无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 1141-1148.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220033
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
吴静1( ), 余立兵1, 刘帅帅1, 黄秋艳1, 姜姗姗1, ANTON Matveev2, 王连莉3, 宋二红4(
), 余立兵1, 刘帅帅1, 黄秋艳1, 姜姗姗1, ANTON Matveev2, 王连莉3, 宋二红4( ), 肖蓓蓓1(
), 肖蓓蓓1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-20
修回日期:2022-04-06
出版日期:2022-10-20
网络出版日期:2022-05-09
通讯作者:
肖蓓蓓, 副教授. E-mail: xiaobb11@mails.jlu.edu.cn;作者简介:吴静(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wjjust20@163.com
WU Jing1( ), YU Libing1, LIU Shuaishuai1, HUANG Qiuyan1, JIANG Shanshan1, ANTON Matveev2, WANG Lianli3, SONG Erhong4(
), YU Libing1, LIU Shuaishuai1, HUANG Qiuyan1, JIANG Shanshan1, ANTON Matveev2, WANG Lianli3, SONG Erhong4( ), XIAO Beibei1(
), XIAO Beibei1( )
)
Received:2022-01-20
Revised:2022-04-06
Published:2022-10-20
Online:2022-05-09
Contact:
XIAO Beibei, associate professor. E-mail: xiaobb11@mails.jlu.edu.cn;About author:WU Jing(1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: wjjust20@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
工业上应用哈伯工艺法合成氨过程要求严苛, 需要消耗大量能源且二氧化碳排放量大。因此, 开发在常规环境条件下通过电催化氮还原反应的清洁技术, 对未来可持续的能源转化进程具有重要意义。本研究采用密度泛函理论计算方法, 对TM1N4/TM2嵌入石墨烯的氮还原反应进行了全面研究。在充分考虑活性和稳定性的情况下, 研究结果表明, NiN4/Cr锚定石墨烯通过酶促反应途径表现出最佳的催化活性, 其中第一次加氢为电位决定步骤, 起始电位为0.57 V, 优于商业Ru基材料。此外, 与单一的Cr原子修饰的石墨烯相比, 引入NiN4官能团降低了ΔGmax并提高了电催化性能。根据Mulliken电荷分析, 催化剂的催化活性主要来源于载体和反应中间体之间的电子转移。上述结果为高效合成氨提供了电极候选材料, 进一步深化了相应的电催化机理。
中图分类号:
吴静, 余立兵, 刘帅帅, 黄秋艳, 姜姗姗, ANTON Matveev, 王连莉, 宋二红, 肖蓓蓓. NiN4/Cr修饰的石墨烯电化学固氮电极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1141-1148.
WU Jing, YU Libing, LIU Shuaishuai, HUANG Qiuyan, JIANG Shanshan, ANTON Matveev, WANG Lianli, SONG Erhong, XIAO Beibei. NiN4/Cr Embedded Graphene for Electrochemical Nitrogen Fixation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1141-1148.
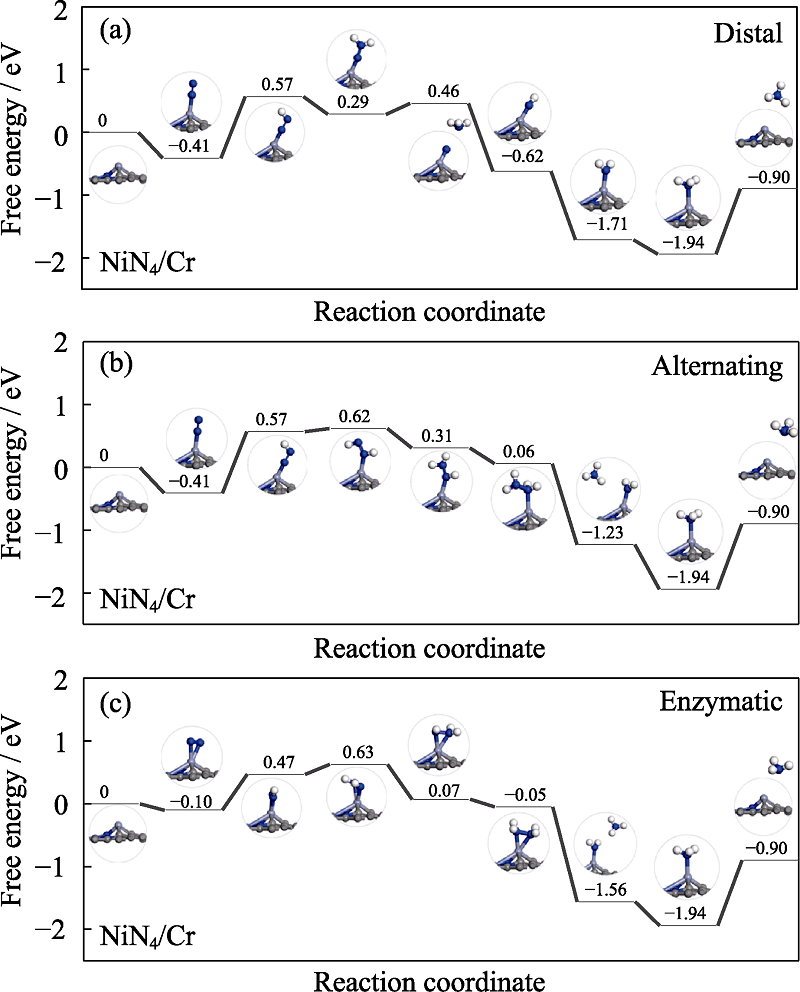
Fig. 4 Free energy diagrams and the corresponding configuration of the NRR intermediates on NiN4/Cr NRR mechanisms are (a) distal, (b) alternating and (c) enzymatic
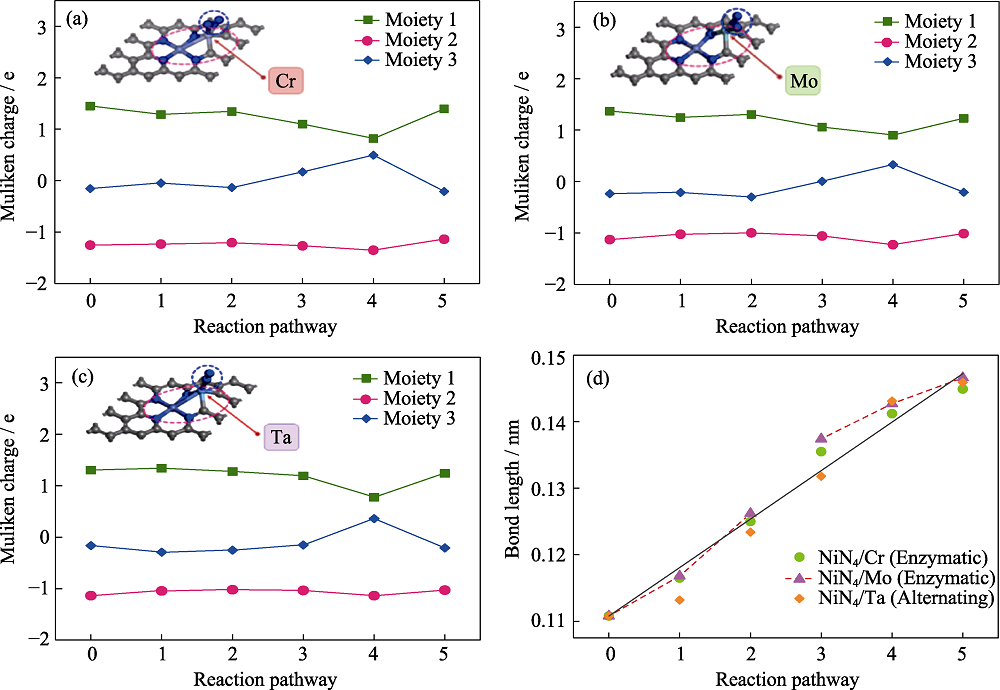
Fig. 5 (a-c) Charge variation of the three moieties along the optimal pathway and (d) N-N bond length change in NRR along preferred pathway Moieties 1, 2, 3 represent the graphene substrate, active center, and NRR intermediates, respectively
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.22 | -0.36 | -0.62 | -0.72 | -1.02 | -1.07 | -0.89 | -0.59 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | 0.12 | -0.02 | -1.17 | -0.35 | -0.59 | -0.51 | -0.33 | -0.19 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.75 | 0.20 | -0.18 | -0.14 | -0.19 | -0.20 | -0.22 | -0.38 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.14 | -0.22 | -1.05 | -0.70 | -0.73 | -0.99 | -0.73 | -1.30 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.13 | 0.11 | -0.42 | -0.43 | -0.47 | -0.44 | -0.25 | -0.96 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.78 | 0.25 | -0.87 | -0.38 | 0.51 | -0.11 | -0.33 | -1.06 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.35 | -0.60 | -1.57 | -1.23 | -1.30 | -1.08 | -0.52 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | 0.07 | 0.02 | -0.32 | -1.48 | -0.88 | -0.68 | -0.44 | -0.23 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.65 | -0.01 | -1.33 | -0.92 | -0.88 | -0.81 | -0.87 | -0.99 |
