无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 1203-1216.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220164
所属专题: 【生物材料】肿瘤治疗
收稿日期:2022-03-21
修回日期:2022-04-19
出版日期:2022-05-09
网络出版日期:2022-05-09
通讯作者:
朱敏, 副教授. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn;作者简介:吴爱军(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wuaijun1233@163.com
基金资助:
WU Aijun1,2( ), ZHU Min1(
), ZHU Min1( ), ZHU Yufang2(
), ZHU Yufang2( )
)
Received:2022-03-21
Revised:2022-04-19
Published:2022-05-09
Online:2022-05-09
Contact:
ZHU Min, associate professor. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn;About author:WU Aijun (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wuaijun1233@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
为了清除皮肤肿瘤手术切除后的残余肿瘤细胞并促进皮肤伤口愈合, 开发一种具有肿瘤治疗和促进皮肤伤口愈合功能的水凝胶具有重要意义。本研究以水合硅酸钙纳米线为基体材料, 以NaCl和KCl为熔盐介质, CuSO4•5H2O为铜源, 采用熔盐法制备了含铜硅酸钙(Cu-CS)纳米棒, 并将其复合到海藻酸钠水凝胶得到Cu-CS纳米棒复合水凝胶(Cu-CS/SA)。实验结果表明, 随着铜盐添加量增大和熔盐处理温度升高, Cu-CS纳米棒的Cu含量逐渐上升, 但其催化过氧化氢(H2O2)生成羟基自由基(•OH)的性能呈现先升高后下降的趋势; 在3%铜盐添加量和熔盐处理温度700 ℃条件下所制备的3Cu-CS纳米棒具有最佳的催化性能, Cu元素均匀地分布在纳米棒表面, 其价态为+2价, 且Cu元素的含量极低, 仅为0.61%。细胞实验发现Cu-CS纳米棒含量不超过20%的复合水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性, 并且Cu- CS/SA水凝胶在模拟肿瘤微环境条件下能催化H2O2生成高细胞毒性的•OH, 进而实现化学动力学治疗肿瘤的效果, 同时还能促进血管内皮细胞和成纤维细胞的增殖和迁移。因此, Cu-CS纳米棒复合水凝胶有望用于皮肤肿瘤术后治疗。
