无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1281-1291.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230209
汤亚1,2( ), 孙盛睿2, 樊佳1,2, 杨庆峰3, 董满江2, 寇佳慧1(
), 孙盛睿2, 樊佳1,2, 杨庆峰3, 董满江2, 寇佳慧1( ), 刘阳桥2(
), 刘阳桥2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-28
修回日期:2023-05-29
出版日期:2023-06-01
网络出版日期:2023-06-01
通讯作者:
刘阳桥, 研究员. E-mail: yqliu@mail.sic.ac.cn;作者简介:汤 亚(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: tangya153@163.com
基金资助:
TANG Ya1,2( ), SUN Shengrui2, FAN Jia1,2, YANG Qingfeng3, DONG Manjiang2, KOU Jiahui1(
), SUN Shengrui2, FAN Jia1,2, YANG Qingfeng3, DONG Manjiang2, KOU Jiahui1( ), LIU Yangqiao2(
), LIU Yangqiao2( )
)
Received:2023-04-28
Revised:2023-05-29
Published:2023-06-01
Online:2023-06-01
Contact:
LIU Yangqiao, professor. E-mail: yqliu@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:About author: TANG Ya (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: tangya153@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
随着工业的快速发展, 相关制造领域排放的污水重金属铜离子污染愈发严重。与此同时, 催化领域对铜金属资源的需求却不断增加。本研究利用粉煤灰和改性剂聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)制备了低成本改性水合硅酸钙(PCSH), 用于吸附水溶液中的铜离子(Cu(II)), 并进一步碱处理固定于表面的Cu(II), 形成铜基活性材料用于有机污染物的催化降解。相比于未改性的样品(CSH), PCSH对Cu(II)的饱和吸附容量提高100%, 高达588 mg/g。研究发现, 这主要是因为添加PEI有利于形成较大的比表面积、优良的孔隙结构以及Cu(II)与-NH2之间的强络合。从PCSH获得的铜基催化剂呈现纺锤形多孔形貌, 作为催化剂分别用于活化过氧硫酸氢钾(PMS)氧化降解罗丹明B(RhB)和活化硼氢化钠(NaBH4)还原降解4-硝基苯酚(4-NP), 速率常数达到0.7135 /min (pH (7.0±0.3); [RhB]= 20 mg/L; [PMS]= 0.12 g/L; [催化剂]= 0.8 g/L)和11.47×10-3 /s (pH (11.0±0.3); [4-NP]= 10-4 mol/L; [NaBH4]= 5×10-3 mol/L; [催化剂]= 0.167 g/L), 是CSH催化剂体系的20和19倍。本工作利用固体废弃物粉煤灰实现了水溶液中铜元素的再利用, 为水中污染物的有效处理和利用提供了新启示。
中图分类号:
汤亚, 孙盛睿, 樊佳, 杨庆峰, 董满江, 寇佳慧, 刘阳桥. 粉煤灰衍生水合硅酸钙PEI改性及吸附去除Cu(II)与催化降解有机污染物[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291.
TANG Ya, SUN Shengrui, FAN Jia, YANG Qingfeng, DONG Manjiang, KOU Jiahui, LIU Yangqiao. PEI Modified Hydrated Calcium Silicate Derived from Fly Ash and Its adsorption for Removal of Cu (II) and Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291.
