无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1257-1264.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230153
所属专题: 【结构材料】超高温结构陶瓷(202312)
收稿日期:2023-03-27
修回日期:2023-05-19
出版日期:2023-05-22
网络出版日期:2023-05-22
通讯作者:
陈代荣, 教授. E-mail: cdr@sdu.edu.cn作者简介:贾玉娜 (1976-), 女, 高级工程师. E-mail: jiayuna@sdu.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIA Yuna1( ), CAO Xu2, JIAO Xiuling1, CHEN Dairong1(
), CAO Xu2, JIAO Xiuling1, CHEN Dairong1( )
)
Received:2023-03-27
Revised:2023-05-19
Published:2023-05-22
Online:2023-05-22
Contact:
CHEN Dairong, professor. E-mail: cdr@sdu.edu.cnAbout author:JIA Yuna (1976-), female, senior engineer. E-mail: jiayuna@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
作为一种性能优异的耐高温结构增强材料, 氧化铝连续纤维应用广泛, 但其规模化制备流程长, 技术难度大。本研究以自制的铝溶胶和市售硅溶胶为前驱体, 研究了铝溶胶的微观结构和组成, 探讨了溶胶具有优异可纺性的原因。通过溶胶-凝胶结合干法纺丝技术制备了氧化铝基凝胶连续纤维, 纤维长度可达1500 m以上, 进一步高温陶瓷化后形成了直径约为10 μm、主晶相为γ-Al2O3和无定型SiO2的氧化铝陶瓷连续纤维, 其中在1100 ℃下煅烧30 min所制备的纤维单丝平均拉伸强度达到2.0 GPa。微观结构分析表明陶瓷纤维结构致密, 其中粒度仅为10~ 20 nm的γ-Al2O3晶粒均匀分布于无定型SiO2中, 使纤维表现出优异的力学性能。该制备过程绿色简单可控, 具有产业化应用前景。进一步对氧化铝连续纤维的耐高温性能进行了分析, 结果表明氧化铝连续纤维可在1000 ℃长时间使用, 短时使用温度可达1300 ℃。
中图分类号:
贾玉娜, 曹旭, 焦秀玲, 陈代荣. 无机酸铝体系氧化铝连续纤维的制备技术研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1257-1264.
JIA Yuna, CAO Xu, JIAO Xiuling, CHEN Dairong. Preparation of Alumina Ceramic Continuous Fibers with Inorganic Acidic Aluminum Sol as Precursor[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1257-1264.
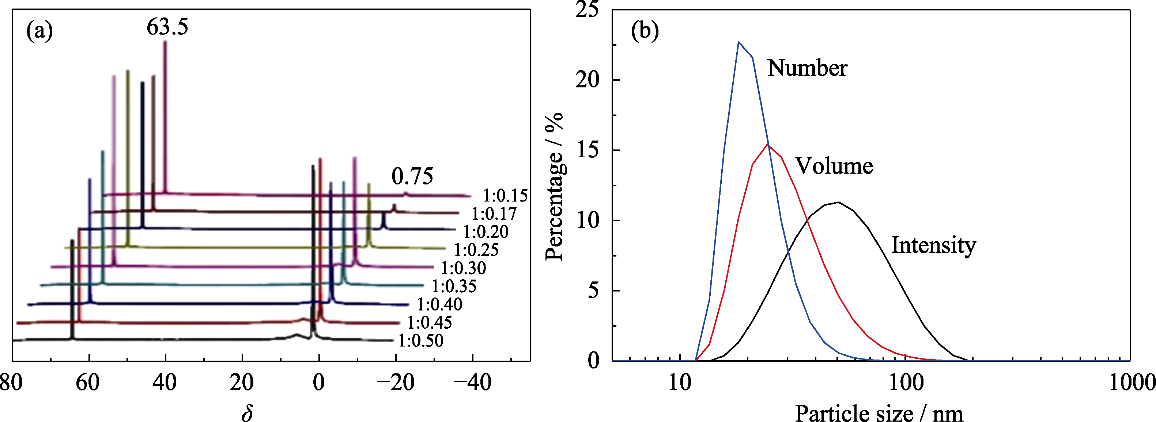
图1 不同n(Al(OH)3)∶n(AlCl3)的铝溶胶的27Al核磁谱(a)和n(Al(OH)3)∶n(AlCl3)=1:0.35时, 复合溶胶的粒径分布曲线(b)
