无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 1181-1191.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220089
雷伟岩1( ), 王岳2, 武世然2, 石东新2, 沈毅1,2(
), 王岳2, 武世然2, 石东新2, 沈毅1,2( ), 李锋锋2
), 李锋锋2
收稿日期:2022-02-23
修回日期:2022-03-17
出版日期:2022-05-09
网络出版日期:2022-05-09
通讯作者:
沈毅, 教授. E-mail: shenyilzt@163.com作者简介:雷伟岩(1992-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: leiphd@163.com
基金资助:
LEI Weiyan1( ), WANG Yue2, WU Shiran2, SHI Dongxin2, SHEN Yi1,2(
), WANG Yue2, WU Shiran2, SHI Dongxin2, SHEN Yi1,2( ), LI Fengfeng2
), LI Fengfeng2
Received:2022-02-23
Revised:2022-03-17
Published:2022-05-09
Online:2022-05-09
Contact:
SHEN Yi, professor. E-mail: shenyilzt@163.comAbout author:LEI Weiyan (1992-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: leiphd@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
纳米材料在不同技术领域均有广泛应用, 且在解决基础科学新发现上拥有巨大潜力。其中单元素构成的纳米材料因合成容易、制备简单而倍受关注, 尤其VA族二维单元素纳米材料(包括黑磷、砷烯等)的物理、化学、电子和光学特性优异, 在生物成像、药物递送和诊断治疗等生物医学领域应用前景广阔。本文总结了VA族二维单元素纳米材料的一般特性、合成和修饰方法, 重点介绍了其面向各种生物医学应用的纳米平台的研究进展, 最后, 讨论了其在生物医学领域所面临的挑战并展望了未来的发展方向。
中图分类号:
雷伟岩, 王岳, 武世然, 石东新, 沈毅, 李锋锋. VA族单元素二维纳米材料在生物医用领域的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1181-1191.
LEI Weiyan, WANG Yue, WU Shiran, SHI Dongxin, SHEN Yi, LI Fengfeng. 2D Nanomaterials from Group VA Single-element: Research Progress in Biomedical Fields[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1181-1191.
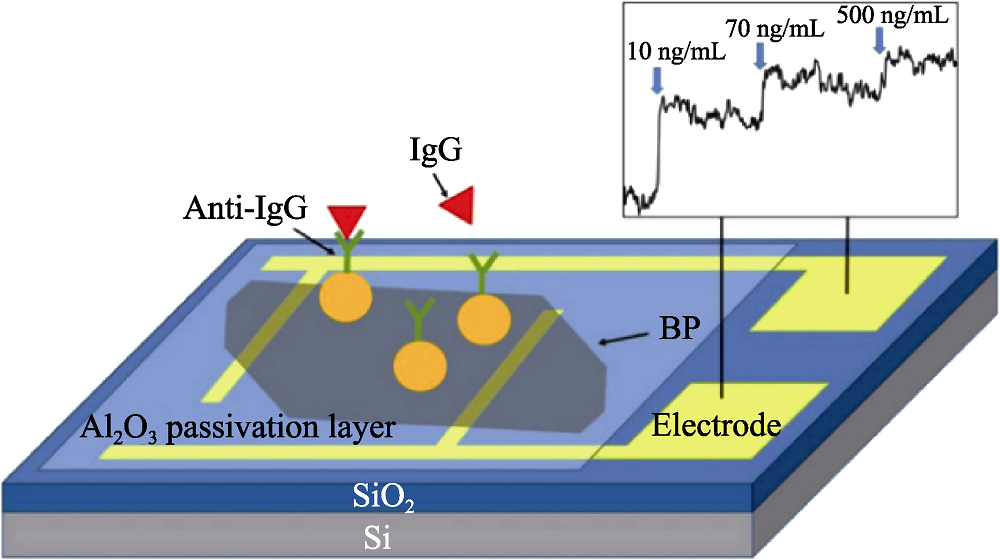
图3 用于IgG检测的黑磷FET生物传感器示意图[62]
Fig. 3 Schematic illustration of black phosphorus (BP) field effect transistor (FET) biosensor for IgG detection[62] The color figure can be obtained from online edition
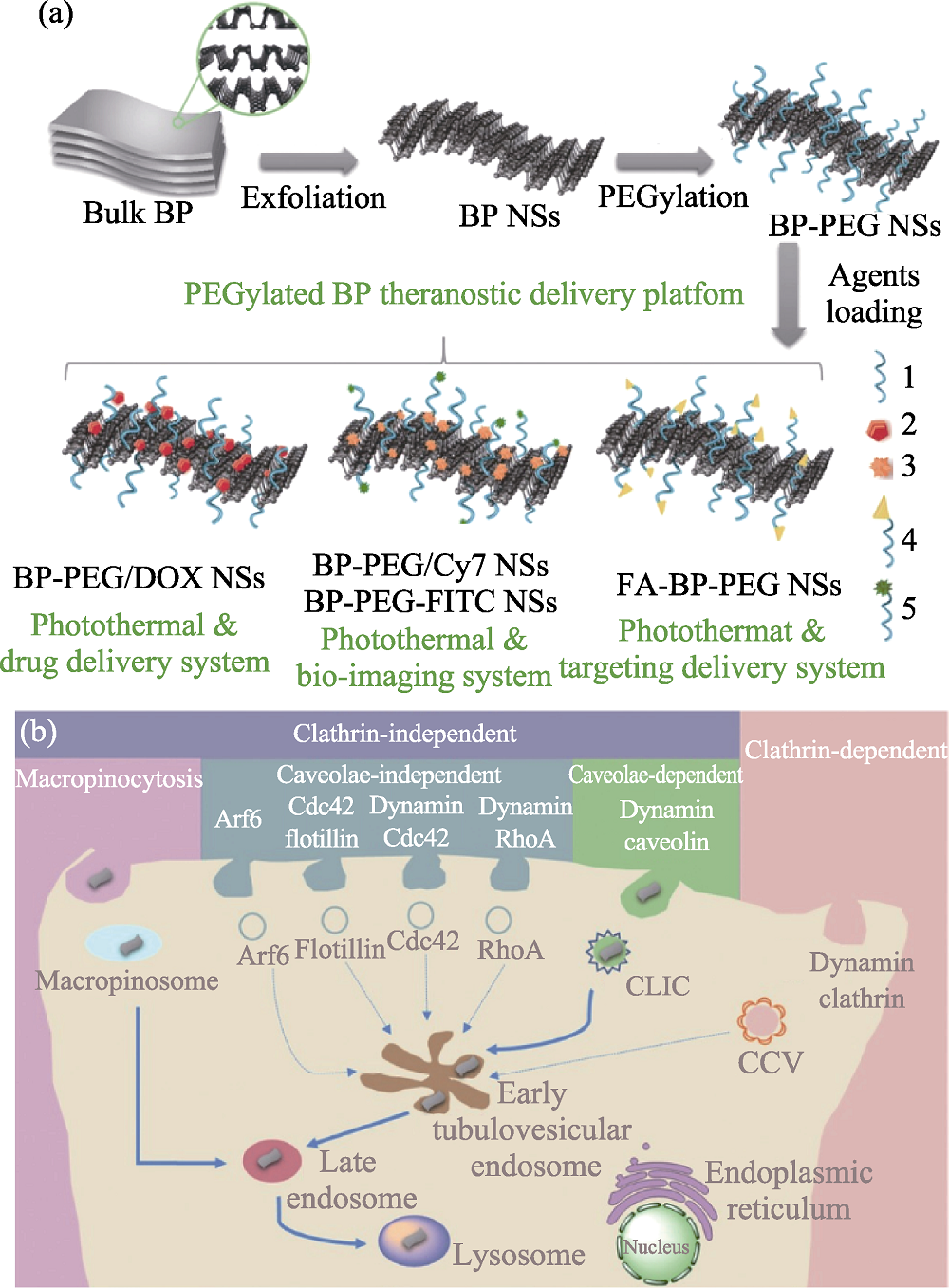
图4 PEG化黑磷纳米片的合成方法及作用机理[11]
Fig. 4 Synthesis method and mechanism of PEGylated black phosphorus nanosheets (BP NSs)[11] The color figure can be obtained from online edition
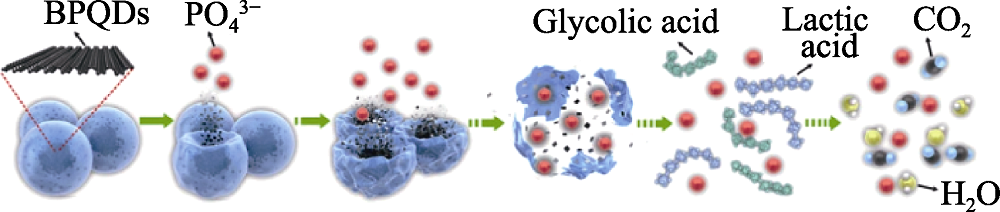
图5 BPQDs/PLGA纳米球在生理环境中的降解过程示意图[52]
Fig. 5 Schematic illustration of the degradation process of the PLGAylated black phosphorus quantum dots (BPQDs/PLGA) nanospheres in the physiological environment[52] The color figure can be obtained from online edition
