无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 991-1004.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230105
所属专题: 【能源环境】钙钛矿(202312); 【能源环境】太阳能电池(202312)
陈雨1,2( ), 林埔安1,2, 蔡冰2(
), 林埔安1,2, 蔡冰2( ), 张文华1,2(
), 张文华1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-02
修回日期:2023-05-30
出版日期:2023-09-20
网络出版日期:2023-06-16
通讯作者:
蔡 冰, 博士. E-mail: bingcai@caep.cn;作者简介:陈 雨(1993-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: 434980565@qq.com
基金资助:
CHEN Yu1,2( ), LIN Puan1,2, CAI Bing2(
), LIN Puan1,2, CAI Bing2( ), ZHANG Wenhua1,2(
), ZHANG Wenhua1,2( )
)
Received:2023-03-02
Revised:2023-05-30
Published:2023-09-20
Online:2023-06-16
Contact:
CAI Bing, PhD. E-mail: bingcai@caep.cn;About author:CHEN Yu (1993-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: 434980565@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
有机−无机杂化钙钛矿太阳能电池(PSCs)因高能量转换效率(PCE)和低制造成本而受到了广泛关注。尽管认证PCE已经高达26%, 但在高温、高湿度和持续光照下PSCs的稳定性仍然明显落后于传统太阳能电池, 这成为其商业化道路中最大的阻碍。开发和应用高稳定性的无机空穴传输材料(HTMs)是目前解决器件光热稳定性的有效方法之一, 引入无机HTMs可以有效屏蔽水和氧对钙钛矿吸光层的侵蚀, 从而避免形成离子迁移通道。本文概述了应用于有机−无机杂化钙钛矿太阳能电池的无机HTMs的分类和光电特性, 介绍了相关研究进展, 总结了针对无机HTMs器件的性能优化策略, 包括元素掺杂、添加剂工程和界面工程, 最后展望了无机HTMs未来的发展方向。下一步需要更深入地研究无机HTMs的微观结构及其与PSCs性能的关系, 从而实现更高效、更稳定的PSCs器件。
中图分类号:
陈雨, 林埔安, 蔡冰, 张文华. 钙钛矿太阳能电池无机空穴传输材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 991-1004.
CHEN Yu, LIN Puan, CAI Bing, ZHANG Wenhua. Research Progress of Inorganic Hole Transport Materials in Perovskite Solar Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 991-1004.
| Material | Hole concentration, N/cm-3 | Hole mobility, μ/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | Conductivity, σ/(S·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sprio-OMeTAD with Li-TFSI, etc. | 7.13×1015[ | 0.779[ | 1.53×10-3[ |
| NiO | 5.3×1018[ | 0.12[ | 1.66×10-4[ |
| Cu:NiO | 7.3×1019[ | ~0.2[ | 1.25×10-3[ |
| Ni0.8Li0.05Mg0.15O | 6.46×1018[ | - | 2.23×10-3[ |
| CuGaO2 | 3.098×1019[ | - | 4.625×10-3[ |
| Zn:CuGaO2 | 1.328×1020[ | - | 1.39×10-2[ |
| CuCrO2 | - | 0.1-1.0[ | 2.9×10-2[ |