Table S1 Adsorption energies Eads on Mn1N4/TM2 (Eads in eV)
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.22 | -0.36 | -0.62 | -0.72 | -1.02 | -1.07 | -0.89 | -0.59 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | 0.12 | -0.02 | -1.17 | -0.35 | -0.59 | -0.51 | -0.33 | -0.19 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.75 | 0.20 | -0.18 | -0.14 | -0.19 | -0.20 | -0.22 | -0.38 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.14 | -0.22 | -1.05 | -0.70 | -0.73 | -0.99 | -0.73 | -1.30 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.13 | 0.11 | -0.42 | -0.43 | -0.47 | -0.44 | -0.25 | -0.96 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.78 | 0.25 | -0.87 | -0.38 | 0.51 | -0.11 | -0.33 | -1.06 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.35 | -0.60 | -1.57 | -1.23 | -1.30 | -1.08 | -0.52 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | 0.07 | 0.02 | -0.32 | -1.48 | -0.88 | -0.68 | -0.44 | -0.23 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.65 | -0.01 | -1.33 | -0.92 | -0.88 | -0.81 | -0.87 | -0.99 |
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.75 | -0.26 | -0.52 | -0.94 | -1.06 | -0.88 | -0.53 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.21 | -0.37 | -0.35 | -0.41 | -0.59 | -0.54 | -0.25 | -0.56 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.93 | 0.33 | 0.27 | -0.02 | -0.14 | -0.25 | -0.11 | -0.37 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.14 | -0.22 | -0.20 | -0.62 | -0.88 | -0.96 | -0.76 | -0.49 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | 0.22 | -0.20 | -0.20 | 0.01 | -0.58 | -0.41 | -0.27 | 0.01 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.90 | 0.21 | 0.17 | -0.23 | -0.12 | -0.12 | -0.09 | -0.33 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.20 | -0.31 | -0.64 | -0.91 | -1.15 | -1.27 | -1.09 | -0.26 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.20 | 0.07 | -0.49 | -0.77 | -0.94 | -0.68 | -0.48 | 0.22 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.77 | 0.01 | -0.73 | -0.84 | -0.68 | -0.78 | -0.72 | -0.99 |
Table S2 Adsorption energies Eads on Fe1N4/TM2 (Eads in eV)
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.75 | -0.26 | -0.52 | -0.94 | -1.06 | -0.88 | -0.53 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.21 | -0.37 | -0.35 | -0.41 | -0.59 | -0.54 | -0.25 | -0.56 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.93 | 0.33 | 0.27 | -0.02 | -0.14 | -0.25 | -0.11 | -0.37 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.14 | -0.22 | -0.20 | -0.62 | -0.88 | -0.96 | -0.76 | -0.49 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | 0.22 | -0.20 | -0.20 | 0.01 | -0.58 | -0.41 | -0.27 | 0.01 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.90 | 0.21 | 0.17 | -0.23 | -0.12 | -0.12 | -0.09 | -0.33 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.20 | -0.31 | -0.64 | -0.91 | -1.15 | -1.27 | -1.09 | -0.26 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.20 | 0.07 | -0.49 | -0.77 | -0.94 | -0.68 | -0.48 | 0.22 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.77 | 0.01 | -0.73 | -0.84 | -0.68 | -0.78 | -0.72 | -0.99 |
