无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 79-86.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220242
李涛1( ), 曹鹏飞1, 胡力涛1, 夏勇1, 陈一1, 刘跃军1, 孙翱魁1,2(
), 曹鹏飞1, 胡力涛1, 夏勇1, 陈一1, 刘跃军1, 孙翱魁1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-23
修回日期:2022-05-31
出版日期:2022-06-16
网络出版日期:2022-06-16
通讯作者:
孙翱魁, 副教授. E-mail: aksun@hut.edu.cn作者简介:李 涛(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 17404200515@stu.hut.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Tao1( ), CAO Pengfei1, HU Litao1, XIA Yong1, CHEN Yi1, LIU Yuejun1, SUN Aokui1,2(
), CAO Pengfei1, HU Litao1, XIA Yong1, CHEN Yi1, LIU Yuejun1, SUN Aokui1,2( )
)
Received:2022-04-23
Revised:2022-05-31
Published:2022-06-16
Online:2022-06-16
Contact:
SUN Aokui, associate professor. E-mail: aksun@hut.edu.cnAbout author:LI Tao (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 17404200515@stu.hut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
二硫化钼(MoS2)作为水系锌离子电池的正极材料, 受到锌离子(Zn2+)与主体框架之间的强静电相互作用表现出缓慢的反应动力学。并且MoS2的层间距较窄难以嵌入大尺寸水合Zn2+, 导致MoS2电极呈现出较低的放电比容量。本研究通过一种简单的氨水辅助水热法制备了NH4+扩层的二硫化钼(MoS2-N)电极, 氨水分解产生的氨气在促进硫代乙酰胺水解和提供还原性S2-的同时, 还会产生大量NH4+作为插层离子, 将MoS2的层间距由0.62 nm扩展至0.92 nm, 进而大大降低了Zn2+嵌入能垒(改性电极的电荷转移电阻Rct低至35 Ω)。当电流密度为0.1 A·g-1时, MoS2-N电极的初始放电比容量相比未扩层的MoS2电极提高了1倍, 高达149.9 mAh·g−1。同时在1.0 A·g-1电流密度下放电比容量稳定在110 mAh·g-1左右, 循环200圈后库仑效率将近100%。本研究提出的氨水辅助扩层法, 丰富了提升MoS2电化学性能的改性策略, 为后续的正极材料开发提供了新的思路。
中图分类号:
李涛, 曹鹏飞, 胡力涛, 夏勇, 陈一, 刘跃军, 孙翱魁. NH4+扩层MoS2的制备及其储锌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 79-86.
