无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 481-492.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210502
所属专题: 【虚拟专辑】锂金属电池,钠离子电池和水系电池(2020~2021)
王禹桐1( ), 张非凡1, 许乃才2, 王春霞1, 崔立山1, 黄国勇1(
), 张非凡1, 许乃才2, 王春霞1, 崔立山1, 黄国勇1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-13
修回日期:2021-10-22
出版日期:2022-05-20
网络出版日期:2021-11-01
通讯作者:
黄国勇, 教授. E-mail: huanggy@cup.edu.cn
作者简介:王禹桐(1992-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: 1248736790@qq.com;
基金资助:
WANG Yutong1( ), ZHANG Feifan1, XU Naicai2, WANG Chunxia1, CUI Lishan1, HUANG Guoyong1(
), ZHANG Feifan1, XU Naicai2, WANG Chunxia1, CUI Lishan1, HUANG Guoyong1( )
)
Received:2021-08-13
Revised:2021-10-22
Published:2022-05-20
Online:2021-11-01
Contact:
HUANG Guoyong, professor. E-mail:huanggy@cup.edu.cn
About author:WANG Yutong (1992-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: 1248736790@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
锂离子电池作为一种绿色可充电电池, 具有较高的能量密度及功率密度, 但市售锂离子电池主要以有机物为电解液, 当电池过充或短路时存在一定的燃烧及爆炸风险。为应对此问题, 水系锂离子电池逐渐走进人们的视野, 它具有清洁环保、安全性能高等优点, 其工作电压为1.5~2.0 V, 主要应用于储能领域。考虑到水系电池的析氢析氧反应, 常规负极材料无法应用于水系锂离子电池, 因此水系锂离子电池的研发关键在于负极材料的选取。LiTi2(PO4)3具有开放的三维通道以及合适的嵌锂电位, 可以作为水系锂离子电池的负极材料。LiTi2(PO4)3的合成方法主要有高温固相法、溶胶-凝胶法和水热法等。为进一步提高LiTi2(PO4)3的电化学性能, 可以采用颗粒纳米化、形貌控制、元素掺杂及碳包覆等方式进行改性。本文从合成方法及改性手段的角度, 对近年来国内外水系锂离子电池负极材料LiTi2(PO4)3的研究进行综述, 并对LiTi2(PO4)3负极材料的发展前景做出展望。
中图分类号:
王禹桐, 张非凡, 许乃才, 王春霞, 崔立山, 黄国勇. 水系锂离子电池负极材料LiTi2(PO4)3的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 481-492.
WANG Yutong, ZHANG Feifan, XU Naicai, WANG Chunxia, CUI Lishan, HUANG Guoyong. Research Progress of LiTi2(PO4)3 Anode for Aqueous Lithium-ion Batteries[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 481-492.
| Type | Operating voltage/V | Safety | Electrolyte | Solvent | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Li-ion battery | 3.6-4.2 | Low | LiPF6, LiAsF6, etc | EC, DMC, DEC, etc | High |
| Aqeuous Li-ion battery | 1.5-2.0 | High | Li2SO4, LiNO3, etc | H2O | Moderate |
表1 水系锂离子电池和有机系锂离子电池的特征比较[8]
Table 1 Comparison of the characteristics of aqeuous and organic lithium-ion batteries[8]
| Type | Operating voltage/V | Safety | Electrolyte | Solvent | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Li-ion battery | 3.6-4.2 | Low | LiPF6, LiAsF6, etc | EC, DMC, DEC, etc | High |
| Aqeuous Li-ion battery | 1.5-2.0 | High | Li2SO4, LiNO3, etc | H2O | Moderate |
| Anode material | Specific capacity/ (mAh·g-1) | Potential/ V(vs. Li+/Li) | Potential/ V(vs. NHE) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiTi2(PO4)3 | 138 | 2.5 | -0.5 | Moderate specific capacity, stable framework |
| TiP2O7 | 121 | 2.6 | -0.4 | Low specific capacity, high Li-intercalation potential |
| VO2 | 250 | 2.6 | -0.4 | High specific capacity, poor cycling performance |
| LiV3O8 | 250 | 2.6 | -0.4 | Fragile during cycling |
表2 部分水系锂离子电池的负极材料的参数[14]
Table 2 Parameters of some anode materials for aqeuous lithium-ion battery[14]
| Anode material | Specific capacity/ (mAh·g-1) | Potential/ V(vs. Li+/Li) | Potential/ V(vs. NHE) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiTi2(PO4)3 | 138 | 2.5 | -0.5 | Moderate specific capacity, stable framework |
| TiP2O7 | 121 | 2.6 | -0.4 | Low specific capacity, high Li-intercalation potential |
