无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 205-212.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220432
于业帆1( ), 徐玲2, 倪忠斌1, 施冬健1, 陈明清1(
), 徐玲2, 倪忠斌1, 施冬健1, 陈明清1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-22
修回日期:2022-10-08
出版日期:2023-02-20
网络出版日期:2022-10-19
通讯作者:
陈明清, 教授. E-mail: mqchen@jiangnan.edu.cn作者简介:于业帆(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 6190606052@stu.jiangnan.edu.cn
基金资助:
YU Yefan1( ), XU Ling2, NI Zhongbing1, SHI Dongjian1, CHEN Mingqing1(
), XU Ling2, NI Zhongbing1, SHI Dongjian1, CHEN Mingqing1( )
)
Received:2022-07-22
Revised:2022-10-08
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-10-19
Contact:
CHEN Mingqing, professor. E-mail: mqchen@jiangnan.edu.cnAbout author:YU Yefan (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 6190606052@stu.jiangnan.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
以氮、磷污染物导致的水体富营养化问题在我国普遍存在。本研究将普鲁士蓝与改性生物炭相结合, 得到普鲁士蓝/生物炭复合材料。通过多种表征手段研究了复合材料的形貌及结构并通过模拟废水测试了其吸附性能。结果表明, 复合材料在pH 8时达到最佳吸附效果, 氨氮去除率在95%以上, 最大吸附量为24.4 mg/g, 比未改性生物碳提高101.3%。对复合材料吸附机理的研究表明, 复合材料通过普鲁士蓝对氨氮的配位作用对多组分污水中氨氮实现了选择性吸附。此外, 复合材料在外加H2O2溶液的条件下可形成芬顿氧化体系, 能实现同步催化降解有机污染物和促进氨氮的吸附, 因此有望在多组分富营养化污水治理中投入实际应用。
中图分类号:
于业帆, 徐玲, 倪忠斌, 施冬健, 陈明清. 普鲁士蓝/生物炭材料的制备及其氨氮吸附机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 205-212.
YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212.
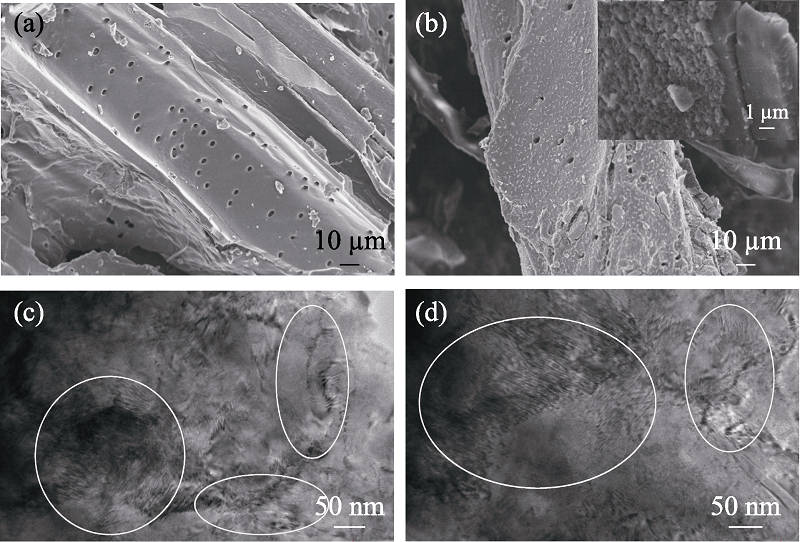
图1 BC700 (a)和BC700-PB (b)的SEM照片, BC700 (c)和BC700-PB (d)的TEM照片
Fig. 1 SEM images of BC700 (a) and BC700-PB (b), and TEM images of BC700 (c) and BC700-PB (d)
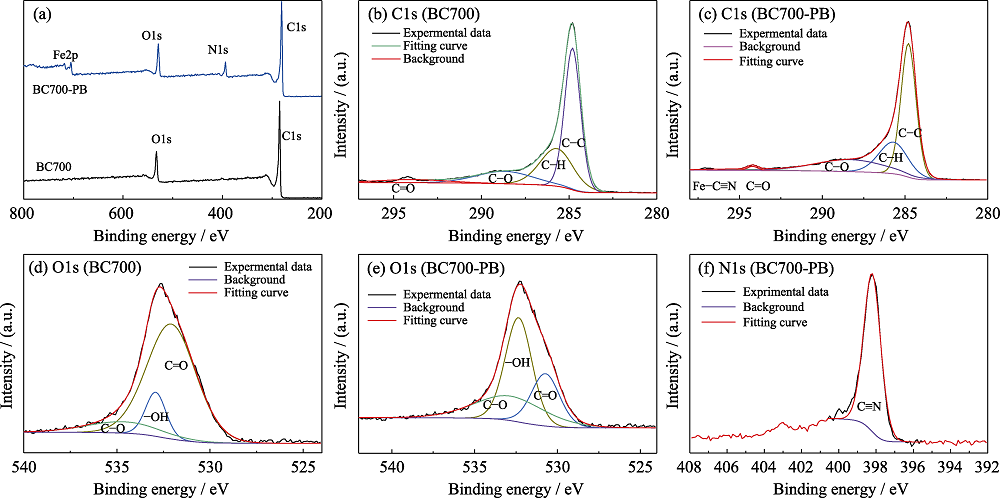
图4 BC700和BC700-PB的XPS全谱(a), BC700(b, d)和BC700-PB (c, e)的C1s(b, c)与O1(d, e)与BC700-PB的N1s(f)XPS谱图
