无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 29-37.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210547
所属专题: 【能源环境】CO2绿色转换; 2022年度中国知网高下载论文
• 专栏: CO 2 绿色转化(特邀编辑: 欧阳述昕, 王文中) • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2021-09-04
修回日期:2021-10-22
出版日期:2022-01-20
网络出版日期:2021-11-01
通讯作者:
原 弘, 教授. E-mail: yuanhong@mail.ccnu.edu.cn
作者简介:郭李娜(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: gln@mails.ccnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
GUO Lina( ), HE Xuebing, LYU Lin, WU Dan, YUAN Hong(
), HE Xuebing, LYU Lin, WU Dan, YUAN Hong( )
)
Received:2021-09-04
Revised:2021-10-22
Published:2022-01-20
Online:2021-11-01
Contact:
YUAN Hong, professor. E-mail: yuanhong@mail.ccnu.edu.cn
About author:GUO Lina (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: gln@mails.ccnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
电催化二氧化碳还原反应可将温室气体二氧化碳转化为化工原料或者有机燃料, 为克服全球变暖和电能向化学能转化提供了一条可行途径。该技术的主要挑战是产物分布广, 导致单一产物选择性低, 而调控催化剂的表面性质是解决这一难题的可行策略。本研究通过对氧化亚铜、硫化亚铜进行氧化制备表面性质不同的氧化铜, 其中, 氧化硫化亚铜制得的CuO-FS催化剂提高了电还原二氧化碳的活性和还原产物甲酸的选择性。该催化剂表现出较高的总电流密度, 而且在一个较大的测试电压范围(-0.8 ~ -1.1 V)内, 甲酸的法拉第效率可以保持在70%以上, 在-0.9 V时达到最大值78.4%。反应机理探究表明, CuO-FS优异的电还原二氧化碳性能归因于其较大的电化学活性表面积提供了大量表面活性位点, 产生较高的总电流密度; 而且电催化过程中催化剂表面产生较少的零价Cu, 减少了乙烯的生成, 使产物更集中于甲酸。
中图分类号:
郭李娜, 何雪冰, 吕琳, 吴丹, 原弘. 调控CuO表面性质选择性电催化还原CO2制HCOOH[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 29-37.
GUO Lina, HE Xuebing, LYU Lin, WU Dan, YUAN Hong. Modulation of CuO Surface Properties for Selective Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to HCOOH[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 29-37.
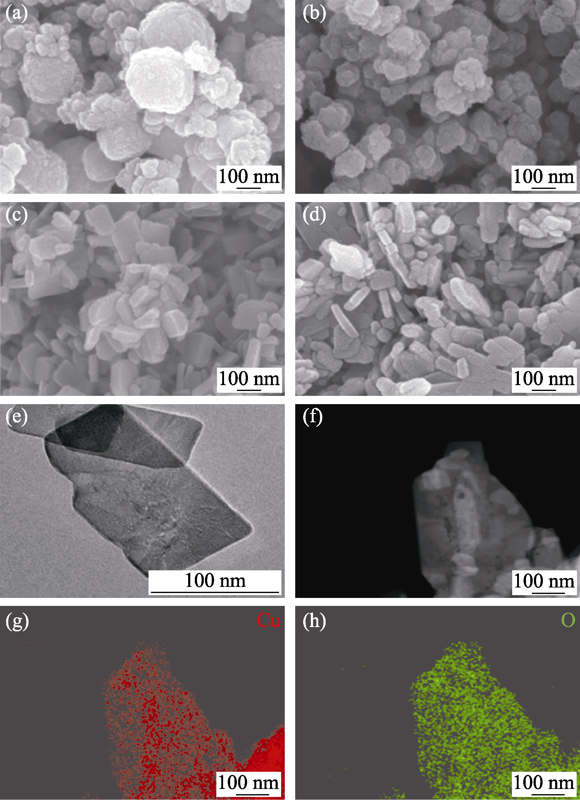
图1 样品的形貌与元素组成
Fig. 1 Morphologies and element composition of samples FESEM images of (a) Cu2O, (b) Cu2S, (c) CuO-FO and (d) CuO-FS; (e) TEM image of CuO-FS; (f) HAADF image of the CuO-FS; (g, h) Corresponding EDS elemental mapping

