无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 1281-1288.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220129
所属专题: 【结构材料】隔热材料
罗艺1( ), 夏书海2, 牛波2, 张亚运2, 龙东辉2(
), 夏书海2, 牛波2, 张亚运2, 龙东辉2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-08
修回日期:2022-05-06
出版日期:2022-12-20
网络出版日期:2022-05-27
通讯作者:
龙东辉, 教授. E-mail: longdh@ecust.edu.cn作者简介:罗 艺(1993-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: sosolyi@163.com
LUO Yi1( ), XIA Shuhai2, NIU Bo2, ZHANG Yayun2, LONG Donghui2(
), XIA Shuhai2, NIU Bo2, ZHANG Yayun2, LONG Donghui2( )
)
Received:2022-03-08
Revised:2022-05-06
Published:2022-12-20
Online:2022-05-27
Contact:
LONG Donghui, professor. E-mail: longdh@ecust.edu.cnAbout author:LUO Yi (1993-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: sosolyi@163.com
摘要:
二氧化硅气凝胶以其低密度、高孔隙率等特性在高温隔热领域显示出广阔的应用前景, 但其脆性和高成本的超临界干燥方式限制了其应用。本研究以乙烯基三甲氧基硅烷(VTMS)和乙烯基甲基二甲氧基硅烷(VMDMS)为前驱体, 通过溶胶凝胶、常压干燥制备了具有高柔性的海绵状有机硅气凝胶, 并研究了前驱体摩尔比对气凝胶微观结构和压缩回弹性能的影响, 以及气凝胶分别在高温有氧和无氧环境中的无机化转变过程。结果表明, 随着前驱体中VTMS/VMDMS比例增加, 气凝胶颗粒变小且堆积更紧密, 其压缩回弹性能也随之降低; 在800 ℃空气氛围中, 气凝胶通过侧基的氧化和主链Si-O-Si的断裂、重排转化为无机SiO2; 在800 ℃ N2氛围中, 气凝胶通过裂解反应转化为无机SiO2和游离碳的混合体, 1000~1400 ℃进一步处理后SiO2和游离碳经碳热还原反应生成SiO4、SiCO3、SiC2O2和SiC3O等无定形的Si-O-C结构和少量β-SiC纳米线; 经1200 ℃碳热还原反应生成的Si-O-C结构具有最优的耐高温氧化性能, 可为制备耐高温氧化Si-O-C气凝胶提供参考。