Fig. 1 (a) 27Al NMR spectra of aluminum sol prepared with different n(Al(OH)3)∶n(AlCl3) and (b) particle size distributions of hybrid sol with n(Al(OH)3)∶n(AlCl3) at 1:0.35
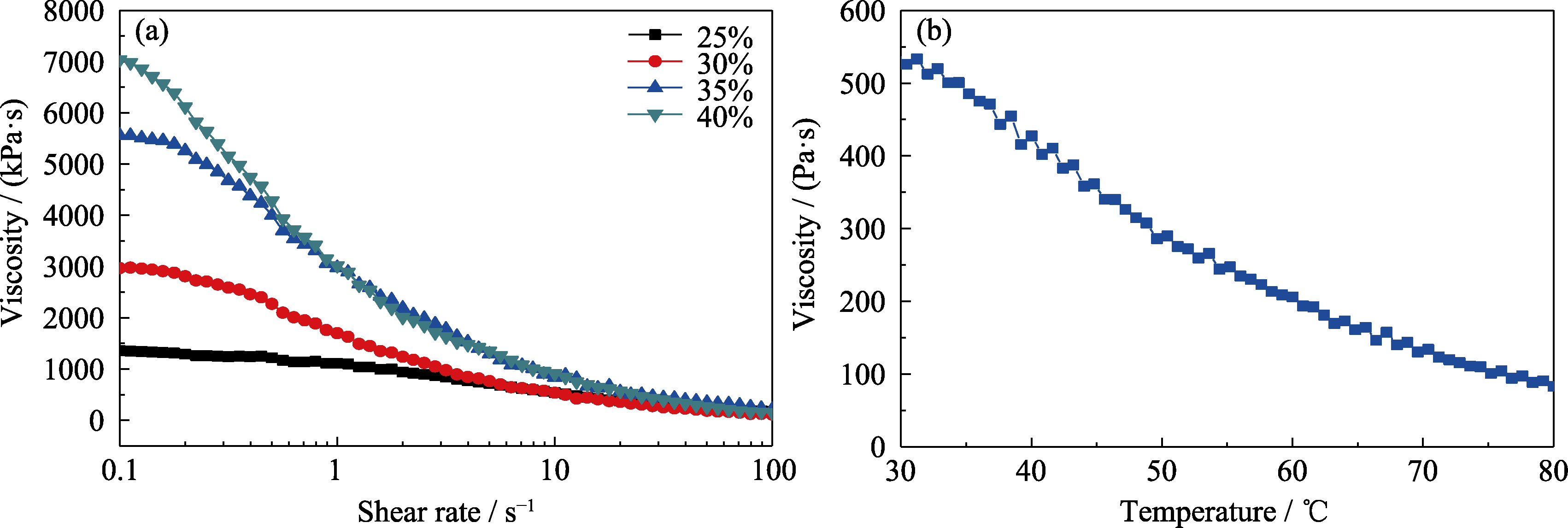
图2 溶胶的流变曲线
Fig. 2 Rheological curves of sol (a) Apparent viscosities of the sol with different solid contents as a function of shear rate, and (b) relationship between apparent viscosity of spinnable sol and temperature

图4 凝胶纤维的红外谱图(a)、热分析(TG-DSC)曲线(b)和不同温度煅烧后纤维的XRD图谱(c)
Fig. 4 FT-IR spectra (a), TG-DSC curves (b) of the gel fibers, and (c) XRD patterns of the fibers calcined at different temperatures
| Calcination conditions | Tensile strength/GPa | Cv of tensile strength/% | Density/(g·cm-3) | Crystalline size/nm | Phase composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900 ℃/30 min | 1.5 | 12.33 | 2.86 | 9.80 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1000 ℃/30 min | 1.6 | 11.26 | 2.91 | 10.36 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1100 ℃/30 min | 2.0 | 12.68 | 2.95 | 10.77 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1200 ℃/30 min | 1.4 | 12.17 | 2.85 | 11.63 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
表1 不同煅烧温度所制备纤维的密度及强度
Table 1 Densities and strengths of fibers calcined at different temperatures
| Calcination conditions | Tensile strength/GPa | Cv of tensile strength/% | Density/(g·cm-3) | Crystalline size/nm | Phase composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900 ℃/30 min | 1.5 | 12.33 | 2.86 | 9.80 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1000 ℃/30 min | 1.6 | 11.26 | 2.91 | 10.36 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1100 ℃/30 min | 2.0 | 12.68 | 2.95 | 10.77 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1200 ℃/30 min | 1.4 | 12.17 | 2.85 | 11.63 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
