无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 413-420.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220712
• 专栏:神经形态材料与器件(特邀编辑:万青) • 上一篇 下一篇
田雨1,2( ), 朱小健2(
), 朱小健2( ), 孙翠2, 叶晓羽2, 刘慧媛2, 李润伟2
), 孙翠2, 叶晓羽2, 刘慧媛2, 李润伟2
收稿日期:2022-11-28
修回日期:2022-12-17
出版日期:2023-04-20
网络出版日期:2022-12-28
通讯作者:
朱小健, 研究员. E-mail: zhuxj@nimte.ac.cn作者简介:田雨(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: tianyu@nimte.ac.cn
基金资助:
TIAN Yu1,2( ), ZHU Xiaojian2(
), ZHU Xiaojian2( ), SUN Cui2, YE Xiaoyu2, LIU Huiyuan2, LI Runwei2
), SUN Cui2, YE Xiaoyu2, LIU Huiyuan2, LI Runwei2
Received:2022-11-28
Revised:2022-12-17
Published:2023-04-20
Online:2022-12-28
Contact:
ZHU Xiaojian, professor. E-mail: zhuxj@nimte.ac.cnAbout author:TIAN Yu (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: tianyu@nimte.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
研制具有生物神经元信息功能的柔性电子器件对于发展智能穿戴技术具有重要意义。传统阈值型忆阻器可模仿神经元信息整合功能, 但因缺乏本征柔韧性, 难以满足应用需求。本工作制备了一种基于本征可拉伸阈值型忆阻器的柔性人工神经元, 它由银纳米线-聚氨酯复合介质薄膜和液态金属电极构成。在外加电压下, 器件呈现良好的阈值电阻转变特性, 这归因于银纳米线间形成非连续银导电细丝的动态通断。该器件可模仿生物神经元的信息整合-发放及脉冲强度和脉冲间隔调制的尖峰放电功能。在20%拉伸应变下, 器件工作参数基本保持稳定, 性能未发生明显退化。本工作为发展可拉伸柔性人工神经元及下一代智能穿戴设备提供重要材料和技术参考。
中图分类号:
田雨, 朱小健, 孙翠, 叶晓羽, 刘慧媛, 李润伟. 本征可拉伸阈值型忆阻器及其神经元仿生特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 413-420.
TIAN Yu, ZHU Xiaojian, SUN Cui, YE Xiaoyu, LIU Huiyuan, LI Runwei. Intrinsically Stretchable Threshold Switching Memristor for Artificial Neuron Implementations[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 413-420.
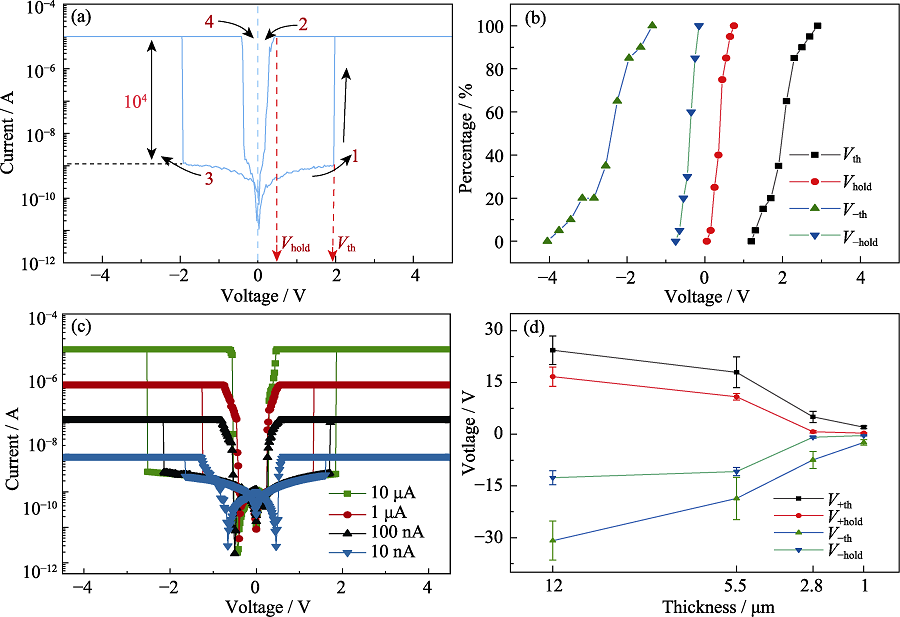
图2 液态金属/银纳米线-聚氨酯复合薄膜/液态金属器件的I-V特性
Fig. 2 I-V characteristics of the Cu@GaIn/AgNWs-PU/Cu@GaIn device (a) I-V curve of the Cu@GaIn/AgNWs-PU/Cu@GaIn device; (b) Cumulative distribution function of the operation voltages; (c) I-V curves of the device under different compliance currents; (d) Dependence of the operation voltage on the thickness of the AgNWs-PU film

图3 液态金属/银纳米线-聚氨酯复合薄膜/液态金属器件的工作机制
Fig. 3 Working mechanism of the Cu@GaIn/AgNWs-PU/Cu@GaIn device (a) Dependence of the device resistance at the LRS on the compliance currents; (b) Illustration of the dynamic Ag filament formation/rupture between AgNWs during threshold switching process
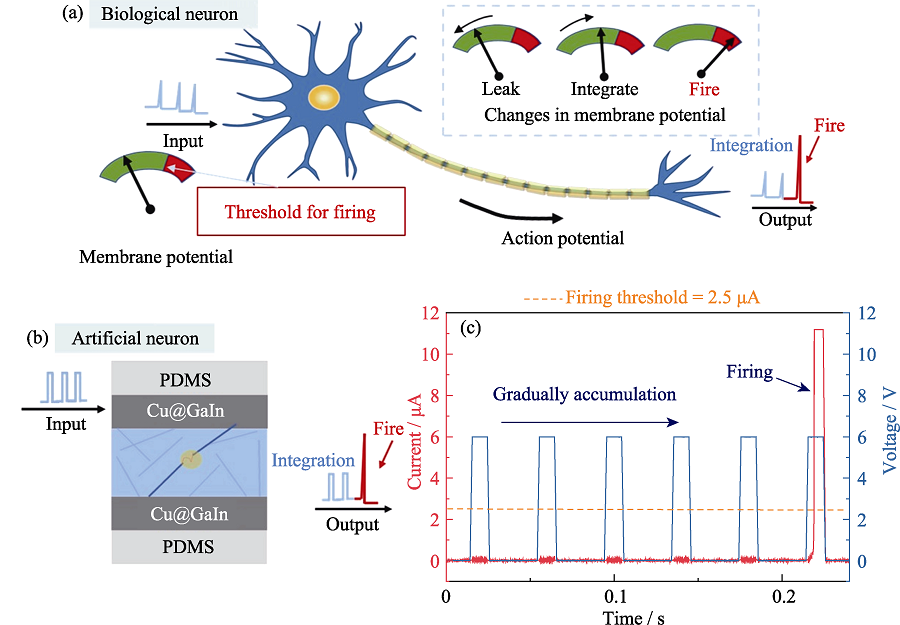
