无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 155-162.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220326
收稿日期:2022-06-11
修回日期:2022-08-08
出版日期:2023-02-20
网络出版日期:2022-09-15
通讯作者:
胡海龙, 副教授. E-mail: hailonghu@csu.edu.cn作者简介:陈雷(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: sccl@mail.ustc.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2022-06-11
Revised:2022-08-08
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-09-15
Contact:
HU Hailong, associate professor. E-mail: hailonghu@csu.edu.cnAbout author:CHEN Lei (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: sccl@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
与其它储能设备相比, 由介电复合材料制得的介质电容器在快速充放电能力与高功率密度方面极具优势, 如何提高介电复合材料能量密度与优化其击穿性能已成为当前研究热点之一。为进一步调控并兼顾介电常数与击穿性能, 本工作基于DBM(Dielectric Breakdown Model, 介电击穿模型), 采用有限元数值模拟, 研究了无机填料的分布对柔性聚二甲硅氧烷(PDMS)基介电复合材料体系的电场与发生介电击穿时击穿损伤形貌演变的具体影响。研究结果表明: 填料与基体边界处存在较大的介电差异, 可以使用较大介电常数的聚合物基体或较小介电常数的无机填料来减小其界面处的高电场区域, 继而提高复合材料的耐击穿能力;同时发现当无机填料分散更均匀时, 其树状损伤通道更容易产生分支, 此种情况将使介电击穿的树状损伤通道的损伤位点增多, 延缓其损伤速度, 继而提高复合材料的耐击穿性能。该研究结果将为开发高储能密度且具有优异击穿性能的有机-无机复合电介质材料提供坚实的理论依据。
中图分类号:
陈雷, 胡海龙. 柔性PDMS基介电复合材料的电场及击穿损伤形貌演变规律研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 155-162.
CHEN Lei, HU Hailong. Evolution of Electric Field and Breakdown Damage Morphology for Flexible PDMS Based Dielectric Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 155-162.
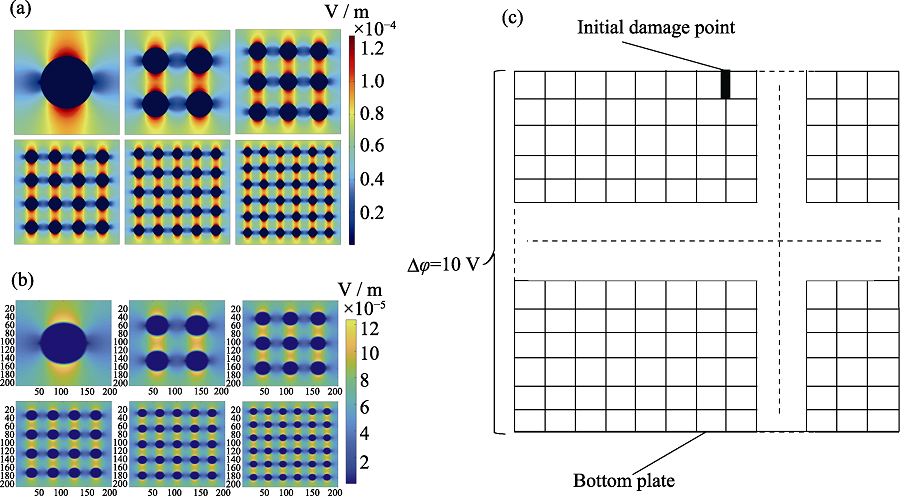
图3 DBM模型的计算方法
Fig. 3 Calculation method of DBM model (a) Electric field distribution determined by finite element analysis; (b) Electric field distribution determined by MATLAB; (c) Two-dimensional array model consisting of 200×200 grid points Colorful figures are available on website
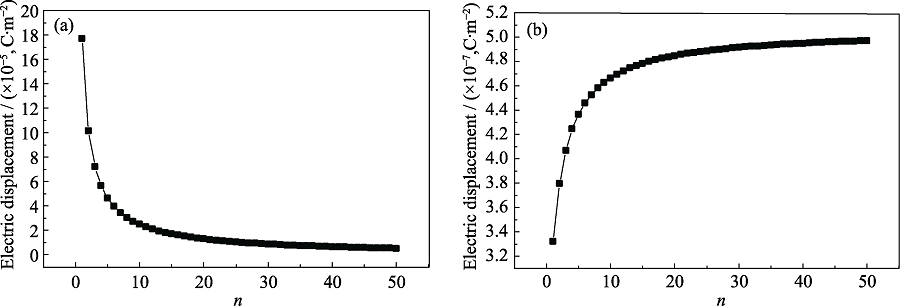
图4 改变填料与基体介电常数之比时, 介电复合材料电位移的变化
Fig. 4 Electrical displacement evolution of dielectric composite material with varied ratio n between fillers and matrix dielectric constant (a)When the dielectric composite filler is selected to be BaTiO3; (b) When the dielectric composite matrix is selected to be PDMS
