | 付亚康,翁杰,刘耀文,张科宏. 钛网表面含hBMP-2的复合涂层制备及hBMP-2的释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [7] | 李旭勤, 谭志勇, 成来飞, 周灵柯, 高健. 先驱体浸渍裂解C/SiCN复合材料的拉伸行为与基体开裂机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1227-1233. |
| [8] | 周炎哲, 刘敏, 杨焜, 曾威, 宋进兵, 邓春明, 邓畅光. 大气等离子喷涂MoSi2-30Al2O3电热涂层的组织结构及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 646-652. |
| [9] | 余汉青, 董志军, 袁观明, 丛野, 李轩科, 罗永明. B-C掺杂SiC纤维的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(5): 493-501. |
| [10] | 王国栋, 宋永才. 熔融纺丝过程优化制备细直径碳化硅纤维及其对力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 721-727. |
| [11] | 吴楠, WANLynnYuqin, 王应德, FRANKKO. 静电纺聚碳硅烷制备SiOC超细纤维[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(3): 357-362. |
| [12] | 丁珊珊, 陈鑫鑫, 李雨臻, 韩文锋, 吕德义, 李瑛, 唐浩东. 模板法制备高比表面积的氟化镁及其在HFC-152a脱HF反应中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(11): 1186-1192. |
| [13] | 贾营坤, 陈培, 张青红, 孙静. 高温热还原氧化石墨烯/聚酰亚胺复合涂层的制备及防腐蚀性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(12): 1257-1263. |
| [14] | 张 程, 龚俊捷, 董志军, 孟 剑, 周思成, 袁观明, 李轩科. HfC前驱体的合成及其裂解行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(10): 1095-1101. |
| [15] | 何 玲, 李乾坤, 李文生, 崔 帅. 三基色镍基自敏复合涂层的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(1): 56-62. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||