中图分类号:
吴爱军, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 含铜硅酸钙纳米棒复合水凝胶用于肿瘤治疗和皮肤伤口愈合性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1203-1216.
WU Aijun, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Copper-incorporated Calcium Silicate Nanorods Composite Hydrogels for Tumor Therapy and Skin Wound Healing[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1203-1216.
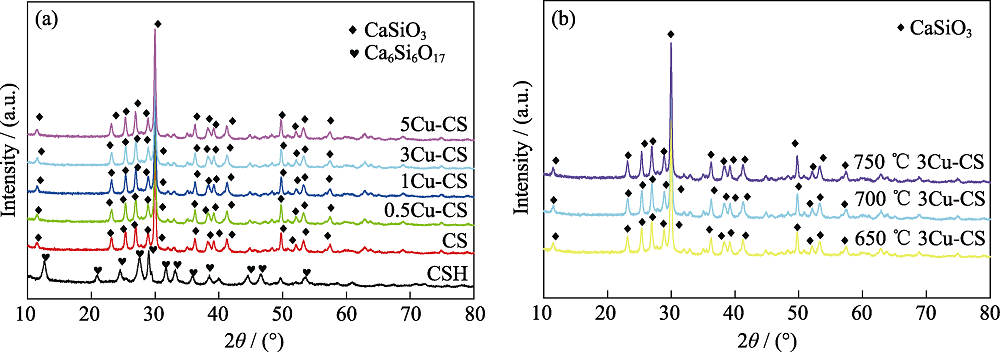
图1 (a)不同铜盐添加量和(b)不同温度熔盐处理制备的Cu-CS粉体的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Cu-CS powders prepared by molten salt method with (a) different amounts of copper salt and (b) different temperatures
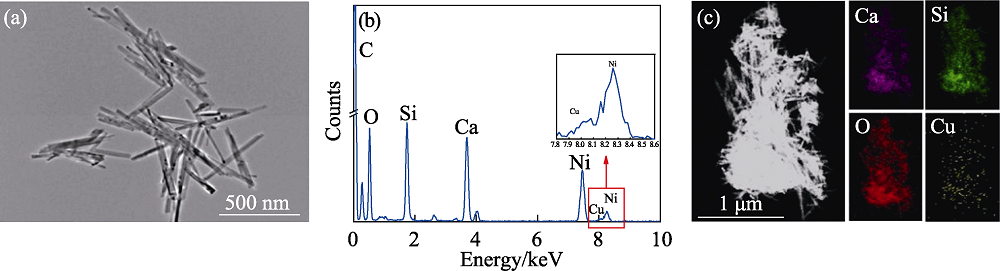
图3 3Cu-CS纳米棒的(a) TEM照片-(b) EDS谱图和(c)元素分布图
Fig. 3 (a) TEM image, (b) EDS spectrum and (c) elemental mapping of 3Cu-CS nanorods The color figure can be obtained from online edition
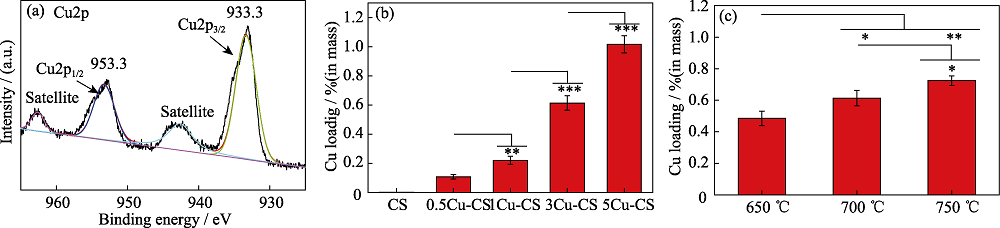
图4 3Cu-CS纳米棒的(a)Cu2p XPS图谱, ICP-AES方法测定的(b)不同铜盐添加量和(c)不同熔盐处理温度制备的Cu-CS纳米棒的Cu负载量