Fig. 4 Full XPS spectra (a) of BC700 and BC700-PB, core-level XPS spectra of the elemental C1s (b, c) and O1s (d, e) of BC700 (b, d) and BC700-PB (c, e), and N1s (f) of BC700-PB Colorful figures are available on website
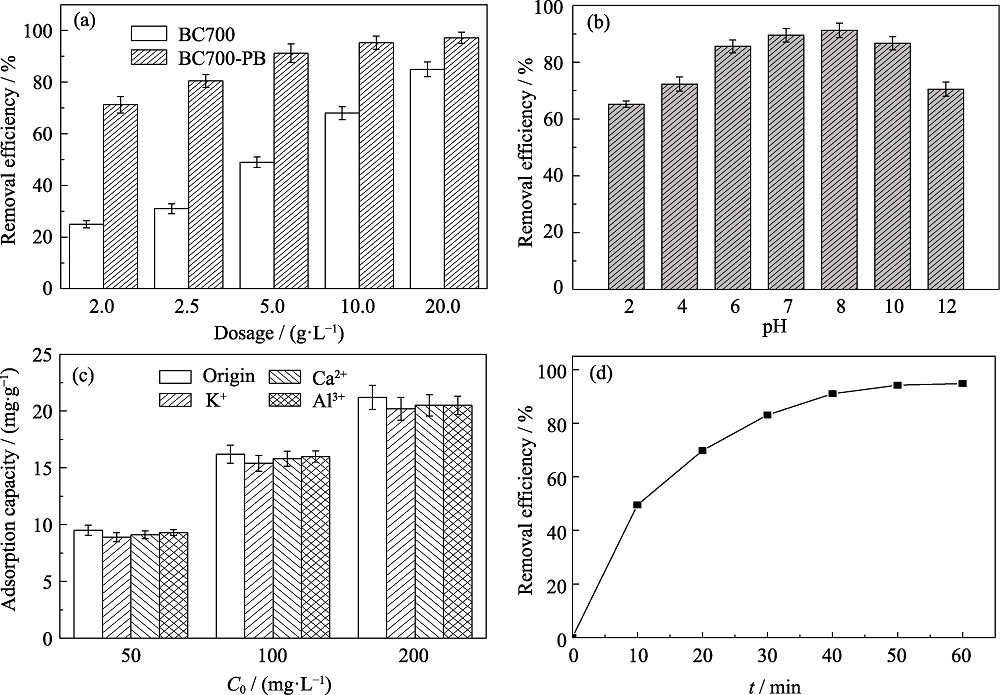
图5 BC700和BC700-PB添加量对吸附氨氮效果的影响(a)(pH 8, C0=50 mg/L, t=60 min), 和体系pH(b)(dosage=5 g/L, C0=50 mg/L, t=60 min)、在不同共存离子(50 mg/L)中污染物初始浓度(c)(dosage=5 g/L, pH 8, t=60 min)以及反应时间(d)(dosage=5 g/L, pH 8, C0=50 mg/L)对BC700-PB吸附氨氮效果的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of dosage on the removal of NH3-N by of BC700 and BC700-PB (pH 8, C0=50 mg/L, t=60 min) (a), effects of pH (dosage=5 g/L, C0=50 mg/L, t=60 min) (b), initial concentration and coexisting ions (C0=50 mg/L, dosage=5 g/L, pH 8, t=60 min) (c), and reaction time(dosage=5 g/L, pH 8, C0=50 mg/L) (d) on the removal of NH3-N by BC700-PB

图7 BC700-PB对氨氮的吸附热力学的Langmuir模型(a)和Freundlich模型(b)拟合; BC700-PB对氨氮的吸附动力学的拟一级动力学模型(c)和拟二级动力学模型(d)拟合
Fig. 7 Langmuir (a) and Freundlich models (b) of NH3-N on BC700-PB, and pseudo-first-order kinetic (c) and pseudo-second-order kinetic (d) models of NH3-N on BC700-PB

图9 不同吸附剂、添加剂对氨氮和HA双组分污水的吸附效果的影响(pH 2, dosage=5 g/L, C0=50 mg/L) (a)和BC700-PB体系中添加了DMPO的EPR谱图(b)
Fig. 9 Effects of adsorbents and additive on the removal efficiency for mixed solution of NH3-N and HA(pH 2, dosage=5 g/L, C0=50 mg/L) (a), and EPR spectra of DMPO-OH (b) adducts in the systems of BC700-PB
| [1] |
LIN S, SHEN S L, ZHOU A, et al. Assessment and management of lake eutrophication: a case study in Lake Erhai, China. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 751(1): 141618.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