LI Tao, CAO Pengfei, HU Litao, XIA Yong, CHEN Yi, LIU Yuejun, SUN Aokui. NH4+ Assisted Interlayer-expansion of MoS2: Preparation and Its Zinc Storage Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 79-86.
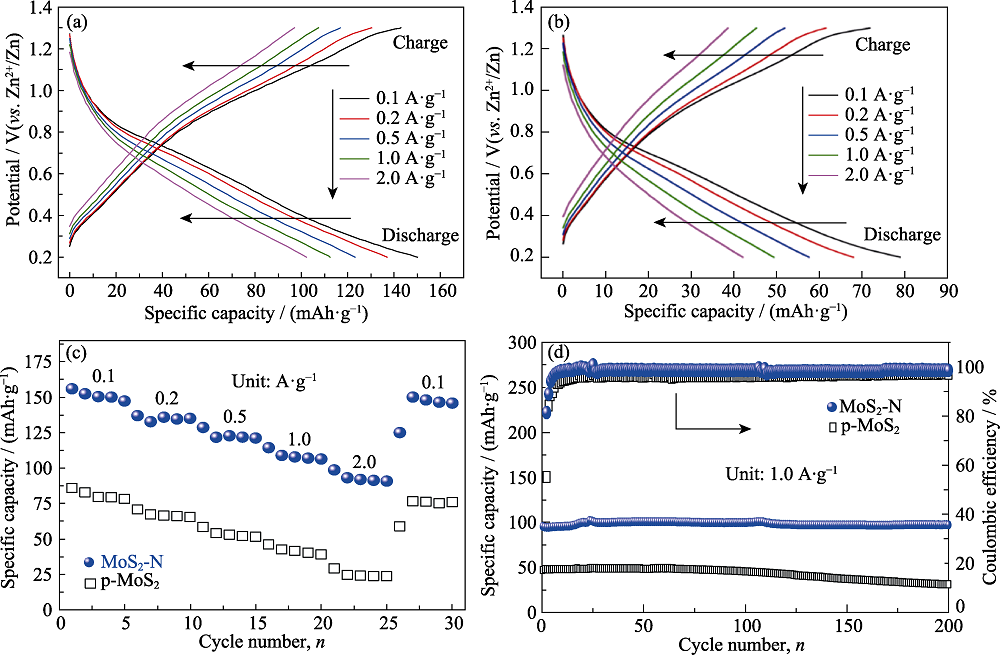
图4 (a) MoS2-N和(b) p-MoS2在不同电流密度下的恒电流充放电曲线, (c) MoS2-N和p-MoS2在不同电流密度下的倍率性能和(d)在1.0 A·g−1下的循环性能
Fig. 4 GCD curves under different current densities of (a) MoS2-N and (b) p-MoS2, (c) rate capabilities under different current densities and (d) cyclic performance at 1.0 A·g−1 of MoS2-N and p-MoS2 Colorful figures are available on website
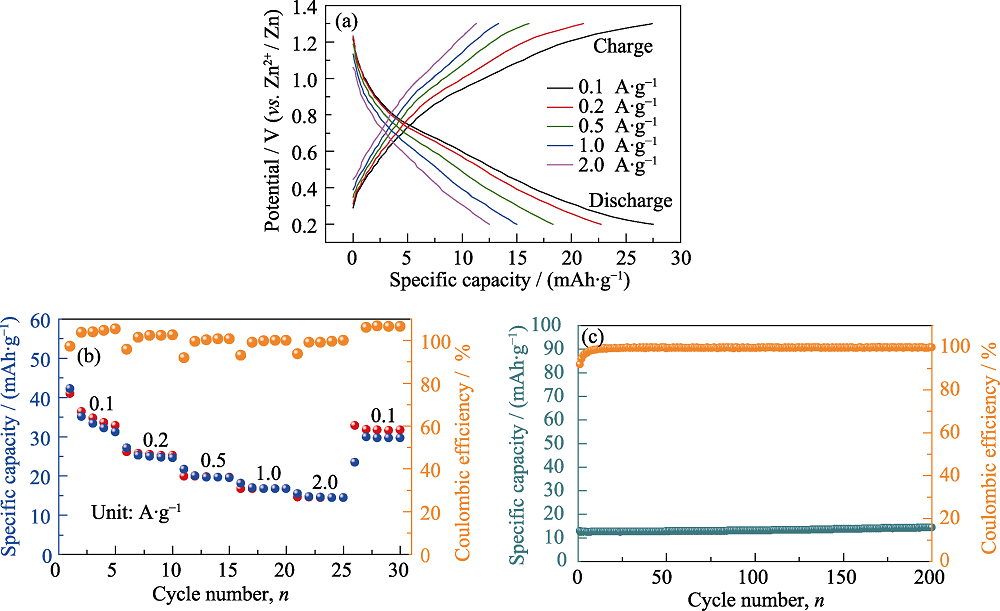
图S2 (a) A-MoS2-N的恒电流充放电曲线, (b)倍率性能和(c)在0.1 A·g-1下的循环性能
Fig. S2 (a) GCD curves, (b) rate capability under different current densities and (c) cyclic performance at 1.0 A·g-1 of A-MoS2-N

图5 储能机理分析
Fig. 5 Analysis of energy storage mechanism (a) CV curves at different scan rates from 0.2 to 1.0 mV·s−1; (b) Fitting lines of lgi vs. lgv; (c) Fitting lines of v1/2 vs. i/v1/2; (d) Histogram of capacitive-controlled (blue) and diffusion controlled (orange) distributions at different scan rates for of MoS2-N electrode Colorful figures are available on website
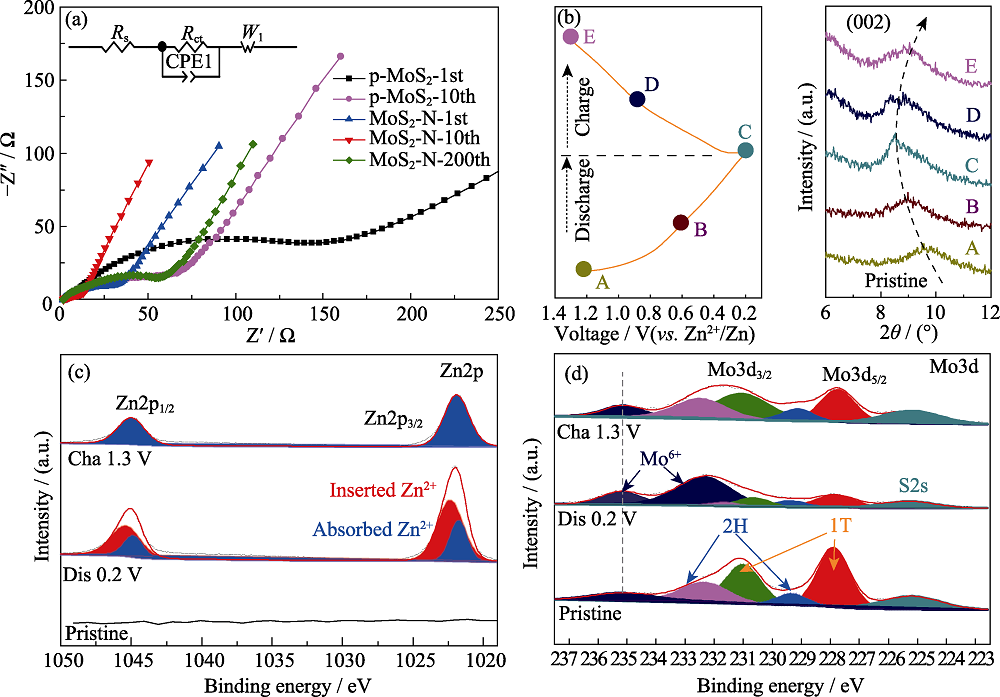
图S3 (a) MoS2-N和p-MoS2在不同循环圈数下的Nyquist图谱; MoS2-N在不同放电深度的(b)异位XRD图谱,以及(c) Zn2p和(d) Mo3d异位XPS高分辨率谱图
Fig. S3 (a) Nyquist plots of MoS2-N and p-MoS2 under different cycles, (b) ex-situ XRD patterns and ex-situ XPS high resolution spectra of (c) Zn2p, (d) Mo3d of MoS2-N electrode collected at different charge/discharge depths
| [1] |
