无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 809-820.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220014
收稿日期:2022-01-11
修回日期:2022-03-03
出版日期:2022-08-20
网络出版日期:2022-03-10
作者简介:王士维(1964-), 男, 研究员. E-mail: swwang51@mail.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:Received:2022-01-11
Revised:2022-03-03
Published:2022-08-20
Online:2022-03-10
About author:WANG Shiwei (1964-), male, professor. E-mail: swwang51@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
自发凝固成型是一种新型的陶瓷浆料原位固化成型方法, 通过吸附在陶瓷颗粒表面的分子链间弱作用(氢键, 疏水作用)实现浆料的固化, 具有普适性和适于常温大气环境操作的特点, 已成为先进陶瓷制备领域的研究热点。本文简述发现兼具分散和凝固功能的阴离子型高分子分散剂的历程, 以及自发凝固成型与其它原位固化成型的异同。在此基础上, 基于疏水作用设计合成了系列自发凝固成型剂, 进而满足以不同尺寸颗粒为原料的致密陶瓷和泡沫陶瓷的自发凝固成型。综述了面向实际应用所开发的陶瓷无界面连接、晶粒定向构造、干燥脱水等关键技术, 以及致密陶瓷和泡沫陶瓷制备等研发进展, 展望了未来自发凝固成型的发展方向。
中图分类号:
王士维. 基于疏水作用的陶瓷浆料自发凝固成型研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 809-820.
WANG Shiwei. Progress of Spontaneous Coagulation Casting of Ceramic Slurries Based on Hydrophobic Interaction[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 809-820.