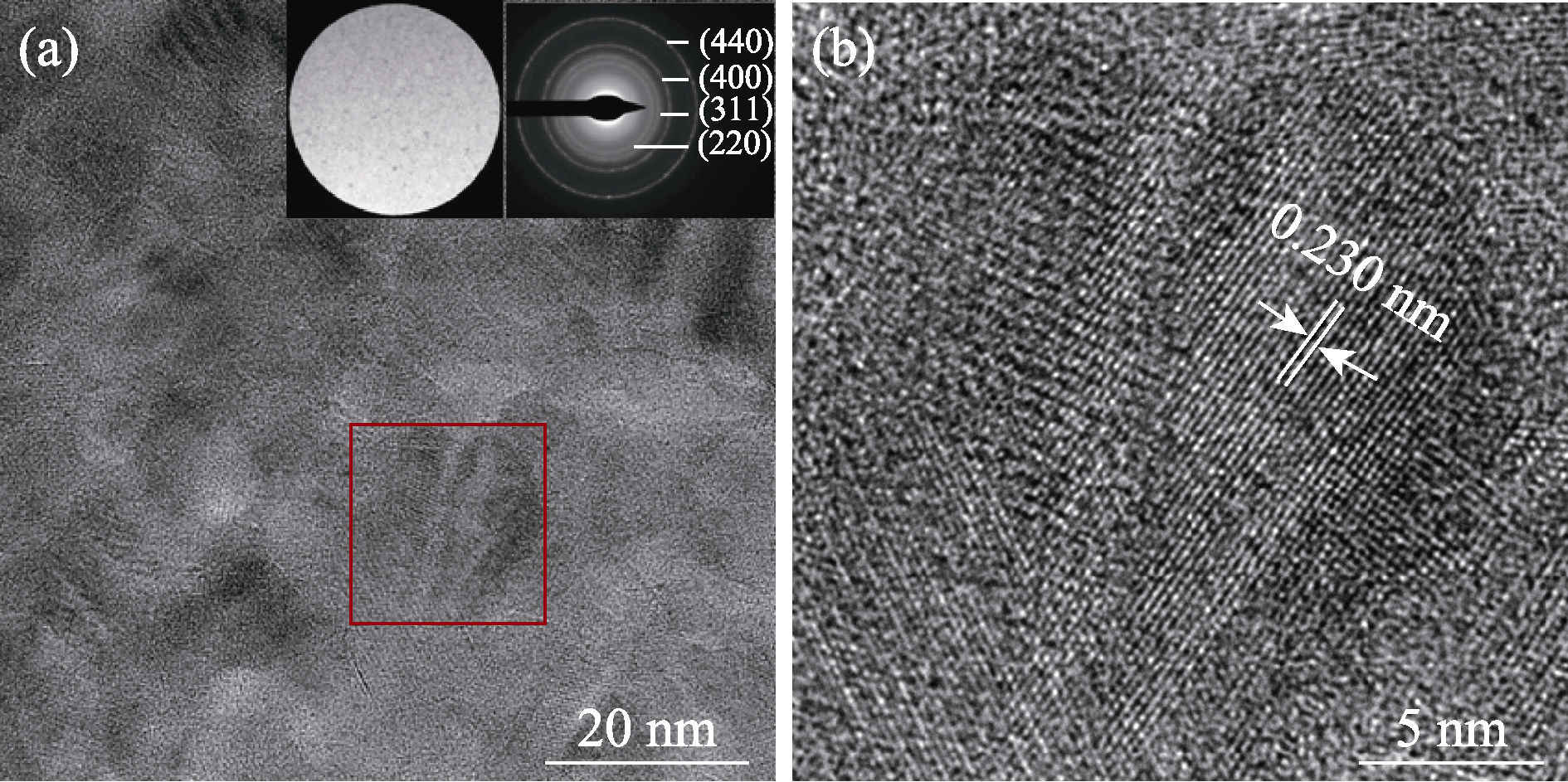
图6 氧化铝陶瓷连续纤维的TEM(a)和高分辨TEM(b)照片
Fig. 6 TEM (a) and high resolution TEM (b) images of alumina ceramic continuous fiber with insets in (a) showing low magnification image and SAED pattern of the fiber
| Calcination conditions | Shrinkage ratio of diameter/% | Tensile strength/GPa | Cv of tensile strength/% | Retention rate/% | Phase composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original fiber | — | 2.035 | 13.70 | — | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1000 ℃/1 h | 0 | 2.002 | 12.89 | 98.38 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1100 ℃/1 h | 0 | 1.933 | 13.01 | 94.99 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1200 ℃/1 h | 0.82 | 1.842 | 14.02 | 90.52 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1300 ℃/0.5 h | 1.95 | 1.579 | 14.57 | 77.59 | Mullite +γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1400 ℃/0.5 h | 2.36 | 0.419 | 15.03 | 20.59 | Mullite |
| 1000 ℃/20 h | 0.28 | 1.926 | 13.24 | 94.64 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1000 ℃/40 h | 1.66 | 1.857 | 13.95 | 91.25 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
表2 不同条件热处理后氧化铝连续纤维的力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of alumina continuous fibers after heat treatment under different conditions