中图分类号:
罗艺, 夏书海, 牛波, 张亚运, 龙东辉. 柔性有机硅气凝胶的制备及其高温无机化转变研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1281-1288.
LUO Yi, XIA Shuhai, NIU Bo, ZHANG Yayun, LONG Donghui. Preparation and High Temperature Inorganic Transformation of Flexible Silicone Aerogels[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1281-1288.
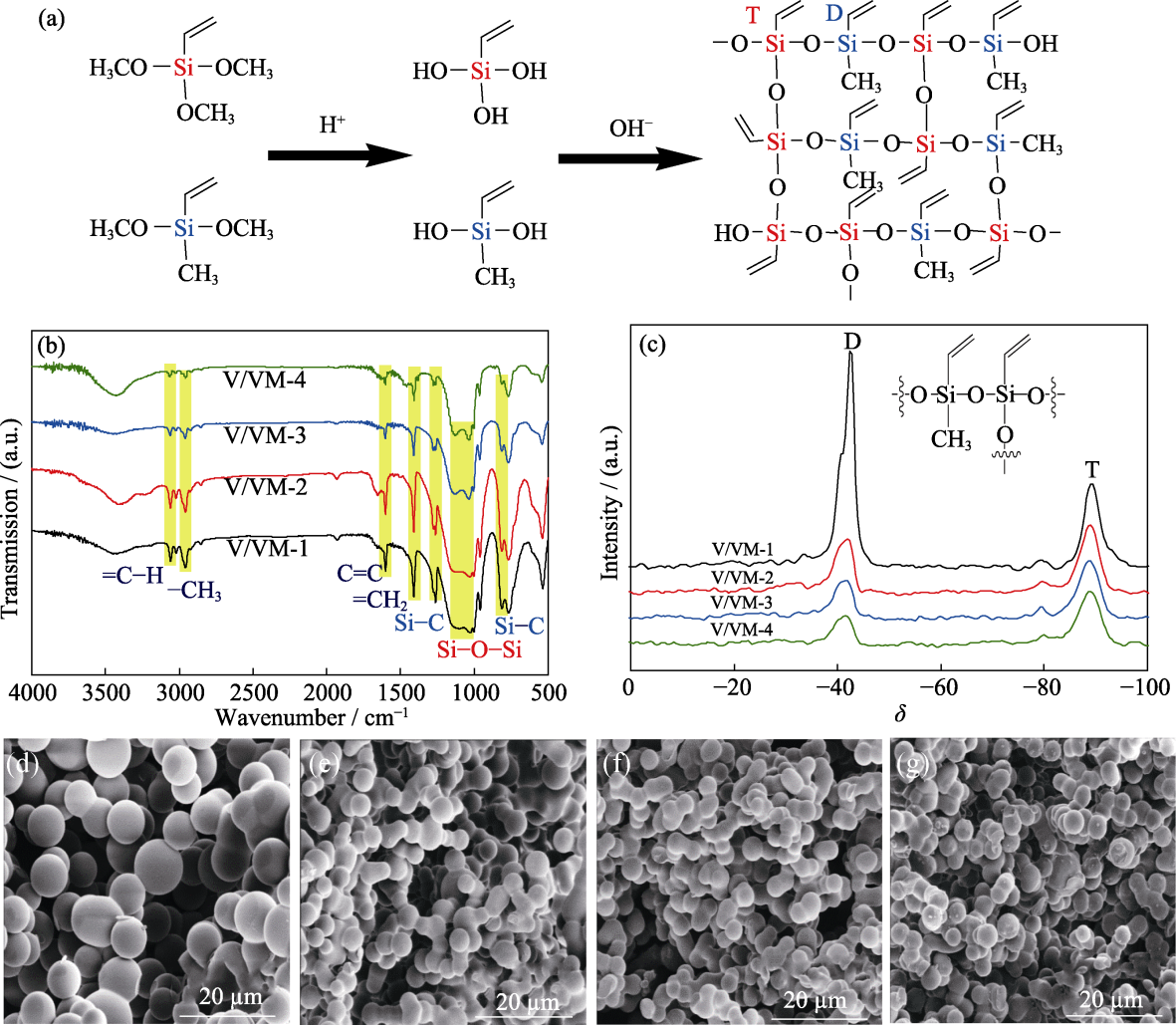
图1 溶胶-凝胶过程示意图(a), 气凝胶样品的红外谱图(b)、核磁谱图(c)和SEM照片(d~g)
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of Sol-Gel process (a), IR spectra (b), NMR spectra (c) and SEM images (d-g) of aerogel samples Molar ratios of VTMS/VMDMS for aerogels (d-g) are 1, 2, 3, 4, respectively
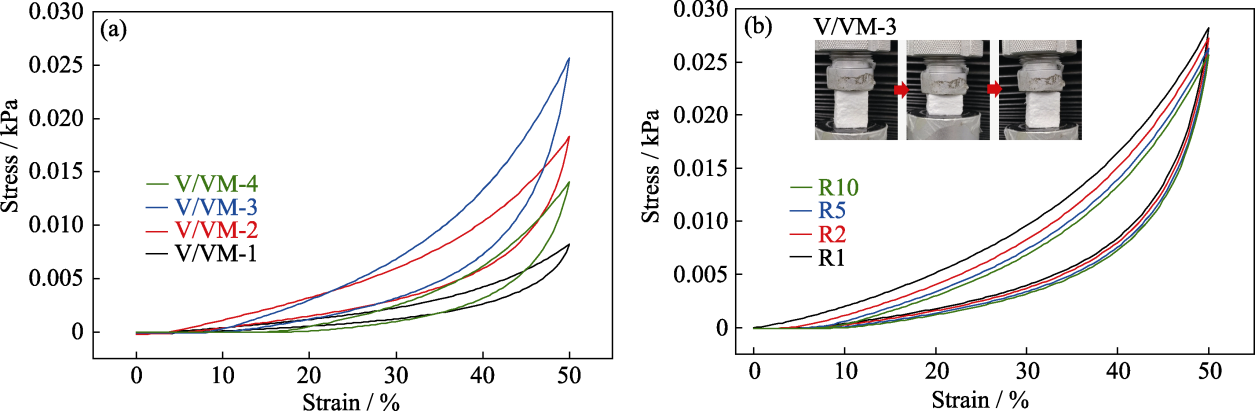
图2 气凝胶样品的循环压缩应力-应变曲线
Fig. 2 Cyclic compression stress-strain curves of aerogels (a) Stress-strain curves after 10-cycle compression; (b) Cyclic compression stress-strain curves of sample V/VM-3 Colorful figures are available on website
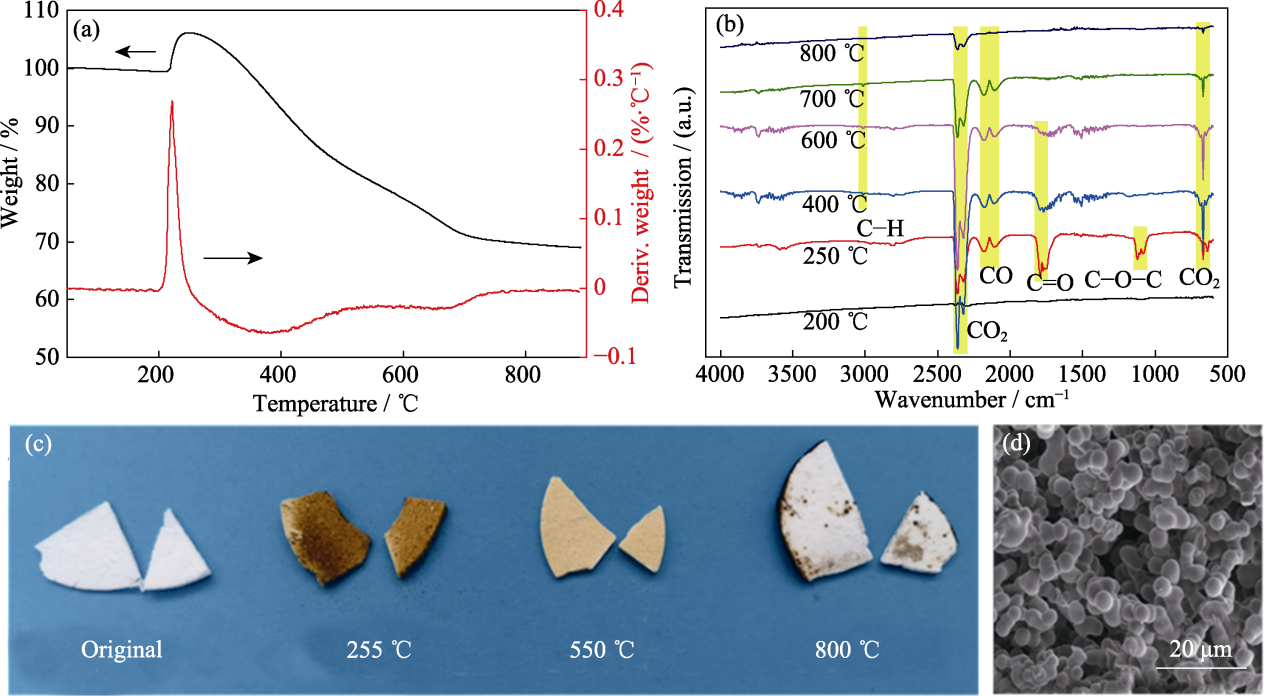