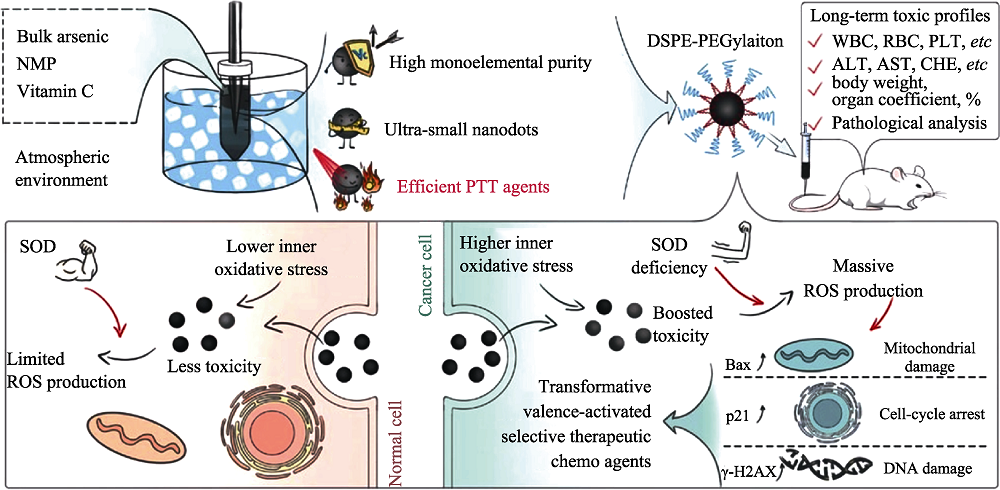
图7 AsNDs@PEG的制备以及应用于正常细胞和癌细胞的示意图[67]
Fig. 7 Schematic illustration of the preparation of PEGylated arsenic nanodots (AsNDs@PEG) and their application to normal and cancer cells[67] The color figure can be obtained from online edition
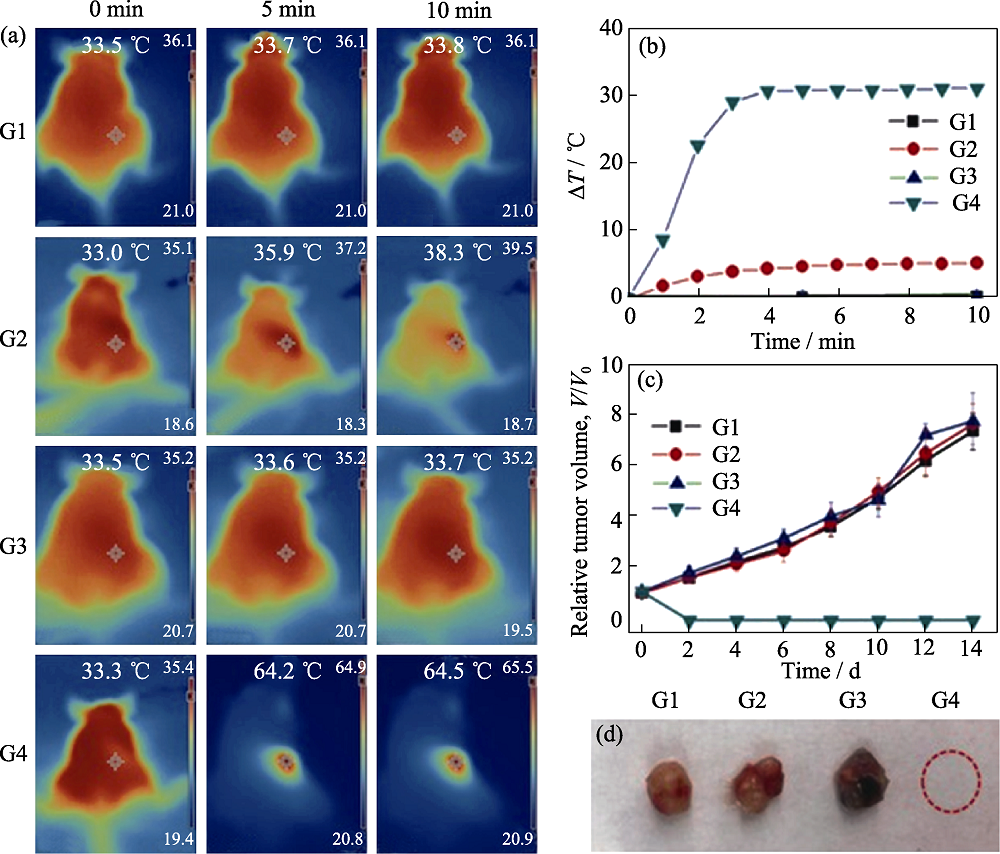
图8 PEG修饰的锑烯量子点的光热治疗效果
Fig. 8 Photothermal effects of PEG-modified antimonene quantum dots (a) Infrared images of tumor-bearing mice under different treatments. (G1: saline; G2: NIR only; G3: PEG-modified antimonene quantum dots; G4: PEG-modified antimonene quantum dots + NIR (808 nm, 1 W·cm-2)); (b) Temperature changes at the tumor site; (c) Relative tumor volume; (d) Representative images of tumors harvested at 14 d[68]The color figures can be obtained from online edition
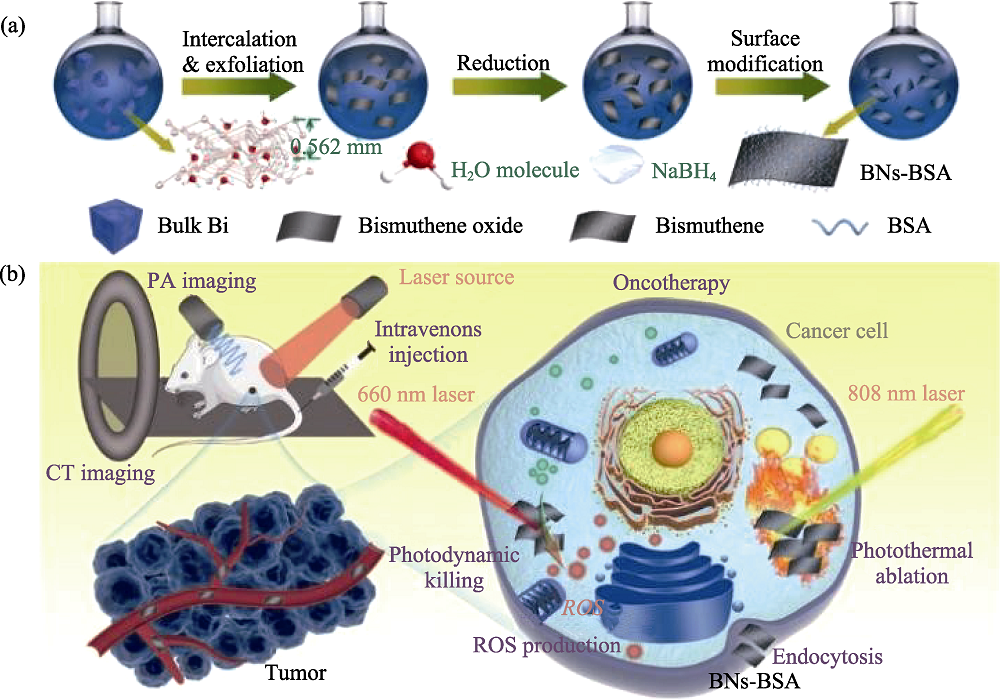
图9 二维多功能铋纳米片的合成、BSA表面修饰以及多模式 PA/CT 成像引导的光子癌症治疗(协同PTT和PDT)示意图[70]
Fig. 9 Schematic illustration of synthetic procedure of 2D multifunctional bismuthene and followed surface modification with bovine serum albumin (BSA), and underlying biomedical applications in multimodal photoacoustic imaging (PAI)/computed tomography (CT) imaging guided photonic cancer treatment (synergistic Photothermal Therapy (PTT) and Photodynamic Therapy (PDT))[70] The color figure can be obtained from online edition
| [1] |
HUANG H, FENG W, CHEN Y. Two-dimensional biomaterials: material science, biological effect and biomedical engineering applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(20): 11381-11485.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
WANG C, ZHAN Y, WANG Z. TiO2, MoS2, and TiO2/MoS2 heterostructures for use in organic dyes degradation. ChemistrySelect, 2018, 3(6): 1713-1718.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIANG B, ZHANG W. BN nanosheet modified SnO materials for enhancing photocatalytic properties. International Journal of Materials Research, 2020, 111(2): 177-182.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DUAN S F, TAO C L, GENG Y Y, et al. Phosphorus-doped isotype g-C3N4/g-C3N4: an efficient charge transfer system for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(2): 729-736.
