无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 1217-1224.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220140
吴凌1,2( ), 谭继1, 钱仕1,3, 葛乃建4, 刘宣勇1,2,3(
), 谭继1, 钱仕1,3, 葛乃建4, 刘宣勇1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-13
修回日期:2022-04-18
出版日期:2022-05-07
网络出版日期:2022-05-07
通讯作者:
刘宣勇, 研究员. E-mail: xyliu@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:吴凌(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 18373153250@163.com
基金资助:
WU Ling1,2( ), TAN Ji1, QIAN Shi1,3, GE Naijian4, LIU Xuanyong1,2,3(
), TAN Ji1, QIAN Shi1,3, GE Naijian4, LIU Xuanyong1,2,3( )
)
Received:2022-03-13
Revised:2022-04-18
Published:2022-05-07
Online:2022-05-07
Contact:
LIU Xuanyong, professor. E-mail: xyliu@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:WU Ling (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 18373153250@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
镍钛合金血管支架植入后可引发血栓和支架再狭窄, 且对损伤的血管内壁无修复作用, 需进行表面改性赋予其抗凝血和促内皮化生物学功能。本研究采用等离子体浸没离子注入与沉积(PIII&D)技术将钽(Ta)注入至镍钛合金, 研究Ta离子注入对镍钛表面理化特性及生物学性能的影响规律。结果表明, 调控Ta离子注入时间, 可在镍钛表面分别构建含Ta、Ta/Ta2O5、Ta/Ta2O5-x/Ta2O5三种不同组分的改性层。