| Calcination conditions | Shrinkage ratio of diameter/% | Tensile strength/GPa | Cv of tensile strength/% | Retention rate/% | Phase composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original fiber | — | 2.035 | 13.70 | — | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1000 ℃/1 h | 0 | 2.002 | 12.89 | 98.38 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1100 ℃/1 h | 0 | 1.933 | 13.01 | 94.99 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1200 ℃/1 h | 0.82 | 1.842 | 14.02 | 90.52 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1300 ℃/0.5 h | 1.95 | 1.579 | 14.57 | 77.59 | Mullite +γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1400 ℃/0.5 h | 2.36 | 0.419 | 15.03 | 20.59 | Mullite |
| 1000 ℃/20 h | 0.28 | 1.926 | 13.24 | 94.64 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
| 1000 ℃/40 h | 1.66 | 1.857 | 13.95 | 91.25 | γ-Al2O3 + amorphous |
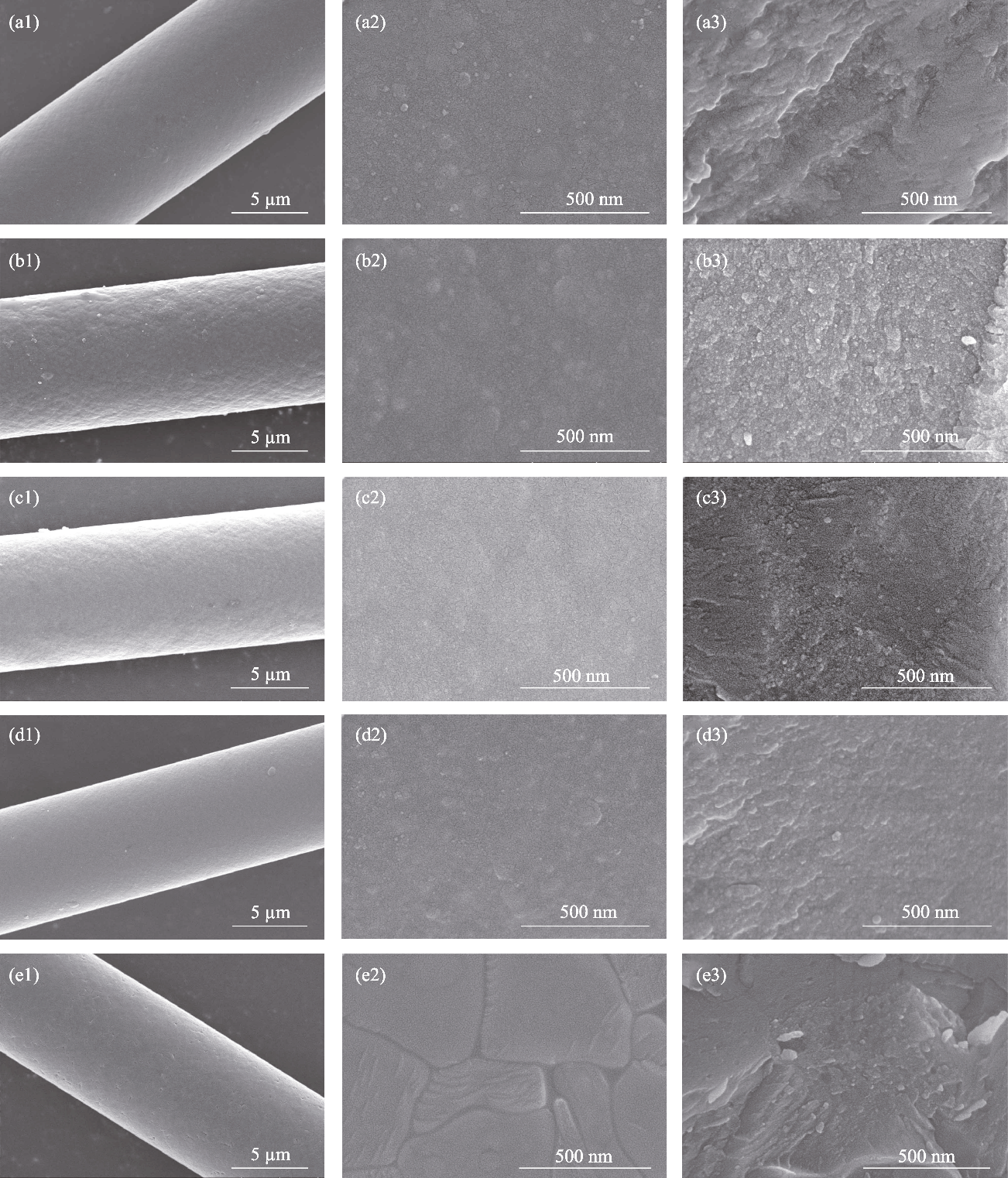
图S1 氧化铝陶瓷连续纤维经不同温度热处理后的SEM照片(全貌(1)、表面(2)、截面(3))
Fig. S1 SEM images of alumina ceramic continuous fiber after heat-treatment at different temperatures (overview (a1-e1), surface (a2-e2), cross section (a3-e3)) (a) 1000 ℃/1 h; (b) 1100 ℃/1 h; (c) 1200 ℃/1 h; (d) 1300 ℃/0.5 h; (e) 1400 ℃/0.5 h

图S2 1000 ℃不同保温时间的氧化铝陶瓷连续纤维的SEM照片(全貌(1)、表面(2)、截面(3))
Fig. S2 SEM images of alumina ceramic continuous fiber at 1000 ℃ with different holding time (overview (a1-b1), surface (a2-b2), cross section (a3-b3)) (a) 1000 ℃/20 h; (b) 1000 ℃/40 h
| [1] |