| In:CuCrO2 | 7.1×1018[ | 0.75[ | 6.9×10-2[ |
| CuScO2 | - | - | 2.11×10-3[ |
| CuSCN | - | 1.2×10-3[ | - |
| Co3O4 | - | 1.49×10-2[ | - |
| Co3O4-SrCO3 | - | 6.33×10-2[ | - |
表1 无机空穴传输材料的基本性质(Spiro-OMeTAD作为对比)
Table 1 Properties of inorganic hole transport materials (Spiro-OMeTAD for comparison)
| Material | Hole concentration, N/cm-3 | Hole mobility, μ/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | Conductivity, σ/(S·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sprio-OMeTAD with Li-TFSI, etc. | 7.13×1015[ | 0.779[ | 1.53×10-3[ |
| NiO | 5.3×1018[ | 0.12[ | 1.66×10-4[ |
| Cu:NiO | 7.3×1019[ | ~0.2[ | 1.25×10-3[ |
| Ni0.8Li0.05Mg0.15O | 6.46×1018[ | - | 2.23×10-3[ |
| CuGaO2 | 3.098×1019[ | - | 4.625×10-3[ |
| Zn:CuGaO2 | 1.328×1020[ | - | 1.39×10-2[ |
| CuCrO2 | - | 0.1-1.0[ | 2.9×10-2[ |
| In:CuCrO2 | 7.1×1018[ | 0.75[ | 6.9×10-2[ |
| CuScO2 | - | - | 2.11×10-3[ |
| CuSCN | - | 1.2×10-3[ | - |
| Co3O4 | - | 1.49×10-2[ | - |
| Co3O4-SrCO3 | - | 6.33×10-2[ | - |
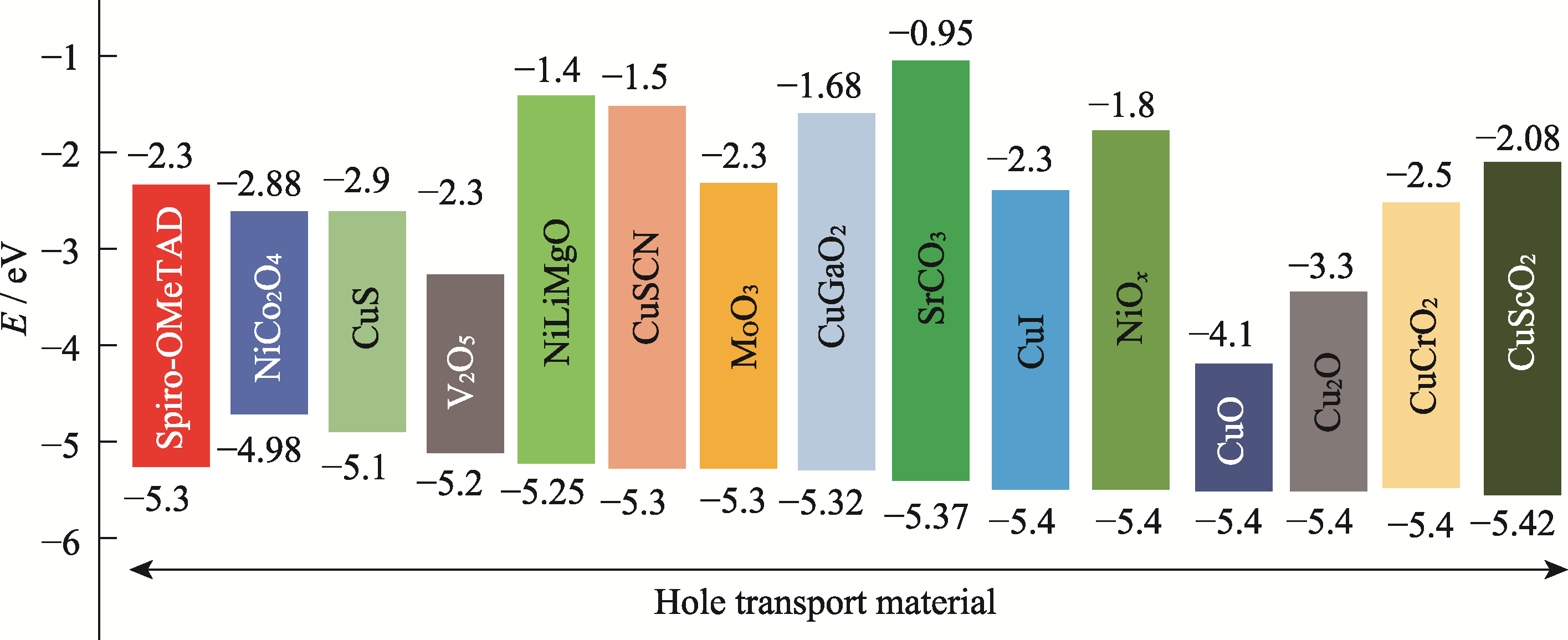
图2 代表性的无机空穴传输材料的最高占据分子轨道(HOMO)(或价带)和最低未占据分子轨道(LUMO)(或导带)能级(Spiro-OMeTAD作为对比)[18]
Fig. 2 Highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) (or valence-band) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) (or conduction-band) energy levels relative to the vacuum of representative inorganic hole transport materials (HOMO and LUMO of Spiro-OMeTAD for comparison)[18]

图3 镍基氧化物的物理形貌、合成工艺和相关性能
Fig. 3 Physical morphology, synthesis process and related properties of nickel-based oxide materials (a) Comparison of conductivity mapping results for NiO (left) and Li0.05Mg0.15Ni0.8O (right) films[21]; (b) J-V curve of NiOx-based PSCs with molecular doping of F6TCNNQ[34]; (c) Synthetic process of the SRE NiOx (top), Ni species changed with different synthetic processes (bottom-left) and spectrum changes in Ni species caused by SRE (bottom-right), and (d) champion J-V curves of PSCs[35]; (e) Schematic diagram of synthesis process and (f) high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of NiCo2O4 nanocrystals, as well as (g) J-V curves of the champion PSCs[37]. Colorful figures are available on website