| VO2 | 250 | 2.6 | -0.4 | High specific capacity, poor cycling performance |
| LiV3O8 | 250 | 2.6 | -0.4 | Fragile during cycling |
| Method | Starting materials | Product characteristic | Features | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li source | Ti source | P source | Morphology | |||
| Solid state | LiH2PO4 | TiO2 | NH4H2PO4 | Irregular particles | Long calcination time, high temperature | [ |
| Sol-Gel | CH3COOLi | Ti(C4H9O)4 | H3PO4 | Particles | Short calcination time, low temperature | [ |
| Hydrothermal synthesis | CH3COOLi | Ti(C4H9O)4 | NH4H2PO4 | Regular particles | Regular particle morphology, great crystallinity | [ |
| Co-precipitation method | LiOH | Ti(C4H9O)4 | H3PO4 | Particles | Requiring precise control | [ |
| Electrospinning | CH3COOLi | Ti(C4H9O)4 | NH4H2PO4 | Fiber | Ideal electrochemical performance, difficult industrialization | [ |
表3 常见LiTi2(PO4)3合成方法比较
Table 3 Comparison of common synthetic methods of LiTi2(PO4)3
| Method | Starting materials | Product characteristic | Features | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li source | Ti source | P source | Morphology | |||
| Solid state | LiH2PO4 | TiO2 | NH4H2PO4 | Irregular particles | Long calcination time, high temperature | [ |
| Sol-Gel | CH3COOLi | Ti(C4H9O)4 | H3PO4 | Particles | Short calcination time, low temperature | [ |
| Hydrothermal synthesis | CH3COOLi | Ti(C4H9O)4 | NH4H2PO4 | Regular particles | Regular particle morphology, great crystallinity | [ |
| Co-precipitation method | LiOH | Ti(C4H9O)4 | H3PO4 | Particles | Requiring precise control | [ |
| Electrospinning | CH3COOLi | Ti(C4H9O)4 | NH4H2PO4 | Fiber | Ideal electrochemical performance, difficult industrialization | [ |
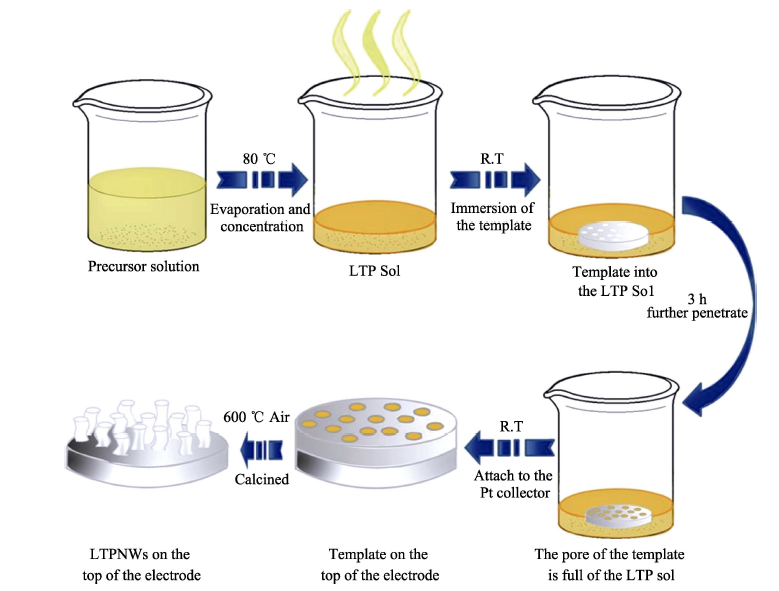
图3 LiTi2(PO4)3 纳米线(LTPNMs)的制备过程示意图[38]
Fig. 3 Schematical illustration of the fabrication process of lithium titranium phosphate nanowires (LTPNMs)[38]
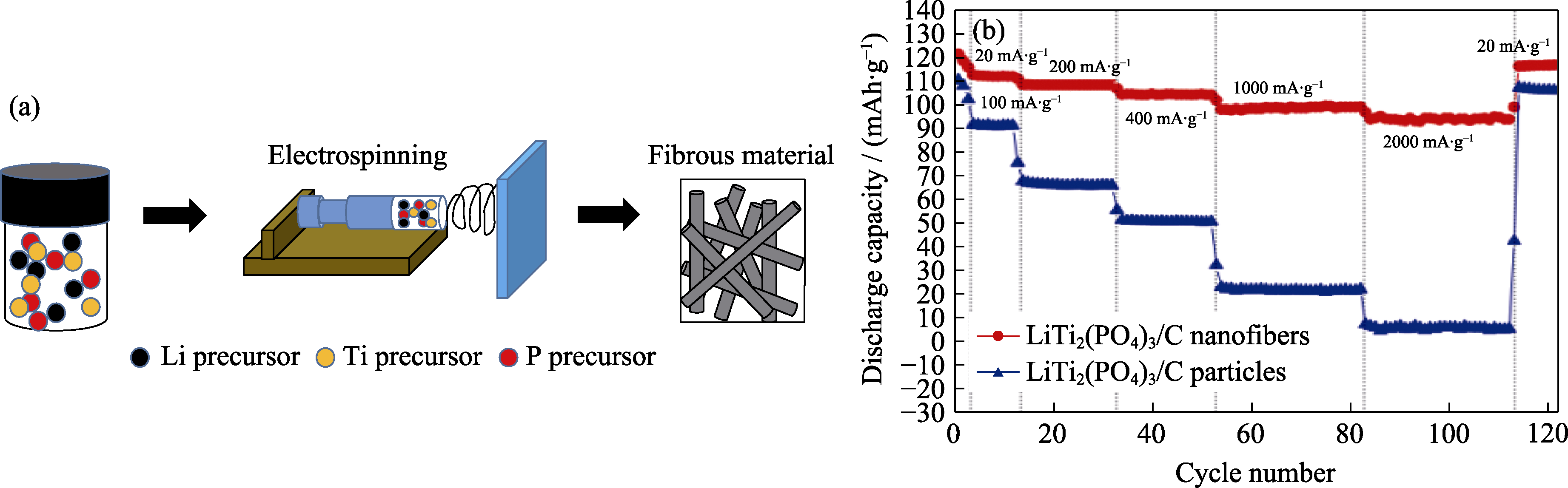
图4 静电纺丝法示意图(a), LiTi2(PO4)3纤维与颗粒的倍率性能曲线(b)[24]
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of electrospinning (a), comparison of rate performance between LiTi2(PO4)3 fibers and particles (b)[24]
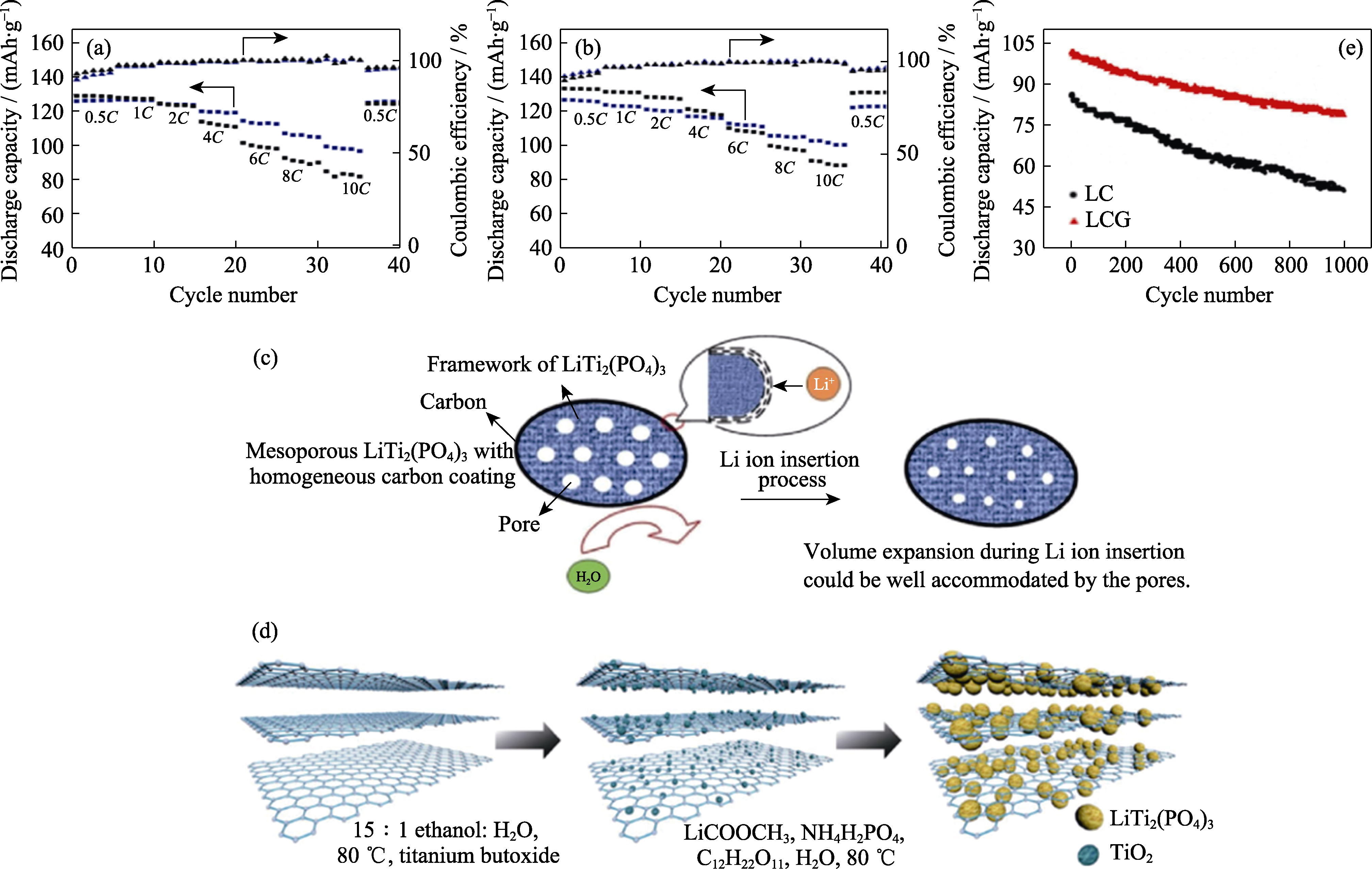
图5 四种包覆碳源的倍率性能图 (a, b)[72]((a)蓝、黑分别为聚多巴胺和酚醛树脂; (b)蓝、黑分别为聚丙烯腈和葡萄糖), 具有均质碳层的介孔LiTi2(PO4)3中Li+插入的机制示意图(c)[75], rGO-LTP的合成步骤示意图(d)[78], LC和LCG在5C下循环1000次的循环性能曲线(e)[80]
Fig. 5 Comparison chart of rate performance of four coated carbon sources (a, b)[72](Blue and black in (a) indicating polydopamine and phenolic resin; blue and black in (b) indicating polyacrylonitrile and glucose), schematic illustration of the tentative Li+ insertion mechanism in mesoporous LiTi2(PO4)3 with carbon coating layer (c)[75], schematic diagram of the synthesis steps of rGO-LTP (d)[78], and cyclic performance of LC and LCG anodes at 5C for 1000 cycles (e)[80] Colorful figures are available on website
| Calcination parameter | Coating method | Carbon source | Weight percentage of carbon/% | Current density/(mA·g-1) | Specific capacity (cycles)/(mAh·g-1) | Capacity retention/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 ℃-12 h | In-situ | Citric acid | 6.2 | 138 | 106.1(1)-89(1300) | 84 | [36] |
| 900 ℃-12 h | Ex-situ | Toluene | 12 | 700 | 100(1)-83(200) | 83 | [31] |