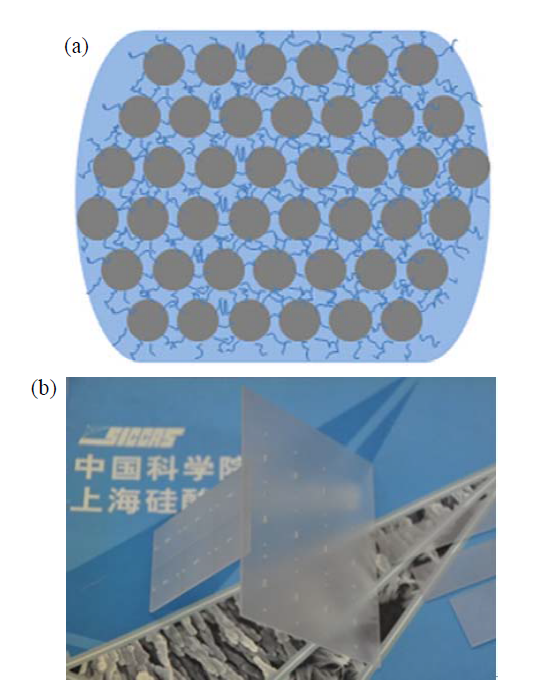
图1 三维有机网络固化陶瓷颗粒示意图(a)和半透明Al2O3薄板照片(100 mm×100 mm×1 mm) (b)
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of ceramic particles solidified by three-dimensional organic network (a) and photo of translucent Al2O3 sheet (100 mm × 100 mm × 1 mm) (b)
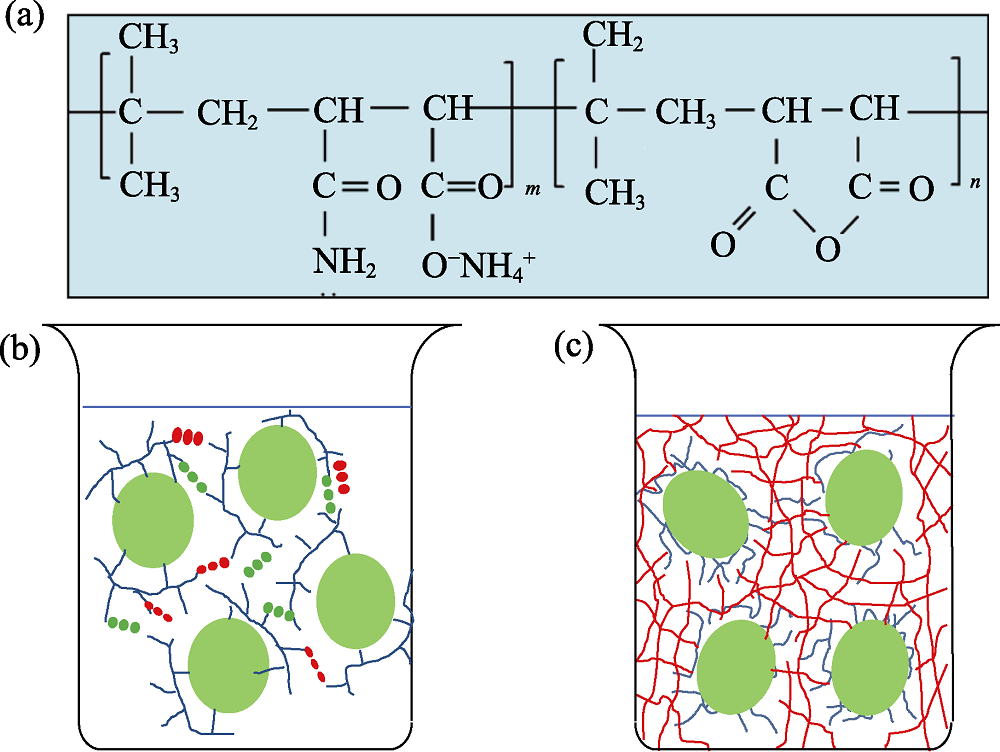
图2 PIBM分子结构简式(a)以及自发凝固(b)和注凝(c)所制备坯体中颗粒间低密度和高密度有机网络示意图
Fig. 2 Simplified structure of PIBM molecule (a) and schematic diagrams of organic network with low and high density by spontaneous coagulation casting (b) and gelcasting (c), respectively
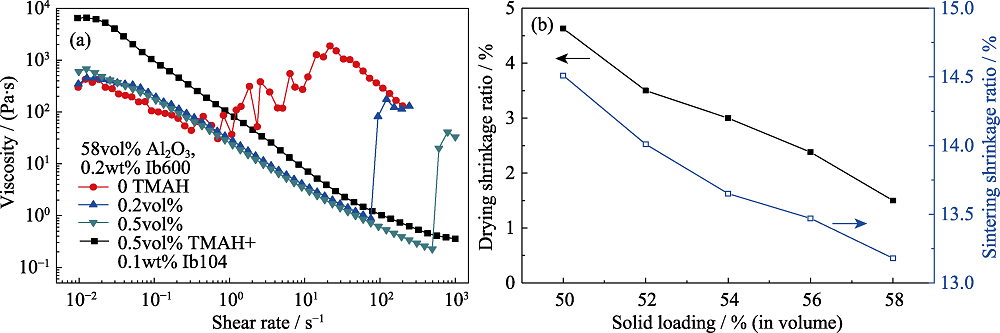
图3 TMAH含量对氧化铝浆料流变性的影响(a)以及浆料固含量对陶瓷坯体干燥及烧结收缩率的影响(b)[43]
Fig. 3 Effect of TMAH content on the rheology of alumina slurry (a), and effect of slurry solid content on drying and sintering shrinkage (b)[43]
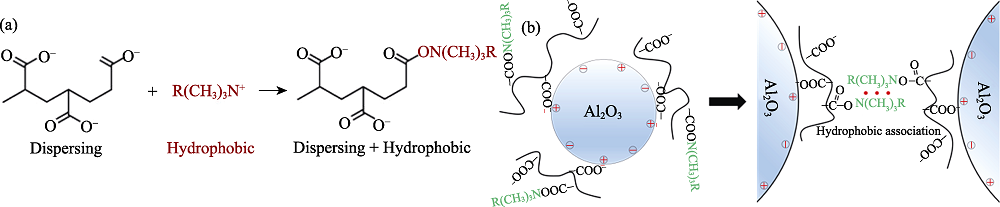
图4 疏水基团对自发凝固成型的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of hydrophobic groups on spontaneous coagulation (a) Hydrophobic modification reaction; (b) Schematic diagram of ceramic particle dispersion and hydrophobic association curing mechanism