图4 铜基氧化物的物理形貌和相关性能
Fig. 4 Morphology and related properties of copper-based oxide materials (a) Cross-sectional SEM image and (b) stability performance of the device with different HTL (Spiro-OMeTAD and Cu2O)[26]; (c) Preparation technology, device structure, energy level diagram and (d) J-V curves of Cu2O and CuO films[40]; (e) TEM image of CuGaO2 nanocrystals and (f) stability of the device[45]; (g) J-V curves, structure diagram (PC61BM: [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester) and (h) stability of device based on mp-CuGaO2[39]; (i) Schematic diagram of nanocrystalline structure and (j) stability of devices based on CuCrO2[46]; (k) TEM image of CuScO2 nanocrystals and (l) J-V curves of PSCs[28]. Colorful figures are available on website
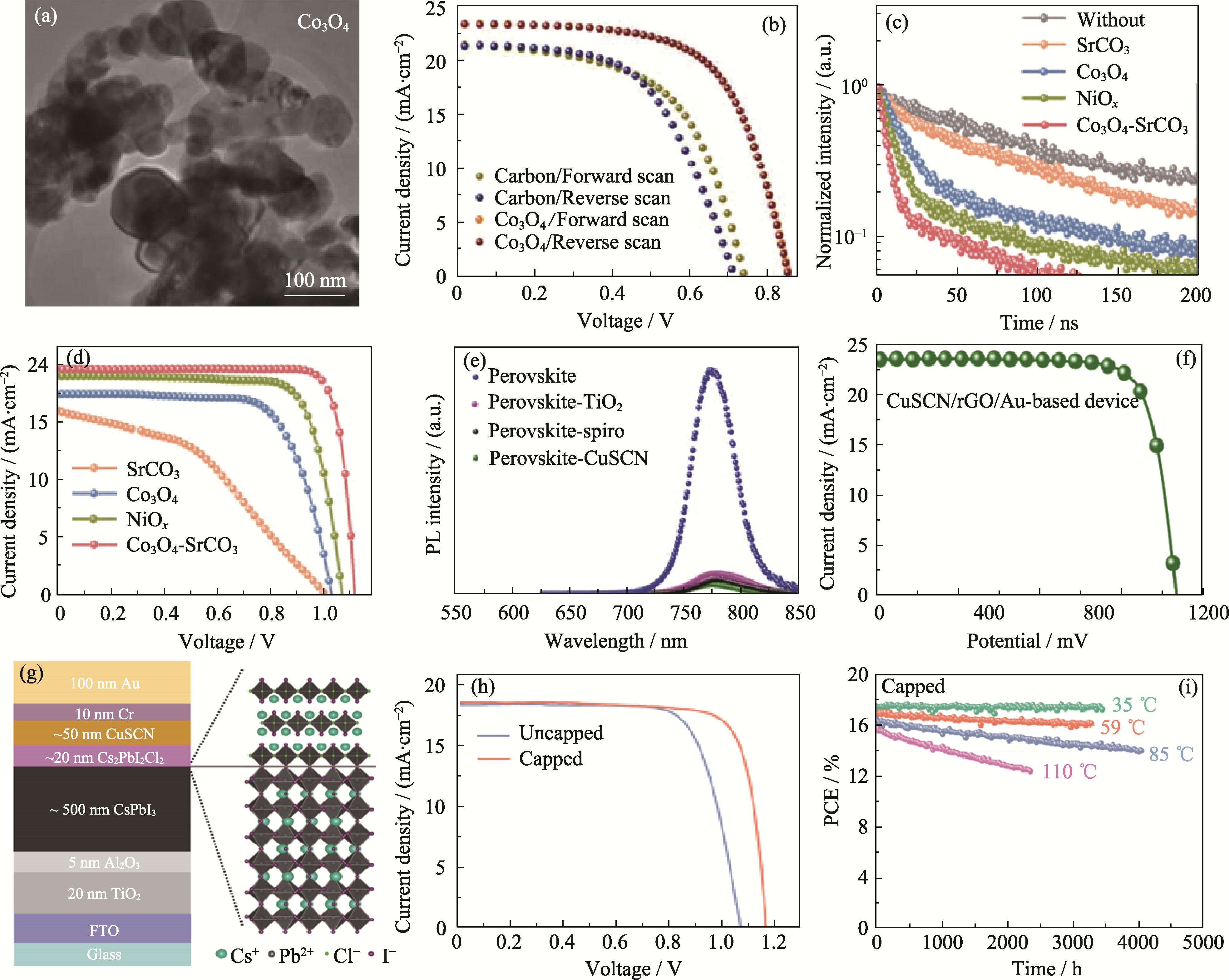
图5 其他氧化物和非氧化物的物理形貌和相关性能
Fig. 5 Physical morphology and related properties of other oxides and non-oxides (a) High-resolution TEM image of Co3O4 and (b) J-V curves of PSCs[47]; (c) Time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) spectra and (d) J-V curves of PSCs based on Co3O4-SrCO3[50]; (e) PL absorption spectra and (f) J-V curve of PSCs based on CuSCN HTL[16]; (g) Diagram of device structure, (h) J-V curves and (i) light stability of capped PSCs (under constant illumination and different temperature) based on CuSCN HTL and 2D Cs2PbI2Cl2 capping layers[55]
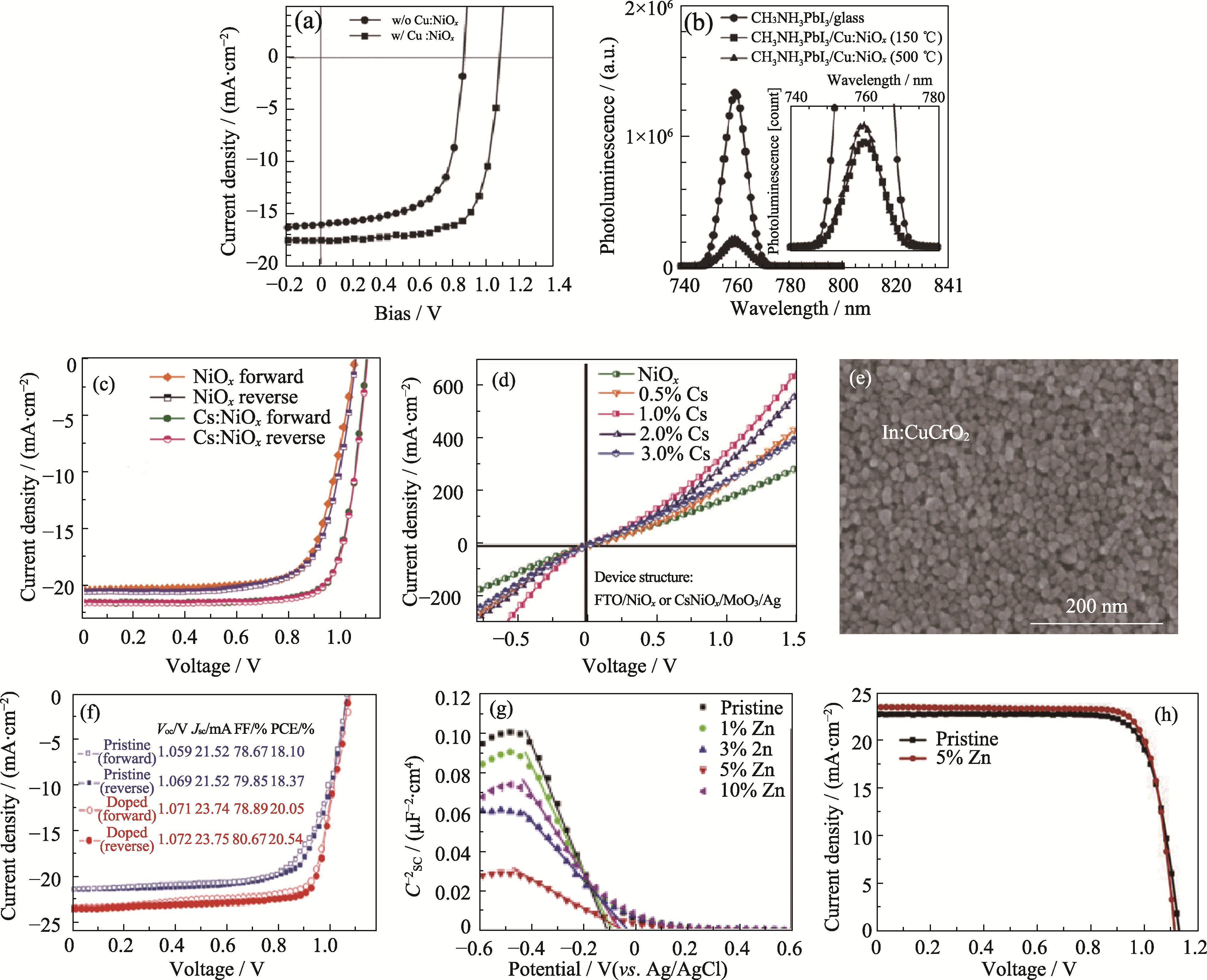
图6 元素掺杂对于器件性能的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of element doping on device performance (a) J-V curves and (b) PL spectra of PSCs based on Cu:NiOx HTL[23]; (c) J-V curves of PSCs and (d) electrical conductivity of Cs:NiOx film[27]; (e) SEM image of In doped CuCrO2 film and (f) J-V curves of PSCs[57]; (g) Mott-Schottky curves and (h) J-V curves of PSCs based on the Zn doped CuGaO2[25]
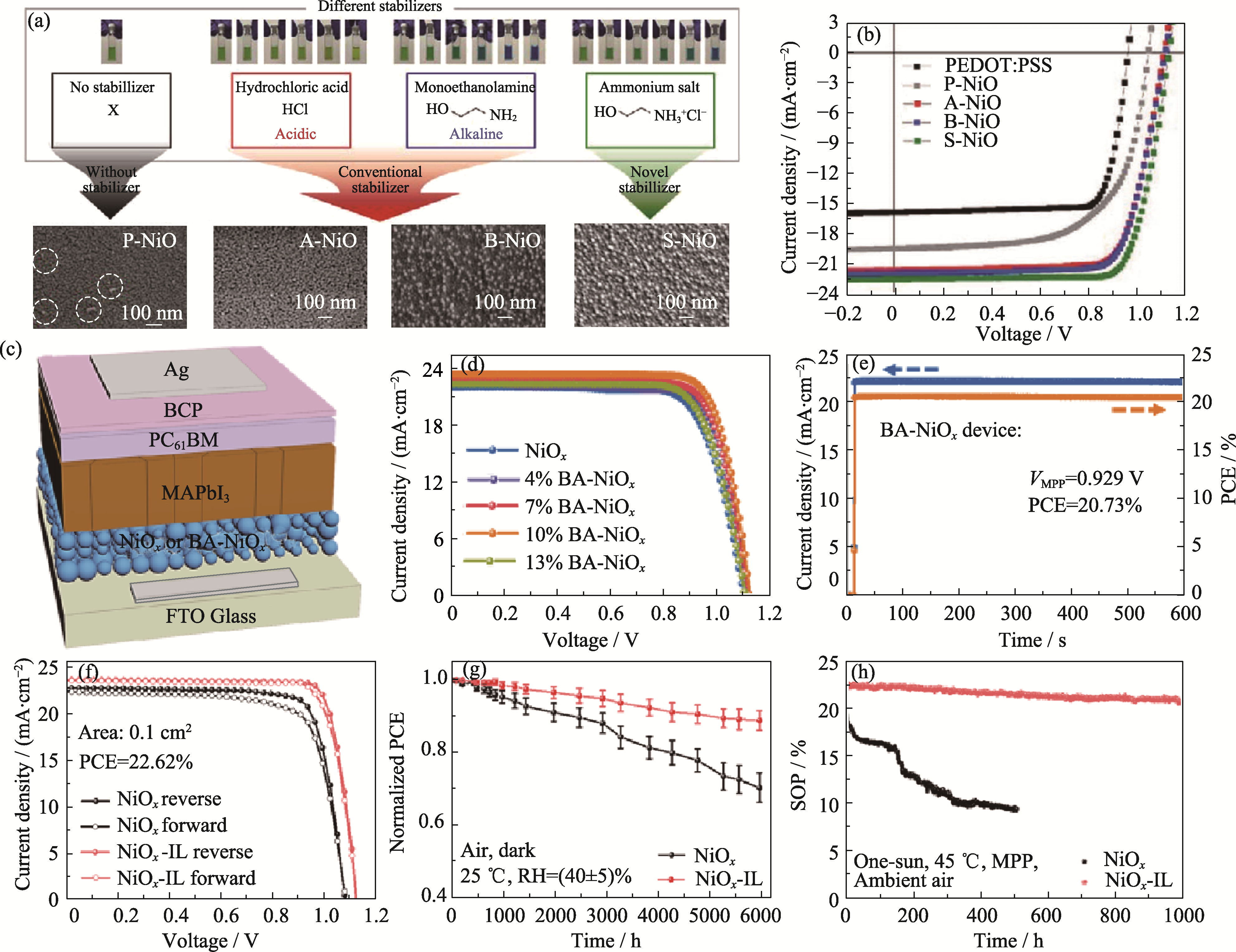