| 800 ℃-12 h | Ex-situ | Acetylene Black | 18 | 140 | 106.3(1)-86.5(100) | 81 | [81] |
| 850 ℃-12 h | Ex-situ | Acetylene Black | - | 1400 | 91.3(1)-74.4(100) | 81 | [82] |
| 700 ℃-12 h | In-situ | Pitch | 17.5 | 1380 | 107(1)-75.5(1000) | 70 | [83] |
| 550 ℃-24 h | In-situ | Sucrose | 3.5 | 1400 | 110(1)-104(800) | 94 | [17] |
| 750 ℃-5 h | In-situ | Polyaniline | 5.9 | 276 | 115.2(1)-94.6(1000) | 82 | [84] |
| 750 ℃-5 h | In-situ | Polyacrylonitrile | 5.9 | 690 | 95(1)-82.1(1000) | 86 | [85] |
| 900 ℃-12 h | In-situ | Graphene oxide | 1.79 | ~1380 | 110(1)-100(100) | 91 | [78] |
| 800 ℃-10 h | In-situ | Graphene oxide | - | ~276 | 105(1)-97.86(100) | 93.2 | [77] |
| 700 ℃-5 h | In-situ | Graphene oxide, phenolic resin | 16.2 | ~690 | 101.1(1)-78(1000) | 77.2 | [80] |
| 800 ℃-8 h | Ex-situ | β-Cyclodextrin | 3.13 | ~690 | 120(1)-(200)111.3 | 88.7 | [86] |
表4 溶胶-凝胶法不同碳源和包覆方式的电性能比较
Table 4 Comparison of electrochemical performance of different carbon sources and coating methods by Sol-Gel
| Calcination parameter | Coating method | Carbon source | Weight percentage of carbon/% | Current density/(mA·g-1) | Specific capacity (cycles)/(mAh·g-1) | Capacity retention/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 ℃-12 h | In-situ | Citric acid | 6.2 | 138 | 106.1(1)-89(1300) | 84 | [36] |
| 900 ℃-12 h | Ex-situ | Toluene | 12 | 700 | 100(1)-83(200) | 83 | [31] |
| 800 ℃-12 h | Ex-situ | Acetylene Black | 18 | 140 | 106.3(1)-86.5(100) | 81 | [81] |
| 850 ℃-12 h | Ex-situ | Acetylene Black | - | 1400 | 91.3(1)-74.4(100) | 81 | [82] |
| 700 ℃-12 h | In-situ | Pitch | 17.5 | 1380 | 107(1)-75.5(1000) | 70 | [83] |
| 550 ℃-24 h | In-situ | Sucrose | 3.5 | 1400 | 110(1)-104(800) | 94 | [17] |
| 750 ℃-5 h | In-situ | Polyaniline | 5.9 | 276 | 115.2(1)-94.6(1000) | 82 | [84] |
| 750 ℃-5 h | In-situ | Polyacrylonitrile | 5.9 | 690 | 95(1)-82.1(1000) | 86 | [85] |
| 900 ℃-12 h | In-situ | Graphene oxide | 1.79 | ~1380 | 110(1)-100(100) | 91 | [78] |
| 800 ℃-10 h | In-situ | Graphene oxide | - | ~276 | 105(1)-97.86(100) | 93.2 | [77] |
| 700 ℃-5 h | In-situ | Graphene oxide, phenolic resin | 16.2 | ~690 | 101.1(1)-78(1000) | 77.2 | [80] |
| 800 ℃-8 h | Ex-situ | β-Cyclodextrin | 3.13 | ~690 | 120(1)-(200)111.3 | 88.7 | [86] |
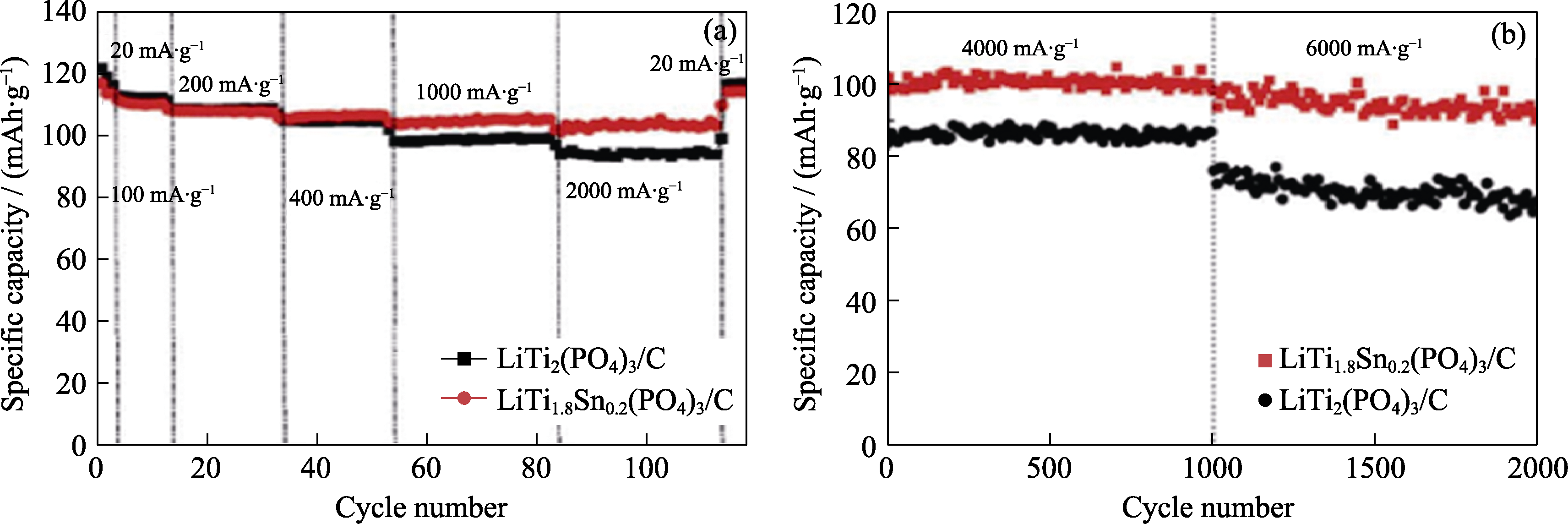
图6 LiTi2(PO4)3/C和LiTi1.8Sn0.2(PO4)3/C在不同电流密度下连续循环的放电容量(a), 电流密度为4和6 A·g-1时的长期循环性能(b)[24]
Fig. 6 Discharge capacity for successive cycling at different current densities (a), long-term cycling behavior at current densities of 4 and 6 A·g-1 (b) of LiTi2(PO4)3/C and LiTi1.8Sn0.2(PO4)3/C[24]
| [1] | WENG Y, XU S, HUANG G, et al. Synthesis. Synthesis and performance of Li[(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)(1-x)Mgx]O2 prepared from spent lithium ion batteries. Jounral of Hazard Materials, 2013, 246- 247:163-172. |
| [2] | KIM T, SONG W, SON D Y,et al. Lithium-ion batteries: outlook on present, future, and hybridized technologies. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7(7):2942-2964. |
| [3] | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries. Nature, 2008,451:652-657. |
| [4] | ZHANG H, ZHAO H, KHAN M A,et al. Recent progress in advanced electrode materials, separators and electrolytes for lithium batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(42):20564-20620. |