各种改性样品中, 含Ta/Ta2O5-x/Ta2O5的改性镍钛表面亲水性均更好, 可提供更多细胞附着位点, 促进人脐静脉内皮细胞早期粘附和铺展, 并提高其增殖能力。相比仅含单质Ta的改性镍钛表面, 含Ta/Ta2O5-x/Ta2O5改性镍钛表面的血液相容性更高, 血小板粘附数量显著减少, 且基本保持为未被激活的球形状态; 各组改性表面的溶血率远低于5%阈值, 均未发生明显溶血现象。上述结果说明, Ta离子注入改性镍钛血管支架在降低血栓形成、加速内皮化方面具有潜在应用。
中图分类号:
吴凌, 谭继, 钱仕, 葛乃建, 刘宣勇. 钽离子注入对镍钛合金表面生物学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1217-1224.
WU Ling, TAN Ji, QIAN Shi, GE Naijian, LIU Xuanyong. Biological Property Investigation of Nitinol Surface Implanted with Tantalum[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1217-1224.
| Parameters | Target | Cathodic arc |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage pulse duration/μs | 500 | 800 |
| Pulsing frequency/Hz | 10 | 10 |
| Implantation voltage/kV | -15 | - |
| Implantation time/min | 30, 60, 120 | - |
表1 钽等离子体浸没离子注入与沉积工艺参数
Table 1 Process parameters of tantalum plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition
| Parameters | Target | Cathodic arc |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage pulse duration/μs | 500 | 800 |