图7 添加剂工程对于器件性能的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of additive engineering on device performance (a) SEM images of NiO film with different ammonium stabilizers and different concentrations and (b) J-V curves of PSCs[30]; (c) Schematic structure, (d) J-V curves and (e) I-t curves of PSCs based on NiO film with boric acid[59]; (f) J-V curves, (g) long-term stability and (h) maximum power output stability of PSCs based on ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of NiO NPs[60]; BCP: Bathocuproin; VMPP: Output voltage at maximum power. Colorful figures are available on website
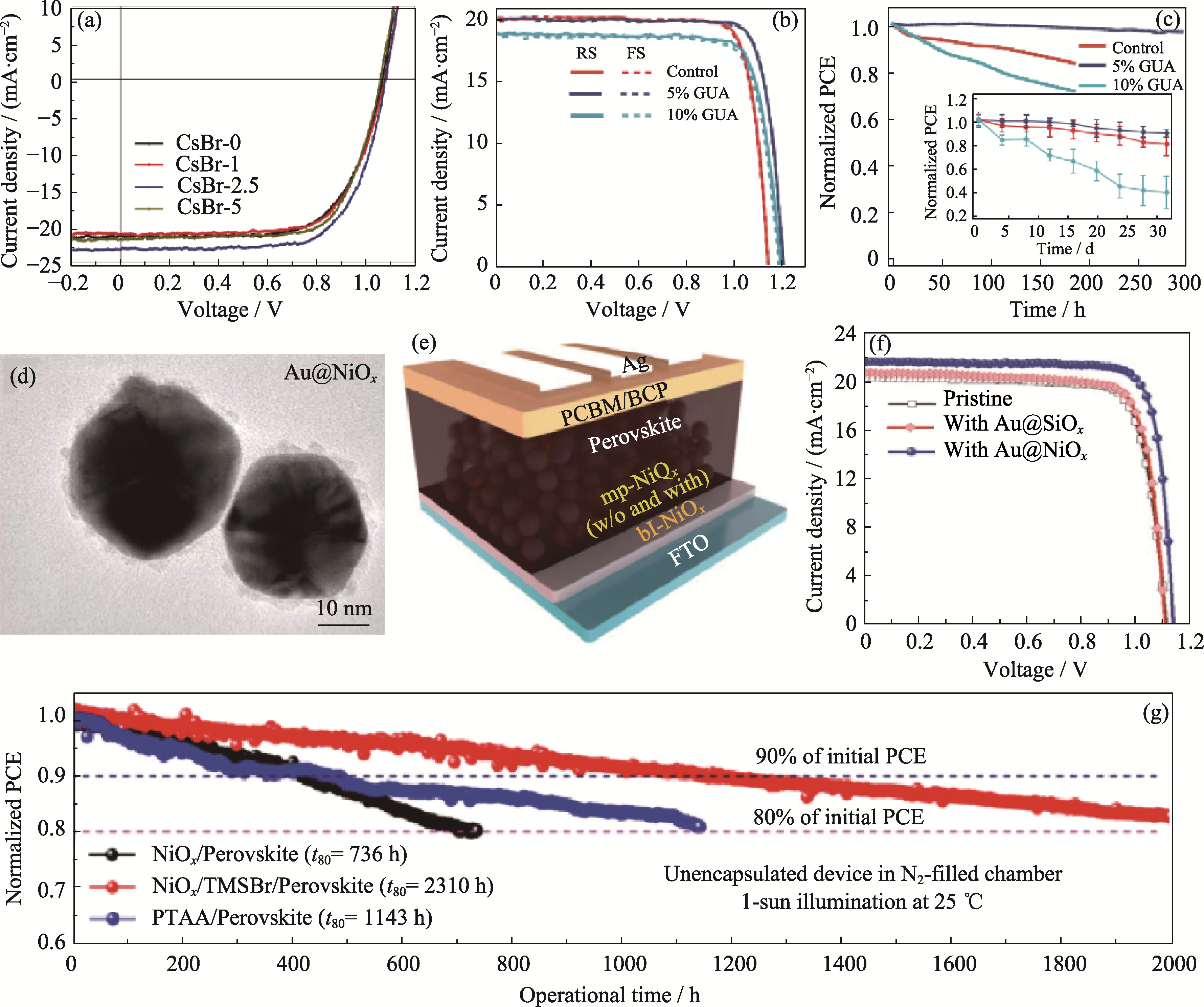
图8 界面工程对于器件性能的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of interface engineering on device performance (a) J-V curves of devices based on surface modification with different concentrations of CsBr, and stability of PSCs[63]; (b) J-V curves and (c) MPP stability of PSCs based on GUAI surface modification at different concentrations (in molar) with inset showing environmental stability[64]; (d) High-resolution TEM images of Au@NiOx NPs, (e) corresponding structure diagram and (f) J-V curves of PSCs[65]; (g) MPP stability of devices with TMSBr surface modification[66]; CsBr-2.5: 2.5 mg/mL CsBr; RS: reverse scan; FS: forward scan; T80: the time maintaining 80% initial PCE. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | The National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Best research cell efficiency chart[2023-06-05]. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cellefficiency.html. |
| [2] |
MENG W, ZHANG K, OSVET A, et al. Revealing the strain- associated physical mechanisms impacting the performance and stability of perovskite solar cells. Joule, 2022, 6(2): 458.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN R, ZHANG W, GUAN X, et al. Rear electrode materials for perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(26): 2200651.
DOI URL |
| [4] | NAZIR G, LEE S Y, LEE J H, et al. Stabilization of perovskite solar cells: recent developments and future perspectives. Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(50): e2204380. |