| [5] | GOODENOUGH J B, PARK K S. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: a perspective. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013,135(4):1167-1176. |
| [6] | SUO L, L H. The past, present and future of lithium ion batteries. Physics, 2020,49(1):17-23. |
| [7] | LI W, DAHN J R, WAINWRIGHT D S. Rechargeable lithium batteries with aqueous electrolytes. Science, 1994,264(5162):1115-1118. |
| [8] | ZHOU D. A New Anode Material of Na2V6O16 Nanowires for Aqueous Rechargeable Lithium Battery. Changsha: Central South University, Master Dissertation, 2013. |
| [9] | LI W, MCKINNON W R, R D J. Lithium intercalation from aqueous solutions. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 1994,141:2310-2316. |
| [10] | TANG W, ZHU Y, HOU Y,et al. Aqueous rechargeable lithium batteries as an energy storage system of superfast charging. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013,6(7):2093-2104. |
| [11] | DEMIR-CAKAN R, PALACIN M R, CROGUENNEC L. Rechargeable aqueous electrolyte batteries: from univalent to multivalent cation chemistry. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7(36):20519-20539. |
| [12] | LUO J Y, CUI W J, HE P,et al. Raising the cycling stability of aqueous lithium-ion batteries by eliminating oxygen in the electrolyte. Nature Chemistry, 2010,2(9):760-765. |
| [13] | LIU Z, HUANG Y, HUANG Y,et al. Voltage issue of aqueous rechargeable metal-ion batteries. Chemical Society Review, 2020,49(1):180-232. |
| [14] | LIU W, WANG B, LI L. Recent progress in electrode materials for aqueous lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2014,3(1):9-20. |
| [15] | AATIQ A, MENETRIER M, CROGUENNEC L,et al. On the structure of Li3Ti2(PO4)3. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2002,12(10):2971-2978. |
| [16] | GIAROLA M, SANSON A, TIETZ F,et al. Structure and vibrational dynamics of nasicon-type LiTi2(PO4)3. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017,121(7):3697-3706. |
| [17] | EL-SHINAWI H, JANEK J. Low-temperature synthesis of macroporous LiTi2(PO4)3/C with superior lithium storage properties. RSC Advances, 2015,5(19):14887-14891. |
| [18] | GUTIERREZ A, BENEDEK N A, MANTHIRAM A. Crystal- chemical guide for understanding redox energy variations of M 2+/ 3+ couples in polyanion cathodes for lithium-ion batteries . Chemistry of Materials, 2013,25(20):4010-4016. |
| [19] | DELMAS C, NADIRI A, SOUBEYROUX L J. The nasicon-type titatium phosphates ATi2(PO4)3(A=Li, Na) as electrode materials. Solid State Ionics, 1988, 28-30:419-423. |
| [20] | WANG H, HUANG K, ZENG Y,et al. Electrochemical properties of TiP2O7 and LiTi2(PO4)3 as anode material for lithium ion battery with aqueous solution electrolyte. Electrochimica Acta, 2007,52(9):3280-3285. |
| [21] | JIANG Z, LI Y, HAN C,et al. K doping on Li site enables LiTi2(PO4)3/C excellent lithium storage performance. Solid State Ionics, 2019,341:115036. |
| [22] | YU S, TEMPEL H, SCHIERHOLZ R,et al. LiTi2(PO4)3/C anode material with a spindle-like morphology for batteries with high rate capability and improved cycle life. ChemElectroChem, 2016,3(7):1157-1169. |
| [23] | SUN J, SUN Y, GAI L,et al. Carbon-coated mesoporous LiTi2(PO4)3 nanocrystals with superior performance for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,200:66-74. |