| Pulsing frequency/Hz | 10 | 10 |
| Implantation voltage/kV | -15 | - |
| Implantation time/min | 30, 60, 120 | - |
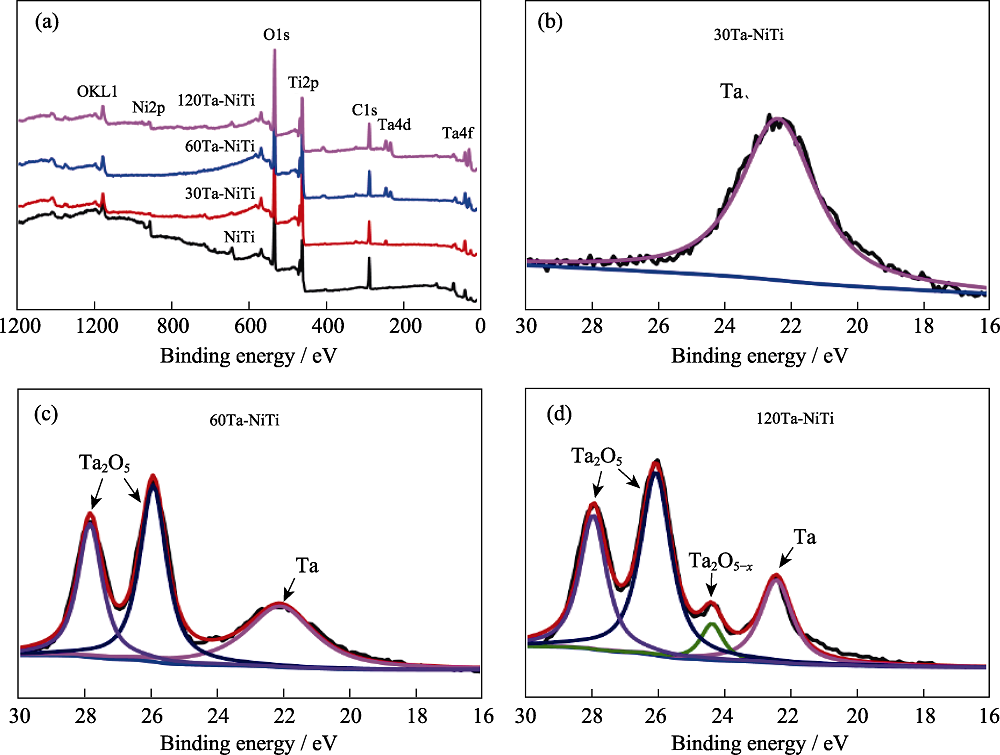
图3 (a)样品表面的XPS全谱和(b~d)Ta4f 高分辨图谱
Fig. 3 (a) XPS full spectra and (b-d) Ta4f high-resolution XPS spectra detected from samples’ surfaces The color figures can be obtained from online edition.
| Sample | Ecorr /V | Icorr/(A∙cm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| NiTi | -0.288 | 5.65×10-6 |
| 30Ta-NiTi | -0.288 | 6.37×10-6 |
| 60Ta-NiTi | -0.261 | 6.69×10-6 |
| 120Ta-NiTi | -0.251 | 6.62×10-6 |
表2 样品的腐蚀电位与腐蚀电流
Table 2 Corrosion potentials and corrosion currents of various samples
| Sample | Ecorr /V | Icorr/(A∙cm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| NiTi | -0.288 | 5.65×10-6 |
| 30Ta-NiTi | -0.288 | 6.37×10-6 |
| 60Ta-NiTi | -0.261 | 6.69×10-6 |
| 120Ta-NiTi | -0.251 | 6.62×10-6 |
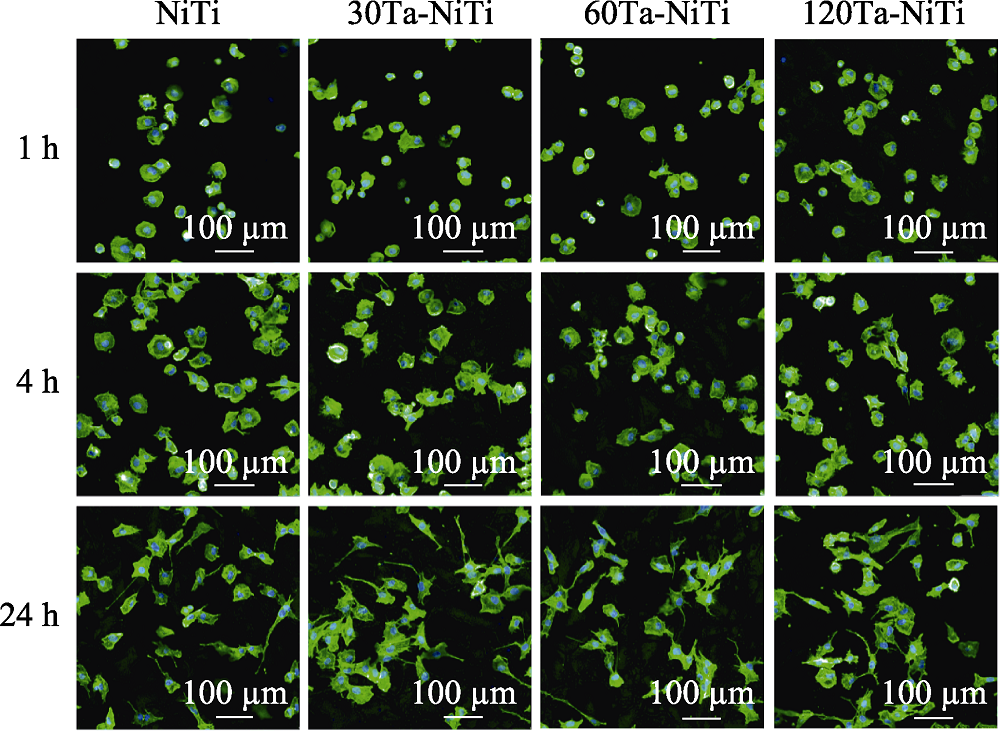
图6 HUVECs在样品表面培养1、4、24 h的荧光照片
Fig. 6 Fluorescent images of HUVECs adhered to various samples at 1, 4, and 24 h The color figures can be obtained from online edition
