无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 865-872.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220123
所属专题: 【能源环境】光催化降解有机分子; 【信息功能】Max层状材料、MXene及其他二维材料
薛虹云1,2( ), 王聪宇1, MAHMOOD Asad1(
), 王聪宇1, MAHMOOD Asad1( ), 于佳君1,2, 王焱1, 谢晓峰1, 孙静1(
), 于佳君1,2, 王焱1, 谢晓峰1, 孙静1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-07
修回日期:2022-04-05
出版日期:2022-08-20
网络出版日期:2022-04-26
通讯作者:
MAHMOOD Asad. E-mail: amkhan036@yahoo.com;作者简介:薛虹云(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: hyxue0310@163.com
XUE Hongyun1,2( ), WANG Congyu1, MAHMOOD Asad1(
), WANG Congyu1, MAHMOOD Asad1( ), YU Jiajun1,2, WANG Yan1, XIE Xiaofeng1, SUN Jing1(
), YU Jiajun1,2, WANG Yan1, XIE Xiaofeng1, SUN Jing1( )
)
Received:2022-03-07
Revised:2022-04-05
Published:2022-08-20
Online:2022-04-26
Contact:
MAHMOOD Asad. E-mail: amkhan036@yahoo.com;About author:XUE Hongyun (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: hyxue0310@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
光催化剂失活是影响其在去除低浓度VOCs的实际应用中的主要因素之一。本研究将TiO2与2D石墨碳氮化碳(g-C3N4)复合, 显著提高了光催化剂的稳定性。当Ag改性的Ag-TiO2(AT)用于降解乙醛气体时, 反应60 min后开始发生失活现象, 反应延长至400 min则完全失活。而AT与g-C3N4复合改性后的样品g-C3N4/ Ag-TiO2(CAT)具有优异的光催化性能和稳定性, 反应至600 min未发生失活。原位FT-IR、PL和光电流的研究表明, 当AT催化降解乙醛时, 反应中间体会在表面积累导致催化剂失活。而引入的g-C3N4可以为中间体提供更多的吸附位点, 从而提高稳定性。此外, 引入g-C3N4还有利于电荷分离和产生活性氧物种, 促进乙醛和中间体降解。本研究揭示了2D材料在开发稳定可持续降解VOCs的光催化剂方面的实用性。
中图分类号:
薛虹云, 王聪宇, MAHMOOD Asad, 于佳君, 王焱, 谢晓峰, 孙静. 二维g-C3N4与Ag-TiO2复合光催化剂降解气态乙醛抗失活研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 865-872.
XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872.
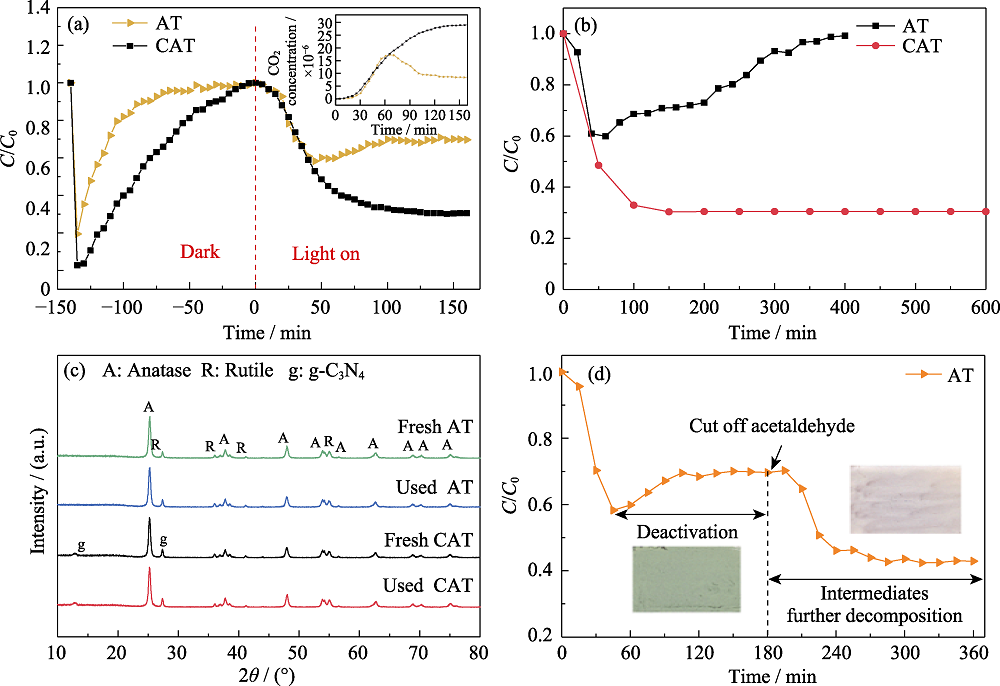
Fig. 1 Activation maintained by CAT for gaseous acetaldehyde (a) Adsorption, photodegradation and CO2 generation curves of acetaldehyde gas by AT and CAT samples; (b) Photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by AT sample under visible light irradiation for 400 min and CAT sample under visible light irradiation for 600 min; (c) XRD patterns of AT and CAT samples before and after degradation of acetaldehyde gas (160 min) under visible light irradiation; (d) Photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by AT sample under visible light irradiation for 360 min, and cutting off acetaldehyde inlet at 180 min
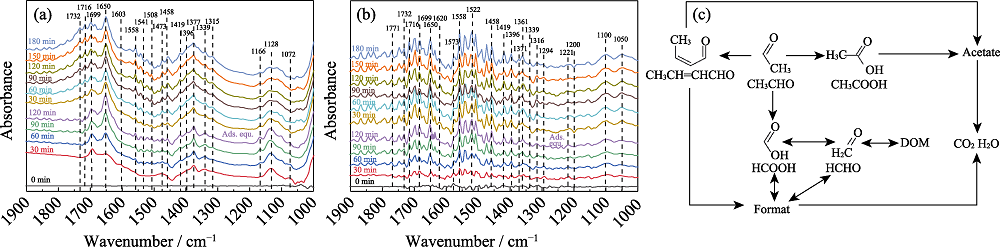
Fig. 2 In-situ DRIFTS spectra of (a) AT and (b) CAT photocatalysts degrading acetaldehyde gas under visible light irradiation, and (c) photocatalytic reaction routes of acetaldehyde
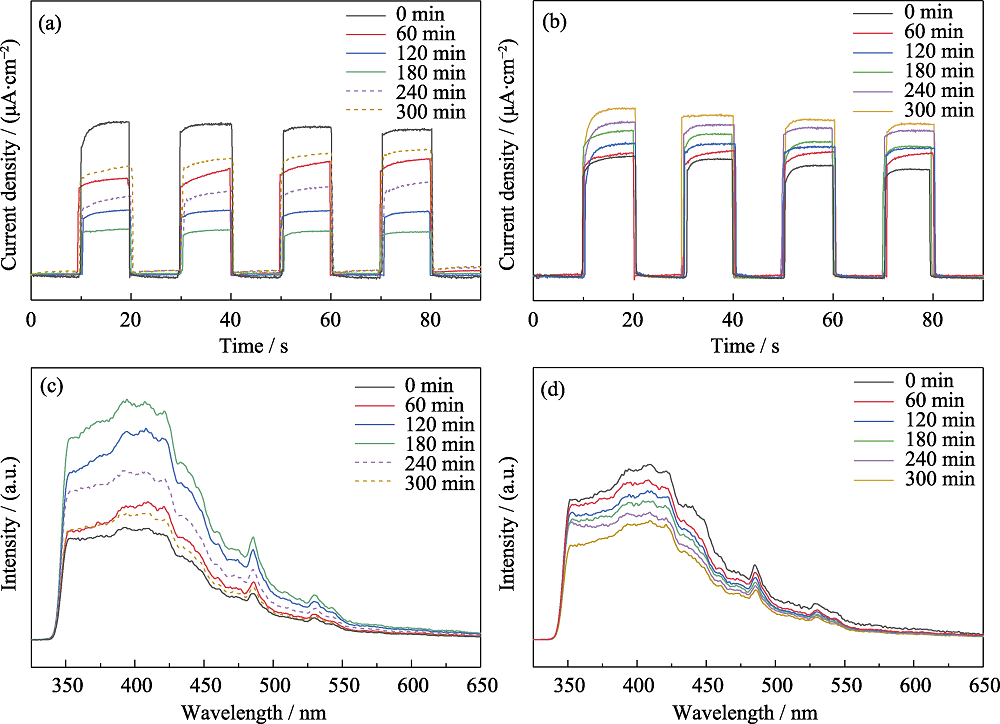