| [24] | LIU L, SONG T, HAN H,et al. Electrospun Sn-doped LiTi2(PO4)3/C nanofibers for ultra-fast charging and discharging. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015,3(19):10395-10402. |
| [25] | WANG G X, BRADHURST D H, DOU S X,et al. LiTi2(PO4)3 with NASICON-type structure as lithium-storage materials. Journal of Power Sources, 2003,124(1):231-236. |
| [26] | LI W,R. D J. Lithium-ion cells with aqueous electrolytes. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 1995,142:1742-1746. |
| [27] | KOHLER J, MAKIHARA H, UEGAITO H,et al. LiV3O8: characterization as anode material for an aqueous rechargeable Li-ion battery system. Electrochim. Acta, 2000,46:59-65. |
| [28] | ZHENG W. Solid-state Synthesis and Surface Modification of LiFePO4 and LiTi2(PO4)3 for Lithium Ion Electrode Materials. Zhengjiang: Zhengjiang University,Doctoral Dissertation, 2010. |
| [29] | FENG C, LI L, TANG J,et al. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of a new type of anode material LiTi2(PO4)3. Power Technology, 2015,39(2):242-244. |
| [30] | LI W, LI Y, CAO M,et al. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of alginic acid-based carbon-coated Li3V2(PO4)3 composite by rheological phase method. Acta Phys-ChimSin, 2017,33(11):2261-2267. |
| [31] | LUO J Y, XIA Y Y. Aqueous lithium-ion battery LiTi2(PO4)3/LiMn2O4 with high power and energy densities as well as superior cycling stability. Advanced Functional Materials, 2007,17(18):3877-3884. |
| [32] | TANG Z K, XUE Y F, TEOBALDI G,et al. The oxygen vacancy in Li-ion battery cathode materials. Nanoscale Horizons, 2020,5(11):1453-1466. |
| [33] | LUO J Y, CHEN L J, ZHAO Y J,et al. The effect of oxygen vacancies on the structure and electrochemistry of LiTi2(PO4)3 for lithium-ion batteries: a combined experimental and theoretical study. Journal of Power Sources, 2009,194(2):1075-1080. |
| [34] | CHENG C. Study of Anode Materials for Aqueous Rechargeable Lithium-ion Batteries. Changsha: Xiangtan University, Master Dissertation, 2010. |
| [35] | MARIAPPAN C R, GALVEN C, CROSNIER-LOPEZ M P,et al. Synthesis of nanostructured LiTi2(PO4)3 powder by a Pechini-type polymerizable complex method. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2006,179(2):450-456. |
| [36] | WESSELLS C, HUGGINS R A, CUI Y. Recent results on aqueous electrolyte cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2011,196(5):2884-2888. |
| [37] | ZHOU X L, YAN Z G, LI S Y,et al. Single crystalline LiTi2(PO4)3 nanowires by porous template with improved electrochemical performance. Materials Today Energy, 2018,7:113-121. |
| [38] | ZHOU X. Lithium Titanium Phosphate and Carbon/copper Composite Electrode Materials: Controlled Preparation, Structural Study and Electrochemical Performance. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, Doctoral Dissertation, 2014. |
| [39] | ZHOU D, LI J, CHEN C,et al. A hydrothermal synthesis of Ru-doped LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 cathode materials for enhanced electrochemical performance. RSC Advances, 2021,11(21):12549-12558. |
| [40] | SONG Y, XIE B, SONG S,et al. Regeneration of LiFePO4 from spent lithium-ion batteries via a facile process featuring acid leaching and hydrothermal synthesis. Green Chemistry, 2021,23(11):3963-3971. |