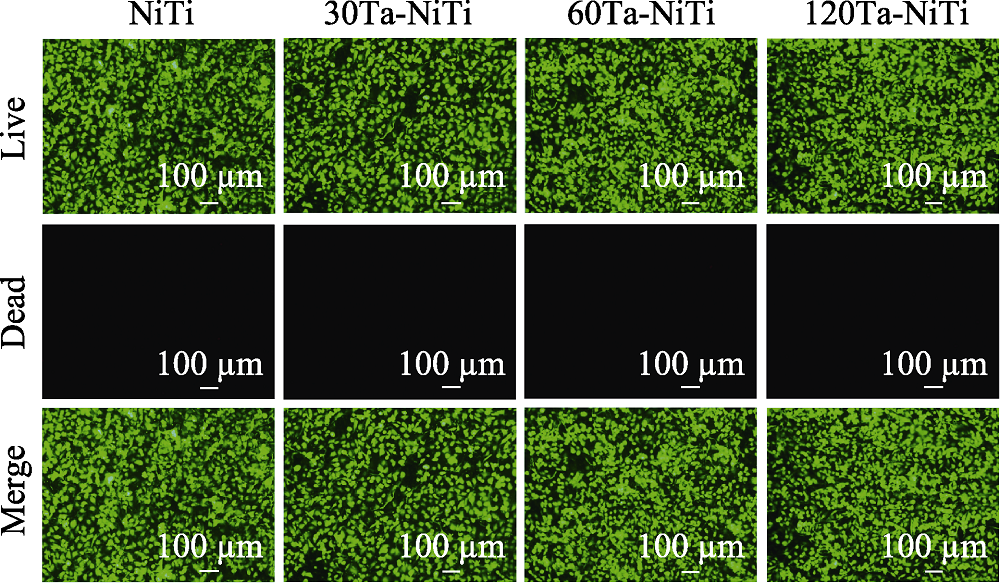
图7 样品表面培养4 d的HUVECs的活/死细胞染色荧光图像
Fig. 7 Live (green)/dead (red) cell staining fluorescent images of HUVECs seeded on samples for 4 d The color figures can be obtained from online edition
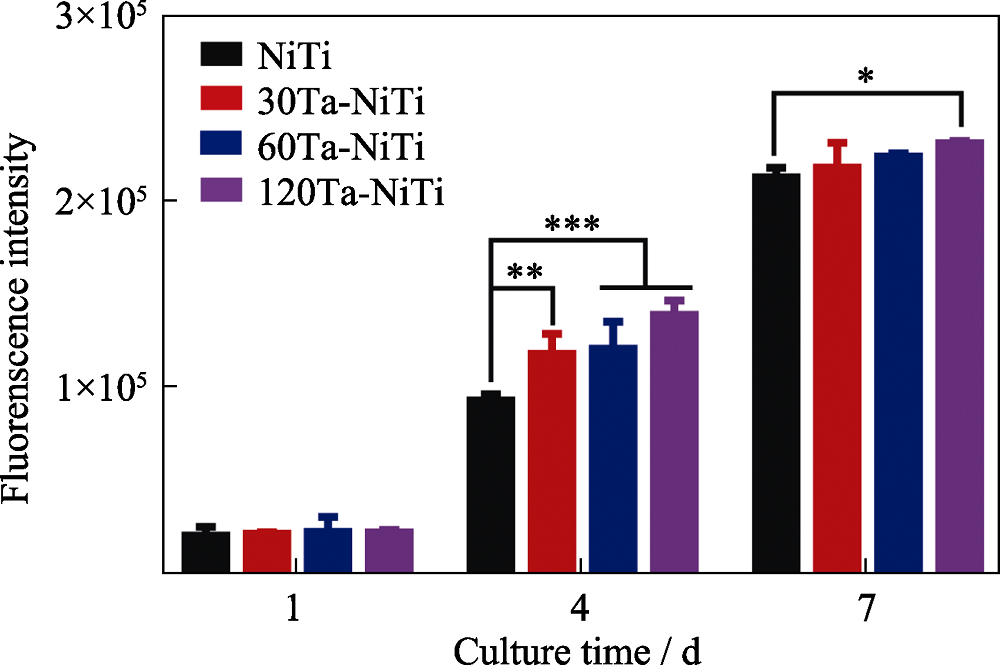
图8 HUVECs在样品表面培养1、4、7 d的细胞活性
Fig. 8 Cell viability of HUVECs cultured on sample surfaces for 1, 4 and 7 d The color figures can be obtained from online edition *: p<0.05, *: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001
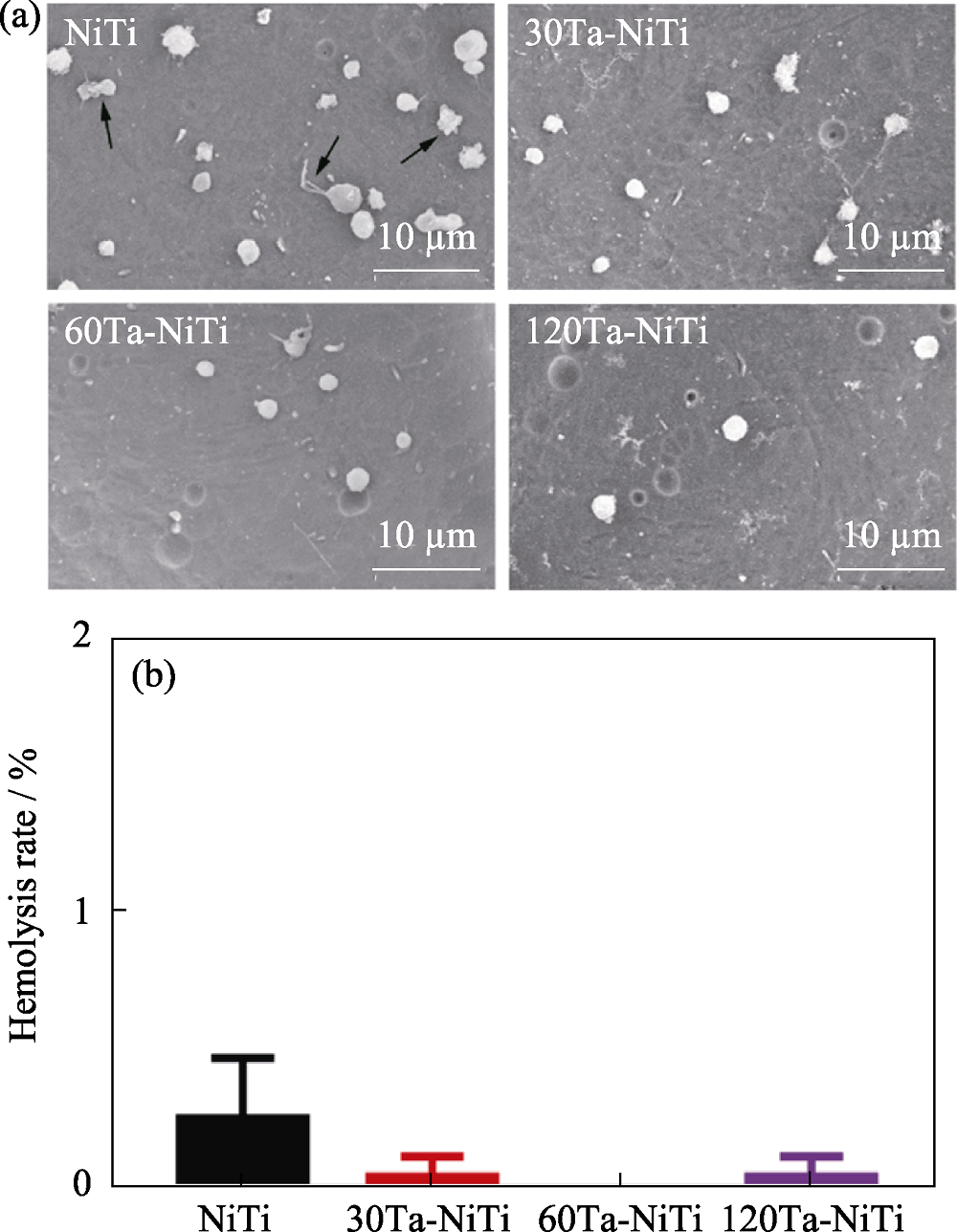
图9 (a)样品表面的血小板粘附SEM照片和(b)各组样品的溶血率
Fig. 9 (a) SEM images of adhered platelets on sample surfaces and (b) hemolysis rate of various samples Arrows indicate the stimulated platelets; The color figures can be obtained from online edition
| [1] | The Writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. Report on cardiovascular health and diseases burden in China:an updated summary of 2020. Chinese Circulation Journal, 2021, 36(6): 582-590. |
| [2] | BRASH J L, HORBETT T A, LATOUR R A, et al. The blood compatibility challenge. Part 2: protein adsorption phenomena governing blood reactivity. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 94: 11-24. |
| [3] | JIANG L, YAO H, LUO X, et al. Copper-mediated synergistic catalytic titanium dioxide nanofilm with nitric oxide generation and anti-protein fouling for enhanced hemocompatibility and inflammatory modulation. Applied Materials Today, 2020, 20: 100663-12. |
| [4] | SUROVTSEVA M A, POVESCHENKO O V, KUZMIN O S, et al. Titanium oxide- and oxynitride-coated nitinol: effects of surface structure and composition on interactions with endothelial cells. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 578: 152059-14. |
| [5] | ZHAO Y, WANG Z, BAI L, et al. Regulation of endothelial functionality through direct and immunomodulatory effects by Ni-Ti-O nanospindles on NiTi alloy. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 2021, 123: 112007-10. |
| [6] |
COCKERILL I, SEE C W, YOUNG M L, et al. Designing better cardiovascular stent materials: a learning curve. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(1): 2005361-23.