LIU J, ZUO S Y, XU X J, et al. Cathodes for aqueous Zn-ion batteries: materials, mechanisms, and kinetics. Chem. Eur. J., 2020, 27(3): 830.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WANG X, ZHANG Z C Y, XI B J, et al. Advances and perspectives of cathode storage chemistry in aqueous zinc-ion batteries. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(6): 9244.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | LIU Z X, QIN L P, LU B G, et al. Issues and opportunities facing aqueous Mn2+/MnO2 based batteries. ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(10): e202200348. |
| [4] |
LIU Z X, YANG Y Q, LIANG S Q, et al. pH-buffer contained electrolyte for self-adjusted cathode-free Zn-MnO2 batteries with coexistence of dual mechanisms. Small Struct., 2021, 2(11): 2100119.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ZHANG K, LI P, GUO S Y, et al. An angstrom-level d-spacing controlling synthetic route for MoS2 towards stable intercalation of sodium ions. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(45): 22513.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG B Y, QIN L P, FANG Y, et al. Tuning Zn2+ coordination tunnel by hierarchical gel electrolyte for dendrite-free zinc anode. Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(9): 955.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI P, JEONG J Y, JIN B J, et al. Vertically oriented MoS2 with spatially controlled geometry on nitrogenous graphene sheets for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(19): 1703300.