DOI URL |
| [5] | LI W, LIU D, YANG N, et al. Molybdenum diselenide-black phosphorus heterostructures for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 467: 328-334. |
| [6] |
WU Q, CHEN G, GONG K, et al. MnO2-laden black phosphorus for MRI-guided synergistic PDT, PTT, and chemotherapy. Matter, 2019, 1(2): 496-512.
DOI URL |
| [7] | HUANG H, XIAO Q, WANG J, et al. Black phosphorus: a two- dimensional reductant for in situ nanofabrication. npj 2D Materials and Applications, 2017, 1: 20-8. |
| [8] | JANA D, JIA S R, BINDRA A K, et al. Clearable black phosphorus nanoconjugate for targeted cancer phototheranostics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(16): 18342-18351. |
| [9] |
QI F, JI P, CHEN Z, et al. Photosynthetic cyanobacteria-hybridized black phosphorus nanosheets for enhanced tumor photodynamic therapy. Small, 2021, 17(42): 2102113-9.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU J, YI K, ZHANG Q, et al. Strong penetration-induced effective photothermal therapy by exosome-mediated black phosphorus quantum dots. Small, 2021, 17(49): 2104585-9.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
OUYANG J, FENG C, ZHANG X, et al. Black phosphorus in biological applications: evolutionary journey from monoelemental materials to composite materials. Accounts of Materials Research, 2021, 2(7): 489-500.
DOI URL |
| [12] | LATIFF N M, MAYORGA-MARTINEZ C C, SOFER Z, et al. Cytotoxicity of phosphorus allotropes (black, violet, red). Applied Materials Today, 2018, 13: 310-319. |
| [13] |
LATIFF N M, TEO W Z, SOFER Z, et al. The cytotoxicity of layered black phosphorus. Chemistry-a European Journal, 2015, 21(40): 13991-13995.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
LI Q, HUANG H, CHEN Z, et al. Thickness-dependent structural stability and anisotropy of black phosphorus. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2019, 5(3): 1800712-5.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHAO Y, WANG H, HUANG H, et al. Surface coordination of black phosphorus for robust air and water stability. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(16): 5003-5007.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
KIM J, BAEK S K, KIM K S, et al. Long-term stability study of graphene-passivated black phosphorus under air exposure. Current Applied Physics, 2016, 16(2): 165-169.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CHIA H L, LATIFF N M, GUSMAO R, et al. Cytotoxicity of shear exfoliated pnictogen (As, Sb, Bi) nanosheets. Chemistry-a European Journal, 2019, 25(9): 2242-2249.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
ZHOU W, PAN T, CUI H, et al. Black phosphorus: bioactive nanomaterials with inherent and selective chemotherapeutic effects. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2019, 58(3): 769-774.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
QU G, XIA T, ZHOU W, et al. Property-activity relationship of black phosphorus at the nano-bio interface: from molecules to organisms. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(4): 2288-2346.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | XUE T, LIANG W, LI Y, et al. Ultrasensitive detection of miRNA with an antimonene-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 28-9. |
| [21] |
DENG N, TIAN H, ZHANG J, et al. Black phosphorus junctions and their electrical and optoelectronic applications. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(8): 081001-13.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HAN R, FENG S, SUN D, et al. Properties and photodetector applications of two-dimensional black arsenic phosphorus and black phosphorus. Science China-Information Sciences, 2021, 64(4): 140402-14.