| Organic ammonium salt | Molecular weight | Solubility of Isobam after hydrophobic modification |
|---|---|---|
| TMAC (Tetramethyl ammonium chloride) | 109.6 | Soluble |
| TEAC (Tetraethylammonium chloride) | 165.7 | Soluble |
| MTAC (Methyltributylammonium chloride) | 235.8 | Soluble |
| OTAC (Octyltrimethylammonium chloride) | 207.8 | Insoluble |
| DTAC (Dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride) | 263.0 | Insoluble |
表1 不同疏水链改性后Isobam 600 AF的溶解情况
Table 1 Dissolution of Isobam 600 AF after different hydrophobic chain modification
| Organic ammonium salt | Molecular weight | Solubility of Isobam after hydrophobic modification |
|---|---|---|
| TMAC (Tetramethyl ammonium chloride) | 109.6 | Soluble |
| TEAC (Tetraethylammonium chloride) | 165.7 | Soluble |
| MTAC (Methyltributylammonium chloride) | 235.8 | Soluble |
| OTAC (Octyltrimethylammonium chloride) | 207.8 | Insoluble |
| DTAC (Dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride) | 263.0 | Insoluble |
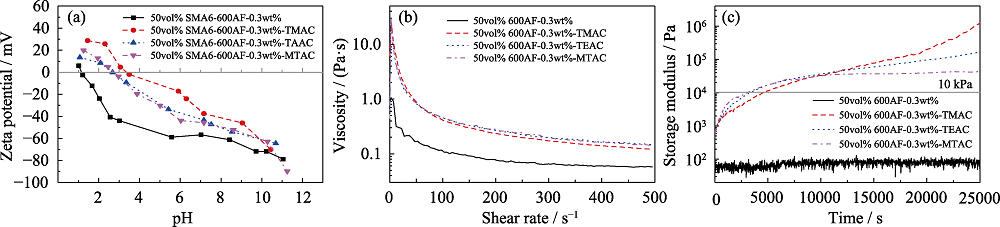