图3 样品V/VM-3在空气氛围下的TG-IR谱图(a, b), 经不同温度处理后的实物图(c)和在800 ℃处理后的SEM照片(d)
Fig. 3 (a, b) TG-IR spectra of sample V/VM-3 tested in air; (c) Photographs of sample V/VM-3 after heat-treated at different temperatures; (d) SEM image of sample V/VM-3 after heat-treated at 800 ℃
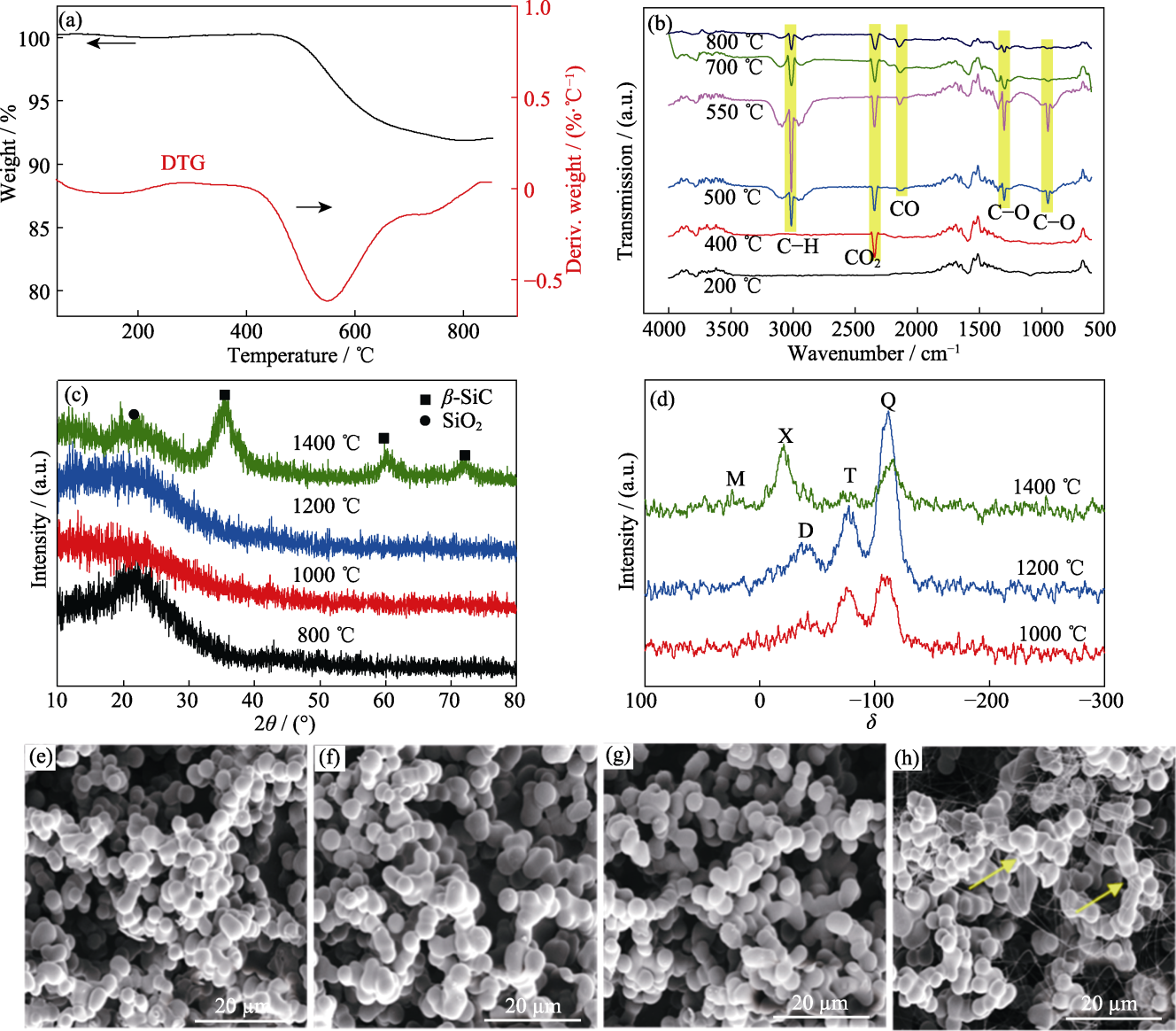
图4 样品V/VM-3在N2氛围下的TG-IR谱图(a, b), 在不同温度处理后的XRD谱图(c)、核磁谱图(d)和SEM照片(e~h)
Fig. 4 (a, b) TG-IR spectra of sample V/VM-3 under N2 atmosphere; (c) XRD patterns, (d) NMR spectra and (e-h) SEM image of sample V/VM-3 after heat-treated at different temperatures (e) 800 ℃; (f) 1000 ℃; (g) 1200 ℃; (h) 1400 ℃
| [1] |
SONG J W, CHEN C J, YANG Z, et al. Highly compressible, anisotropic aerogel with aligned cellulose nanofibers. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(1): 140.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
HAN X, HASSAN K T, HARVEY A, et al. Bioinspired synthesis of monolithic and layered aerogels. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(23): 1706294.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
OU H H, YANG P J, LIN L H, et al. Carbon nitride aerogels for the photoredox conversion of water. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(36): 10905-10910.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CAI B, SAYEVICH V, GAPONIK N, et al. Emerging hierarchical aerogels: self-assembly of metal and semiconductor nanocrystals. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(33): 1707518.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KHALILY M A, EREN H, AKBAYRAK S, et al. Facile synthesis of three-dimensional Pt-TiO2 nano-networks: a highly active catalyst for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia-borane. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(40): 12257-12261.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HAGEDORN K, LI W, LIANG Q J, et al. Catalytically doped semiconductors for chemical gas sensing: aerogel-like aluminum- containing zinc oxide materials prepared in the gas phase. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(20): 3424-3437.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
NICOLA H, ULRICH S. Aerogels-airy materials: chemistry, structure, and properties. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 1998, 37(1/2): 22-45.