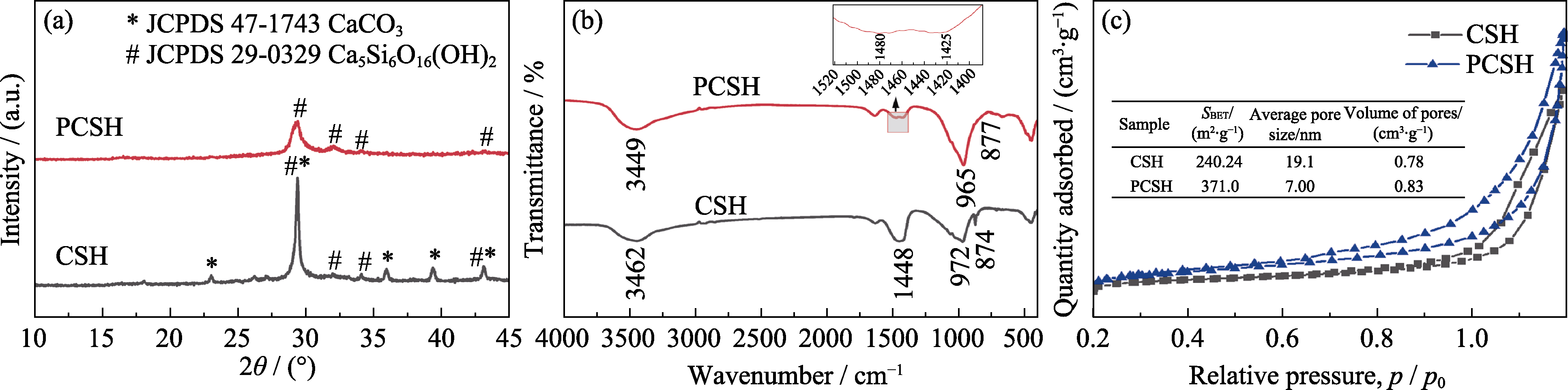
图1 CSH与PCSH的(a) XRD图谱, (b) FT-IR图谱以及(c) N2吸附脱附曲线
Fig. 1 (a) XRD patterns, (b) FT-IR spectra and (c) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of CSH and PCSH

图3 样品吸附性能表征
Fig. 3 Adsorption characteristics of samples (a) Variation of adsorption capacity of samples with time; (b) Effect of pH on the adsorption capacity of PCSH; (c) Adsorption isotherms of samples; (d) Variation of adsorption capacity of samples with initial concentration of Zn(II)-Pb(II)

图4 吸附Cu后样品的表征
Fig. 4 Characteristics of Cu-absorbed samples (a) XRD patterns; (b) Survey scans and high-resolution scans of (c) Cu2p, (d) N1s XPS spectra
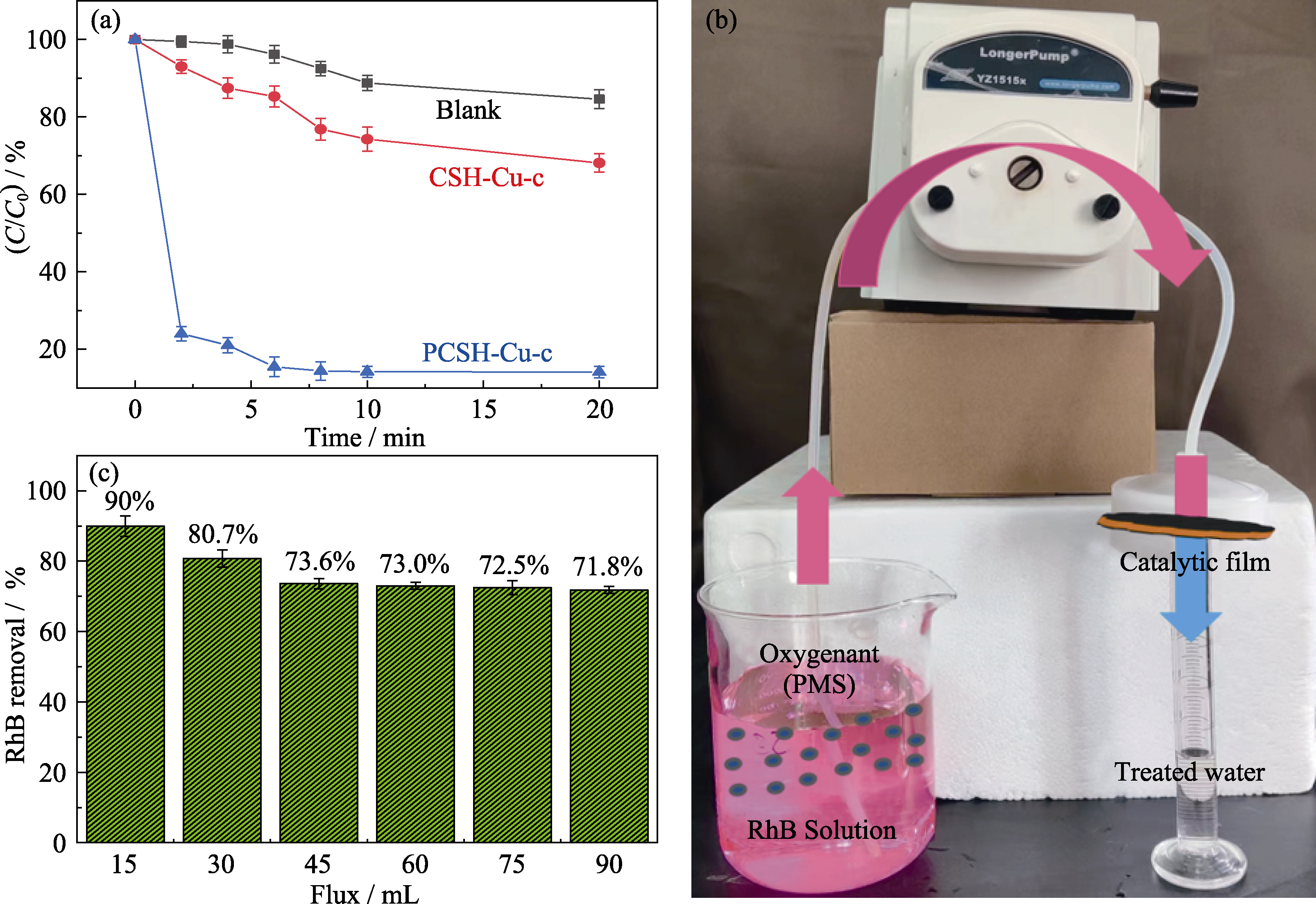
图7 CSH-Cu-c和PCSH-Cu-c催化PMS降解RhB的性能
Fig. 7 Degradation of RhB by PMS with CSH-Cu-c and PCSH-Cu-c (a) RhB residue percentage; (b) Photo of catalytic device; (c) Catalytic performance of PCSH-Cu-c-M
| Catalyst | C1/(g·L-1) | CPMS/(g·L-1) | CRhB/(mg·L-1) | k/min-1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPC | 1 | 0.616 | 20 | 0.013 | [ |
| α-MnO2/Pal | 0.1 | 0.1 | 20 | 0.0204 | [ |
| Vis/BiVO4 | 0.5 | 0.616 | 10 | 0.04 | [ |
| rGO-CoPc | 0.3 | 0.616 | 10 | 0.288 | [ |
| CSH-Cu-c | 0.8 | 0.12 | 20 | 0.036 | This work |
| PCSH-Cu-c | 0.8 | 0.12 | 20 | 0.7135 | This work |
表1 不同材料催化PMS降解RhB的速率常数(k)
Table 1 Rate constants (k) for the degradation of RhB by PMS with different catalysts
| Catalyst | C1/(g·L-1) | CPMS/(g·L-1) | CRhB/(mg·L-1) | k/min-1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPC | 1 | 0.616 | 20 | 0.013 | [ |