图5 引入不同疏水链制备的氧化铝浆料的Zeta电位(a)、粘度(b)和储能模量(c)[47]
Fig. 5 Zeta potential (a), viscosity (b), and storage modulus (c) of alumina slurry prepared by introducing different hydrophobic chains[47]
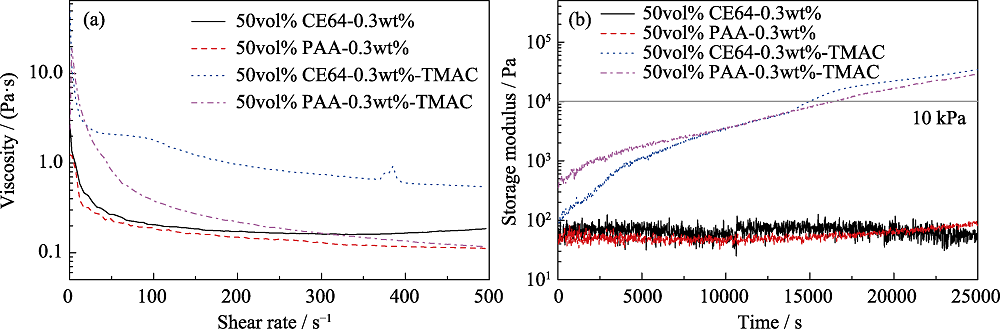
图6 TMAC对添加PAA和CE-64所配制氧化铝浆料粘度(a)和储能模量(b)的影响[47]
Fig. 6 Effect of TMAC on viscosity (a) and storage modulus (b) of alumina slurry prepared by adding PAA and CE-64[47]
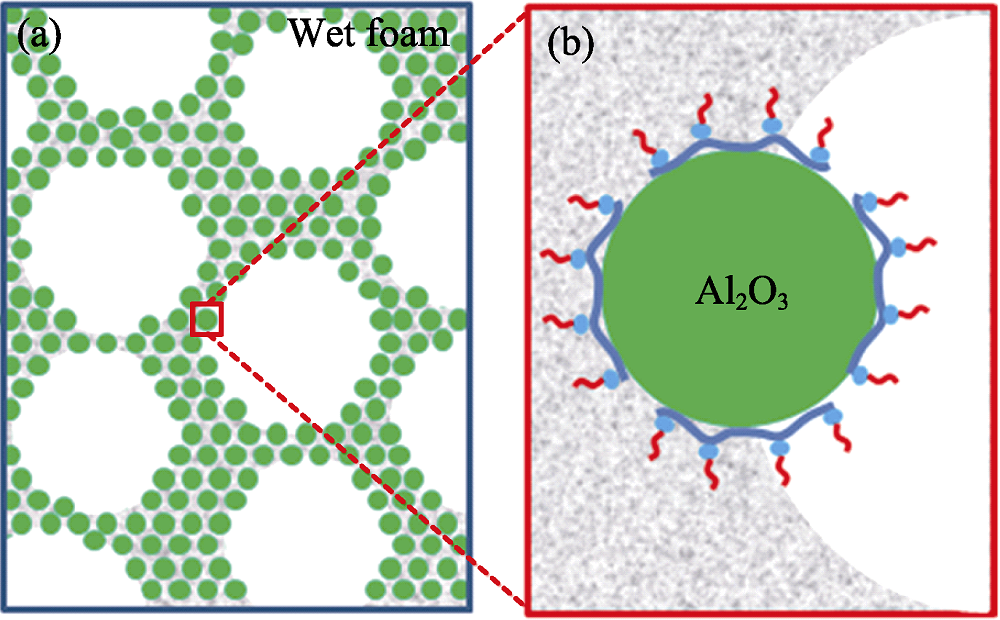
图7 疏水化的陶瓷颗粒稳定泡沫示意图(a)及其局部放大图(展示颗粒表面疏水修饰的分散剂) (b)
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of stabilized foam with hydrophobized ceramic particles (a) and corresponding magnification part (showing a modified dispersant on a particle) (b)
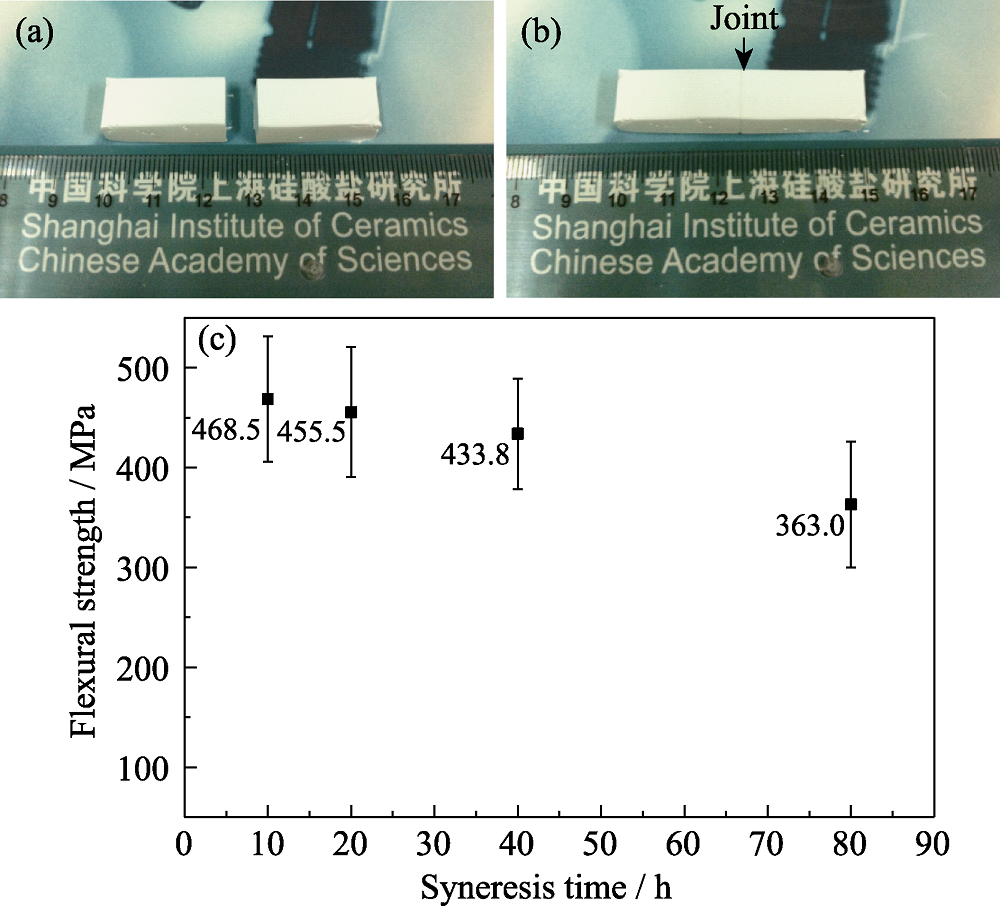
图8 氧化铝陶瓷坯体无界面连接前(a)后(b)的照片和脱水收缩时间对陶瓷烧结后(1600 ℃×2 h)抗弯强度的影响(c)[54]
Fig. 8 Pictures of wet green bodies before (a) and after (b) joining, and effect of syneresis time on flexural strength of sintered samples (1600 ℃×2 h) derived from wet green bodies (c) [54]
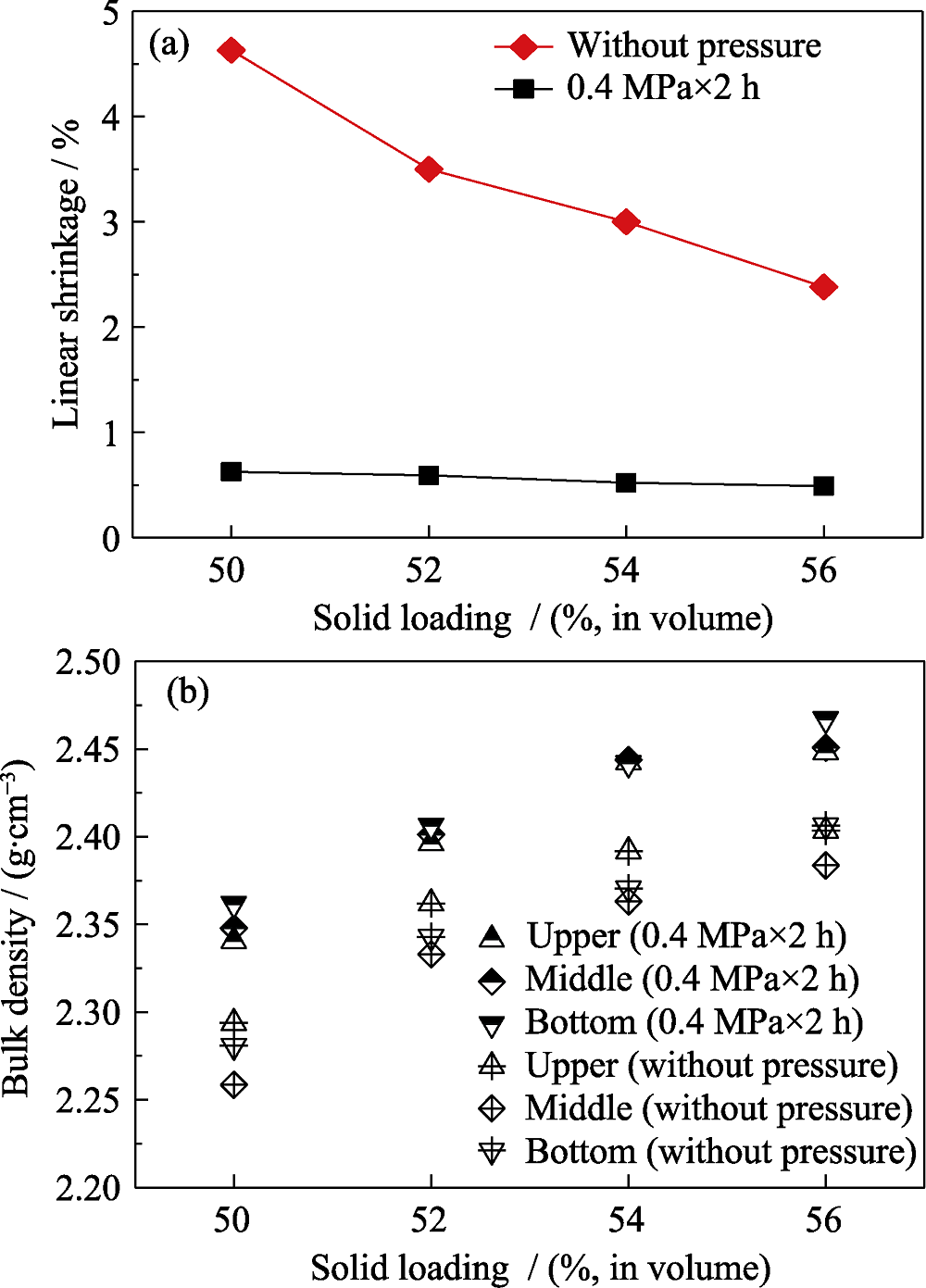
图9 氧化铝陶瓷凝胶和压滤后样品干燥的线性收缩率(a)和干燥后素坯的密度分布(b)[55]