图3 CuO-FS和CuO-FO的XPS图谱
Fig. 3 XPS spectra of CuO-FS and CuO-FO (a, b) Survey spectrum; (c) High resolution XPS spectra of Cu2p; (d) High resolution XPS spectra of O1s
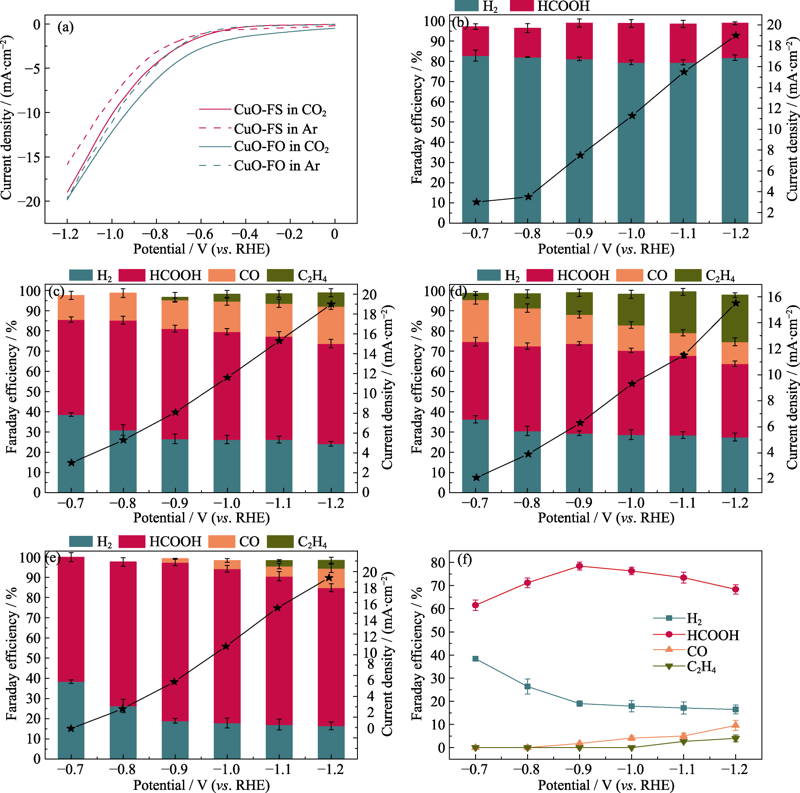
图4 (a)CuO-FO和CuO-FS在注入CO2/Ar饱和的0.1 mol/L KHCO3电解液中的阴极极化曲线; (b)Cu2S、(c)Cu2O、(d)CuO-FO和 (e)CuO-FS上所有产物的法拉第效率和电流密度; (f)CuO-FS在不同测试电压下所有产物的法拉第效率
Fig. 4 (a) Cathodic polarization curves of CuO-FO and CuO-FS in 0.1 mol/L KHCO3 electrolyte saturated with CO2/Ar, FE of all products and current density over (b) Cu2S, (c) Cu2O, (d) CuO-FO, and (e) CuO-FS, and (f) FE of all products of CuO-FS tested at different voltages Colorful figures are available on website
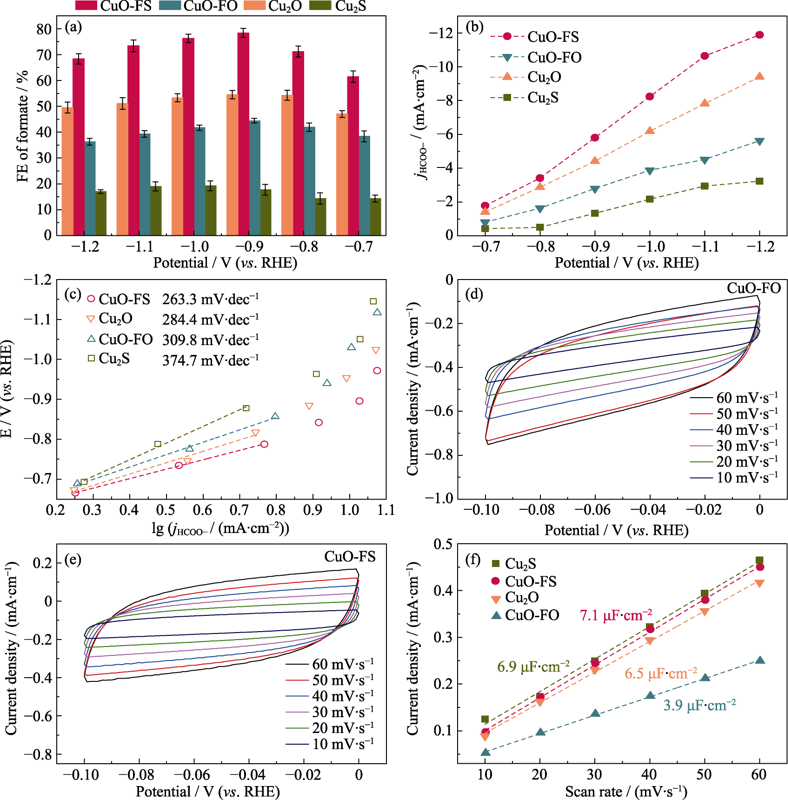
图5 Cu2S、Cu2O、CuO-FO和CuO-FS上HCOOH的 (a) 法拉第效率, (b) 部分电流密度和(c) Tafel曲线; (d) CuO-FS和(e) CuO-FO在不同测试电压扫描速率下的CV曲线; (f) 四种样品在不同测试电压扫描速率的电流密度
Fig. 5 (a) FE, (b) partial current densities, (c) Tafel plots of HCOOH over Cu2S, Cu2O, CuO-FO and CuO-FS; (d,e) CV curves of (d) CuO-FO and (e) CuO-FS at various test voltage scan rates, and (f) current density of four samples at various test voltage scan rates Colorful figures are available on website

图6 CuO-FS在-0.9 V下的长期稳定性测试以及不同产物对应的法拉第效率
Fig. 6 Long-term stability test at the voltage of -0.9 V for the CuO-FS and corresponding FE of different products
| [1] | VASILEFF A, YAO Z, SHI Z Q. Carbon solving carbon's problems: recent progress of nanostructured carbon-based catalysts for the electrochemical reduction of CO2. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(21):724-761. |
| [2] |
PETERS, GLEN, ANDERSON. et al. The trouble with negative emissions. Science, 2016, 354(6309):182-183.
DOI URL |
| [3] | ZHANG S, ZHAO S, QU D, et al. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 toward C2 valuables on Cu@Ag core-shell tandem catalyst with tunable shell thickness. Small, 2021, 2102293. |
| [4] |