Fig. 4 (a) Cu2p XPS spectrum of 3Cu-CS nanorods, Cu amounts of Cu-CS nanorods prepared with (b) different copper salt additions and (c) different temperatures by ICP-AES method, respectively. *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, ***p< 0.001 The color figures can be obtained from online edition
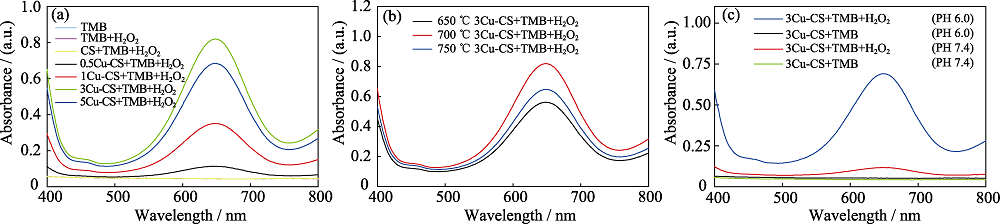
图5 Cu-CS纳米棒的化学动力学性能
Fig. 5 Chemodynamic effects of Cu-CS nanorods (a, b) UV-Vis absorption spectra of TMB solutions with pH 6.0 and H2O2 (100 mmol/L) after adding Cu-CS nanorod (1 mg/mL) prepared by a molten salt method with (a) different copper salt additions and (b) different treatment temperatures for 30 min; (c) UV-Vis absorption spectra of TMB solutions after adding 3Cu-CS nanorods (1 mg/mL) into TMB solutions under pH 6.0 or pH 7.4 conditions and with or without H2O2 for 20 min The color figures can be obtained from online edition
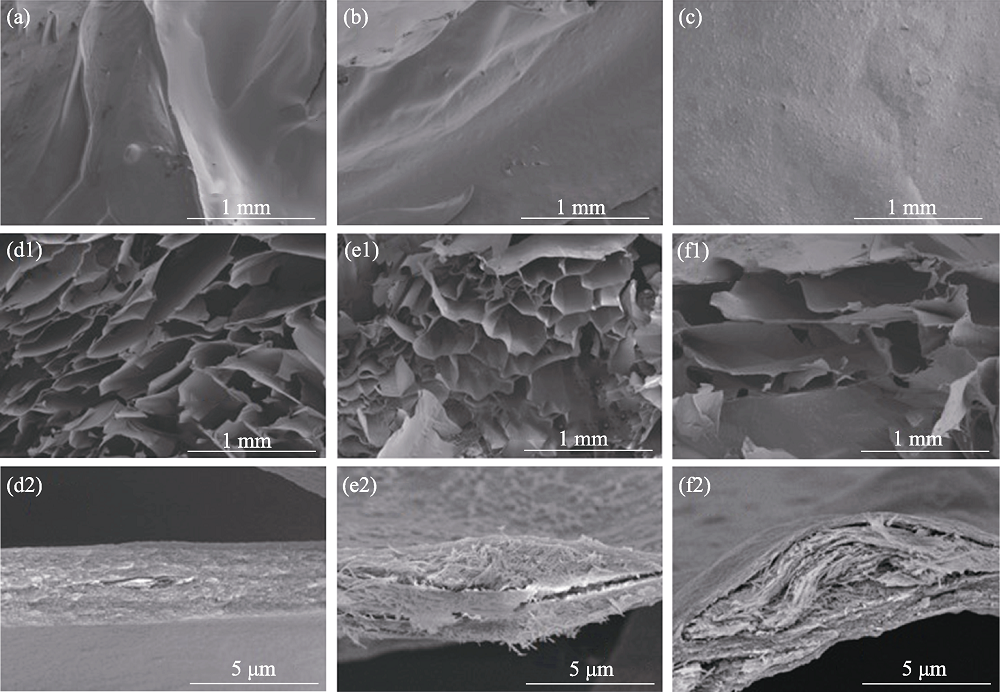
图6 (a, d1, d2) SA、(b, e1, e2) 20%-CS/SA和(c, f1, f2) 20%-Cu-CS/SA水凝胶的表面以及断面SEM照片
Fig. 6 SEM images of the surfaces and cross sections for (a, d1, d2) SA, (b, e1, e2) 20%-CS/SA and (c, f1, f2) 20%-Cu-CS/SA hydrogels
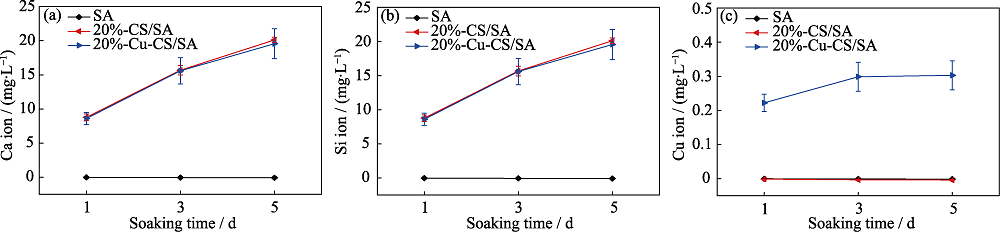
图7 SA、20%-CS/SA和20%-Cu-CS/SA水凝胶在Tris-HCl缓冲液中的(a) Ca、(b) Si、(c) Cu离子释放