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.37 | -0.68 | -0.84 | -1.01 | -1.05 | -0.85 | -0.46 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.20 | -0.37 | -0.29 | -0.51 | -0.64 | -0.53 | -0.26 | -0.56 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 1.02 | 0.37 | -0.09 | -0.08 | -0.36 | -0.13 | -0.07 | -0.28 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.12 | -0.19 | -0.44 | -0.61 | -0.82 | -0.93 | -0.75 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.13 | -0.20 | -0.03 | -0.29 | -0.57 | -0.42 | -0.25 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 1.03 | 0.42 | -0.12 | -0.22 | -0.07 | -0.07 | -0.03 | -0.26 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.20 | -0.29 | -0.62 | -0.86 | -1.08 | -1.23 | -1.07 | -0.49 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.21 | -0.29 | -0.28 | -0.63 | -0.89 | -0.67 | -0.46 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.82 | 0.23 | -0.50 | -0.75 | -0.63 | -0.72 | -0.69 | -0.87 |
Table S3 Adsorption energies Eads on Co1N4/TM2 (Eads in eV)
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.37 | -0.68 | -0.84 | -1.01 | -1.05 | -0.85 | -0.46 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.20 | -0.37 | -0.29 | -0.51 | -0.64 | -0.53 | -0.26 | -0.56 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 1.02 | 0.37 | -0.09 | -0.08 | -0.36 | -0.13 | -0.07 | -0.28 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.12 | -0.19 | -0.44 | -0.61 | -0.82 | -0.93 | -0.75 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.13 | -0.20 | -0.03 | -0.29 | -0.57 | -0.42 | -0.25 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 1.03 | 0.42 | -0.12 | -0.22 | -0.07 | -0.07 | -0.03 | -0.26 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.20 | -0.29 | -0.62 | -0.86 | -1.08 | -1.23 | -1.07 | -0.49 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.21 | -0.29 | -0.28 | -0.63 | -0.89 | -0.67 | -0.46 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.82 | 0.23 | -0.50 | -0.75 | -0.63 | -0.72 | -0.69 | -0.87 |
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.41 | -0.72 | -0.91 | -1.04 | -1.07 | -0.79 | -0.58 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.19 | 0.02 | -0.41 | -0.63 | -0.66 | -0.50 | / | -0.58 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.97 | 0.19 | -0.14 | -0.40 | -0.23 | -0.22 | -0.18 | -0.27 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.12 | -0.24 | -0.51 | -0.70 | -0.91 | -0.98 | -0.73 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.13 | -0.20 | -0.23 | -0.63 | -0.61 | -0.44 | -0.21 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.97 | 0.15 | -0.33 | -0.22 | -0.12 | -0.13 | -0.16 | -0.25 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.20 | -0.33 | -0.74 | -0.98 | -1.17 | -1.30 | -1.06 | -0.65 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.20 | 0.06 | -0.49 | -0.94 | -0.95 | -0.68 | -0.41 | -0.65 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.85 | 0.02 | -0.71 | -0.66 | -0.69 | -0.82 | -0.81 | -0.93 |
Table S4 Adsorption energies Eads on Ni1N4/TM2 (Eads in eV)
| 3d | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.21 | -0.41 | -0.72 | -0.91 | -1.04 | -1.07 | -0.79 | -0.58 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.19 | 0.02 | -0.41 | -0.63 | -0.66 | -0.50 | / | -0.58 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.97 | 0.19 | -0.14 | -0.40 | -0.23 | -0.22 | -0.18 | -0.27 |