| α-MnO2/Pal | 0.1 | 0.1 | 20 | 0.0204 | [ |
| Vis/BiVO4 | 0.5 | 0.616 | 10 | 0.04 | [ |
| rGO-CoPc | 0.3 | 0.616 | 10 | 0.288 | [ |
| CSH-Cu-c | 0.8 | 0.12 | 20 | 0.036 | This work |
| PCSH-Cu-c | 0.8 | 0.12 | 20 | 0.7135 | This work |
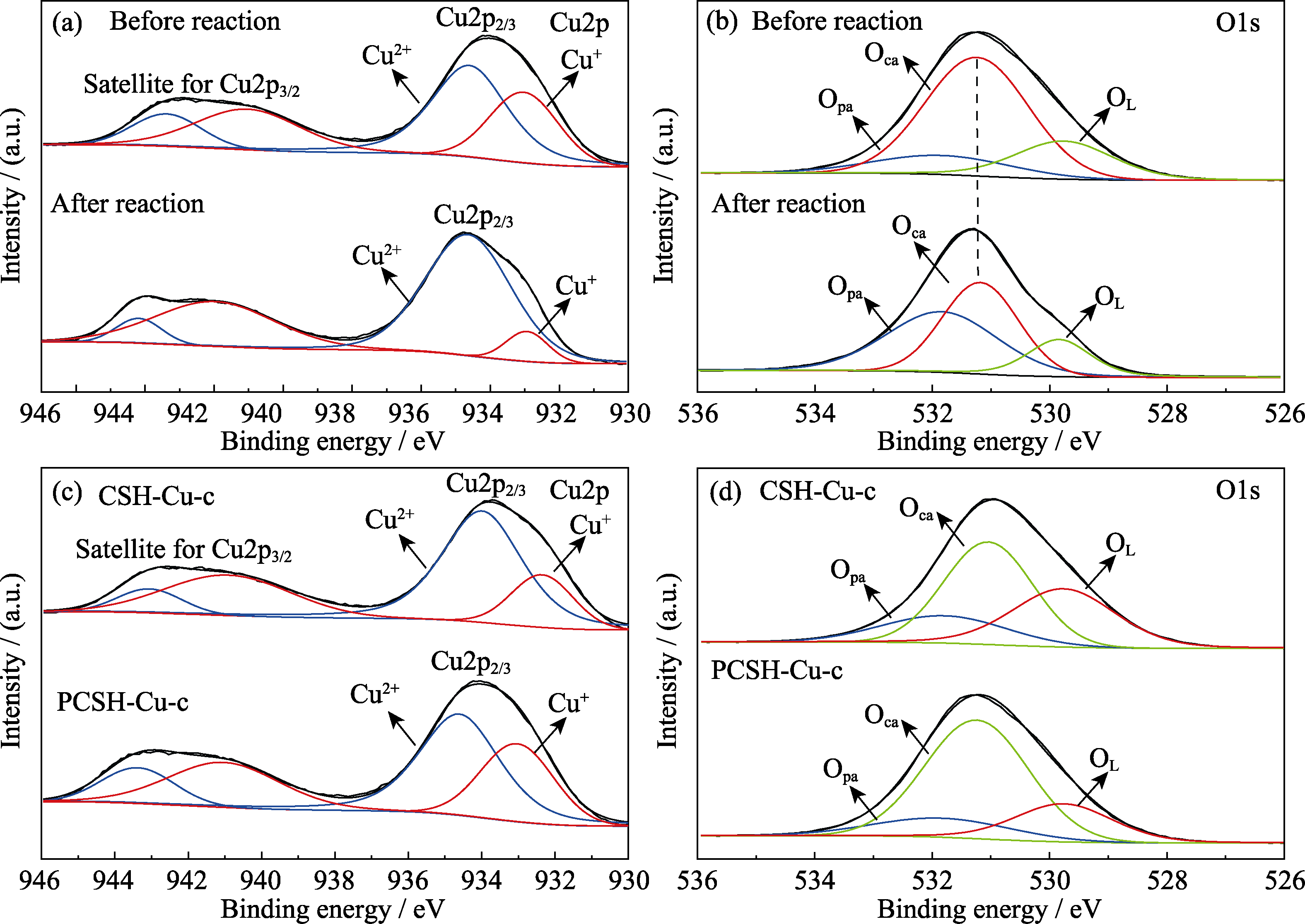
图8 样品表面元素和化学状态表征
Fig. 8 Suface elements and chemical status of samples (a) Cu2p and (b) O1s XPS spectra of PCSH-Cu-c before and after reaction; (c) Cu2p and (d) O1s XPS spectra of CSH-Cu-c and PCSH-Cu-c before reaction
| Catalyst | C1/ (g·L-1) | CNaBH4/ (mmol·L-1) | C4-NP/ (mmol·L-1) | k/(×10-3, s-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO NLs | 0.307 | 10 | 0.12 | 0.36 | [ |
| Ag-NP/C | 0.333 | 6.667 | 4.7×10-2 | 1.69 | [ |
| Cu2−xSe/ rGO/PVP | 2.5 | 62.5 | 0.125 | 2.3 | [ |
| Pd-FG | 0.5 | 10 | 0.1 | 2.35 | [ |
| CSH-Cu-c | 0.167 | 5 | 0.1 | 0.61 | This work |
| PCSH-Cu-c | 0.167 | 5 | 0.1 | 11.47 | This work |
表2 不同材料催化NaBH4降解4-NP的速率常数(k)
Table 2 Rate constants (k) for the degradation of 4-NP by NaBH4 with different catalysts
| Catalyst | C1/ (g·L-1) | CNaBH4/ (mmol·L-1) | C4-NP/ (mmol·L-1) | k/(×10-3, s-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO NLs | 0.307 | 10 | 0.12 | 0.36 | [ |
| Ag-NP/C | 0.333 | 6.667 | 4.7×10-2 | 1.69 | [ |
| Cu2−xSe/ rGO/PVP | 2.5 | 62.5 | 0.125 | 2.3 | [ |
| Pd-FG | 0.5 | 10 | 0.1 | 2.35 | [ |
| CSH-Cu-c | 0.167 | 5 | 0.1 | 0.61 | This work |
| PCSH-Cu-c | 0.167 | 5 | 0.1 | 11.47 | This work |
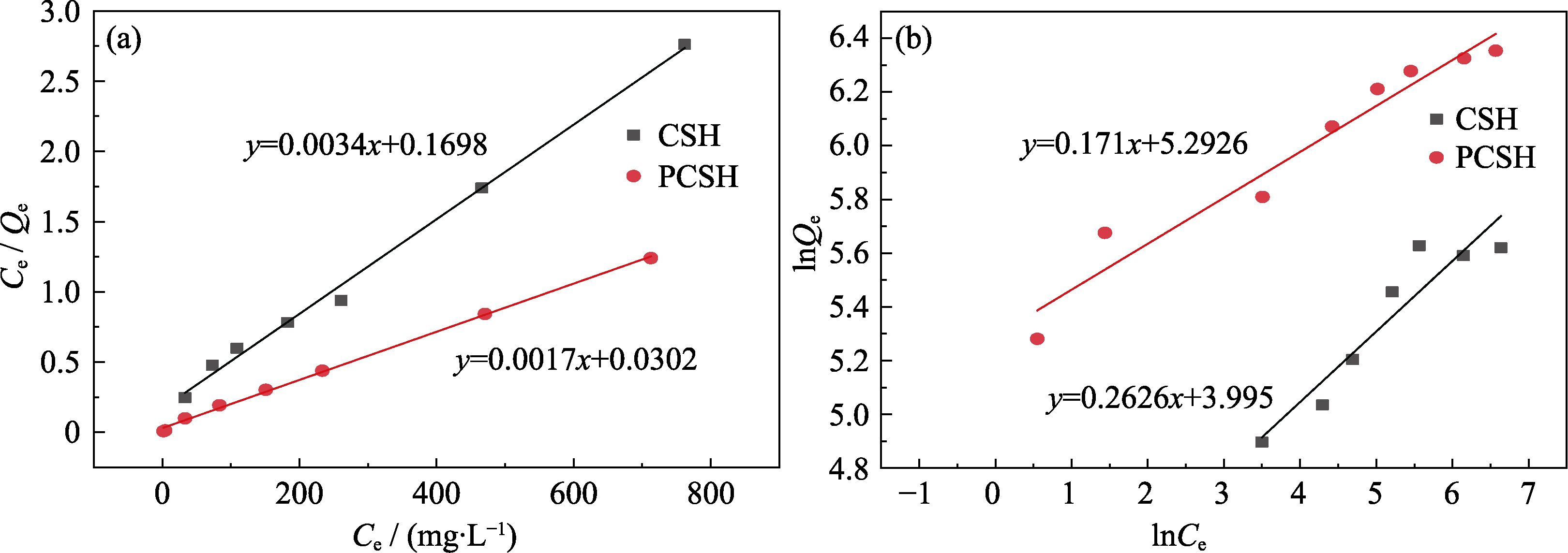
图S3 CSH与PCSH在(a) Langmuir模型和(b) Freundlich模型中的吸附等温线拟合