Fig. 9 Linear shrinkage (a) and bulk density distribution (b) of the gelled and pressure-filtrated samples after drying[55]

图10 不同分散体系制备的陶瓷素坯的密度差(a)和烧结后样品 (280 mm×130 mm×20 mm)的照片(b)[56]
Fig. 10 Density difference of ceramic green bodies prepared by different dispersion systems (a) and photos of sintered samples (280 mm×130 mm×20 mm)(b)[56]
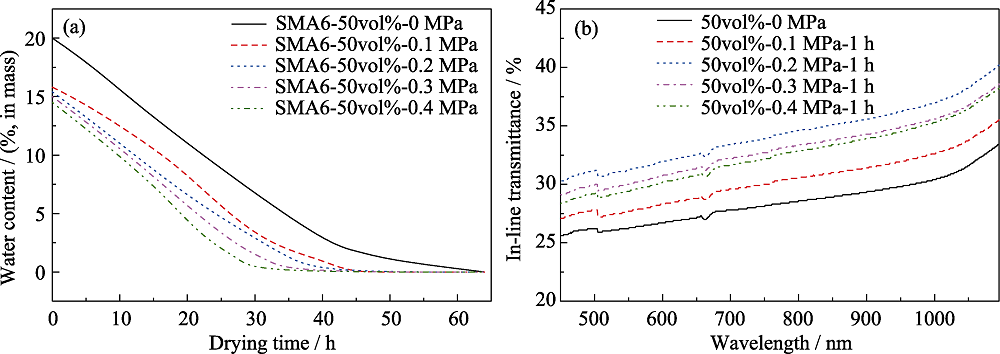
图11 不同压力下湿坯的干燥曲线(a)和制备的陶瓷直线透过率(样品厚 1mm)(b)[57]
Fig. 11 Drying curves of wet bodies under different pressures (a) and in-line transmittance of corresponding ceramics (1 mm thick) (b)[57]
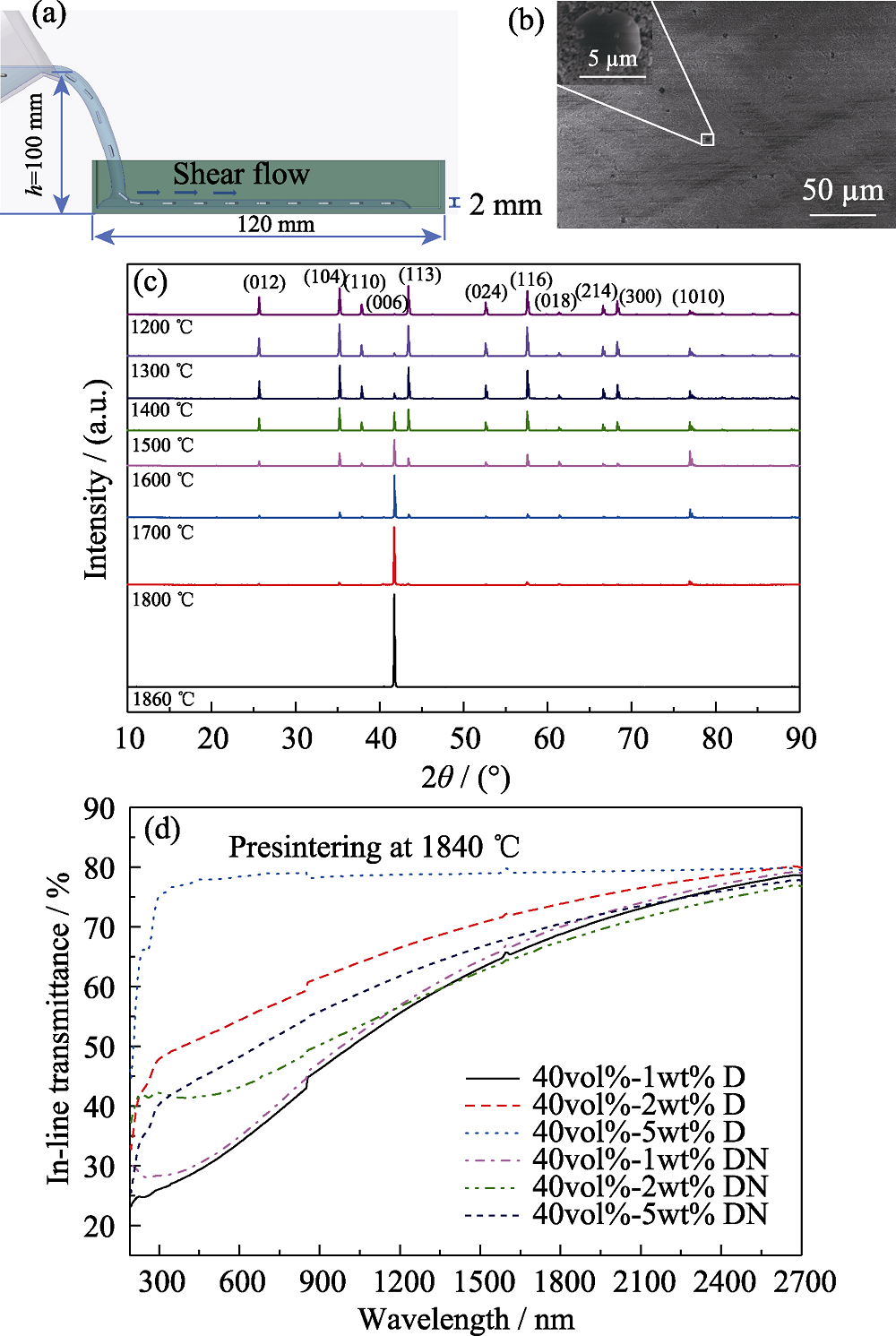
图12 片晶在剪切流下定向排布的示意图(a)、添加片晶所制备的素坯表面(b)、素坯经不同温度烧结后的XRD图谱(c)以及片晶含量和种类对陶瓷直线透过率的影响(样品厚1 mm)(d)[61]
Fig. 12 Schematic diagram of orientation of the platelet under shear flow (a), surface of the green body with platelet (b), XRD patterns of the green bodies sintered at different temperatures (c), and the influence of the content and type of the platelet on the linear transmittance of the ceramic (1 mm thick) (d)[61]
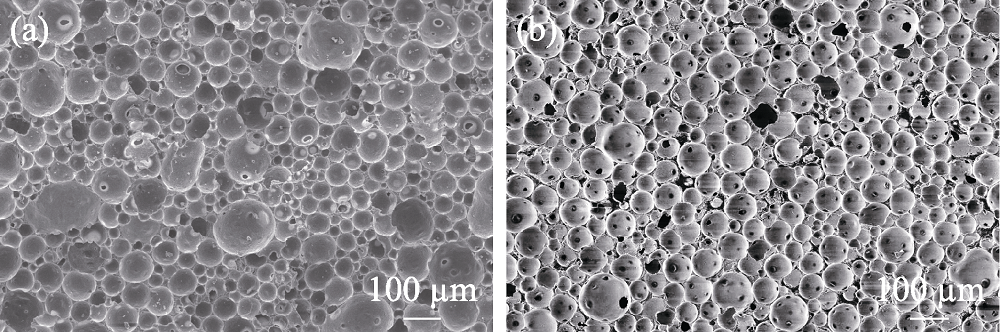