| [41] | WANG J, QIN X, GUO J,et al. A porous hierarchical micro/nano LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for Li-ion batteries synthesized by a urea-assisted hydrothermal method. Dalton Transactions, 2018,47(21):7333-7343. |
| [42] | QIN X, ZHOU M, ZONG B,et al. Urea-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of a hollow hierarchical LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material with tunable morphology characteristics. RSC Advances, 2018,8(53):30087-30097. |
| [43] | YUE Y, PANG W. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of LiTi2(PO4)3. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1990,9:1392. |
| [44] | LIANG Y, HISAMO T, SUMI S,et al. Direct fabrication of thin-film LiTi2(PO4)3 electrodes using the hydrothermal method. Solid State Ionics, 2016,296:7-12. |
| [45] | LI M, LIU L, ZHANG N,et al. Mesoporous LiTi2(PO4)3/C composite with trace amount of carbon as high-performance electrode materials for lithium ion batteries. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,749:1019-1027. |
| [46] | HOU P, ZHANG H, ZI Z,et al. Core-shell and concentration- gradient cathodes prepared via co-precipitation reaction for advanced lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(9):4254-4279. |
| [47] | LI H, LI Z, CUI Y,et al. Long-cycled Li2ZnTi3O8/TiO2 composite anode material synthesized via a one-pot co-precipitation method for lithium ion batteries. New Journal of Chemistry, 2017,41(3):975-981. |
| [48] | 杨勇. 固态电化学. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2017. |
| [49] | 盖利刚, 孙家香, 姜海辉. 一种碳包覆介孔磷酸钛锂的制备方法: 中国. ZL201510957301.8. 2015. 12. 18. |
| [50] | OGHBAEI M, MIRZAEE O. Microwave versus conventional sintering: a review of fundamentals, advantages and applications. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010,494(1/2):175-189. |
| [51] | RIQUET G, MARINEL S, BREARD Y,et al. Direct and hybrid microwave solid state synthesis of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramic: microstructures and dielectric properties. Ceramics International, 2018,44(13):15228-15235. |
| [52] | ZHANG M, GARCIA-ARAEZ N, HECTOR A L. Understanding and development of olivine LiCoPO4 cathode materials for lithium- ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(30):14483-14517. |
| [53] | LUDWIG J, NORDLUND D, DOEFF M M,et al. Synthesis and characterization of metastable, 20 nm-sized Pna21-LiCoPO4 nanospheres. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2017,248:9-17. |
| [54] | GUO X, JIA X, HU H,et al. Synthesis of LiTi2(PO4)3 ultrafine powder by Sol-Gel and microwave heating method. Materials Reports, 2007,21(11A):68-71. |
| [55] | HU J, HUANG W, YANG L,et al. Structure and performance of the LiFePO4 cathode material: from the bulk to the surface. Nanoscale, 2020,12(28):15036-15044. |
| [56] | YANG C, LEE D J, KIM H,et al. Synthesis of nano-sized urchin-shaped LiFePO4 for lithium ion batteries. RSC Advances, 2019,9(24):13714-13721. |
| [57] | XIANG J, ZHANG P, LV S,et al. Spinel LiMn2O4 nanoparticles fabricated by the flexible soft template/Pichini method as cathode materials for aqueous lithium-ion capacitors with high energy and power density. RSC Advances, 2021,11(25):14891-14898. |