Fig. 3 Photocurrent and PL plots of the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde (a) Photocurrent and (c) PL plots of AT sample for the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde under visible light irradiation; (b) Photocurrent and (d) PL plots of the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by CAT sample under visible light irradiation for 300 min 0, 60, 120, 180 min represent the photocatalytic reaction time of which the dotted lines of 240 and 300 min represent 1 and 2 h, respectively, when acetaldehyde was stopped but the light was kept on
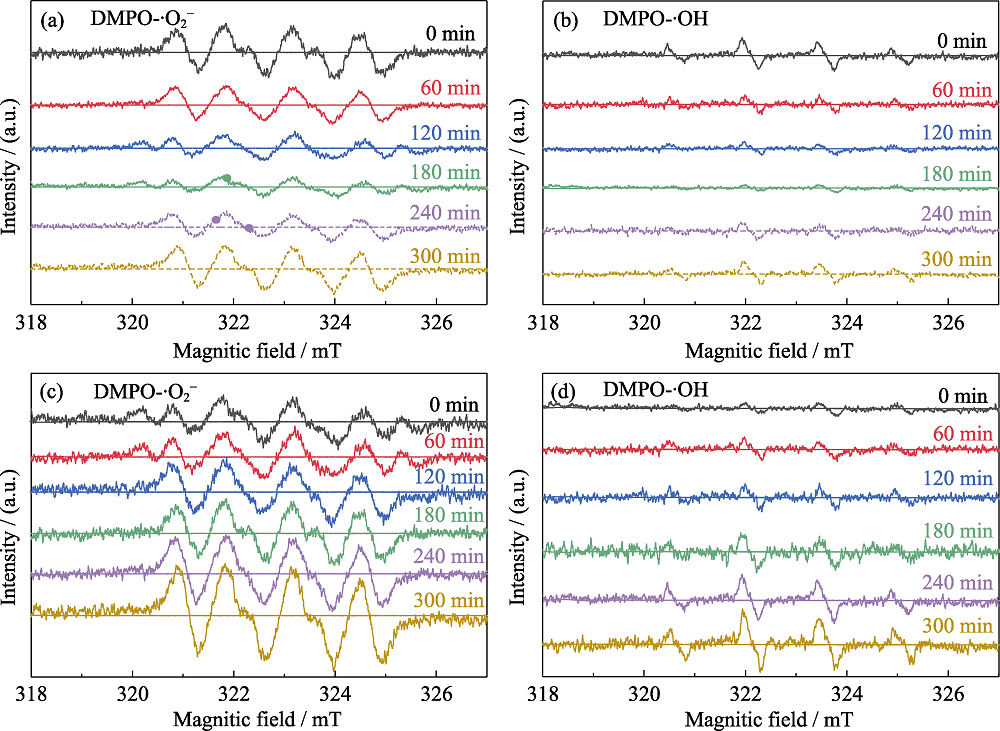
Fig. 4 ESR profiles of (a, c) DMPO-•O2- and (b, d) DMPO-•OH for the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by AT(a, b) and CAT (c, d) sample Under visible light irradiation for 300 min 0, 60, 120, 180 min represent the photocatalytic reaction time, of which the dotted lines of 240 and 300 min represent 1 and 2 h, respectively, when acetaldehyde was stopped but the light was kept on
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1072 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1128, 1166 | v(C-C) |
| 3 | 1315 | δ(CH3) |
| 4 | 1339 | δas(CH3) |
| 5 | 1377 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 7 | 1458, 1473 | δ(CH2) |
| 8 | 1541, 1558 | vas(COO) |
| 9 | 1603 | v(C=C) |
| 10 | 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
Table S1 Assignment of FT-IR bands observed for AT sample in the process of dark adsorption and photocatalytic degradation for acetaldehyde
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1072 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1128, 1166 | v(C-C) |
| 3 | 1315 | δ(CH3) |
| 4 | 1339 | δas(CH3) |
| 5 | 1377 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 7 | 1458, 1473 | δ(CH2) |
| 8 | 1541, 1558 | vas(COO) |
| 9 | 1603 | v(C=C) |
| 10 | 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1050, 1100 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1200 | r(CH2) |
| 3 | 1221, 1294 | v(C-O) |
| 4 | 1316 | δ(CH3) |
| 5 | 1339, 1371 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1361 | δ(CH) |
| 7 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 8 | 1458 | δ(CH2) |
| 9 | 1522, 1558,1573 | vas(COO) |
| 10 | 1620 | v(C=C) |
| 11 | 1771, 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
Table S2 Assignment of FT-IR bands observed for CAT sample in the process of dark adsorption and photocatalytic degradation for acetaldehyde
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1050, 1100 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1200 | r(CH2) |