图13 由疏水化的陶瓷颗粒稳定泡沫所制备的闭孔氧化铝泡沫陶瓷
Fig. 13 Closed-cell alumina foam ceramics prepared by hydrophobized ceramic particles (a) Coarse-grained[65]; (b) Fine-grained[67]

图15 自发凝固成型制备复杂形状氧化铝半球状部件(a), 氧化铝导轨(b)以及氮化铝部件(c)
Fig. 15 Pictures of alumina dome (a) and guide (b), and AlN ceramic hat sink (c) prepared by spontaneous coagulation casting
| [1] | 鈴木宏, 内村勝次, 藤原徳仁. セラミックス大型部品用浸透Ⅴプロセスの開発. 素形材, 2007, 12: 21-24. |
| [2] | www.surmet.com/products and applications/Domes and IR optics/ index.php. 2021-12-22. |
| [3] | OMATETE O O, JANNEY M A, STREHLOW R A. Gelcasting-a new ceramic forming process. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull., 1991, 70: 1641-1649. |
| [4] |
YANG J L, YU J L, HUANG Y. Recent development in gelcasting of ceramics. J. Euro. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 31(4): 2569-2591.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
TALLON C, FRANK G V. Recent trends in shape forming from colloidal processing: a review. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 2011, 119(1387): 147-160.