| [5] |
BING J, CARO L G, TALATHI H P, et al. Perovskite solar cells for building integrated photovoltaics-glazing applications. Joule, 2022, 6(7): 1446.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PARK H H. Efficient and stable perovskite solar cells based on inorganic hole transport materials. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(1): 112.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG X, ZHANG H, LI Y, et al. Recent progress in hole-transporting layers of conventional organic solar cells with p-i-n structure. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(44): 2205398.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CAI B, XING Y, YANG Z, et al. High performance hybrid solar cells sensitized by organolead halide perovskites. Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6(5): 1480.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG T, WANG F, KIM H B, et al. Ion-modulated radical doping of Spiro-OMeTAD for more efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 377(6605): 495.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
CHEN Y, WANG Q, TANG W, et al. Heterocyclic amino acid molecule as a multifunctional interfacial bridge for improving the efficiency and stability of quadruple cation perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy, 2023, 107: 108154.
DOI URL |
| [11] | GAO D, LI B, LI Z, et al. Highly efficient flexible perovskite solar cells through pentylammonium acetate modification with certified efficiency of 23.35%. Adv. Mater., 2023, 35(3): e2206387. |
| [12] |
LI Z, LI B, WU X, et al. Organometallic-functionalized interfaces for highly efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 376(6591): 416.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