| [58] | JO J, NAM S, HAN S,et al. One-pot pyro synthesis of a nanosized-LiMn2O4/C cathode with enhanced lithium storage properties. RSC Advances, 2019,9(42):24030-24038. |
| [59] | QI W, SHAPTER J G, WU Q,et al. Nanostructured anode materials for lithium-ion batteries: principle, recent progress and future perspectives. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(37):19521-19540. |
| [60] | TIAN L, YU H, ZHANG W,et al. The star material of lithium ion batteries, LiFePO4: basic properties, optimize moderation and future prospects. Materials Reports, 2019,33(11):3561-3579. |
| [61] | DENG W, WANG X, LIU C,et al. Touching the theoretical capacity: synthesizing cubic LiTi2(PO4)3/C nanocomposites for high-performance lithium-ion battery. Nanoscale, 2018,10(14):6282-6287. |
| [62] | WU Y, CHONG S, LIU Y,et al. High electrochemical performance of nanocrystallized carbon-coated LiFePO4 modified by tris (pentafluorophenyl) borane as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Advances, 2018,8(51):28978-28986. |
| [63] | WANG Y, WANG X, JIANG A,et al. A versatile nitrogen-doped carbon coating strategy to improve the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,810:151889. |
| [64] | PARK G D, HONG J H, JUNG D S,et al. Unique structured microspheres with multishells comprising graphitic carbon-coated Fe3O4 hollow nanopowders as anode materials for high-performance Li-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7(26):15766-15773. |
| [65] | KU D J, LEE J H, LEE S J,et al. Effects of carbon coating on LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries using an atmospheric microwave plasma torch. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019,376:25-30. |
| [66] | SUN W, LIU J, LIU X,et al. Bimolecular-induced hierarchical nanoporous LiTi2(PO4)3/C with superior high-rate and cycling performance. Chemical Communications, 2017,53(62):8703-8706. |
| [67] | TAN Y, XUE B. Research progress on lithium titanate as anode material in lithium-ion battery. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018,33(5):475-482. |
| [68] | LI H, ZHOU H. Enhancing the performances of Li-ion batteries by carbon-coating: present and future. Chemical Communications, 2012,48(9):1201-1217. |
| [69] | YE J, LI C, RAO M,et al. Effects of different carbon solutions on electrochemical performance of LiTi2(PO4)3/C composite anode material. Power Technology, 2020,44(3):322-325. |
| [70] | LUO S, TIAN Y, TANG Z,et al. Effect of the structure of pyrolytic carbon on the performance of LiFePO4/C composite cathode material. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009,38:13-15. |
| [71] | CHEN Y, HE H, LIU L,et al. Thermal decomposition of glucose and sucrose by kinetics analysis. The Chinese Joumal of Process Engineering, 2010,10(4):720-725. |
| [72] | ZHANG C, WEN Y, ZHANG P,et al. Effect of organic carbon source on performance of LiTi2(PO4)3/C composite electrodes in aqueous solutions. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2020,41(6):1352-1361. |
| [73] | LIN L, CONG Z, CAO J,et al. Multifunctional Fe3O4@Polydopamine core-shell nanocomposites for intracellular mRNA detection and imaging-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano, 2014,8(4):3876-3883. |