DOI URL |
| [6] | GRAULE T J, BAADER F H, GAUCKLER L J. Casting uniform ceramics with direct coagulation. Chemtech, 1995, 25(6): 31-31. |
| [7] | 杨燕, 岛井骏藏, 周国红, 等. 一种制备陶瓷坯体的方法. CN103130509B. |
| [8] |
MORISSETTE S L, LEWIS J A. Chemorheoloy of aqueous-based alumina-poly(vinyl alcohol) gelcasting suspensions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1999, 82(3): 521-528.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CHABERT F, DUNSTAN D E, FRANKS G V. Cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol as a binder for gelcasting and green machining. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 91(10): 3138-3146.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HANSEN E W, HOLM K H, JAHR D M, et al. Reaction of poly(vinyl alcohol) and dialdehydes during gel formation probed by 1H N.M.R.-a kinetic study. Polymer, 1997, 38(19): 4863-4871.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JOHNSON S B, DUNSTAN D E, FRANKS G V. A novel thermally activated crosslinking agent for chitosan in aqueous solution: a rheological investigation. Colloid Poly. Sci., 2004, 282: 602-612.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MAO X J, SHIMAI S, DONG M J, et al. Gelcasting of alumina using epoxy resin as gelling agent. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90(3): 986-988.
DOI URL |
| [13] | TALLON C, JACH D, MORENO, et al. Gelcasting of alumina suspensions containing nanoparticles with glycerol monoacrylate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 29: 875-880. |
| [14] |
WIECINSKA P, SZAFRAN M, SAKKA Y, et al. Gelcasting of alumina with a new monomer synthesized from glucose. J. Euro. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 30(8): 1795-1801.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
FANELLI A J, SILVERS R D, FREI W S, et al. New aqueous injection molding process for ceramic powder. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1989, 72(10): 1833-1836.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JIA Y, KANNO Y, XIE Z P. Fabrication of alumina green body through gelcasting process using alginate. Mater. Lett., 2003, 57(16): 2530-2534.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LYCKFELDT O, BRANDT J, LESCA S. Protein forming-a novel shaping technique for ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2000, 20(14/15): 2551-2559.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ADOLFSSON E. Gelcasting of zirconia using agarose. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89(6): 1897-1902.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
CHEN Y L, XIE Z P, HUANG Y. Alumina casting based on gelation of gelatin. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 1999, 19(2): 271-275.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 杨金龙, 许杰, 干科. 陶瓷浓悬浮体新型固化技术及其原理. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2020. |
| [21] | 卜景龙, 刘开琪, 王志发, 等. 凝胶注模成型制备高温结构陶瓷. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| [22] | 杨金龙, 黄勇. 陶瓷新型胶态成型工艺, 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2010. |
| [23] | 陈大明. 先进陶瓷材料的注凝技术与应用. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011. |
| [24] | 王小锋, 王日初. 氧化铍陶瓷的凝胶注模成型. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2012. |
| [25] |
MAO X J, SHIMAI S, DONG M J, et al. Gelcasting of alumina using epoxy resin as a gelling agent. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90(3): 986-988.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MAO X J, SHIMAI S, DONG M J, et al. Gelcasting and pressureless sintering of translucent alumina ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 91(5): 1700-1702.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
MAO X J, SHIMAI S, WANG S W. Gelcasting of alumina foams consolidated by epoxy resin. J. Europ. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 28(1): 217-222.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
JIN L L, MAO X J, WANG S W, et al. Optimization of the rheological properties of yttria suspensions. Ceram. Int., 2009, 35(2): 925-927.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
XUE J F, DONG M J, LI J, et al. Gelcasting of aluminum nitride ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 93(4): 928-930.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
DONG M J, MAO X J, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Gelcasting of SiC using epoxy resin as gel former. Ceram. Int., 2009, 35(4): 1363-1366.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YANG Y, SHIMAI S, WANG S W. Room-temperature gelcasting of alumina with a water-soluable copolymer. J. Mater. Res., 2013, 28(11): 1512-1516.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
SHIMAI S Z, YANG Y, WANG S W, et al. Spontaneous gelcasting of translucent alumina ceramics. Optical Materials Express, 2013, 3: 1000-1006.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
QIN X, ZHOU G H, YANG Y, et al. Gelcasting of transparent YAG ceramics by a new gelling system. Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(8): 12745-12750.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHANG P, LIU P, SUN Y, et al. Aqueous gelcasting of the transparent MgAl2O4 spinel ceramics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 646: 833-836.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
SUN Y, SHIMAI S, PENG X, et al. Fabrication of transparent Y2O3ceramics via aqueous gelcasting. Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(6): 8841-8845.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG J, ZHANG F, CHEN F, et al. Fabrication of aluminum oxynitride (γ-AlON) transparent ceramics with modified gelcasting. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2014, 97(5): 1353-1355.