| 4d | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.12 | -0.24 | -0.51 | -0.70 | -0.91 | -0.98 | -0.73 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.13 | -0.20 | -0.23 | -0.63 | -0.61 | -0.44 | -0.21 | -0.48 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.97 | 0.15 | -0.33 | -0.22 | -0.12 | -0.13 | -0.16 | -0.25 |
| 5d | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt |
| Eads(TM2) N2 end-on | -0.20 | -0.33 | -0.74 | -0.98 | -1.17 | -1.30 | -1.06 | -0.65 |
| Eads(TM2) N2 side-on | -0.20 | 0.06 | -0.49 | -0.94 | -0.95 | -0.68 | -0.41 | -0.65 |
| Eads(TM2) H | 0.85 | 0.02 | -0.71 | -0.66 | -0.69 | -0.82 | -0.81 | -0.93 |
| System | Mechanisms | N2 adsorption | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | NH3 desorption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiN4/Cr | Distal | -0.41 | 0.98 | -0.28 | 0.17 | -1.08 | -1.09 | -0.23 | 1.04 |
| Alternating | -0.41 | 0.98 | 0.05 | -0.31 | -0.25 | -1.29 | -0.71 | 1.04 | |
| Enzymatic | -0.10 | 0.57 | 0.16 | -0.56 | -0.12 | -1.51 | -0.38 | 1.04 | |
| NiN4/Mo | Distal | -0.27 | 0.92 | -0.08 | -0.22 | -1.14 | -0.71 | -0.20 | 1.04 |
| Alternating | -0.27 | 0.92 | 0.16 | -0.56 | 0.06 | -1.52 | -0.49 | 1.04 | |
| Enzymatic | -0.11 | 0.60 | 0.18 | -0.89 | 0.50 | -1.54 | -0.44 | 1.04 | |
| NiN4/Ta | Distal | -0.18 | 0.69 | -0.37 | -0.06 | -1.22 | -1.02 | 0.22 | 1.04 |
| Alternating | -0.18 | 0.69 | 0.05 | -0.88 | 0.11 | -1.78 | 0.05 | 1.04 | |
| Enzymatic | 0.04 | 0.11 | -0.23 | -0.70 | 0.58 | -1.70 | -0.04 | 1.04 |
Table S5 Free energy change ΔG (ΔG in eV), Ri stands for the ith protonation step
| System | Mechanisms | N2 adsorption | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | NH3 desorption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiN4/Cr | Distal | -0.41 | 0.98 | -0.28 | 0.17 | -1.08 | -1.09 | -0.23 | 1.04 |
| Alternating | -0.41 | 0.98 | 0.05 | -0.31 | -0.25 | -1.29 | -0.71 | 1.04 | |
| Enzymatic | -0.10 | 0.57 | 0.16 | -0.56 | -0.12 | -1.51 | -0.38 | 1.04 | |
| NiN4/Mo | Distal | -0.27 | 0.92 | -0.08 | -0.22 | -1.14 | -0.71 | -0.20 | 1.04 |
| Alternating | -0.27 | 0.92 | 0.16 | -0.56 | 0.06 | -1.52 | -0.49 | 1.04 | |
| Enzymatic | -0.11 | 0.60 | 0.18 | -0.89 | 0.50 | -1.54 | -0.44 | 1.04 | |
| NiN4/Ta | Distal | -0.18 | 0.69 | -0.37 | -0.06 | -1.22 | -1.02 | 0.22 | 1.04 |
| Alternating | -0.18 | 0.69 | 0.05 | -0.88 | 0.11 | -1.78 | 0.05 | 1.04 | |
| Enzymatic | 0.04 | 0.11 | -0.23 | -0.70 | 0.58 | -1.70 | -0.04 | 1.04 |
| Distal | Alternating | Enzymatic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDS | ΔGmax | RDS | ΔGmax | RDS | ΔGmax | |
| Cr | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.03 | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.03 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.66 |
| NiN4/Cr | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.98 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.98 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.57 |
| Mo | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.27 | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.27 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.43 |
| NiN4/Mo | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.92 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.92 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.60 |