Fig. 7 Release behaviors of (a) Ca, (b) Si and (c) Cu ions from SA, 20%-CS/SA and 20%-Cu-CS/SA hydrogels in Tris-HCl buffer The color figures can be obtained from online edition
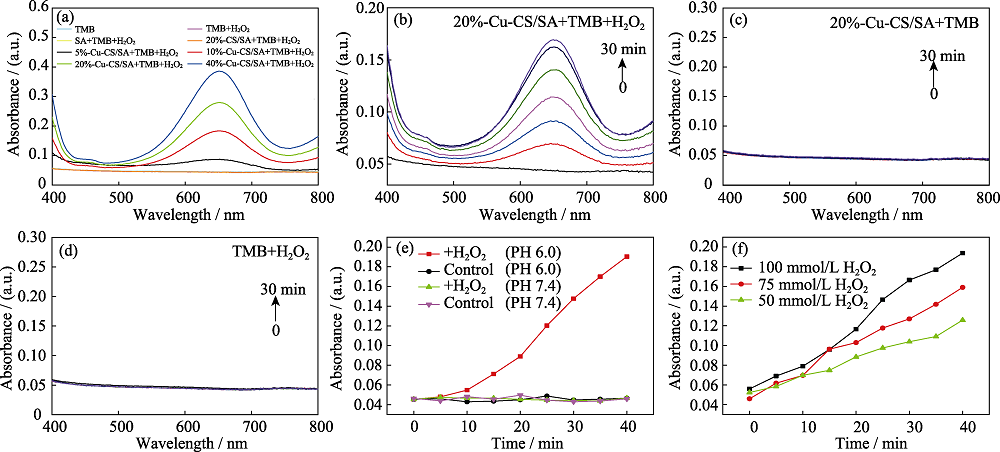
图8 Cu-CS/SA水凝胶的化学动力学性能
Fig. 8 Chemodynamic effects of Cu-CS/SA hydrogels (a) UV-Vis absorption spectra of TMB solutions with pH 6.0 and H2O2 (100 mmmol/L) after adding Cu-CS/SA hydrogel (0.1 g/mL) with different contents of Cu-CS nanorods for 60 min; (b) UV-Vis absorption spectra changes of TMB solutions with time after adding 20%-Cu-CS/SA hydrogel (0.1 g/mL) under a condition of pH 6.0 and H2O2 (100 mmmol/L); (c) UV-Vis absorption spectra changes of TMB solutions with time after adding 20%-Cu-CS/SA hydrogel (0.1 g/mL) under a condition of pH 6.0; (d) UV-Vis absorption spectra changes of TMB solutions with time under a condition of pH 6.0 and H2O2 (100 mmmol/L); (e) Absorbance changes at 652 nm versus time for TMB solutions with 20%-Cu-CS/SA hydrogel under pH 6.0 or pH 7.4 conditions and with or without H2O2; (f) Absorbance changes at 652 nm versus time for TMB solutions with different concentrations of H2O2 at pH 6.0 after adding 20%-Cu-CS/SA hydrogel (0.1 g/mL). The color figures can be obtained from online edition
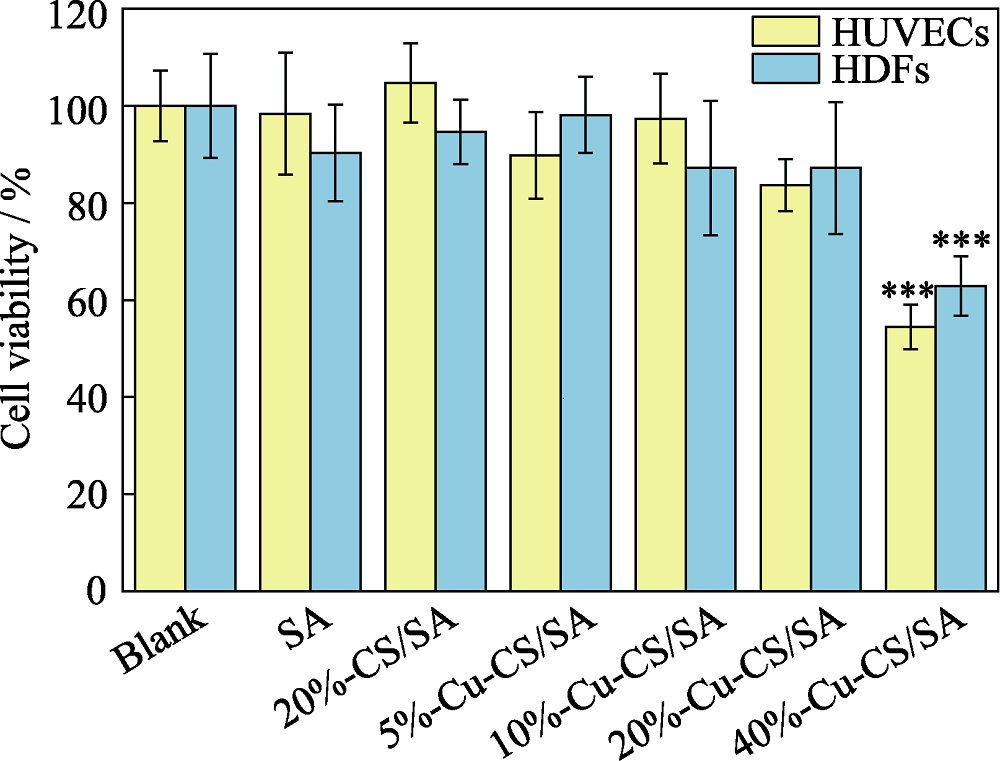