Fig. S3 Linear fitting curves of (a) Langmuir model and (b) Freundlich model for isotherms of CSH and PCSH
| Sample | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| CSH | 294.10 | 0.0200 | 0.9945 | 3.810 | 54.00 | 0.8670 |
| PCSH | 588.23 | 0.0563 | 0.9982 | 5.848 | 198.86 | 0.9450 |
表S1 Langmuir和Freundlich等温线拟合参数
Table S1 Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm fitting parameters
| Sample | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| CSH | 294.10 | 0.0200 | 0.9945 | 3.810 | 54.00 | 0.8670 |
| PCSH | 588.23 | 0.0563 | 0.9982 | 5.848 | 198.86 | 0.9450 |
| Sample | q / (mg·g-1) | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activated carbon | 10 | 921 | [S1] |
| Modified SBA-15 mesoporous silica | 46 | 317 | [S2] |
| MCM-48 | 126 | 511 | [S3] |
| Citrate-LDH | 137 | 8 | [S4] |
| Mesoporous silica | 153 | 462 | [S5] |
| Humulus scandens-derived biochars | 221 | 450 | [S6] |
| Steel slag-derived CSH | 244 | 77 | [S7] |
| Amorphous molybdenum sulphide | 259 | 28 | [S8] |
| NPCS-PEI | 276 | 491 | [S9] |
| CSH | 294 | 240 | This work |
| PCSH | 588 | 371 | This work |
表S2 文献中报道的各种吸附剂对Cu(II)的最大吸附能力比较
Table S2 Comparison of maximum adsorption capacities of various sorbents as reported in the literature for Cu(II)
| Sample | q / (mg·g-1) | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activated carbon | 10 | 921 | [S1] |
| Modified SBA-15 mesoporous silica | 46 | 317 | [S2] |
| MCM-48 | 126 | 511 | [S3] |
| Citrate-LDH | 137 | 8 | [S4] |
| Mesoporous silica | 153 | 462 | [S5] |
| Humulus scandens-derived biochars | 221 | 450 | [S6] |
| Steel slag-derived CSH | 244 | 77 | [S7] |