DOI URL |
| [8] | RUAN P C, LIANG S Q, LU B G, et al. Design strategies for high-energy-density aqueous zinc batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(17): e202200598. |
| [9] | LEE W S V, XIONG T, WANG X P, et al. Unraveling MoS2 and transition metal dichalcogenides as functional zinc-ion battery cathode: a perspective. Small Methods, 2020, 5(1): 20008115. |
| [10] | XIE J, ZHANG H, LIU Q, et al. Recent progress of molybdenum-based materials in aqueous rechargeable batteries. Mater. Today Adv., 2020, 8: 100100. |
| [11] |
LI T, LI H X, YUAN J C, et al. Recent advance and modification strategies of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) in aqueous zinc ion batteries. Mater., 2022, 15(7): 2654.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIU W B, HAO J W, XU C J, et al. Investigation of zinc ion storage of transition metal oxides, sulfides, and borides in zinc ion batteries system. Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(51): 6872.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI S W, LIU Y C, ZHAO X D, et al. Sandwich-like heterostructures of MoS2/graphene with enlarged interlayer spacing and enhanced hydrophilicity as high-performance cathodes for aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(12): 2007480.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HUANG M H, MAI Y J, ZHAO L J, et al. Hierarchical MoS2@CNTs hybrid as a long-life and high-rate cathode for aqueous rechargeable Zn-ion batteries. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(20): 4218.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG Z C, LI W, WANG R X, et al. Crystal water assisting MoS2 nanoflowers for reversible zinc storage. J. Alloys. Compd., 2021, 872: 159599.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIU J P, XU P T, LIANG J M, et al. Boosting aqueous zinc-ion storage in MoS2 via controllable phase. Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 389: 124405.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HUANG M H, MAI Y J, FAN G W, et al. Toward fast zinc-ion storage of MoS2 by tunable pseudocapacitance. J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 871: 159541.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU J P, GONG N, PENG W C, et al. Vertically aligned 1T phase MoS2 nanosheet array for high-performance rechargeable aqueous Zn-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 428: 130981.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
CAI C Y, TAO Z R, ZHU Y F, et al. A nano interlayer spacing and rich defect 1T-MoS2 as cathode for superior performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Nanoscale Adv., 2021, 3(13): 3780.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIANG H F, CAO Z, MING F W, et al. Aqueous zinc-ion storage in MoS2 by tuning the intercalation energy. Nano Lett., 2019, 19(5): 3199.
DOI URL |
| [21] | XU W W, SUN C L, ZHAO K N, et al. Defect engineering activating (Boosting) zinc storage capacity of MoS2. Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 16: 527. |
| [22] |
JIA H, QIU M H, TAWIAH B, et al. Interlayer-expanded MoS2 hybrid nanospheres with superior zinc storage behavior. Compos. Commun., 2021, 27: 100841.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CAO P F, CHEN N, TANG W J, et al. Template-assisted hydrothermal synthesized hydrophilic spherical 1T-MoS2 with excellent zinc storage performance. J. Alloys. Compd., 2022, 898: 162854.
DOI URL |
| [24] | LIU H Y, WANG J G, HUA W, et al. Boosting zinc-ion intercalation in hydrated MoS2 nanosheets toward substantially improved performance. Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 35: 731. |
| [25] | LI H F, YANG Q, MO F N, et al. MoS2 nanosheets with expanded interlayer spacing for rechargeable aqueous Zn-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 19: 94. |
| [26] |
HUANG M H, MAI Y J, ZHAO L J, et al. Tuning the kinetics of zinc ion in MoS2 by polyaniline intercalation. Electrochim. Acta., 2021, 388: 138624.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG D Z, ZHANG X Y, BAO S Y, et al. Phase engineering of a multiphasic 1T/2H MoS2 catalyst for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(6): 2681.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG D Z, XIAO Y Y, LUO X N, et al. Swollen ammoniated MoS2 with 1T/2H hybrid phases for high-rate electrochemical energy storage. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017, 5(3): 2509.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WU Z Z, YU K, XIE L, et al. Dual-ion intercalated 1T/2H MoS2 with expanded interlayers as supercapacitor electrode materials. Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(8): 085534.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
GENG X M, SUN W W, WU W, et al. Pure and stable metallic phase molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 10672.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
ZHENG J, ZHANG H, DONG S H, et al. High yield exfoliation of two-dimensional chalcogenides using sodium naphthalenide. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 2995.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
LIN Y C, DUMCENCO D O, HUANG Y S, et al. Atomic mechanism of the semiconducting-to-metallic phase transition in single-layered MoS2. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2014, 9(5): 391.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
VENKATESHWARAN S, JOSLINE M J, SENTHIL K S M. Fine-tuning interlayer spacing in MoS2 for enriching 1T phase via alkylated ammonium ions for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(12): 8377.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
XIE J F, ZHANG H, LI S, et al. Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(40): 5807.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
CHANG K, HAI X, PANG H, et al. Targeted synthesis of 2H-and 1T-phase MoS2 monolayers for catalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(45): 10033.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 黄美红. 水系锌离子电池扩层二硫化钼正极材料的可控制备及性能研究. 广州: 广东工业大学博士论文, 2021. |
| [37] |
CHAO D L, LIANG P, CHEN Z, et al. Pseudocapacitive Na-ion storage boosts high rate and areal capacity of self-branched 2D layered metal chalcogenide nanoarrays. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(11): 10211.