图9 内皮细胞和成纤维细胞与不同Cu-CS纳米棒含量的Cu-CS/SA复合水凝胶培养24 h后的细胞存活率
Fig. 9 Cell viabilities of HUVECs and HDFs after 24 h incubation with hydrogels incorporated with different contents of Cu-CS nanorods The color figure can be obtained from online edition ***: p< 0.001
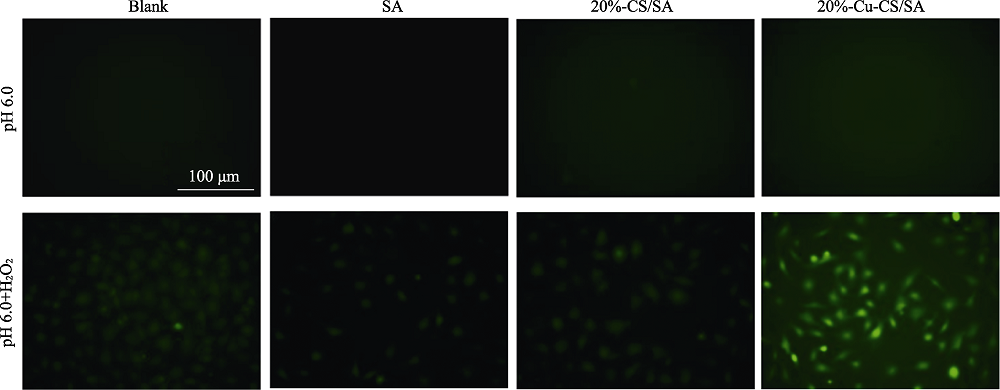
图10 不同条件处理后B16F10细胞内ROS荧光显微照片
Fig. 10 Fluorescence images of B16F10 cells after different treatments for observing intracellular ROS The color figures can be obtained from online edition
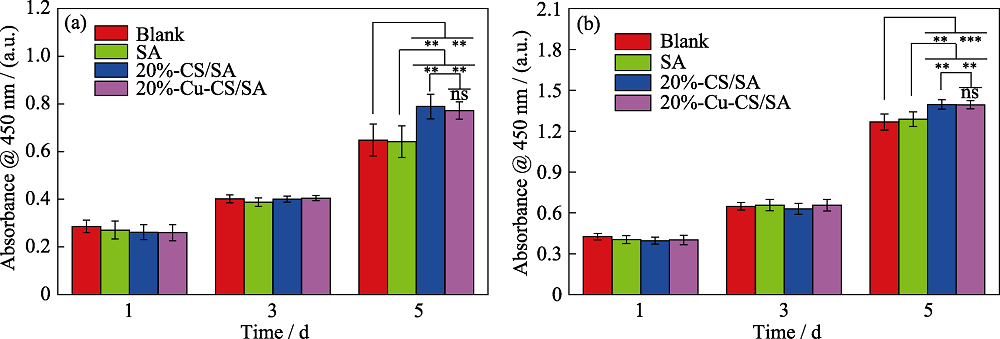
图12 与不同水凝胶共培养的(a)血管内皮细胞和(b)成纤维细胞的增殖状况
Fig. 12 Cell proliferations of (a) HUVECs and (b) HDFs cultured with different hydrogels ns: p>0.05, **: p< 0.01, ***: p< 0.001; The color figures can be obtained from online edition
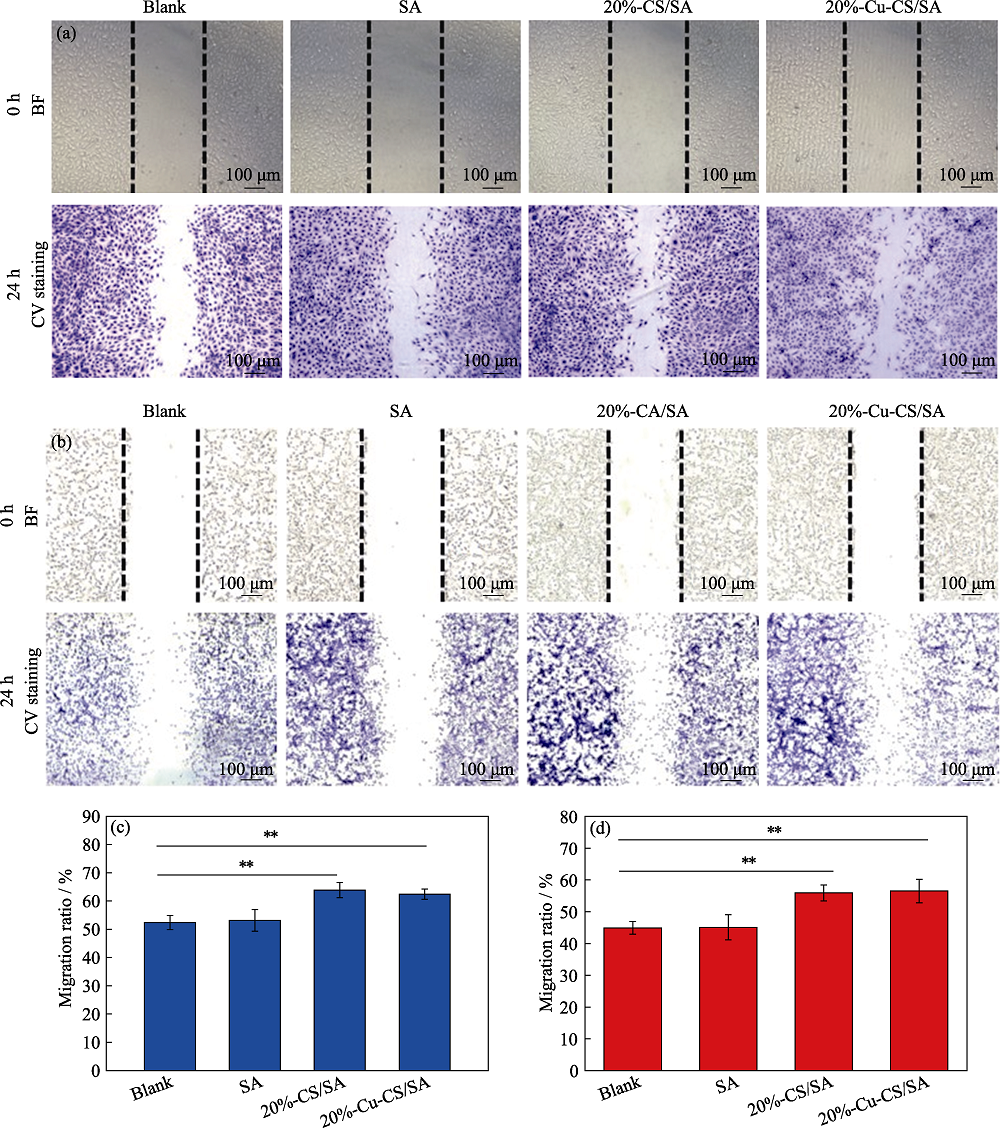
图13 与SA、20%-CS/SA或20%-Cu-CS/SA水凝胶共培养24 h后(a, c)内皮细胞和(b, d)成纤维细胞的迁移显微照片以及(c, d)相应定量统计的细胞迁移率(**p< 0.01)
Fig. 13 (a, b) Cell migration images and (c, d) corresponding migration rates of (a, c) HUVECs and (b, d) HDFs after cultured with SA, 20%-CS/SA and 20%-Cu-CS/SA hydrogels for 24 h, respectively ( **: p< 0.01) The color figures can be obtained from online edition
| [1] | CULLEN J K, SIMMONS J L, PARSONS PG, et al. Topical treatments for skin cancer. Advance Drug Delivery Reviews, 2020, 153: 54-64. |
| [2] | JEMA A, BRAY F, CENTER M M, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA-A Caner Journal for Clinicians, 2011, 61(2): 69-90. |
| [3] | CHEN Q, KE H, DAI Z, et al. Nanoscale theranostics for physical stimulus-responsive cancer therapies. Biomaterials, 2015, 73: 214-230. |
| [4] | MA B, DANG W, YANG Z, et al. MoS2 nanoclusters-based biomaterials for disease-impaired wound therapy. Applied Material Today, 2020, 20: 100735-15. |
| [5] |
MA H, ZHOU Q, CHANG J, et al. Grape seed-inspired smart hydrogel scaffolds for melanoma therapy and wound healing. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(4): 4302-4311.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
LIU C, XING J, AKAKURU O U, et al. Nanozymes-engineered mental-organic frameworks for catalytic cascades-enhanced syner- gistic cancer therapy. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(8): 5674-5682.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
TANG Z, LIU Y, HE M, et al. Chemodynamic therapy: tumor microenvironment-mediated Fenton and Fenton-like reaction. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(4): 946-956.