VOLKMANN E, TUSHTEV K, KOCH D, et al. Assessment of three oxide/oxide ceramic matrix composites: mechanical performance and effects of heat treatments. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2015, 68: 19.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALMEIDA R S M, BERGMÜLLER E L, EGGERT B G F, et al. Thermal exposure effects on the strength and microstructure of a novel mullite fiber. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(5): 1709.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN X, GU L. The Sol-Gel transition of mullite spinning solution in relation to the formation of ceramic fibers. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2008, 46(1): 23.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 焦健, 陈明伟. 新一代发动机高温材料—陶瓷基复合材料的制备、性能及应用. 航空制造技术, 2014(7): 62. |
| [5] | 陈代荣, 周新贵, 朱陆益, 等. 连续陶瓷纤维的制备, 结构, 性能和应用: 研究现状及发展方向. 现代技术陶瓷, 2018, 39(3): 151. |
| [6] | 曹峰, 李效东, 冯春祥, 等. 连续氧化铝纤维制造、性能与应用. 宇航材料工艺, 1999, 6: 6. |
| [7] | SCHAWALLER D, CLAUß B, BUCHMEISER M R. Ceramic filament fibers-a review. Macromolecular Materials & Engineering, 2012, 297(6): 502. |
| [8] |
OKADA K, YASOHAMA S, HAYASHI S, et al. Mullite long fibres prepared by Sol-Gel method using water solvent systems. Key Engineering Materials, 1997, 132-136: 1946.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Committee on Advanced Fibers for High-Temperature Ceramic Composites National Materials Advisory Board, Commission on Engineering and Technical Systems National Research Council. Ceramic Fibers and Coatings. National Academy Press, Washington D C. 1998. |
| [10] | 王涛平, 沈湘黔, 刘涛. 氧化物陶瓷纤维的制备及应用. 矿冶工程, 2004(1): 72. |
| [11] |
CASEY W H. Large aqueous aluminum hydroxide molecules. Chemical Reviews, 2006, 106(1): 1.