DOI URL |
| [8] | BEAMISH J, HERMAN T. Adsorption and desorption of helium in aerogels. Physica B Condensed Matter, 2003, 329: 340-341. |
| [9] | BELLUNATO T, BRAEM A, BUZYKAEV A R, et al. Aerogel as cherenkov radiator for rich detectors. Nuclear Inst & Methods in Physics Research A, 2003, 502(1): 227-230. |
| [10] | KISTLER S S. Coherent expanded aerogel jellies. Nature, 1931, 127(3211): 741. |
| [11] |
DU A, ZHOU B, ZHANG Z, et al. A special material or new state of matter: a review and reconsideration of the aerogel. Materials, 2013, 6(3): 941-968.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
HE F, YU W J, FANG M H, et al. An overview on silica aerogels synthesized by siloxane co-precursors. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1243-1253.
DOI |
| [13] | NADARGI D Y, LATTHE S S, HIRASHIMA H, et al. Studies on rheological properties of methyltriethoxysilane (MTES) based flexible superhydrophobic silica aerogels. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2009, 117(3): 617-626. |
| [14] |
KANAMORI K, AIZAWA M, NAKANISHI K, et al. New transparent methylsilsesquioxane aerogels and xerogels with improved mechanical properties. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(12): 1589-1593.
DOI URL |
| [15] | RAO A V, BHAGAT S D, HIRASHIMA H, et al. Synthesis of flexible silica aerogels using methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) precursor. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2006, 300(1): 279-285. |
| [16] |
ZU G Q, SHIMIZU T, KANAMORI K, et al. Transparent, superflexible doubly cross-linked polyvinylpolymethylsiloxane aerogel superinsulators via ambient pressure drying. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(1): 521-532.
DOI URL |
| [17] | ZU G Q, SHEN J, ZOU L P, et al. Preparation, mechanical properties and thermal properties of elastic aerogels. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(4): 417-422. |
| [18] |
HONG J Y, BAK B M, WIE J J, et al. Reversibly compressible, highly elastic, and durable graphene aerogels for energy storage devices under limiting conditions. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(7): 1053-1062.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HAYASE G, KANAMORI K, HASEGAWA G, et al. A superamphiphobic macroporous silicone monolith with marshmallow- like flexibility. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(41): 10788-10791.
DOI URL |
| [20] | QIU F X, ZHOU Y M, LIU J Z, et al. Study of 29Si MAS NMR spectroscopy and electro-optic property based on polyimide/SiO2. Photographic Science and Photochemistry, 2006, 24(1): 55-60. |
| [21] |
SHIMIZU T, KANAMORI K, MAENO A, et al. Transparent ethylene-bridged polymethylsiloxane aerogels and xerogels with improved bending flexibility. Langmuir, 2016, 32(50): 13427-13434.
PMID |
| [22] |
ZHANG Z, WANG X D, SHEN J. Effect of organic-inorganic crosslinking degree on the mechanical and thermal properties of aerogels. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 454-460.