图4 液态金属/银纳米线-聚氨酯复合薄膜/液态金属器件模拟生物神经元的整合发放功能
Fig. 4 Emulation of the integrate-and-fire behaviors of biological neurons with the Cu@GaIn/AgNWs-PU/Cu@GaIn device (a, b) Schematic diagram for (a) biological neuron and (b) artificial neuron; (c) Typical integrate-and-fire behavior of the memristor based artificial neuron; Colorful figures are available on website
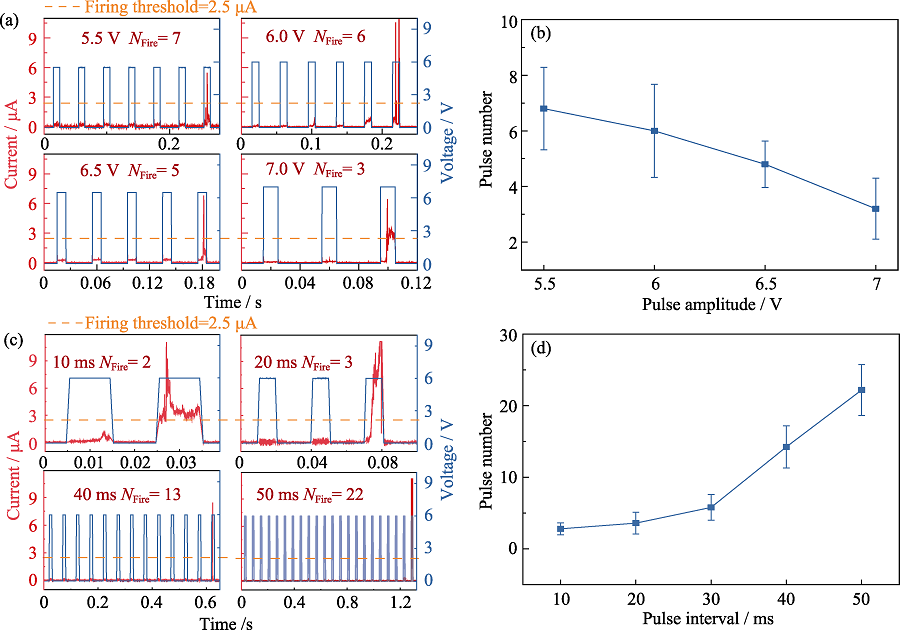
图5 输入脉冲幅值、间隔对阈值型忆阻人工神经元整合发放功能的影响
Fig. 5 Influences of the voltage pulse amplitude and interval on the integrate-and-fire behaviors of the memristor based artificial neuron (a) Integrate-and-fire behaviors of the device as a function of the voltage pulse amplitude with pulse interval and width at 30 ms and 10 ms, respectively; (b) Relationship between the required pulse number for device firing (NFire) and the pulse amplitude; (c) Integrate-and-fire behaviors of the device as a function of the voltage pulse interval with pulse amplitude and width at 6 V and 10 ms, respectively; (d) Relationship between the required pulse number for device firing (NFire) and the pulse interval; Colorful figures are available on website

图6 拉伸应变条件下液态金属/银纳米线-聚氨酯复合薄膜/液态金属器件的阈值转变电压研究
Fig. 6 Threshold switching voltages of the Cu@GaIn/AgNWs-PU/Cu@GaIn device under different tensile strain conditions (a) Schematics of the device stretching under tensile strain; (b) Optical images of the device before and after being stretched by 20%; (c, d) Evolution of the operation voltage for the device with tensile strain in (c) x and (d) y directions
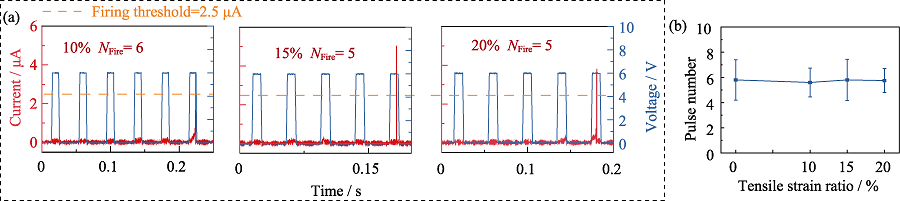
图7 拉伸应变条件下人工神经元的整合发放功能测试
Fig. 7 Integrate-and-fire function test of artificial neuron under tensile strain conditions (a) Control pulse interval (30 ms), width (10 ms) and amplitude (6 V) being unchanged, and the NFire change of the device by changing tensile strain ratio of the device in the x direction; (b) Evolution of NFire of the device with tensile strain ratio
| [1] |
WANG T Y, MENG J L, CHEN L, et al. Flexible 3D memristor array for binary storage and multi-states neuromorphic computing applications. InfoMat, 2021, 3(2):212.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HAN X, Xu Y, Sun B, et al. Highly transparent flexible artificial nociceptor based on forming-free ITO memristor. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 120(9):094103.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