SHENG K, ZHANG P, OU S J, et al. Spatiotemporal nutrient patterns, composition, and implications for eutrophication mitigation in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2022, 266(5): 107749.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HUANG W, ZHANG Y, LI D. Adsorptive removal of phosphate from water using mesoporous materials: a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 193(15): 470.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
ZHANG M, SONG G, GELARDI D L, et al. Evaluating biochar and its modifications for the removal of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate in water. Water Research, 2020, 186(1): 116303.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LU Y, CAI Y, ZHANG S, et al. Application of biochar-based photocatalysts for adsorption-(photo)degradation/reduction of environmental contaminants: mechanism, challenges and perspective. Biochar, 2022, 4: 45.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
QIU M, LIU L, LING Q, et al. Biochar for the removal of contaminants from soil and water: a review. Biochar, 2022, 4: 19.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIANG L, XI F, TAN W, et al. Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar, 2021, 3(1): 255.
DOI URL |
| [8] | GONG Y P, NI Z Y, XIONG Z Z, et al. Phosphate and ammonium adsorption of the modified biochar based on Phragmites australis after phytoremediation. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2017, 24(9): 8326. |
| [9] |
YI A, MP A, MVSA B, et al. A SAXS study of the pore structure evolution in biochar during gasification in H2O, CO2 and H2O/CO2. Fuel, 2021, 292: 120384.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
XIAO Y, WU Z J, CUI M, et al. Co-modification of biochar and bentonite for adsorption and stabilization of Pb2+ ions. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1083.