DOI URL |
| [7] | CHERIAN A M, NAIR S V, MANIYAL V, et al. Surface engineering at the nanoscale: a way forward to improve coronary stent efficacy. APL Bioengineering, 2021, 5(2): 1508-23. |
| [8] | LAI Y L, CHENG P Y, YANG C C, et al. Electrolytic deposition of hydroxyapatite/calcium phosphate-heparin/gelatin-heparin tri-layer composites on NiTi alloy to enhance drug loading and prolong releasing for biomedical applications. Thin Solid Films, 2018, 649: 192-201. |
| [9] |
WANG D, PENG F, LI J, et al. Butyrate-inserted Ni-Ti layered double hydroxide film for H2O2-mediated tumor and bacteria killing. Materials Today, 2017, 20(5): 238-257.
DOI URL |
| [10] | QI Y, QI H, HE Y, et al. Strategy of metal-polymer composite stent to accelerate biodegradation of iron-based biomaterials. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(1): 182-192. |
| [11] | ZHAO Y, SUN Y H, LAN W W, et al. Self-assembled nanosheets on NiTi alloy facilitate endothelial cell function and manipulate macrophage immune response. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 78: 110-120. |
| [12] |
YU H, LIU Y, WANG Y, et al. A study on poly (N-vinyl-2- pyrrolidone) covalently bonded NiTi surface for inhibiting protein adsorption. Progress in Natural Science-Materials International, 2016, 26(6): 584-589.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZANG D, YI H, GU Z, et al. Interfacial engineering of hierarchically porous NiTi/hydrogels nanocomposites with exceptional antibiofouling surfaces. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(2): 1602869-7.
DOI URL |
| [14] | QIU H, QI P, LIU J, et al. Biomimetic engineering endothelium- like coating on cardiovascular stent through heparin and nitric oxide-generating compound synergistic modification strategy. Biomaterials, 2019, 207: 10-22. |
| [15] | MOHAMMADI F, GOLAFSHAN N, KHARAZIHA M, et al. Chitosan-heparin nanoparticle coating on anodized NiTi for improvement of blood compatibility and biocompatibility. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 127: 159-168. |
| [16] | WANG F, ZHANG Y, CHEN X M, et al. ALD mediated heparin grafting on nitinol for self-expanded carotid stents. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces, 2016, 143: 390-398. |
| [17] | SU L C, CHEN Y H, CHEN M C. Dual drug-eluting stents coated with multilayers of hydrophobic heparin and sirolimus. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(24): 12944-12953. |
| [18] |
PARK C, LEE S W, KIM J, et al. Reduced fibrous capsule formation at nano-engineered silicone surfaces via tantalum ion implantation. Biomaterials Science, 2019, 7(7): 2907-2919.
DOI URL |
| [19] | PARK C, PARK S, KIM J, et al. Enhanced endothelial cell activity induced by incorporation of nano-thick tantalum layer in artificial vascular grafts. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 508: 144801-12. |
| [20] | PARK C, SEONG Y J, KANG I G, et al. Enhanced osseointegration ability of poly(lactic acid) via tantalum sputtering-based plasma immersion ion implantation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(11): 10492-10504. |
| [21] | ZHU S L, YANG X J, FU D H, et al. Stress-strain behavior of porous NiTi alloys prepared by powders sintering. Materials Science and Engineering Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2005, 408(1/2): 264-268. |
| [22] | WAKABAYASHI H, SAN-NO T, TORIYAMA T, et al. The effect of temperature during helium ion implantation-induced crystallization of iron-based amorphous alloys. 14th International Conference on Ion Implantation Technology, Taos, New Mexico, 2003: 591-593. |
| [23] | ZIER M, OSWALD S, REICHE R, et al. XPS investigations of thin tantalum films on a silicon surface. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry Research, 2003, 375(7): 902-905. |
| [24] |
GENG X, XU W, WANG P, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of nonstoichiometric crystalline TaO2F and Ta2O5 with carbon coating. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(2): 1857-1868.