PARK H L, LEE Y, KIM N, et al. Flexible neuromorphic electronics for computing, soft robotics, and neuroprosthetics. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(15):1903558.
DOI URL |
| [4] | LI Z Y, ZHU L Q, GUO L Q, et al. Mimicking neurotransmitter activity and realizing algebraic arithmetic on flexible protein-gated oxide neuromorphic transistors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(6):7784. |
| [5] |
LI H X, HU J Y, CHEN A Z, et al. Single-transistor neuron with excitatory-inhibitory spatiotemporal dynamics applied for neuronal oscillations. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(51):2207371.
DOI URL |
| [6] | STOLIAR P, TRANCHANT J, CORRAZE B, et al. A leaky integrate-and-fire neuron analog realized with a Mott insulator. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(11):1604740. |
| [7] |
BO Y, ZHANG P, LUO Z, et al. NbO2 memristive neurons for burst-based perceptron. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2020, 2(8):2000066.
DOI URL |
| [8] | YANG J Q, WANG R, WANG Z P, et al. Leaky integrate-and-fire neurons based on perovskite memristor for spiking neural networks. Nano Energy, 2020, 74: 104828. |
| [9] |
SHI Q W, WANG J, AZIZ I, et al. Stretchable and wearable resistive switching random-access memory. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2020, 2(7):2000007.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CHEN P, ZHANG X, WU Z, et al. High-yield and uniform NbOx-based threshold switching devices for neuron applications. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2022, 69(5):2391.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUA Q, WU H Q, GAO B, et al. Low-voltage oscillatory neurons for memristor-based neuromorphic systems. Global Challenges, 2019, 3(11):1900015.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XU Y, WANG H, YE D, et al. Electrohydrodynamically printed flexible organic memristor for leaky integrate and fire neuron. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2021, 43(1):116.