| Ta | *NNH2+H→*N | 0.72 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.66 | *NH*NH2+H→*NH2*NH2 | 0.49 |
| NiN4/Ta | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.69 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.69 | *NH*NH2+H→*NH2*NH2 | 0.58 |
Table S6 Potential determining step and its free energy change ΔGmax(ΔGmax in eV)
| Distal | Alternating | Enzymatic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDS | ΔGmax | RDS | ΔGmax | RDS | ΔGmax | |
| Cr | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.03 | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.03 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.66 |
| NiN4/Cr | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.98 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.98 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.57 |
| Mo | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.27 | *N2+H→*NNH | 1.27 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.43 |
| NiN4/Mo | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.92 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.92 | *N*N+H→*N*NH | 0.60 |
| Ta | *NNH2+H→*N | 0.72 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.66 | *NH*NH2+H→*NH2*NH2 | 0.49 |
| NiN4/Ta | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.69 | *N2+H→*NNH | 0.69 | *NH*NH2+H→*NH2*NH2 | 0.58 |
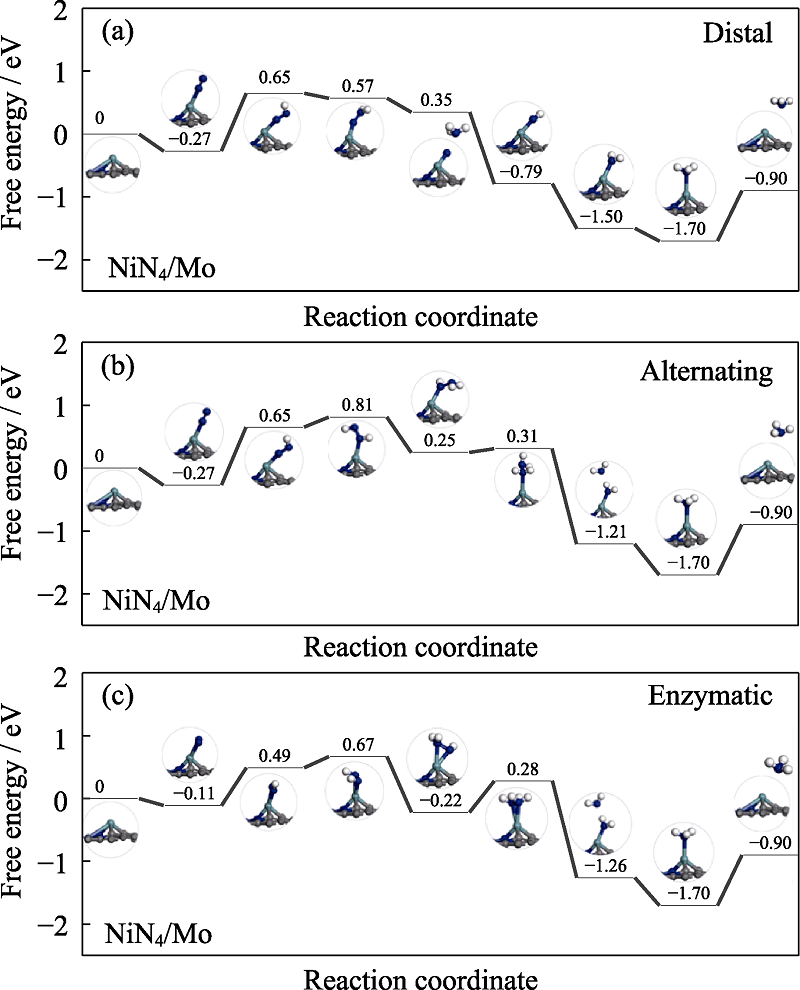
Fig. S2 Free energy diagrams and the corresponding configuration of the NRR intermediates on NiN4/Mo NRR mechanisms are (a) distal, (b) alternating, and (c) enzymatic, respectively
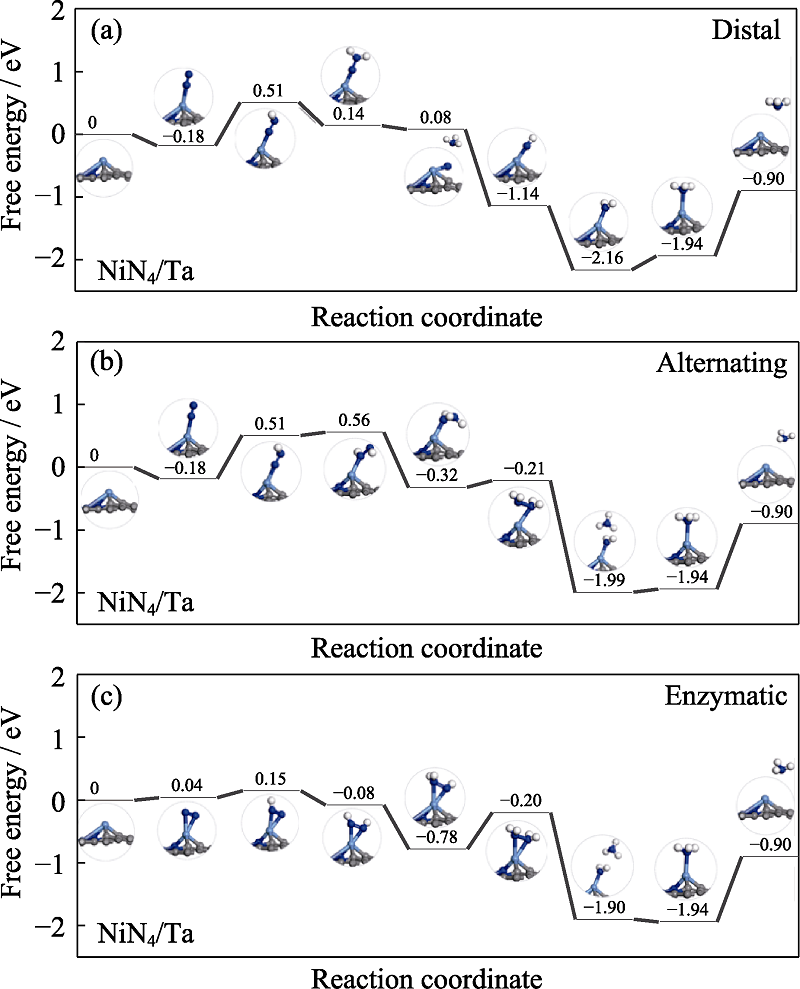
Fig. S3 Free energy diagrams and the corresponding configuration of the NRR intermediates on NiN4/Ta NRR mechanisms are (a) distal, (b) alternating, and (c) enzymatic, respectively
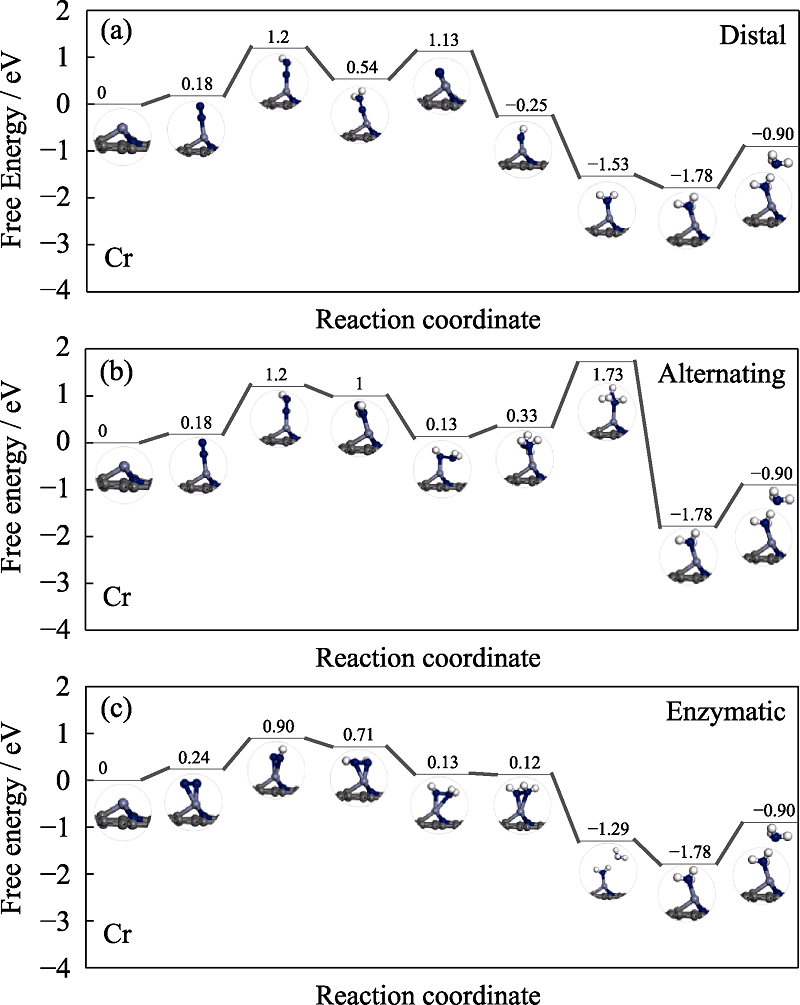
Fig. S4 Free energy diagrams and the corresponding configuration of the NRR intermediates on Cr embedded nitrogen functionalized graphene NRR mechanisms are (a) distal, (b) alternating, and (c) enzymatic, respectively
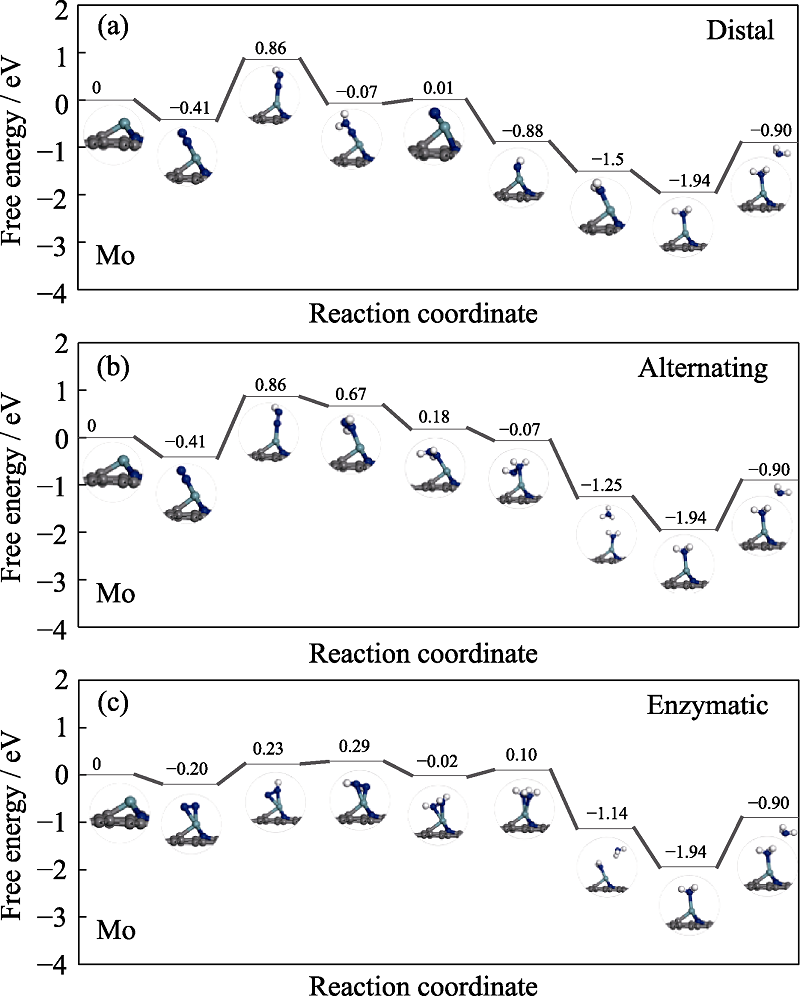
Fig. S5 Free energy diagrams and the corresponding configuration of the NRR intermediates on Mo embedded nitrogen functionalized graphene NRR mechanisms are (a) distal, (b) alternating, and (c) enzymatic, respectively
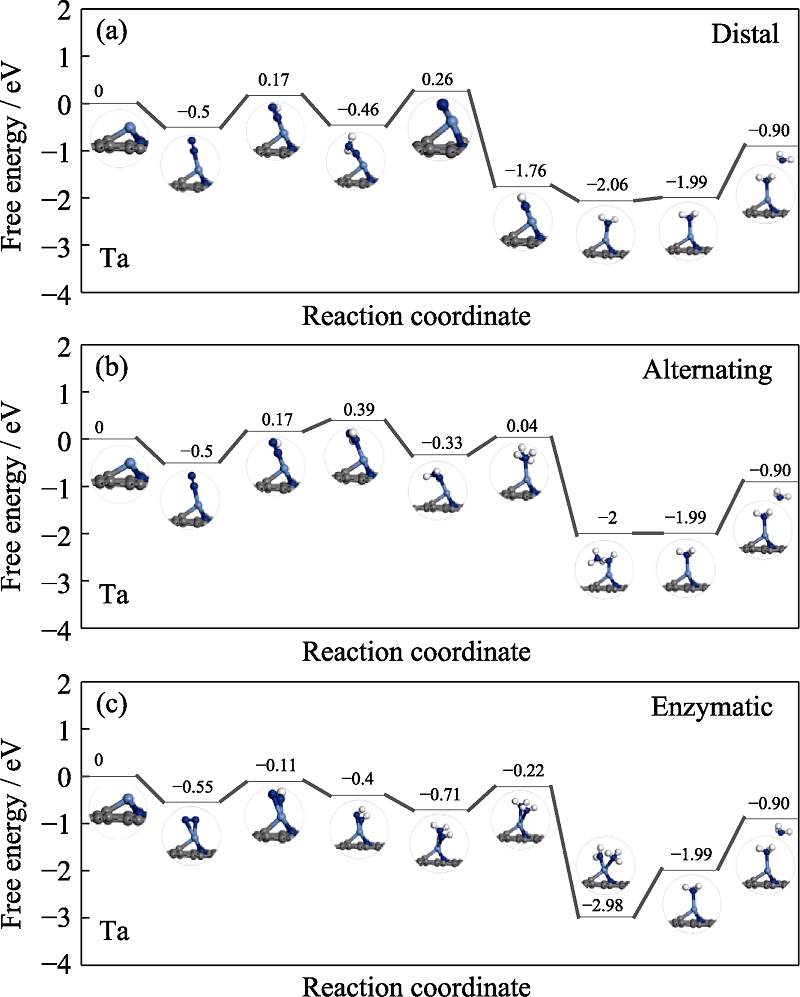
Fig. S6 Free energy diagrams and the corresponding configuration of the NRR intermediates on Ta embedded nitrogen functionalized graphene NRR mechanisms are (a) distal, (b) alternating, and (c) enzymatic, respectively
| [1] | WANG Y, JIA K, PAN Q, et al. Boron-doped TiO2 for efficient electrocatalytic N2 fixation to NH3 at ambient conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Engineer., 2018, 7(1): 117-122. |
| [2] |
LI H Y, YANG L, WANG Z X, et al. N-heterocyclic carbene as a promising metal-free electrocatalyst with high efficiency for nitrogen reduction to ammonia. J. Energy Chem., 2020, 46(7): 78-86.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LI Q Y, HE L Z, SUN C H, et al. Computational study of MoN2 monolayer as electrochemical catalysts for nitrogen reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(49): 27563-27568.