DOI URL |
| [23] | ZHOU L, LIU C, SUN Z, et al. Black phosphorus based fiber optic biosensor for ultrasensitive cancer diagnosis. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2019, 137: 140-147. |
| [24] | SRIVASTAVA A, VERMA A, DAS R, et al. A theoretical approach to improve the performance of SPR biosensor using MXene and black phosphorus. Optik, 2020, 203: 163430. |
| [25] |
SU M, CHEN X, TANG L, et al. Black phosphorus (BP)-graphene guided-wave surface plasmon resonance (GWSPR) biosensor. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(14): 4265-4272.
DOI URL |
| [26] | PENG F, ZHAO F, SHAN L, et al. Black phosphorus nanosheets- based platform for targeted chemo-photothermal synergistic cancer therapy. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces, 2021, 198: 111467-13. |
| [27] | AKSOY I, KUCUKKECECI H, SEVGI F, et al. Photothermal antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of black phosphorus/gold nanocomposites against pathogenic bacteria. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(24): 26822-26831. |
| [28] | ZHANG D, LIU H M, SHU X, et al. Nanocopper-loaded black phosphorus nanocomposites for efficient synergistic antibacterial application. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 393: 122317-9. |
| [29] | LIU W, ZHU Y, LIU Q, et al. 2D black phosphorus-based cytomembrane mimics with stimuli-responsive antibacterial action inspired by endotoxin-associated toxic behavior. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(36): 43820-43829. |
| [30] |
JING Y, TANG Q, HE P, et al. Small molecules make big differences: molecular doping effects on electronic and optical properties of phosphorene. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(9): 095201-9.
DOI URL |
| [31] | XIA F, WANG H, JIA Y. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4458-6. |
| [32] | QIAO J, KONG X, HU Z, et al. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4475-7. |
| [33] |
WEI Q, PENG X. Superior mechanical flexibility of phosphorene and few-layer black phosphorus. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(25): 251915-5.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
XU F, MA H, LEI S, et al.. In situ TEM visualization of superior nanomechanical flexibility of shear-exfoliated phosphorene. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(28): 13603-13610.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LV H Y, LU W J, SHAO D F, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of phosphorene by strain-induced band convergence. Physical Review B, 2014, 90(8): 085433-8.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
FEI R, FAGHANINIA A, SOKLASKI R, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric efficiency via orthogonal electrical and thermal conductances in phosphorene. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(11): 6393-6399.
DOI URL |
| [37] | EZAWA M. Topological origin of quasi-flat edge band in phosphorene. New Journal of Physics, 2014, 16: 115004-13. |
| [38] |
SANSONE G, MASCHIO L, USVYAT D, et al. Toward an accurate estimate of the exfoliation energy of black phosphorus: a periodic quantum chemical approach. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016, 7(1): 131-136.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
SHULENBURGER L, BACZEWSKI A D, ZHU Z, et al. The nature of the inter layer interaction in bulk and few-layer phosphorus. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(12): 8170-8175.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
APPALAKONDAIAH S, VAITHEESWARAN G, LEBEGUE S, et al. Effect of van der Waals interactions on the structural and elastic properties of black phosphorus. Physical Review B, 2012, 86(3): 035105-9.
DOI URL |
| [41] | KANG J, WELLS S A, WOOD J D, et al. Stable aqueous dispersions of optically and electronically active phosphorene. Proceeding of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America, 2016, 113(42): 11688-11693. |
| [42] |
TAN Z, YIN Y, GUO X, et al. Natural organic matter inhibits aggregation of few-layered black phosphorus in mono- and divalent-electrolyte solutions. Environmental Science-Nano, 2019, 6(2): 599-609.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
CASTELLANOS-GOMEZ A, VICARELLI L, PRADA E, et al. Isolation and characterization of few-layer black phosphorus. 2D Materials, 2014, 1(2): 025001.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
LIU H, NEAL A T, ZHU Z, et al. Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(4): 4033-4041.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
GUO Z, ZHANG H, LU S, et al. From black phosphorus to phosphorene: basic solvent exfoliation, evolution of Raman scattering, and applications to ultrafast photonics. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(45): 6996-7002.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
YAN K, LEE H W, GAO T, et al. Ultrathin two-dimensional atomic crystals as stable interfacial layer for improvement of lithium metal anode. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(10): 6016-1022.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
ZHANG X, XIE H, LIU Z, et al. Black phosphorus quantum dots. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(12): 3653-3657.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
WOOD J D, WELLS S A, JARIWALA D, et al. Effective passivation of exfoliated black phosphorus transistors against ambient degradation. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(12): 6964-6970.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
KANG J, WOOD J D, WELLS S A, et al. Solvent exfoliation of electronic-grade, two-dimensional black phosphorus. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(4): 3596-3604.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
BATMUNKH M, BAT-ERDENE M, SHAPTER J G. Phosphorene and phosphorene-based materials-prospects for future applications. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(39): 8586-8617.