DOI URL |
| [13] | ZHU J X, ZHANG X, WANG M R, et al. Flexible memristive spiking neuron for neuromorphic sensing and computing. Acta Physica Sinica, 2022, 71(14):338. |
| [14] |
YI X, YU Z, NIU X, et al. Intrinsically stretchable resistive switching memory enabled by combining a liquid metal-based soft electrode and a metal-organic framework insulator. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2019, 5(2):1800655.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
YANG M, ZHAO X, TANG Q, et al. Stretchable and conformable synapse memristors for wearable and implantable electronics. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(38):18135.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | TANG D X, LIU J Y, WANG Y X, et al. Research progress in flexible resistive random access memory materials. J. Mater. Eng., 2020, 48(7):81. |
| [17] |
YUAN B, ZHAO C, SUN X, et al. Lightweight liquid metal entity. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(14):1910709.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LU Y, GAO S, LI F, et al. Stretchable and twistable resistive switching memory with information storage and computing functionalities. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2021, 6(1):2000810.
DOI URL |
| [19] | ZHAN S Y, WANG Q G, WANG X L, et al.Electric field-induced nonlinear IV characteristic in a AgNWs/PVA film composite. 3rd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering, Shanghai, 2017: 106-111. |
| [20] | LU P, QU Z, WANG Q, et al. Nonlinear conductive behaviour of silver nanowires/silicone rubber composites. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 301(1):012052. |
| [21] |
WANG M, WANG W, LEOW W R, et al. Enhancing the matrix addressing of flexible sensory arrays by a highly nonlinear threshold switch. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(33):1802516.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WANG W, WANG M, AMBSOLI E, et al. Surface diffusion-limited lifetime of silver and copper nanofilaments in resistive switching devices. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1):81.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
ZHU H W, GAO H L, ZHAO H Y, et al. Printable elastic silver nanowire-based conductor for washable electronic textiles. Nano Research, 2020, 13(10):2879.
DOI |
| [24] | 刘峥.IPDI 型水性聚氨酯的固含提高和表面能降低. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学硕士学位论文, 2010. |
| [25] | YANG J, CAO J, HAN J, et al. Stretchable multifunctional self-powered systems with Cu-EGaIn liquid metal electrodes. Nano Energy, 2022, 101: 107582. |
| [26] |
ZHIRNOV V V, MEADE R, CAVIN R K, et al. Scaling limits of resistive memories. Nanotechnology, 2011, 22(25):254027.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LIU D Q, WANG N, WANG G, et al. Nonvolatile bipolar resistive switching in amorphous Sr-doped LaMnO3 thin films deposited by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Applied Physics Letters 2013, 102(13): 134105.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MILANO G, AONO M, BOARINO L, et al. Quantum conductance in memristive devices: fundamentals, developments, and applications. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(32):2201248.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
HUANG C H, MATSUZAKI K, NOMURA K. Threshold switching of non-stoichiometric CuO nanowire for selector application. Applied Physics Letters, 2020, 116(2):023503.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 谢卓琳.氧化物忆阻器的电输运行为调控及其神经元仿生特性研究. 宁波: 中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所博士学位论文, 2021. |
| [31] |
YAN L, PEI Y, WANG J, et al. High-speed Si films based threshold switching device and its artificial neuron application. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 119(15):153507.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ADDA C, CORRAZE B, STOLIAR P, et al. Mott insulators: a large class of materials for leaky integrate-and-fire (LIF) artificial neuron. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 124(15):152124.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHANG Y, FANG Z, YAN X. HfO2-based memristor-CMOS hybrid implementation of artificial neuron model. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 120(21):213502.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHANG Y, XUE W, JI Z, et al. Highly flexible resistive switching memory based on amorphous-nanocrystalline hafnium oxide films. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(21):7037.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [2] | 王彤宇, 冉皓丰, 周广东. 氧化铁忆阻器中缺陷态诱导的模拟型阻变及突触双脉冲易化特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 437-444. |
| [3] | 何慧凯, 杨蕊, 夏剑, 王廷泽, 董德泉, 缪向水. 高均一性二维碲化钼忆阻器阵列及其神经形态计算应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 795-801. |
| [4] | 方华靖, 赵泽天, 武文婷, 汪宏. 柔性电致变色器件研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 140-151. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||