| Amorphous molybdenum sulphide | 259 | 28 | [S8] |
| NPCS-PEI | 276 | 491 | [S9] |
| CSH | 294 | 240 | This work |
| PCSH | 588 | 371 | This work |
| [1] |
CHEN H, WANG X, LI J, et al. Cotton derived carbonaceous aerogels for the efficient removal of organic pollutants and heavy metal ions. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(11): 6073.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GAWANDE M B, GOSWAMI A, FELPIN F X, et al. Cu and Cu-based nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in review catalysis. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(6): 3722.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
KOHANTORABI M, MOUSSAVI G, GIANNAKIS S. A review of the innovations in metal- and carbon-based catalysts explored for heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation, with focus on radical vs. non-radical degradation pathways of organic contaminants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 411: 127957.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ADITYA T, JANA J, SINGH N K, et al. Remarkable facet selective reduction of 4-nitrophenol by morphologically tailored (111) faceted Cu2O nanocatalyst. ACS Omega, 2017, 2(5): 1968.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
TONG T, ZHAO S, BOO C, et al. Relating silica scaling in reverse osmosis to membrane surface properties. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(8): 4396.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
BERA A, TRIVEDI J S, KUMAR S B, et al. Anti-organic fouling and anti-biofouling poly(piperazineamide) thin film nanocomposite membranes for low pressure removal of heavy metal ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 343: 86.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
FU F, WANG Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 407.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
SUN L, WU J, WANG J, et al. CO2-assisted ‘Weathering’ of steel slag-derived calcium silicate hydrate: A generalized strategy for recycling noble metals and constructing SiO2-based nanocomposites. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 622: 1008.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SHAO N, TANG S, LIU Z, et al. Hierarchically structured calcium silicate hydrate-based nanocomposites derived from steel slag for highly efficient heavy metal removal from wastewater. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(11): 14926. |
| [10] |
CHEN L, WANG X, CHEN Y, et al. Recycling heavy metals from wastewater for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 402: 125922.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHEN Z, LI Y, CAI Y, et al. Application of covalent organic frameworks and metal-organic frameworks nanomaterials in organic/inorganic pollutants removal from solutions through sorption-catalysis strategies. Carbon Research, 2023, 2(1): 8.
DOI |
| [12] |