DOI URL |
| [8] | DAI X, DU T, HAN K. Engineering nanoparticles for optimized photodynamic therapy. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2019, 5(12): 6342-6354. |
| [9] |
CHANG M, WANG M, WANG M, et al. A multifunctional cascade bioreactor based on hollow structured Cu2MoS4for synergetic cancer chemodynamic therapy/starvation therapy/phototherapy/ immunotherapy with remarkably enhanced efficacy. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(51): 1905271-10.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI H, CHANG J. Bioactive silicate materials stimulate angiogenesis in fibroblast and endothelial cell co-culture system through paracrine effect. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(6): 6981-6991.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
LI H, ZHAI W, CHANG J. Effects of wollastonite on proliferation and differentiation of human bone marrow-derived stromal cells in PHBV/wollastonite composite scaffolds. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2009, 24(3): 231-246.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
DING S, SHIE M, HOSHIIBA T, et al. Osteogenic differentiation and immune response of human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on injectable calcium-silicate-based bone grafts. Tissue Engineering Part A, 2010, 16(7): 2343-2354.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHAI W, LU H, CHEN L, et al. Silicate bioceramics induce angiogenesis during bone regeneration. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(1): 341-349.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | LI H, HE J, YU H, et al. Bioglass promotes wound healing by affecting gap junction connexin 43 mediated endothelial cell behavior. Biomaterials, 2016, 84: 64-75. |
| [15] | YU H, PENG J, XU Y, et al. Bioglass activated skin tissue engineering constructs for wound healing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(1): 703-715. |
| [16] |
TIAN T, WU C, CHANG J. Preparation and in vitro osteogenic, angiogenic and antibacterial properties of cuprorivaite (CaCuSi4O10, Cup) bioceramics. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(51): 45840-45849.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WU C, ZHOU Y, XU M, et al. Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials, 2013, 34(2): 422-433.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
LIN L, HUANG T, SONG J, et al. Synthesis of copper peroxide nanodots for H2O2 self-supplying chemodynamic therapy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(25): 9937-9945.
DOI URL |
| [19] | CHEN J, CAO Y, LIN S, et al. A responsive microneedle system for efficient anti-melanoma by combining self-enhanced chemodynamic therapy with photothermal therapy. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 432(4): 133466. |
| [20] |
KONG N, LIN K, LI H, et al. Synergy effects of copper and silicon ions on stimulation of vascularization by copper-doped calcium silicate. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014, 2(8): 1100-1110.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | GIANNOULATU V, THEODOROUS G S, ZORBA T, et al. Magnesium calcium silicate bioactive glass doped with copper ions: synthesis and in-vitro bioactivity characterization. Journal of Non- Crystalline Solids, 2018, 500: 98-109. |
| [22] |
JAIRTON D, ROBERTOB F, SOUZA D, et al. Ionic liquid (molten salt) phase organometallic catalysis. Chemical Reviews, 2002, 102(10): 3667-3692.
PMID |
| [23] |
LIU D, FU Q, CHU Y. Molten salt synthesis, formation mechanism, and oxidation behavior of nanocrystalline HfB2 powders. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(1): 35-44.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XIAO M, ZHANG L, LUO B, et al. Moten-salt-mediated synthesis of an atomic nickel Co-catalyst on TiO2 for improved photocatalytic H2 evolution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(18): 7230-7234.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
JONES V, GREY J, HARDING K G. Wound dressings. British Medical Journal, 2006, 332(7544): 777-780.
DOI URL |
| [26] | FERNANDO I P S, LEE W, HAN E J, et al. Alginate-based nano materials: fabrication techniques, properties, and applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 391: 123823-13. |
| [27] |
HERNANDEZ G A C, TELLEZ J L, RODRIGUEZ L L M, et al. Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: a review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 229: 115514.
DOI URL |
| [28] | MA W, MA H, QIU P, et al. Sprayable β-FeSi2 composite hydrogel for portable skin tumor treatment and wound healing. Biomaterials, 2022, 431(4): 133466. |
| [29] |
LIN K, CHANG J, CHEN G, et al. A simple method to synthesize single-crystalline β-wollastonite nanowires. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2006, 300(2): 267-271.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
SHAE S, HENDERSON C M B, KOMANSCHEK B U. Dehydration/recrystallization mechanisms, energetics, and kinetics of hydrated calcium silicate minerals: an in situ TGA/DSC and synchrotron radiation SAXS/WAXS study. Chemical Geology, 2000, 167(1): 141-159.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LI Y, SHAO H, LIN Z, et al. A general Lewis acidic etching route for preparing MXenes with enhanced electrochemical performance in non-aqueous electrolyte. Nature Materials, 2020, 19(8): 894-900.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
YE F, DAI H, PENG K, et al. Effect of Mn doping on the microstructure and magnetic properties of CuFeO2 ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(4): 444-453
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LIN L, SONG J, SONG L, et al. Simultaneous Fenton-like ion delivery and glutathione depletion by MnO2-based nanoagent to enhance chemodynamic therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(18): 4902-4906.