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHOI C, BACK S, KIM N Y, et al. Suppression of hydrogen evolution reaction in electrochemical N2 reduction using single- atom catalysts: a computational guideline. ACS Catal., 2018, 8(8): 7517-7525.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ZHAO W H, ZHANG L F, LUO Q Q, et al. Single Mo1(Cr1) atom on nitrogen-doped graphene enables highly selective electroreduction of nitrogen into ammonia. ACS Catal., 2019, 9(4): 3419-3425.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG S Y, SHI L, BAI X W, et al. Highly efficient photo-/ electrocatalytic reduction of nitrogen into ammonia by dual-metal sites. ACS Central Sci., 2020, 6(10): 1762-1771.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MA B Y, PENG Y, Ma D W, et al. Boron-doped InSe monolayer as a promising electrocatalyst for nitrogen reduction into ammonia at ambient conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 495(30): 143463.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LING C Y, NIU X H, LI Q, et al. Metal-free single atom catalyst for N2 fixation driven by visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(43): 14161-14168.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU X, WANG Z X, ZHAO J, et al. Two-dimensional π-conjugated osmium bis(dithiolene) complex (OsC4S4) as a promising electrocatalyst for ambient nitrogen reduction to ammonia. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 487(1): 833-839.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
JI S, WANG Z X, ZHAO J X. A boron-interstitial doped C2N layer as a metal-free electrocatalyst for N2 fixation: a computational study. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(5): 2392-2399.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHANG X, CHEN A, ZHANG Z H, et al. Double-atom catalysts: transition metal dimer-anchored C2N monolayers as N2 fixation electrocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(38): 18599-18604.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI F F, CHEN L, LIU H M, et al. Enhanced N2-fixation by engineering the edges of two-dimensional transition-metal disulfides. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123(36): 22221-22227.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
QIN G Q, CUI Q Y, DU A J, et al. Transition metal diborides: a new type of high-performance electrocatalysts for nitrogen reduction. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(11): 2624-2633.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHU H R, HU Y L, WEI S H, et al. Single-metal atom anchored on boron monolayer (β12) as an electrocatalyst for nitrogen reduction into ammonia at ambient conditions: a first-principles study. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123(7): 4274-4281.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WANG S M, ZHANG L, QIN Y, et al. Co, N-codoped graphene as efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction: insight into the active centre. J. Power Sources, 2017, 363(30): 260-268.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YANG Y L, LIU J D, WEI Z X, et al. Transition metal-dinitrogen complex embedded graphene for nitrogen reduction reaction. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(12): 2821-2827.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