DOI URL |
| [25] | SIMPSON R, WHITE R G, WATTS J F. XPS investigation of monatomic and cluster argon ion sputtering of tantalum pentoxide. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 405: 79-87. |
| [26] |
BIKONDOA O, PANG C L, ITHNIN R, et al. Direct visualization of defect-mediated dissociation of water on TiO2(110). Nature Materials, 2006, 5(3): 189-192.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 李晶. 多金属偶合腐蚀模型. 腐蚀与防护, 2017, 38(1): 69-72. |
| [28] | 吴维昌译, 赵藻藩, 校. 标准电极电位数据手册, 1版. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991: 154-222. |
| [29] |
ZHUANG Y, ZHANG C, CHENG M, et al. Challenges and strategies for in situ endothelialization and long-term lumen patency of vascular grafts. Bioactive Materials, 2021, 6(6): 1791-1809.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LYU N, DU Z, QIU H, et al. Mimicking the nitric oxide-releasing and glycocalyx functions of endothelium on vascular stent surfaces. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(21): 2002330-12.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHAO T, LI Y, GAO Y, et al. Hemocompatibility investigation of the NiTi alloy implanted with tantalum. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Medicine, 2011, 22(10): 2311-2318.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 孙敬伟, 王洪磊, 孙楚函, 周新贵, 纪小宇. 碳源对先驱体转化法制备TaC陶瓷粉体微观结构及性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 184-192. |
| [2] | 朱嘉桐, 楼志豪, 张萍, 赵佳, 孟轩宇, 许杰, 高峰. 稀土钽酸盐(RETaO4)高熵陶瓷的制备与热学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 411-417. |
| [3] | 李昆强,乔玉琴,刘宣勇. 钛表面铜离子注入对细菌和细胞行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 158-164. |
| [4] | 刘大锐. 非金属S掺杂对NaTaO3可见光下光催化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 409-415. |
| [5] | 李淑慧, 潘秀红, 刘岩, 金蔚青, 张明辉, 余建定, 陈锟, 艾飞. KTa1-xNbxO3晶体生长过程中气泡与界面的相互作用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(11): 1223-1227. |
| [6] | 阳明明, 莫亚娟, 王晓丹, 曾雄辉, 刘雪华, 黄俊, 张纪才, 王建峰, 徐科. AlN: Er薄膜在不同退火温度下应力诱导的微观结构演变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(3): 285-290. |
| [7] | 乔 瑜, 金 腾, 于盛旺, 贺志勇, 申艳艳. 退火气氛对镶嵌在SiO2中Ag纳米颗粒热演变影响效应的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 385-390. |
| [8] | 黄展云, 罗 平, 陈弟虎. 钕掺杂ZnO薄膜的制备及抗凝血性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(9): 993-997. |
| [9] | 甘卫平, 刘继宇, 刘 泓, 李 祥, 马贺然. 钽电容器用钽壳内壁RuO2薄膜电极的表征及电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(8): 882-886. |
| [10] | 刘 敏,王继刚. NiTi合金上沉积氮化碳薄膜的力学和血液相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(3): 491-496. |
| [11] | 徐益,黄楠,孙鸿. 氢等离子体改性TiO2薄膜血液相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(6): 1246-1252. |
| [12] | 李江鸿,张红波,熊翔,肖鹏,赵磊,黄伯. 含钽树脂先驱体转变生成TaC的过程研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(5): 973-978. |
| [13] | 江向平,胡晓萍,江福兰,刘晓冬,殷庆瑞. Li改性铌钽酸钾钠无铅压电陶瓷的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(3): 465-468. |
| [14] | 钟志成,张端明,韩祥云,魏念,杨凤霞,郑克玉. KTa0.6Nb0.4O3粉体溶剂热和水热法合成的对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(1): 45-48. |
| [15] | 相华,徐永东,张立同,成来飞. 液相先驱体转化法制备 TaC抗烧蚀材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(4): 893-898. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||