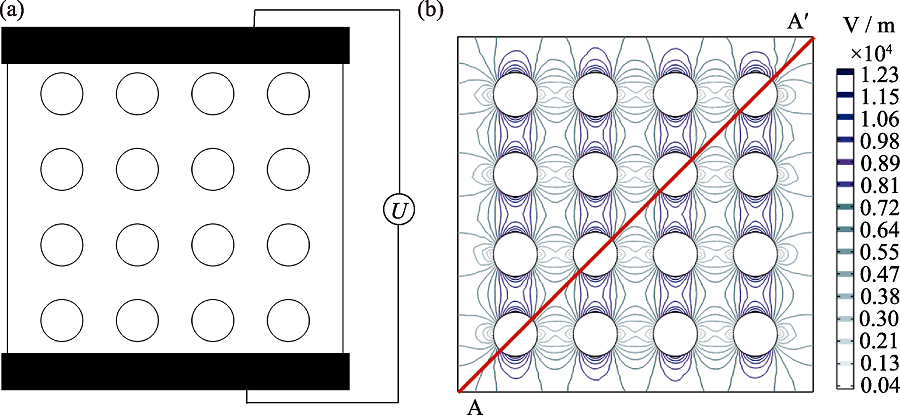
图7 电场分布分析
Fig. 7 Analysis of electric field distribution (a) Dielectric composites composed of filler particles and matrix; (b) Internal electric field distribution in dielectric composites Colorful figures are available on website
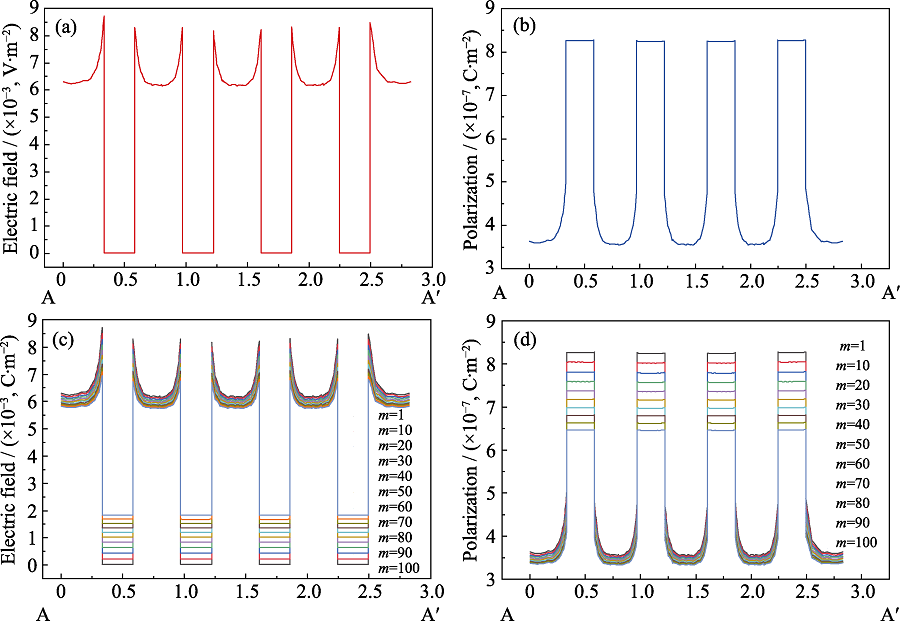
图8 不同介电常数时的电场及电位移场分布
Fig. 8 Electric field and displacement field distribution with different dielectric constant (a) Electric field distribution along AA' transversal; (b) Electric displacement field distribution along AA' transversal; (c) Electric field distribution along AA' transversal with dielectric constant of filler particles reduced by m times; (d) Electric displacement field distribution along AA' transversal with dielectric constant of filler particles reduced by m times Colorful figures are available on website
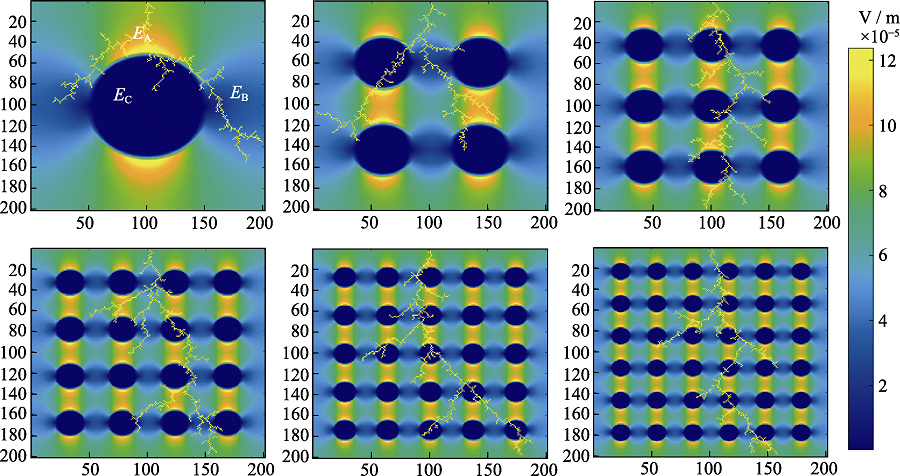
图9 添加不同无机填料含量的介电复合材料的击穿损伤形貌
Fig. 9 Breakdown damage morphologies of dielectric composites with different contents of inorganic fillers Colorful figures are available on website
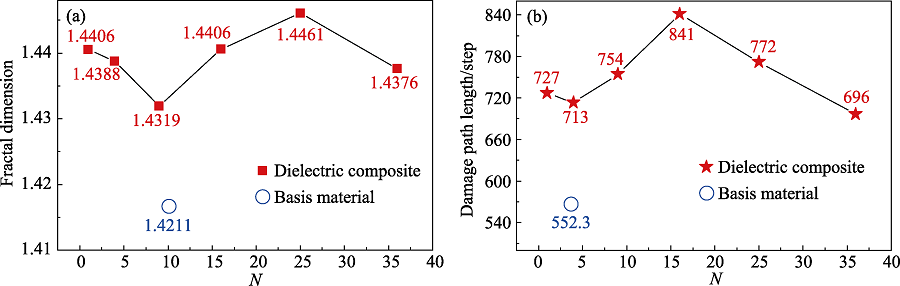
图10 不同含量无机填料的介电复合材料与纯聚合物基体的损伤形貌量化对比分析
Fig. 10 Quantitative analysis of breakdown damage morphology between dielectric composite with different contents of filler particles and pure polymer matrix (a) Fractal dimension; (b) Damage path length
| [1] |
LI D, ZENG X, LI Z, et al. Progress and perspectives in dielectric energy storage ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(4): 675.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHU B, XIN Z, REN K, et al. A dielectric polymer with high electric energy density and fast discharge speed. Science, 2006, 313(5785): 334.
PMID |
| [3] |