DOI |
| [23] |
ZU G Q, KANAMORI K, WANG X D, et al. Superelastic triple-network polyorganosiloxane-based aerogels as transparent thermal superinsulators and efficient separators. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(4): 1595-1604.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
NAZERAN N, MOGHADDAS J. Synthesis and characterization of silica aerogel reinforced rigid polyurethane foam for thermal insulation application. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2017, 461: 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [25] | ZHANG Z, WANG X D, ZU G Q, et al. Resilient, fire-retardant and mechanically strong polyimide-polyvinylpolymethylsiloxane composite aerogel prepared via stepwise chemical liquid deposition. Materials & Design, 2019, 183: 108096. |
| [26] |
CHEN Z Q, CHEN Y F, LIU H B. Pyrolysis of phenolic resin by TG-MS and FTIR analysis. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 631-632: 104-109.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 金晶, 徐晓秋, 杨雄发, 等. 聚硅氧烷热稳定性研究进展. 化工新型材料, 2010, 38(1): 17-19. |
| [28] | HUANG D M, GUO C N, ZHANG M Z, et al. Characteristics of nanoporous silica aerogel under high temperature from 950 ℃ to 1200 ℃. Materials & Design, 2017, 129: 82-90. |
| [29] | YANG G X, BISWAS P. Computer simulation of the aggregation and sintering restructuring of fractal-like clusters containing limited numbers of primary particles. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 1999, 211(1): 142-150. |
| [30] |
LI X K, LIU L, ZHANG Y X, et al. Synthesis of nanometre silicon carbide whiskers from binary carbonaceous silica aerogels. Carbon, 2001, 39(2): 159-165.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
MA J, YE F, LIN S J, et al. Large size and low density SiOC aerogel monolith prepared from triethoxyvinylsilane/tetraethoxysilane. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(7): 5774-5780.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [2] | 刘丹, 赵亚欣, 郭锐, 刘艳涛, 张志东, 张增星, 薛晨阳. 退火条件对磁控溅射MgO-Ag3Sb-Sb2O4柔性薄膜热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1302-1310. |
| [3] | 张晓山, 王兵, 吴楠, 韩成, 刘海燕, 王应德. 高红外遮蔽SiZrOC纳米纤维膜的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 93-100. |
| [4] | 彭飞, 姜勇刚, 冯坚, 蔡华飞, 冯军宗, 李良军. 耐高温氧化铝气凝胶隔热复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 673-684. |
| [5] | 张晓山, 王兵, 吴楠, 韩成, 吴纯治, 王应德. 高温隔热用微纳陶瓷纤维研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 245-256. |
| [6] | 方华靖, 赵泽天, 武文婷, 汪宏. 柔性电致变色器件研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 140-151. |
| [7] | 徐海丰,侯成义,张青红,李耀刚,王宏志. 碲纳米线柔性薄膜的制备及其热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1034-1040. |
| [8] | 潘碧宸,任鹏禾,周特军,蔡圳阳,赵小军,周宏明,肖来荣. 树脂基复合材料表面隔热涂层的组织与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 947-952. |
| [9] | 柳凤琦, 冯坚, 姜勇刚, 李良军. 氮化硼气凝胶的制备及其应用进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1193-1202. |
| [10] | 杨以娜, 王冉冉, 孙静. MXenes在柔性力敏传感器中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 8-18. |
| [11] | 吕喜庆, 张环宇, 李瑞, 张梅, 郭敏. Nb2O5包覆对TiO2纳米阵列/上转换发光复合结构柔性染料敏化太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 590-598. |
| [12] | 李鹏, 聂晓蕾, 田烨, 方文兵, 魏平, 朱婉婷, 孙志刚, 张清杰, 赵文俞. Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3/环氧树脂柔性复合热电厚膜的制备及其面内制冷性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 679-684. |
| [13] | 李亚东, 李伟平, 王琴, 郑道光, 王建新. 碳纤维支撑柔性碳硫复合电极的制备、物性及电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 373-378. |
| [14] | 肖敏, 孙睿智, 李艳芳, 康同同, 秦俊, 杨润, 毕磊. 基于MoS2/SiO2范德华异质结的VO2薄膜转移打印研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1161-1166. |
| [15] | 王晓, 王冉冉, 施良晶, 孙静. 铜纳米线的合成、优化及其透明电极的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(1): 49-59. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||