TAUSTER S J, FUNG S C. Strong metal-support interactions- occurrence among binary oxides of groups IIA-VB. Journal of Catalysis, 1978, 55(1): 29.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GU H, LIU X, WANG S, et al. COF-based composites: extraordinary removal performance for heavy metals and radionuclides from aqueous solutions. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2022, 260(1): 23.
DOI |
| [14] |
WANG X, LI X, WANG J, et al. Recent advances in carbon nitride-based nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 260.
DOI |
| [15] |
GUO H, SUN P, LIANG Y, et al. In-situ fabrication of polyelectrolyte-CSH superhydrophilic coatings via layer-by-layer assembly. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 253: 198.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MEISZTERICS A, ROSTA L, PETERLIK H, et al. Structural characterization of gel-derived calcium silicate systems. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2010, 114(38): 10403.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
KLONKOWSKI A M, GROBENLA B, WIDERNIK T, et al. The coordination state of copper(II) complexes anchored and grafted onto the surface of organically modified silicates. Langmuir, 1999, 15(18): 5814.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
GODIYA C B, REVADEKAR C, KIM J, et al. Amine- bilayer-functionalized cellulose-chitosan composite hydrogel for the efficient uptake of hazardous metal cations and catalysis in polluted water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 436: 129112.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
VICENNATI P, GIULIANO A, ORTAGGI G, et al. Polyethylenimine in medicinal chemistry. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2008, 15(27): 2826.