PMID |
| [12] |
SHAFRAN K, DESCHAUME O, PERRY C C. High-temperature speciation studies of Al-ion hydrolysis. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(10): 836.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 薛明俊, 周世, 王淙, 等. 无机铝溶胶可纺性的研究. 玻璃与搪瓷, 1994(5): 14. |
| [14] | FERRY J D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 3rd. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1980, 154. |
| [15] |
TAN H B, GUO C S, MA X L. Preparation of mullite fibers by Sol-Gel process and study of their morphology. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2011, 26(11): 1374.
DOI URL |
| [16] | SCHMÜCKER M, FLUCHT F, MECHNICH P. Degradation of oxide fibers by thermal overload and environmental effects. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2012, 557: 10. |
| [17] |
SCHOLZ H, VETTER J, HERBORN R, et al. Oxide ceramic fibers via dry spinning process—from lab to fab. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(4): 1636.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 满鑫, 吴南, 张牧, 贺红亮, 孙旭东, 李晓东. Lu2O3-MgO纳米粉体合成及其复相红外透明陶瓷制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1263-1269. |
| [2] | 杨丛纲, 米乐, 冯爱虎, 于洋, 孙大志, 于云. KH-560改性SiO2绝缘薄膜的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1343-1348. |
| [3] | 朱本必,张旺,张志坚,章建忠,IMRAN Zada,张荻. 光热增强光催化性能二氧化钛(B)/玻纤布复合研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 961-966. |
| [4] | 张少丹, 包维维, 马海萍. Cu 2+、Tb 3+共掺杂BaZrO3高近红外反射颜料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 599-604. |
| [5] | 何 飞, 李 亚, 骆 金, 方旻翰, 赫晓东. 具有气凝胶结构特征的C/SiO2和C/SiC复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(5): 449-458. |
| [6] | 陈婷, 查剑锐, 张筱君, 江伟辉, 江莞, 刘健敏, 吴倩. 硅烷偶联剂对制备硅酸锆薄膜及其抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(11): 1154-1158. |
| [7] | 胡亚华, 顾 牡, 张致远, 刘小林, 黄世明, 刘 波, 张娟楠. Lu2O3纳米线阵列的超声辅助溶胶-凝胶模板法制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(8): 807-811. |
| [8] | 尹月锋, 梁桂杰, 张 强, 潘 峥, 李望南, 李在房. 基于Pechini溶胶-凝胶法的染料敏化太阳能电池的优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(7): 739-744. |
| [9] | 张晓欣, 谢建军, 范灵聪, 林德宝, 陈 旭, 施 鹰. Ce、Pr共掺LSO多晶薄膜的溶胶-凝胶法制备及其发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(6): 647-651. |
| [10] | 吴 霜, 刘 波, 邱志澈, 陈士伟, 张娟楠, 刘小林, 顾 牡, 黄世明, 倪 晨. LuTaO4:Ln3+(Ln=Eu,Tb)透明薄膜制备改进与其发光性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(4): 372-376. |
| [11] | 张媛媛, 唐晓东, 陈莹, 王根水, 董显林. La0.7Ca0.3-xSrxMnO3薄膜的电输运特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(3): 274-278. |
| [12] | 徐家跃, 王 杰, 陈 炜, 肖学峰, 杨波波, 王占勇, 李 飞, 谢会东. 大尺寸硅酸铋晶体的原料合成、晶体生长及闪烁性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(10): 1147-1150. |
| [13] | 刘阳龙, 郑玉婴, 尚鹏博. 铕掺杂的TiO2空心微球的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(7): 699-705. |
| [14] | 李燕春, 张秀玲, 詹志彬, 底兰波. 离子液体对可磁分离TiO2光催化材料结构和性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(7): 706-712. |
| [15] | 张 栩, 王 禹, 李 悦, 杨 猛, 赵相玉, 马立群. Ni替代对锂离子电池材料LiMnTiO4性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(7): 739-744. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||