XU K, NING S, CHEN H, et al. Plum pudding-like electrocatalyst of N-doped SnOx@Sn loaded on carbon matrix to construct photovoltaic CO2 reduction system with solar-to-fuel efficiency of 11.3%. Solar RRL, 2020, 4(7):2000116.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
QI Y, SONG L, OUYANG S, et al. Photoinduced defect engineering: enhanced photothermal catalytic performance of 2D black In2O(3-x) nanosheets with bifunctional oxygen vacancies. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(6):1903915.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI R, LI Y, LI Z, et al. A metal-segregation approach to generate CoMn alloy for enhanced photothermal conversion of syngas to light olefins. Solar RRL, 2020, 5(2):2000488.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG C, CAO C, ZHANG Y, et al. Unraveling the role of zinc on bimetallic Fe5C2-ZnO catalysts for highly selective carbon dioxide hydrogenation to high carbon α-olefins. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(4):2121-2133.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
PADILLA M A, LU Q, BATURINA O A. CO2 electroreduction to hydrocarbons on carbon-supported Cu nanoparticles. ACS catalysis, 2014, 4(10):3682-3695.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DUAN X, XU J, WEI Z, et al. Metal-free carbon materials for CO2 electrochemical reduction. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29:1701784.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
JIN S, HAO Z, ZHANG K, et al. Advances and challenges for electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO: from fundamental to industrialization. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60:2-24.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GU J, HSU C S, BAI L, et al. Atomically dispersed Fe3+ sites catalyze efficient CO2 electroreduction to CO. Science, 2019, 364(6445):1091-1094.