DOI URL |
| [34] | GUO M, HE J, MA S, et al. Determination of Hg2+ based on the selective enhancement of peroxidase mimetic activity of hollow porous gold nanoparticles. Nano Brief Reports and Reviews, 2017, 12(4): 1750050-11. |
| [35] | KATHLEEN M, JOCHEN L. Synthesis-structure-activity relationships in Co3O4 catalyzed CO oxidation. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2018, 6: 185-197. |
| [36] |
TARPEY M, FRIDOVICH I. Methods of detection of vascular reactive species nitric oxide, superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and peroxynitrite. Circulation Research, 2001, 89(3): 224.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
CHEN W, LOU G, LEI Q, et al. Overcoming the heat endurance of tumor cells by interfering with the anaerobic glycolysis metabolism for improved photothermal therapy. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(2): 1419-1431.
DOI URL |
| [38] | SHENG D, LIU T, DENG L, et al. Perfluorooctyl bromide & indo- cyanine green co-loaded nanoliposomes for enhanced multimodal imaging-guided phototherapy. Biomaterials, 2018, 165: 1-13. |
| [39] |
SHENG L, ZHANG Z, ZHOU Y, et al. A novel "hot spring"- mimetic hydrogel with excellent angiogenic properties for chronic wound healing. Biomaterials, 2021, 264: 120414.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
MA L, ZHOU Y, LIU Y, et al. Multifunctional bioactive Nd-Ca-Si glasses for fluorescence thermometry, photothermal therapy, and burn tissue repair. Science Advances, 2020, 6(32): eabb1311-12.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 胡佳军, 王凯, 侯鑫广, 杨婷, 夏鸿雁. 熔盐法合成高导热磷化硼及其热管理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [2] | 王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [3] | 舒朝琴, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 熔盐法制备含钴氯磷灰石及其抗氧化性能和细胞相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235. |
| [4] | 郭小炜, 李玉妍, 陈南春, 王秀丽, 解庆林. 负载二甲酸钾缓释抗菌微球的构建[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 181-187. |
| [5] | 丁学强, 张 骋, 董利民, 王 晨,梁彤祥. 水凝胶模板制备纳米TiO2及微流控合成TiO2微球[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(6): 605-609. |
| [6] | 裘慕书, 林 敏, 赵 英, 董宇卿, 卢天健, 徐 峰. 凝胶网络模板法可控制备NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+稀土上转换纳米颗粒[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(5): 545-549. |
| [7] | 吴 星, 栗海峰, 周金玲, 霍敏锋, 程 呈, 沈绪根, 严春杰. 固相-熔盐法非平衡骤热骤冷工艺制备高纯BiFeO3及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(11): 1151-1155. |
| [8] | 龙 震, 魏贤华, 邱晓清. 熔盐法制备立方块状钛酸锶及其表面铜离子团簇修饰[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(10): 1103-1107. |
| [9] | 孙 静, 肖玉梅, 范红松, 张兴栋. 羟基磷灰石对海藻酸钙水凝胶的制备及性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(10): 1087-1091. |
| [10] | 付新建,王宁霞,张圣祖,王 宏,杨亚江. 超分子水凝胶模板法制备项链状TiO2纳米颗粒[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(2): 393-397. |
| [11] | 王智民,韩基新,刘静波. 掺镧改性钛酸钡纳米多晶粉体的制备和表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(5): 945-952. |
| [12] | 宋煜昕,李承恩,晏海学. 熔盐法合成SrBi2Ta2O9粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(1): 145-148. |
| [13] | 汪德强,舒桂明,张丽丹,刘艳玲,王平,郭洪猷. KZrQ6(Q=Se,Te)的中温固相合成[J]. 无机材料学报, 1999, 14(6): 981-984. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||