| 3 | 1221, 1294 | v(C-O) |
| 4 | 1316 | δ(CH3) |
| 5 | 1339, 1371 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1361 | δ(CH) |
| 7 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 8 | 1458 | δ(CH2) |
| 9 | 1522, 1558,1573 | vas(COO) |
| 10 | 1620 | v(C=C) |
| 11 | 1771, 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
| [1] |
WANG S B, ANG H M, TADE M O. Volatile organic compounds in indoor environment and photocatalytic oxidation: state of the art. Environment International, 2007, 33(5): 694-705.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHANG X Y, GAO B, CREAMER A E, et al. Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 102-123.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HUANG R J, ZHANG Y L, BOZZETTI C, et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature, 2014, 514: 218-222.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
KAMAL M S, RAZZAK S A, HOSSAIN M M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)-a review. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 140: 117-134.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GUO Q, ZHOU C Y, MA Z B, et al. Fundamentals of TiO2 photocatalysis: concepts, mechanisms, and challenges. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(50): 1901997.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FU C, LI M J, LI H J, et al. Fabrication of Au nanoparticle/TiO2 hybrid films for photoelectrocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 692: 727-733.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DAI Y Q, COBLEY C M, ZENG J, et al. Synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with exposed {001} facets. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(6): 2455-2459.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI W, WANG F, LIU Y P, et al. General strategy to synthesize uniform mesoporous TiO2/graphene/mesoporous TiO2 sandwich- like nanosheets for highly reversible lithium storage. Nano letters, 2015, 15(3): 2186-2193.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU H H, LI Y, XIANG M M, et al. Single-layered MoS2 directly grown on rutile TiO2(110) for enhanced interfacial charge transfer. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(5): 6083-6089.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIANG H J, ZHANG B, GE H B, et al. Porous TiO2/Pt/TiO2 sandwich catalyst for highly selective semihydrogenation of alkyne to olefin. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10): 6567-6572.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FORZATTI P, LIETTI L. Catalyst deactivation. Catalysis Today, 1999, 52(2/3): 165-181.