PMID |
| [20] |
NOSRATI A, LARSSON M, LINDEN J B, et al. Polyethyleneimine functionalized mesoporous diatomite particles for selective copper recovery from aqueous media. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2017, 166: 29.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
HUANG Y, WU H, SHAO T, et al. Enhanced copper adsorption by DTPA-chitosan/alginate composite beads: Mechanism and application in simulated electroplating wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 339: 322.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHADWICK D, KAROLEWSKI M A. Calibration of XPS core-level binding-energies-influence of the surface chemical-shift. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1981, 24(2): 181.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
SUTIRMAN Z A, SANAGI M M, ABD KARIM K J, et al. Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies of Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions adsorption by modified chitosan beads. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 116: 255.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
PENG B, SONG T, WANG T, et al. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@Cu(OH)2 composites and their arsenic adsorption application. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 299: 15.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAO C M, WANG G C, LI S L, et al. Reaction pathway led by silicate structure transformation on decomposition of CaSiO3 in alkali fusion process using NaOH. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(11): 3827.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHANG S, ZHANG X, BAI C, et al. Effect of TiO2 content on the structure of CaO-SiO2-TiO2 system by molecular dynamics simulation. ISIJ International, 2013, 53(7): 1131.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHU K, LIU C, XIA W, et al. Non-radical pathway dominated degradation of organic pollutants by nitrogen-doped microtube porous graphitic carbon derived from biomass for activating peroxymonosulfate: performance, mechanism and environmental application. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 625: 890.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
HUANG C, WANG Y, GONG M, et al. α-MnO2/palygorskite composite as an effective catalyst for heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate PMS for the degradation of Rhodamine B. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 230: 115877.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LIU Y, GUO H, ZHANG Y, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by BiVO4 under visible light for degradation of Rhodamine B. Chemical Physics Letters, 2016, 653: 101.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MARINESCU C, BEN ALI M, HAMDI A, et al. Cobalt phthalocyanine-supported reduced graphene oxide: a highly efficient catalyst for heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate for Rhodamine B and pentachlorophenol degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 336: 465.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHAO Y, AN H, FENG J, et al. Impact of crystal types of AgFeO2 nanoparticles on the peroxymonosulfate activation in the water. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(8): 4500.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
QIN Q, QIAO N, LIU Y, et al. Spongelike porous CuO as an efficient peroxymonosulfate activator for degradation of Acid Orange 7. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 521: 146479.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LAN Q, SUN S R, WU P, et al. Co-doped CuO/visible light synergistic activation of PMS for degradation of Rhodamine B and its mechanism. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1171.
DOI |
| [34] |
XIAO R, LUO Z, WEI Z, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate/ persulfate by nanomaterials for sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation technologies. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2018, 19: 51.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DUAN X, SU C, MIAO J, et al. Insights into perovskite-catalyzed peroxymonosulfate activation: maneuverable cobalt sites for promoted evolution of sulfate radicals. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2018, 220: 626.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHAO Y, WANG H, LI X, et al. Recovery of CuO/C catalyst from spent anode material in battery to activate peroxymonosulfate for refractory organic contaminants degradation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 420: 126552.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SINGH C, GOYAL A, SINGHAL S. Nickel-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: efficient catalysts for the reduction of nitroaromatic compounds and photo-oxidative degradation of toxic dyes. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(14): 7959.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
BHATTACHARJEE A, AHMARUZZAMAN M. Green synthesis of 2D CuO nanoleaves (NLs) and its application for the reduction of p-nitrophenol. Materials Letters, 2015, 161: 79.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
TANG S, VONGEHR S, MENG X. Carbon spheres with controllable silver nanoparticle doping. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(2): 977.
DOI URL |
| [40] | YANG T, ZOU H Y, HUANG C Z. Synergetic catalytic effect of Cu2-xSe nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide coembedded in electrospu n nanofibers for the reduction of a typical refractory organic compound. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(28): 15447. |
| [41] |
WANG Z, XU C, GAO G, et al. Facile synthesis of well-dispersed Pd-graphene nanohybrids and their catalytic properties in 4-nitrophenol reduction. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(26): 13644.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 兰青, 孙盛睿, 吴萍, 杨庆峰, 刘阳桥. 钴掺杂氧化铜/可见光协同活化PMS降解罗丹明B及其机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1171-1177. |
| [2] | 方美蓉,秦利梅,贾晓博,李永生,牛德超,胡泽岚. 聚乙烯亚胺改性的双介孔氧化硅基因载体构建[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 187-192. |
| [3] | 吴德意,孔海南,赵统刚,王崇,叶春. 合成条件对粉煤灰合成沸石过程中沸石生成和品质的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(5): 1153-1158. |
| [4] | 孙静,孙伟燕,高濂,郭景坤. 聚乙烯亚胺在SiC粉体上的定量吸附研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000, 15(2): 259-263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||