PMID |
| [38] |
KIM H S, COOK J B, LIN H, et al. Oxygen vacancies enhance pseudocapacitive charge storage properties of MoO3-x. Nat. Mater., 2017, 16(4): 454.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
CHE Z Z, LI Y F, CHEN K X, et al. Hierarchical MoS2@RGO nanosheets for high performance sodium storage. J. Power Sources, 2016, 331: 50.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
MAJUMDER S, SHAO M H, DENG Y F, et al. Ultrathin sheets of MoS2/g-C3N4 composite as a good hosting material of sulfur for lithium-sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources, 2019, 431: 93.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WANG J J, WANG J G, LIU H Y, et al. Electrochemical activation of commercial MnO microsized particles for high-performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2019, 438: 226951.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
CHEN L L, YANG Z H, QIN H G, et al. Advanced electrochemical performance of ZnMn2O4/N-doped graphene hybrid as cathode material for zinc ion battery. J. Power Sources, 2019, 425: 162.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 孔国强, 冷明哲, 周战荣, 夏池, 沈晓芳. Sb掺杂O3型Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2钠离子电池正极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 656-662. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 王洋, 范广新, 刘培, 尹金佩, 刘宝忠, 朱林剑, 罗成果. 钾离子掺杂提高锂离子电池正极锰酸锂性能的微观机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [4] | 孙炼, 顾全超, 杨雅萍, 王洪磊, 余金山, 周新贵. 二维过渡金属硫属化合物氧还原反应催化剂的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 697-709. |
| [5] | 何慧凯, 杨蕊, 夏剑, 王廷泽, 董德泉, 缪向水. 高均一性二维碲化钼忆阻器阵列及其神经形态计算应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 795-801. |
| [6] | 袁罡, 马新国, 贺华, 邓水全, 段汪洋, 程正旺, 邹维. 平面应变对二维单层MoSi2N4能带结构和光电性质的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 527-533. |
| [7] | 李文博, 黄民松, 李月明, 李驰麟. 双盐镁电池CoS2正极材料的电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 173-181. |
| [8] | 雷伟岩, 王岳, 武世然, 石东新, 沈毅, 李锋锋. VA族单元素二维纳米材料在生物医用领域的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1181-1191. |
| [9] | 夏芳芳, 王发坤, 胡海龙, 许翔, 李阳, 翟天佑. 二次谐波在二维材料结构表征中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1022-1030. |
| [10] | 杨浏鑫,罗文华,汪长安,徐晨. 新型无机二维材料在气体分离膜领域的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 959-971. |
| [11] | 李能,孔周舟,陈星竹,杨雨菲. 新型二维材料光催化与电催化研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 735-747. |
| [12] | 谭仕林,尹顺达,欧阳钢. 尺寸效应对MoS2/WSe2范德华异质结构层间与俄歇复合的界面调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 682-688. |
| [13] | 郑云,陈亦琳,高碧芬,林碧洲. 磷烯光催化分解水研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 647-653. |
| [14] | 山巍,傅正钱,张发强,马名生,刘志甫,李永祥. SnS2纳米片的制备及其对NO2气体的检测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 497-504. |
| [15] | 高天, 肖庆林, 许晨阳, 王学斌. 发泡法制备二维材料泡沫体的进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1315-1326. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||