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ABBAS N, HUSSAIN M, RUSSO N, et al. Studies on the activity and deactivation of novel optimized TiO2 nanoparticles for the abatement of VOCs. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 175: 330-340.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MO J H, ZHANG Y P, XU Q J, et al. Determination and risk assessment of by-products resulting from photocatalytic oxidation of toluene. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 89(3/4): 570-576.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HE C, CHENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review based on pollutant sorts and sources. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(7): 4471-4568.
DOI URL |
| [15] | YANG X J, SUN H W, LI G Y, et al. Fouling of TiO2 induced by natural organic matters during photocatalytic water treatment: mechanisms and regeneration strategy. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 294: 120252. |
| [16] | HUANG H T, FENG J Y, ZHANG S, et al. Molecular-level understanding of the deactivation pathways during methanol photo- reforming on Pt-decorated TiO2. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 272: 118980. |
| [17] |
WEON S, CHOI W. TiO2 nanotubes with open channels as deactivation-resistant photocatalyst for the degradation of volatile organic compounds. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(5): 2556-2563.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEON S, KIM J, CHOI W. Dual-components modified TiO2 with Pt and fluoride as deactivation-resistant photocatalyst for the degradation of volatile organic compound. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 220: 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DONG X A, CUI W, WANG H, et al. Promoting ring-opening efficiency for suppressing toxic intermediates during photocatalytic toluene degradation via surface oxygen vacancies. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(10): 669-678.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZONG B Y, XU Q K, LI Q J, et al. Novel insights into the unique intrinsic sensing behaviors of 2D nanomaterials for volatile organic compounds: from graphene to MoS2 and black phosphorous. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9: 14411-14421.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
REN Y, DONG Y Z, FENG Y Q, et al. Compositing two- dimensional materials with TiO2 for photocatalysis. Catalysts, 2018, 8(12): 590.