RIYAZ M, GOEL N. Single-atom catalysis using chromium embedded in divacant graphene for conversion of dinitrogen to ammonia. ChemPhysChem, 2019, 20(15): 1954-1959.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
SUN C N, WANG Z L, LANG X Y, et al. Synergistic effect of active sites of double-atom catalysts for nitrogen reduction reaction. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(20): 4593-4600.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHENG X N, YAO Y, WANG Y, et al. Tuning the electronic structure of transition metals embedded in nitrogen-doped graphene for electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction: a first-principles study. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(17): 9696-9707.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | ZHOU Y, SONG E H, CHEN W, et al. Dual-metal interbonding as the chemical facilitator for single-atom dispersions. Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(46): e2003484. |
| [21] | DELLY B. An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys., 1990, 92(1): 508-517. |
| [22] |
DELLY B. From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach. J. Chem. Phys., 2000, 113(18): 7756-7764.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
OERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77(18): 3865-3868.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
DELLY B. Hardness conserving semilocal pseudopotentials. Phys. Rev. B, 2002, 66(15): 155125.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
TODOROVA T, DELLY B. Wetting of paracetamol surfaces studied by DMol3-COSMO calculations. Mol. Simulat., 2008, 34(10/15): 1013-1017.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WEI Z X, ZHANG Y F, WANG S Y, et al. Fe-doped phosphorene for the nitrogen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A, 6(28): 13790-13796.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SHI L, LI Q, LING C Y, et al. Metal-free electrocatalyst for reducing nitrogen to ammonia using a Lewis acid pair. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(9): 4865-4871.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
JIANG C H, ZHOU R Q, PENG Z H, et al. An atomically thin layer of Ru/MoS2 heterostructure: structural, electronic, and magnetic properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(47): 32528-32533.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
YU X M, HAN P, WEI Z X, et al. Boron-doped graphene for electrocatalytic N2 reduction. Joule, 2018, 2(8): 1610-1622.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
NORSKOV J K, ROSSMEISL J, LOGADOTTIR A, et al. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(46): 17886-17892.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YANG L, FENG S, ZHU W. Tuning nitrate electroreduction activity via an equilibrium adsorption strategy: a computational study. J Phys. Chem. Lett., 2022, 13(7): 1726-1733.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIM D H, WILCOX J. Mechanisms of the oxygen reduction reaction on defective graphene-supported Pt nanoparticles from first-principles. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(5): 3653-3660.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
YIN J, FANG Q H, LI Y X, et al. Ni-C-N nanosheets as catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(44): 14546-14549.