HU H, ZHANG F, LUO S, et al. Recent advances in rational design of polymer nanocomposite dielectrics for energy storage. Nano Energy, 2020, 74: 104844.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HU H, ZHANG F, LUO S, et al. Electrocaloric effect in relaxor ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites for solid-state cooling. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(33): 16814.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WANG L, GAO F, XU J, et al. Enhanced dielectric tunability and energy storage properties of plate-like Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3/poly(vinylidene fluoride) composites through texture arrangement. Composites Science and Technology, 2018, 158: 112.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG SIJING, QU PENG, LI CHENG, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of dendritic BaTiO3 ceramic powders and its application in BaTiO3/P(VDF-TrFE) composites. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2017, 14(5): 969.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG Y, WANG L, YUAN Q, et al. Ultrahigh energy density and greatly enhanced discharged efficiency of sandwich-structured polymer nanocomposites with optimized spatial organization. Nano Energy, 2018, 44: 364.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HOLLAND I. Fundamentals of the finite element method. Computers & Structures, 1974, 4(1): 3.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
BERGERO P, PERUANI F, SOLOVEY G, et al. Dielectric breakdown model for conductor-loaded and insulator-loaded composite materials. Physical Review E, 2004, 69(1): 016123.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
NIEMEYER L, PIETRONERO L, WIESMANN H J. Fractal dimension of dielectric breakdown. Physical Review Letters, 1984, 52(12): 1033.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ADILA ISMAIL F, ROZANA A M O, SOBRI IDRIS M, et al. Dielectric and microstructural properties of BaTiO3 and Ba0.9925Er0.0075TiO3 ceramics. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2017, 162: 01051.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MENG X, ZHANG Z, LIN D, et al. Effects of particle size of dielectric fillers on the output performance of piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(5): 991.