DOI URL |
| [12] | LIU G, LI Z, SHI J, et al. Black reduced porous SnO2 nanosheets for CO2 electroreduction with high formate selectivity and low overpotential. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 260:118-134. |
| [13] | LIN L, LIU T, XIAO J, et al. Enhancing CO2 electroreduction to methane with cobalt phthalocyanine and zinc-nitrogen-carbon tandem catalyst. Angewandte Chemie, 2020, 59(50):22408-22413. |
| [14] |
YANG D, ZHU Q, CHEN C, et al. Selective electroreduction of carbon dioxide to methanol on copper selenide nanocatalysts. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1):1-9.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DINH C T, BURDYNY T, KIBRIA M, et al. CO2 electroreduction to ethylene via hydroxide-mediated copper catalysis at an abrupt interface. Science, 2018, 360(6390):783-787.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZANG D, LI Q, DAI G, et al. Interface engineering of Mo8/Cu heterostructures toward highly selective electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide into acetate. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 281:119426.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LV X, SHANG L, ZHOU S, et al. Electron-deficient Cu sites on Cu3Ag1 catalyst promoting CO2 electroreduction to alcohols. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(37):2001987.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZU X, LI X, WEI L, et al. Efficient and robust carbon dioxide electroreduction enabled by atomically dispersed Snδ+ sites. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(15):1808135.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHI Y, JI Y, LONG J, et al. Unveiling hydrocerussite as an electrochemically stable active phase for efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction to formate. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1):3415.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHANG A, LIANG Y, LI H, et al. In-situ surface reconstruction of InN nanosheets for efficient CO2 electroreduction into formate. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(11):8229-8235.
DOI URL |
| [21] | SUN J, ZHENG W, LYU S, et al. Bi/Bi2O3 nanoparticles supported on N-doped reduced graphene oxide for highly efficient CO2 electroreduction to formate. Chinese Chemical Letters, 31(6):8229-8235. |
| [22] |
NITOPI S, BERTHEUSSEN E, SCOTT S B, et al. Progress and perspectives of electrochemical CO2 reduction on copper in aqueous electrolyte. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(12):7610-7672.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LV L, HE X, WANG J, et al. Charge localization to optimize reactant adsorption on KCu7S4/CuO interfacial structure toward selective CO2 electroreduction. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 298:120531.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XIE H, WANG T, LIANG J, et al. Cu-based nanocatalysts for electrochemical reduction of CO2. Nano Today, 2018, 21:41-54.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG X, WANG Z, ZHUANG T T, et al. Efficient upgrading of CO to C3 fuel using asymmetric C-C coupling active sites. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1):5186.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MA M, DJANASHVILI K, SMITH W A. Selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO on CuO-derived Cu nanowires. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(32):20861-20867.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LIU G, LI Z, SHI J, et al. Black reduced porous SnO2 nanosheets for CO2 electroreduction with high formate selectivity and low overpotential. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 260:118134.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
CHOU T C, CHANG C C, YU H L, et al. Controlling the oxidation state of Cu electrode and reaction intermediates for electrochemical CO2 reduction to ethylene. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142:2857-2867.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DAIYAN R, SAPUTERA W H, ZHANG Q, et al. 3D heterostructured copper electrode for conversion of carbon dioxide to alcohols at low overpotentials. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2019, 3(1):1800064.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王虹力, 王男, 王丽莹, 宋二红, 赵占奎. 功能化石墨烯担载型AuPd纳米催化剂增强甲酸制氢反应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 547-553. |
| [2] | 郭小炜, 李玉妍, 陈南春, 王秀丽, 解庆林. 负载二甲酸钾缓释抗菌微球的构建[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 181-187. |
| [3] | 肖剑飞, 乃学瑛, 苟生莲, 叶俊伟, 董亚萍, 李武. 邻苯二甲酸氢钾在制备碱式硫酸镁纳米线过程中的机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1181-1186. |
| [4] | 徐金芳, 邵蒙蒙, 倪哲明, 肖雪春. 反相气相色谱法探究镁铁水滑石及其改性材料的表面性质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(9): 971-976. |
| [5] | 黄晓灵, 林 舟, 练昕怡, 张晓凤, 林 深. Pd/PMo12-GN复合膜的制备及其对甲酸氧化的电催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(7): 722-728. |
| [6] | 江红,冯兰英,朱红,郭志军,张新卫. 掺杂Fe元素对Pd/C催化剂性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 847-850. |
| [7] | 张耀君,张 莉. 复合材料CdS/Al-HMS的制备及可见光催化降解污染物制氢活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 66-70. |
| [8] | 孙静,高濂,郭景坤. SiC粉体表面性质及其浆料流变性质研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000, 15(3): 426-430. |
| [9] | 王清叶,王东利,任敏,孙聚堂. 掺杂三价铽离子的邻苯二甲酸锌发光材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 1998, 13(2): 152-156. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||