PMID |
| [34] |
LIANG H W, BRULLER S, DONG R H, et al. Molecular metal-Nx centres in porous carbon for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6(1): 7992.
DOI URL |
| [35] | LING C Y, OUYANG Y X, LI Q, et al. A general two-step strategy-based high-throughput screening of single atom catalysts for nitrogen fixation. Small Methods, 2019, 3(9): 1-8. |
| [36] |
QI J M, GAO L Y, WEI F F, et al. Design of a high-performance electrocatalyst for N2 conversion to NH3 by trapping single metal atoms on stepped CeO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(50): 47525-47534.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SKULASON E, BLIFAARD T, GUDMUNDSDOTTIR S. A theoretical evaluation of possible transition metal electro- catalysts for N2 reduction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14(3): 1235-1245.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
CHOI W I, WOOD B C, SCHWEGLER E, et al. Combinatorial search for high-activity hydrogen catalysts based on transition- metal-embedded graphitic carbons. Adv. Energy Mater., 2015, 5(23): 1501423.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
LIU C W, LI Q Y, ZHANG J, et al. Conversion of dinitrogen to ammonia on Ru atoms supported on boron sheets: a DFT study. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(9): 4771-4776.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
LI X F, LI Q K, CHENG J, et al. Conversion of dinitrogen to ammonia by FeN3-embedded graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(28): 8706-8709.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
QIU W B, XIE X Y, QIU J D, et al. High-performance artificial nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions using a metal-free electrocatalyst. Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1): 3485.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
GUO Y, GU J X, ZHANG R, et al. Molecular crowding effect in aqueous electrolytes to suppress hydrogen reduction reaction and enhance electrochemical nitrogen reduction. Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11(36): 2101699.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
GUO Y X, YAO Z Y, TIMMER B J J, et al. Boosting nitrogen reduction reaction by bio-inspired FeMoS containing hybrid electrocatalyst over a wide pH range. Nano Energy, 2019, 62: 282-288.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
WANG X, FENG Z, XIAO B, et al. Polyoxometalate-based metal-organic framework-derived bimetallic hybrid materials for upgraded electrochemical reduction of nitrogen. Green Chem., 2020, 22(18): 6157-6169.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHAO J X, CHEN Z F. Single Mo atom supported on defective boron nitride monolayer as an efficient electrocatalyst for nitrogen fixation: a computational study. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(36): 12480-12487.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
LING C Y, BAI X W, OUYANG Y X, et al. Single molybdenum atom anchored on N-doped carbon as a promising electrocatalyst for nitrogen reduction into ammonia at ambient conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122(29): 16842-16847.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
WU Y B, HE C, ZHANG W X. “Capture-backdonation-recapture” mechanism for promoting N2 reduction by heteronuclear metal- free double-atom catalysts. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144(21): 9344-9353.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张祥松, 刘业通, 王永瑛, 武子瑞, 刘振中, 李毅, 杨娟. 自组装制备PtIr合金气凝胶及其高效电催化氨氧化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 511-520. |
| [2] | 陈赛赛, 庞雅莉, 王娇娜, 龚䶮, 王锐, 栾筱婉, 李昕. 绿-黄可逆电热致变色织物的制备及其性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 954-960. |
| [3] | 胡越, 安琳, 韩鑫, 侯成义, 王宏志, 李耀刚, 张青红. RhO2修饰BiVO4薄膜光阳极的制备及其光电催化分解水性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 873-882. |
| [4] | 孙炼, 顾全超, 杨雅萍, 王洪磊, 余金山, 周新贵. 二维过渡金属硫属化合物氧还原反应催化剂的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 697-709. |
| [5] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [6] | 王虹力, 王男, 王丽莹, 宋二红, 赵占奎. 功能化石墨烯担载型AuPd纳米催化剂增强甲酸制氢反应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 547-553. |
| [7] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [8] | 董淑蕊, 赵笛, 赵静, 金万勤. 离子化氨基酸对氧化石墨烯膜渗透汽化过程中水选择性渗透的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 387-394. |
| [9] | 蒋丽丽, 徐帅帅, 夏宝凯, 陈胜, 朱俊武. 缺陷调控石墨烯复合催化剂在氧还原反应中的作用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 215-222. |
| [10] | 付永胜, 毕敏, 李春, 孙敬文, 汪信, 朱俊武. 非贵金属/碳氮复合材料电催化析氧反应的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 163-172. |
| [11] | 蔚海浪, 曹学强, 邓龙辉, 蒋佳宁. LaMeAl11O19/YSZ热障涂层热力学性能和热循环寿命[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1259-1266. |
| [12] | 李铁, 李玥, 王颖异, 张珽. 石墨烯-铁酸铋纳米晶复合材料的制备及其催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 725-732. |
| [13] | 苏莉, 杨建平, 兰悦, 王连军, 江莞. 纳米铁颗粒及其复合材料的界面设计及环境修复应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 561-569. |
| [14] | 向晖, 全慧, 胡艺媛, 赵炜骞, 徐波, 殷江. 类石墨烯单层结构ZnO和GaN的压电特性对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 492-496. |
| [15] | 朱勇, 顾军, 于涛, 何海佟, 姚睿. 铂钴合金纳米电催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 299-305. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||