DOI URL |
| [51] | HANLON D, BACKES C, DOHERTY E, et al. Liquid exfoliation of solvent-stabilized few-layer black phosphorus for applications beyond electronics. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8563-11. |
| [52] | SHAO J, XIE H, HUANG H, et al. Biodegradable black phosphorus-based nanospheres for in vivo photothermal cancer therapy. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12967-13. |
| [53] |
WANG M, LIANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Ultrasmall black phosphorus quantum dots: synthesis, characterization, and application in cancer treatment. Analyst, 2018, 143(23): 5822-5833.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | KUMAR V, BRENT J R, SHORIE M, et al. Nanostructured aptamer-functionalized black phosphorus sensing platform for label-free detection of myoglobin, a cardiovascular disease biomarker. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(35): 22860-22868. |
| [55] |
WAN B, YANG B, WANG Y, et al. Enhanced stability of black phosphorus field-effect transistors with SiO2 passivation. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(43): 435702-6.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
ZHANG L, OUYANG G. Size-dependent interface thermal conductance in black phosphorus/SiO2 heterojunctions. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 2019, 52(2): 025302-19.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
ABDERRAHMANE A, WOO C, KO P J. Black phosphorus/ molybdenum diselenide heterojunction-based photodetector. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2021, 50(10): 5713-5720.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
RUBIO-BOLLINGER G, GUERRERO R, DE LARA D P, et al. Enhanced visibility of MoS2, MoSe2, WSe2 and black-phosphorus: making optical identification of 2D semiconductors easier. Electronics, 2015, 4(4): 847-856.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
JIANG X, ZHANG M, LIU L, et al. Multifunctional black phosphorus/MoS2 van der Waals heterojunction. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(8): 2487-2493.
DOI URL |
| [60] | ZHU J, ZHANG J, XU S, et al. Unintentional doping effects in black phosphorus by native vacancies in h-BN supporting layer. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 402: 175-181. |
| [61] |
AVSAR A, TAN J Y, LUO X, et al. van der Waals bonded Co/h- BN contacts to ultrathin black phosphorus devices. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(9): 5361-5367.
DOI URL |
| [62] | CHEN Y, REN R, PU H, et al. Field-effect transistor biosensors with two-dimensional black phosphorus nanosheets. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2017, 89: 505-510. |
| [63] |
ZHANG S, GUO S, CHEN Z, et al. Recent progress in 2D group-VA semiconductors: from theory to experiment. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(3): 982-1021.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | HU Y, LIANG J, XIA Y, et al. 2D arsenene and arsenic materials: fundamental properties, preparation, and applications. Small, 2022, 18: 2104556-25. |
| [65] |
TAO W, KONG N, JI X, et al. Emerging two-dimensional monoelemental materials (Xenes) for biomedical applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(11): 2891-2912.
DOI PMID |
| [66] |
ARES P, PALACIOS J J, ABELLAN G, et al. Recent progress on antimonene: a new bidimensional material. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(2): 1703771-27.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
LIU C, SUN S, FENG Q, et al. Arsenene nanodots with selective killing effects and their low-dose combination with ss-elemene for cancer therapy. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(37): 2102054-14.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
TAO W, JI X, XU X, et al. Antimonene quantum dots: synthesis and application as near-infrared photothermal agents for effective cancer therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(39): 11896-11900.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
LIU C, SHIN J, SON S, et al. Pnictogens in medicinal chemistry: evolution from erstwhile drugs to emerging layered photonic nanomedicine. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(4): 2260-2279.
DOI PMID |
| [70] |
WANG Y, FENG W, CHANG M, et al. Engineering 2D multifunctional ultrathin bismuthene for multiple photonic nanomedicine. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(6): 2005093-12.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [11] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [12] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [13] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [14] | 谢兵, 蔡金峡, 王铜铜, 刘智勇, 姜胜林, 张海波. 高储能密度聚合物基多层复合电介质的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| [15] | 冯静静, 章游然, 马名生, 陆毅青, 刘志甫. 冷烧结技术的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 125-136. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||