NGUYEN W H, BAILIE C D, UNGER E L, et al. Enhancing the hole-conductivity of Spiro-OMeTAD without oxygen or lithium salts by using Spiro(TFSI)2 in perovskite and dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(31): 10996.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZAI H, MA Y, CHEN Q, et al. Ion migration in halide perovskite solar cells: mechanism, characterization, impact and suppression. J. Energy Chem., 2021, 63: 528.
DOI |
| [15] |
LUO X, LIN X, GAO F, et al. Recent progress in perovskite solar cells: from device to commercialization. Sci. China Chem., 2022, 65(12): 2369.
DOI |
| [16] |
ARORA N, DAR M I, HINDERHOFER A, et al. Perovskite solar cells with CuSCN hole extraction layers yield stabilized efficiencies greater than 20%. Science, 2017, 358(6364): 768.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
LEE J H, JIN I S, NOH Y W, et al. A solution-processed spinel CuCo2O4 as an effective hole transport layer for efficient perovskite solar cells with negligible hysteresis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2019, 7(21): 17661.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG Q, LIN Z, SU J, et al. Recent progress of inorganic hole transport materials for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Nano Select, 2021, 2(6): 1055.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIU J, PATHAK S K, SAKAI N, et al. Identification and mitigation of a critical interfacial instability in perovskite solar cells employing copper thiocyanate hole-transporter. Adv. Mater. Interf., 2016, 3(22): 1600571.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
CHEN W Y, JENG J S, HUANG K L, et al. Modulation of Ni valence in p-type NiO films via substitution of Ni by Cu. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A, 2013, 31(2): 021501.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
CHEN W, WU Y, YUE Y, et al. Efficient and stable large-area perovskite solar cells with inorganic charge extraction layers. Science, 2015, 350(6263): 944.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
EUVRARD J, YAN Y, MITZI D B. Electrical doping in halide perovskites. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2021, 6(6): 531.