DOI |
| [11] |
ANDREAS L. Prussian blue, an inorganic evergreen. Journal of Chemical Education, 1981, 58(12): 1013.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIN H, FANG Q, WANG W, et al. Prussian blue/PVDF catalytic membrane with exceptional and stable Fenton oxidation performance for organic pollutants removal. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020, 273(15): 119047.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
TAKAHASHI A, TANAKA H, PARAJULI D, et al. Historical pigment exhibiting ammonia gas capture beyond standard adsorbents with adsorption sites of two kinds. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(20): 6376.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
TAKAHASHI A, MINAMI K, NODA K, et al. Trace ammonia removal from air by selective adsorbents reusable with water. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2020, 12(13): 15115.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WAN S, QIU L, TANG G, et al. Ultrafast sequestration of cadmium and lead from water by manganese oxide supported on a macro-mesoporous biochar. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 387(1): 124095.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
HUFF M D, LEE J W. Biochar-surface oxygenation with hydrogen peroxide. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 165(1): 17.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
ZHAO G, FENG J J, ZHANG Q L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Prussian blue modified magnetite nanoparticles and its application to the electrocatalytic reduction of H2O2. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2005, 17(12): 3154.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
FENG S S, CAO X, ZHENG W, et al. In-situ formed Prussian blue nanoparticles supported by porous biochar as highly efficient removal of cesium ions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(3): 107972.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
AI J, LU C, BERG F, et al. Biochar catalyzed dichlorination-which biochar properties matter. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 406(15): 124724.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
CHEN L, CHEN X L, ZHOU C H, et al. Environmental-friendly montmorillonite-biochar composites: facile production and tunable adsorption-release of ammonium and phosphate. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 156(10): 648.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SIZMUR T, FRESNO T, AKGUL G, et al. Biochar modification to enhance sorption of inorganics from water. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 246: 34.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
CUI X, HAO H, HE Z, et al. Pyrolysis of wetland biomass waste: potential for carbon sequestration and water remediation. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 173(15): 95.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
YIN L A, NT A, TKL A, et al. Microwave assisted hydrothermal preparation of rice straw hydrochars for adsorption of organics and heavy metals. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 273: 136.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
LI L, LAI C, HUANG F, et al. Degradation of naphthalene with magnetic bio-char activate hydrogen peroxide: synergism of bio-char and Fe-Mn binary oxides. Water Research, 2019, 160(1): 238.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
SUN Y M, ZHOU P, ZHANG P, et al. New insight into carbon materials enhanced Fenton oxidation: a strategy for green iron(III)/ iron(II) cycles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450(15): 138423.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张国庆, 秦鹏, 黄富强. 空间限域铅离子与钙钛矿纳米晶间的可逆转换与信息存储应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 445-451. |
| [2] | 周帆, 毕辉, 黄富强. 用稻壳制备亚甲基蓝高吸附容量的超高比表面积活性炭[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 893-903. |
| [3] | 李大伟, 马腾飞, 田原宇, 朱锡锋, 乔英云 . 碱炭比及活化温度对稻壳活性炭极微孔的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(1): 17-22. |
| [4] | 周述慧, 传秀云. 埃洛石为模板合成中孔炭[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(6): 584-588. |
| [5] | 孙淑英, 张钦辉, 于建国. 低维纳米立方相Li4Mn5O12的制备及锂吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(6): 626-630. |
| [6] | 王维清,冯启明,董发勤,李虎杰,赵晓东. Fe3O4/斜发沸石磁性复合材料的制备及其性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(4): 401-405. |
| [7] | 周新涛,刘起峰,苏达根,来兰梅. 偏高岭土水热合成高硅SAPO-5分子筛及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(3): 581-585. |
| [8] | 田从学,张 昭. 工业硫酸氧钛合成有序介孔TiO2及其机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(2): 225-228. |
| [9] | 王德举,刘仲能,谢在库. 汽相转化法制备无粘结剂小晶粒 ZSM-5沸石[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(3): 592-596. |
| [10] | 刘彩华,王雯娟,程文萍,于心玉,杨建国,何鸣元. 含稳定骨架铁的Fe-MCM-41介孔分子筛的合成与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 171-174. |
| [11] | 李劲,何姣莲,时进刚,陈振华,曾光明. 鼠李糖脂碳吸附剂的制备及其吸附性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(6): 1339-1344. |
| [12] | 张瑛,窦涛,李玉平,石德先,赵震. 沸石降解法合成孔壁含有沸石结构单元的介孔结构材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(6): 1423-1430. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||