DOI URL |
| [13] | FENG X J, LIU X L, ZHAO K, et al. Effects of dopamine- modified BaTiO3 on breakdown strength of BaTiO3/PVDF composites. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2015, 32(3): 699. |
| [14] |
CHEN S S, HU J, GAO L, et al. Enhanced breakdown strength and energy density in PVDF nanocomposites with functionalized MgO nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(40): 33231.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 迟晓红.纳米蒙脱土/聚烯烃复合材料结构形态与电树生长机理研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学博士学位论文, 2015. |
| [16] | 薛福明.基于WZ模型的电树枝生长仿真分析. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学硕士学位论文, 2012. |
| [17] |
IMAI T, SAWA F, OZAKI T, et al. Influence of temperature on mechanical and insulation properties of epoxy-layered silicate nanocomposite. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2006, 13(2): 445.
DOI URL |
| [18] | ZHOU K, BOGGS S A, RAMPRASAD R, et al. Dielectric response and tunability of a dielectric-paraelectric composite. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(10): 325. |
| [19] |
ZHU L. Exploring strategies for high dielectric constant and low loss polymer dielectrics. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2014, 5(21): 3677.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
HUANG X, JIANG P. Core-shell structured high-k polymer nanocomposites for energy storage and dielectric applications. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(3): 546.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [3] | 马晓森, 张丽晨, 刘砚超, 汪全华, 郑家军, 李瑞丰. 13X@SiO2合成及其甲苯吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [4] | 张硕, 付前刚, 张佩, 费杰, 李伟. C/C多孔体的高温热处理对C/C-SiC复合材料摩擦磨损行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 561-568. |
| [5] | 冯静静, 章游然, 马名生, 陆毅青, 刘志甫. 冷烧结技术的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 125-136. |
| [6] | 荆开开, 管皞阳, 朱思雨, 张超, 刘永胜, 王波, 王晶, 李玫, 张程煜. Cansas-II SiCf/SiC复合材料的高温拉伸蠕变行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 177-183. |
| [7] | 胡佳军, 王凯, 侯鑫广, 杨婷, 夏鸿雁. 熔盐法合成高导热磷化硼及其热管理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [8] | 韦婷婷, 徐华蕊, 朱归胜, 龙神峰, 张秀云, 赵昀云, 江旭鹏, 宋金杰, 郭宁杰, 龚祎鹏. BaTiO3陶瓷的低温冷烧结制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 903-910. |
| [9] | 欧阳琴, 王艳菲, 徐剑, 李寅生, 裴学良, 莫高明, 李勉, 李朋, 周小兵, 葛芳芳, 张崇宏, 何流, 杨磊, 黄政仁, 柴之芳, 詹文龙, 黄庆. 核用碳化硅纤维增强碳化硅复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [10] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [11] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 三维碳化硅纳米线增强碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的电磁屏蔽性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 579-584. |
| [12] | 张叶, 姚冬旭, 左开慧, 夏咏锋, 尹金伟, 曾宇平. 原位引入BN-SiC燃烧合成Si3N4-BN-SiC复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 574-578. |
| [13] | 姚晓刚, 彭海益, 顾忠元, 何飞, 赵相毓, 林慧兴. 聚苯醚/钙镧钛微波复合基板[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 493-498. |
| [14] | 叶芬, 江向平, 陈云婧, 黄枭坤, 曾仁芬, 陈超, 聂鑫, 成昊. (0.96NaNbO3-0.04CaZrO3)-xFe2O3反铁电陶瓷的介电及储能性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 499-506. |
| [15] | 王洪达, 冯倩, 游潇, 周海军, 胡建宝, 阚艳梅, 陈小武, 董绍明. SiC/SiC-哈氏合金异质连接机制及其氟熔盐腐蚀特性分析[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 452-458. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