DOI URL |
| [22] | RAO Z P, LU G H, MAHMOOD A, et al. Deactivation and activation mechanism of TiO2 and rGO/Er3+-TiO2 during flowing gaseous VOCs photodegradation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 284: 119813. |
| [23] |
WANG C Y, RAO Z P, MAHMOOD A, et al. Improved photocatalytic oxidation performance of gaseous acetaldehyde by ternary g-C3N4/Ag-TiO2 composites under visible light. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 602: 699-711.
DOI URL |
| [24] | FENG J J, ZHANG D K, ZHOU H P, et al. Coupling P nanostructures with P-doped g-C3N4 as efficient visible light photocatalysts for H2 evolution and RhB degradation. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(5): 6342-6349. |
| [25] |
REN H T, JIA S Y, ZOU J J, et al. A facile preparation of Ag2O/P25 photocatalyst for selective reduction of nitrate. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 176-177: 53-61.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SINGH M, ZHOU N J, DILIP K. PAUL, et al. IR spectral evidence of aldol condensation: acetaldehyde adsorption over TiO2 surface. Journal of Catalysis, 2008, 260(2): 371-379.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
XU B Y, ZHU T, TANG X Y, et al. Heterogeneous reaction of formaldehyde on the surface of TiO2 particles. Science China Chemistry, 2010, 53: 2644-2651.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
BATAULT F, THEVENET F, HEQUET V, et al. Acetaldehyde and acetic acid adsorption on TiO2 under dry and humid conditions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 264: 197-210.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
RASKO´ J, KISS J. Adsorption and surface reactions of acetaldehyde on TiO2, CeO2 and Al2O3. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2005, 287(2): 252-260.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
BIRGER H, DIETER T, SAMMY V, et al. Elucidating the photocatalytic degradation pathway of acetaldehyde: an FTIR in situ study under atmospheric conditions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2011, 106(3/4): 630-638.
DOI URL |
| [31] | ZHANG W P, LI G Y, LIU H L, et al. Photocatalytic degradation mechanism of gaseous styrene over Au/TiO2@CNTs: relevance of superficial state with deactivation mechanism. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 272: 118969. |
| [1] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | 王如意, 徐国良, 杨蕾, 邓崇海, 储德林, 张苗, 孙兆奇. p-n异质结BiVO4/g-C3N4光阳极的制备及其光电化学水解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 87-96. |
| [3] | 马心全, 李喜宝, 陈智, 冯志军, 黄军同. S型异质结BiOBr/ZnMoO4的构建及光催化降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [4] | 陈瀚翔, 周敏, 莫曌, 宜坚坚, 李华明, 许晖. CoN/g-C3N4 0D/2D复合结构及其光催化制氢性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [5] | 洪佳辉, 马冉, 仵云超, 文涛, 艾玥洁. MOFs自牺牲模板法制备CoNx/g-C3N4纳米材料用作高效光催化还原U(VI)[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [6] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [7] | 王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [8] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [9] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [10] | 张弦, 张策, 姜文君, 冯德强, 姚伟. 四元BiMnVO5的合成、电子结构与可见光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [11] | 高娃, 熊宇杰, 吴聪萍, 周勇, 邹志刚. 基于超薄纳米结构的光催化二氧化碳选择性转化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 3-14. |
| [12] | 王潇, 朱智杰, 吴之怡, 张城城, 陈志杰, 肖梦琦, 李超然, 何乐. 钴等离激元超结构粉体催化剂的制备及其光热催化应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 22-28. |
| [13] | 刘彭, 吴仕淼, 吴昀峰, 张宁. Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS光催化材料的制备及其CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [14] | 刘雪晨, 曾滴, 周沅逸, 王海鹏, 张玲, 王文中. 改性氮化碳光催化剂在生物质氧化反应中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [15] | 王路平, 卢占会, 魏鑫, 方明, 王祥科. 改进的灰色模型在光催化数据预测中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 871-876. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||