DOI |
| [23] |
JUNG J W, CHUEH C C, JEN A K Y. A low-temperature, solution- processable, Cu-doped nickel oxide hole-transporting layer via the combustion method for high-performance thin-film perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(47): 7874.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
BOYD C C, SHALLCROSS R C, MOOT T, et al. Overcoming redox reactions at perovskite-nickel oxide interfaces to boost voltages in perovskite solar cells. Joule, 2020, 4(8): 1759.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHEN Y, YANG Z, JIA X, et al. Thermally stable methylammonium- free inverted perovskite solar cells with Zn2+ doped CuGaO2 as efficient mesoporous hole-transporting layer. Nano Energy, 2019, 61: 148.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
NEJAND B A, AHMADI V, GHARIBZADEH S, et al. Cuprous oxide as a potential low-cost hole-transport material for stable perovskite solar cells. ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(3): 302.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
CHEN W, LIU F Z, FENG X Y, et al. Cesium doped NiOx as an efficient hole extraction layer for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7(19): 1700722.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
CHEN Y, SHEN Y, TANG W, et al. Ion compensation of buried interface enables highly efficient and stable inverted MA-free perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(44): 2206703.
DOI URL |
| [29] | CHEN Y, YANG Z, WANG S, et al. Design of an inorganic mesoporous hole-transporting layer for highly efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(52): e1805660. |
| [30] |
PARK S, KIM D W, PARK S Y. Improved stability and efficiency of inverted perovskite solar cell by employing nickel oxide hole transporting material containing ammonium salt stabilizer. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(28): 2200437.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
JENG J Y, CHEN K C, CHIANG T Y, et al. Nickel oxide electrode interlayer in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite/PCBM planar-heterojunction hybrid solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(24): 4107.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHU Z, BAI Y, ZHANG T, et al. High-performance hole-extraction layer of Sol-Gel-processed NiO nanocrystals for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(46): 12571.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
CHEN W, WU Y, LIU J, et al. Hybrid interfacial layer leads to solid performance improvement of inverted perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8(2): 629.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
CHEN W, ZHOU Y, WANG L, et al. Molecule-doped nickel oxide: verified charge transfer and planar inverted mixed cation perovskite solar cell. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(20): 1800515.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DU M, ZHAO S, DUAN L, et al. Surface redox engineering of vacuum-deposited NiOx for top-performance perovskite solar cells and modules. Joule, 2022, 6(8): 1931.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHANG Y, LI C, BI E, et al. Efficient inverted perovskite solar cells with a low-dimensional halide/perovskite heterostructure. Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(48): 2202191.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
OUYANG D, XIAO J, YE F, et al. Strategic synthesis of ultrasmall NiCo2O4 NPs as hole transport layer for highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(16): 1702722.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
JING X, ZHANG Z, CHEN T, et al. Review of inorganic hole transport materials for perovskite solar cells. Energy Technol., 2023, 11(2): 2201005.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
BIDIKOUDI M, KYMAKIS E. Novel approaches and scalability prospects of copper based hole transporting materials for planar perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7(44): 13680.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZUO C, DING L. Solution-processed Cu2O and CuO as hole transport materials for efficient perovskite solar cells. Small, 2015, 11(41): 5528.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
SUN W, LI Y, YE S, et al. High-performance inverted planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells based on a solution-processed CuOx hole transport layer. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(20): 10806.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
SCANLON D O, WALSH A. Polymorph engineering of CuMO2 (M = Al, Ga, Sc, Y) semiconductors for solar energy applications: from delafossite to wurtzite. Acta Crystallogr. B, 2015, 71(6): 702.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
XIONG D, XU Z, ZENG X, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of ultrasmall CuCrO2 nanocrystal alternatives to NiO nanoparticles in efficient p-type dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(47): 24760.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ROBERTSON J, PEACOCK P W, TOWLER M D, et al. Electronic structure of p-type conducting transparent oxides. Thin Solid Films, 2002, 411(1): 96.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHANG H, WANG H, CHEN W, et al. CuGaO2: a promising inorganic hole-transporting material for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(8): 1604984.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHANG H, WANG H, ZHU H, et al. Low-temperature solution- processed CuCrO2 hole-transporting layer for efficient and photostable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(13): 1702762.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
BASHIR A, SHUKLA S, LEW J H, et al. Spinel Co3O4 nanomaterials for efficient and stable large area carbon-based printed perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(5): 2341.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