DOI URL |
| [37] | SHU X, LI J, ZHANG H L, et al. Gelcasting of aluminum nitride using a water-soluble copolymer. J. Inorg. Mater., 2014, 29: 327-330. |
| [38] | MAO X J, CHEN H, ZHAO J, et al. Research progress in spontaneous solidification molding. Modern Technical Ceramics, 2019, 40(6): 398-416. |
| [39] | 美国陆军实验室. http://www.arl.army.mil/arlreports/2016/ARL-TR-7620.pdf. [2021-12-22]. |
| [40] |
YANG Y, WU Y. Tape-casted transparent alumina ceramic wafers. Journal of Materials Research, 2014, 29(19): 2312-2317.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LU Y J, GAN K, HUO W L, et al. Dispersion and gelation behavior of alumina suspensions with Isobam. Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(10): 11357-11363.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
MARSICO C A, ORLICKI J A, BLAIR V L. Investigation of room- temperature super-stabilized suspension casting system mechanism. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 103(3): 1514-1519.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 孙怡. 多官能团一元凝胶体系的改性及应用研究. 北京: 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2016. |
| [44] |
CHEN H, SHIMAI S, ZHAO J, et al. Hydrophobic coagulation of alumina slurries. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 104(1): 284-293.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
PRABHAKARAN K, RAGHUNATH S, MELKERI A, et al. Novel coagulation method for direct coagulation casting of aqueous alumina slurries prepared using a poly(Acrylate) dispersant. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 91(2): 615-619.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
GONZENBACH U T, STUDART A R, TERVOORT E, et al. Macroporous ceramics from particle-stabilized wet foams. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90(1): 16-22.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 陈晗. 类单晶结构氧化铝透明陶瓷的形成机制及制备. 北京: 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2021. |
| [48] | ZHAO J, MAO X J, WANG S W. Alumina ceramic foams with controllable cell structure prepared by direct foaming. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2019, 47(9): 1222-1234. |
| [49] |
GONZENBACH U T, STUDART A R, TERVOORT E, et al. Macroporous ceramics from particle-stabilized wet foams. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90(1): 16-22.
DOI URL |
| [50] | YANG J L, LIN H, XI X Q, et al. Preparation of particle-stabilized foam slurry and porous alumina ceramics. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 36(2): 220-223. |
| [51] |
YU J L, YANG J L, LI S, et al. Preparation of Si3N4 foam ceramics with nest-like cell structure by particle-stabilized foams. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 95(4): 1229-1233.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
CHUANUWATANAKUL C, TALLON C, DUNSTAN D E, et al. Producing large complex-shaped ceramic particle stabilized foams. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2013, 96(5): 1407-1413.
DOI URL |
| [53] | 彭翔. 大尺寸氧化铝陶瓷的注凝成型研究. 北京: 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2016. |
| [54] |
PENG X, SHIMAI S, SUN Y, et al. Wet green-state joining of alumina ceramics without paste. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 98(9): 2728-2731.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
DI Z, SHIMAI S, ZHAO J, et al. Dewatering of spontaneous- coagulation-cast alumina ceramic gel by filtrating with low pressure. Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(10): 12789-12794.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
DI Z, SHIMAI S, ZHAO J, et al. Density difference in pressure- filtrated wet cakes produced from spontaneous gelling slurries. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 103(2): 1396-1403.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
CHEN H, SHIMAI S, ZHAO J, et al. Pressure filtration assisted gel casting in translucent alumina ceramics fabrication. Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(14): 16572-16576.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
KRELL A, BLANK P, MA H W, et al. Processing of high-density submicrometer Al2O3 for new applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2003, 86(4): 546-553.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
MAO X J, WANG S W, SHIMAI S, et al. Transparent polycrystalline alumina ceramics with orientated optical axes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 91(10): 3431-3433.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
YI H L, MAO X J, ZHOU G H, et al. Crystal plane evolution of grain oriented alumina ceramics with high transparency. Ceram. Int., 2012, 38(7): 5557-5561.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
CHEN H, SHIMAI S, ZHAO J, et al. Highly oriented α-Al2O3 transparent ceramics shaped by shear force. J. Europ. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 41(6): 3838-3843.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
CHEN H, ZHAO J, SHIMAI S, et al. High transmittance and grain- orientated alumina ceramics fabricated by adding fine template particles. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(4): 582-588.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
YANG Y, SHIMAI S, SUN Y, et al. Fabrication of porous Al2O3 ceramics by rapid gelation and mechanical foaming. Journal of Materials Research, 2013, 28(15): 2012-2016.
DOI URL |
| [64] | 赵瑾. 表面活性剂疏水修饰陶瓷颗粒制备泡沫陶瓷. 北京: 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2018. |
| [65] |
ZHAO J, YANG C, SHIMAI S, et al. The effect of wet foam stability on the microstructure and strength of porous ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2018, 44: 269-274.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
ZHAO J, SHIMAI S, ZHOU G H, et al. Ceramic foams shaped by oppositely charged dispersant and surfactant. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 537: 210-216.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
WANG L Y, SHIMAI S, WANG S W, et al. High-strength porous alumina ceramics prepared from stable wet foams. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(4): 852-859.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 刘文龙, 赵瑾, 刘娟, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 微波干燥自发凝固成型氧化铝湿坯[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 461-468. |
| [10] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [11] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [12] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [13] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [14] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [15] | 刘岩, 张珂颖, 李天宇, 周菠, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 陶瓷材料电场辅助连接技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