TSENG Z L, CHEN L C, CHIANG C H, et al. Efficient inverted-type perovskite solar cells using UV-ozone treated MoOx and WOx as hole transporting layers. Sol. Energy, 2016, 139: 484.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CHENG M, LI Y, SAFDARI M, et al. Efficient perovskite solar cells based on a solution processable nickel(II) phthalocyanine and vanadium oxide integrated hole transport layer. Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7(14): 1602556.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
GE B, ZHOU Z R, WU X F, et al. Self-organized Co3O4-SrCO3 percolative composites enabling nanosized hole transport pathways for perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(46): 2106121.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
CHRISTIANS J A, FUNG R C M, KAMAT P V. An inorganic hole conductor for organo-lead halide perovskite solar cells. Improved hole conductivity with copper iodide. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(2): 758.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
SUN W, YE S, RAO H, et al. Room-temperature and solution- processed copper iodide as the hole transport layer for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(35): 15954.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
RAO H, SUN W, YE S, et al. Solution-processed CuS NPs as an inorganic hole-selective contact material for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2016, 8(12): 7800.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
WIJEYASINGHE N, ANTHOPOULOS T D. Copper(I) thiocyanate (CuSCN) as a hole-transport material for large-area opto/electronics. Semicond. Sci. Tech., 2015, 30(10): 104002.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHAO X, LIU T, BURLINGAME Q C, et al. Accelerated aging of all-inorganic, interface-stabilized perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 377(6603): 307.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
CHEN W, WU Y, FAN J, et al. Understanding the doping effect on NiO: toward high-performance inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(19): 1703519.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
YANG B, OUYANG D, HUANG Z, et al. Multifunctional synthesis approach of In:CuCrO2 nanoparticles for hole transport layer in high-performance perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(34): 1902600.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
HUYNH U N, LIU Y, CHANANA A, et al. Transient quantum beatings of trions in hybrid organic tri-iodine perovskite single crystal. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1): 1428.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
GE B, LIN Z Q, ZHOU Z R, et al. Boric acid mediated formation and doping of NiOx layers for perovskite solar cells with efficiency over 21%. Sol. RRL, 2021, 5(4): 2000810.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
WANG S, LI Y, YANG J, et al. Critical role of removing impurities in nickel oxide on high-efficiency and long-term stability of inverted perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(18): e202116534.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
CHEN J, PARK N G. Materials and methods for interface engineering toward stable and efficient perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5(8): 2742.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
GAO Z W, WANG Y, CHOY W C H. Buried interface modification in perovskite solar cells: a materials perspective. Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(20): 2104030.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
ZHANG B, SU J, GUO X, et al. NiO/perovskite heterojunction contact engineering for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Sci., 2020, 7(11): 1903044.
DOI URL |
| [64] | CHEN B, CHEN H, HOU Y, et al. Passivation of the buried interface via preferential crystallization of 2D perovskite on metal oxide transport layers. Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(41): e2103394. |
| [65] |
LIU Z, LI Q, CHEN K, et al. Tailoring carrier dynamics in inverted mesoporous perovskite solar cells with interface-engineered plasmonics. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(4): 2394.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
WU T, ONO L K, YOSHIOKA R, et al. Elimination of light- induced degradation at the nickel oxide-perovskite heterojunction by aprotic sulfonium layers towards long-term operationally stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15(11): 4612.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
LI C, WANG X, BI E, et al. Rational design of Lewis base molecules for stable and efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Science, 2023, 379(6633): 690.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [2] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [3] | 柯鑫, 谢炳卿, 王忠, 张敬国, 王建伟, 李占荣, 贺会军, 汪礼敏. 第三代半导体互连材料与低温烧结纳米铜材的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 17-31. |
| [4] | 方万丽, 沈黎丽, 李海艳, 陈薪羽, 陈宗琦, 寿春晖, 赵斌, 杨松旺. NiOx介孔层的成膜过程对碳电极钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1103-1109. |
| [5] | 丁统顺, 丰平, 孙学文, 单沪生, 李琪, 宋健. Fmoc-FF-OH钝化钙钛矿薄膜及其太阳能电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1076-1082. |
| [6] | 张伦, 吕梅, 朱俊. Cs2AgBiBr6钙钛矿太阳能电池研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1044-1054. |
| [7] | 董怡曼, 谭占鳌. 宽带隙钙钛矿基二端叠层太阳电池复合层的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1031-1043. |
| [8] | 郭华军, 安帅领, 孟婕, 任书霞, 王文文, 梁子尚, 宋佳钰, 陈恒彬, 苏航, 赵晋津. 卤化物钙钛矿光电阻变机理研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1005-1016. |
| [9] | 董思吟, 帖舒婕, 袁瑞涵, 郑霄家. 低维卤化物钙钛矿直接型X射线探测器研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1017-1030. |
| [10] | 韩旭, 姚恒大, 吕梅, 陆红波, 朱俊. 单分子液晶添加剂在甲脒铅碘钙钛矿太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1097-1102. |
| [11] | 胡忠良, 傅赟天, 蒋蒙, 王连军, 江莞. Nb/Mg3SbBi界面层热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 931-937. |
| [12] | 刘建, 王凌坤, 许保亮, 赵倩, 王耀萱, 丁艺, 张胜泰, 段涛. 熔盐法低温合成掺钕ZrSiO4陶瓷的物相演变和化学稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 910-916. |
| [13] | 丁浩明, 李勉, 李友兵, 陈科, 肖昱琨, 周洁, 陶泉争, 尹航, 柏跃磊, 张毕堃, 孙志梅, 王俊杰, 张一鸣, 黄振莺, 张培根, 孙正明, 韩美康, 赵双, 王晨旭, 黄庆. 三元层状材料结构调控及性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 845-884. |
| [14] | 肖娅妮, 吕嘉南, 李振明, 刘铭扬, 刘伟, 任志刚, 刘弘景, 杨东旺, 鄢永高. Bi2Te3基热电材料的湿热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 800-806. |
| [15] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||