| [74] | HE Z, JIANG Y, MENG W,et al. Advanced LiTi2(PO4)3@N-doped carbon anode for aqueous lithium ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,222:1491-1500. |
| [75] | SUN D, TANG Y, HE K,et al. Long-lived aqueous rechargeable lithium batteries using mesoporous LiTi2( PO4)3@Canode. Scientific Reports, 2015,5:17452. |
| [76] | XU T, ZHAO M, SU Z,et al. Nanostructured LiTi2(PO4)3 anode with superior lithium and sodium storage capability aqueous electrolytes. Journal of Power Sources, 2021,481:229110. |
| [77] | ROH H K, KIM H K, ROH K C,et al. LiTi2(PO4)3/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Advances, 2014,4(60):31672-31677. |
| [78] | LIM C H, KANNAN A G, LEE H W,et al. A high power density electrode with ultralow carbon via direct growth of particles on graphene sheets. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013,1(20):6183-6190. |
| [79] | WANG H, YANG Y, LIANG Y,et al. LiMn1-xFexPO4 nanorods grown on graphene sheets for ultrahigh-rate-performance lithium ion batteries. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011,50(32):7364-7368. |
| [80] | ZHOU Z, LUO W, HUANG H,et al. LiTi2(PO4)3@carbon/ graphene hybrid as superior anode materials for aqueous lithium ion batteries. Ceramics International, 2017,43(1):99-105. |
| [81] | ZHOU M, LIU L, YI L,et al. Synthesis of LiTi2(PO4)3-acetylene black nanocomposites for lithium ion batteries by the polyvinyl alcohol assisted Sol-Gel method and ball-milling. Journal of Power Sources, 2013,234:292-301. |
| [82] | LIU L, ZHOU M, WANG G,et al. Synthesis and characterization of LiTi2(PO4)3/C nanocomposite as lithium intercalation electrode materials. Electrochimica Acta, 2012,70:136-141. |
| [83] | WENG G M, SIMON TAM L Y, LU Y C. High-performance LiTi2(PO4)3 anodes for high-areal-capacity flexible aqueous lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(23):11764-11771. |
| [84] | HE Z, JIANG Y, ZHU J,et al. N-doped carbon coated LiTi2(PO4)3 as superior anode using PANi as carbon and nitrogen bi-sources for aqueous lithium ion battery. Electrochimica Acta, 2018,279:279-288. |
| [85] | ZHOU Z, XIANG A, XIA M,et al. Advanced LiTi2(PO4)3 anode with high performance for aqueous rechargeable lithium battery. Ceramics International, 2018,44(17):21599-21606. |
| [86] | YE J M, LI C M. Synthesis of LiTi2(PO4)3@carbon anode material with superior performance using beta-cyclodextrin as carbon sources. Ionics, 2020,26(6):2845-2853. |
| [87] | BOUNAR N, BENABBAS A, ROPA P,et al. Synthesis and ionic conductivity of nasicon-structured LiTi2xSnx(PO4)3 anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Advances in Materials and Processing Technologies, 2017,3(3):241-249. |
| [88] | HE Z, JIANG Y, ZHU J,et al. Boosting the performance of LiTi2(PO4)3/C anode for aqueous lithium ion battery by Sn doping on Ti sites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,731:32-38. |
| [89] | LIU N, HE Z, ZHANG X,et al. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of Na-doped LiTi2(PO4)3@carbon composite as anode for aqueous lithium ion batteries. Ceramics International, 2017,43(14):11481-11487. |
| [90] | WANG H, ZHANG H, CHENG Y,et al. Rational design and synthesis of LiTi2(PO4)3-xFx anode materials for high-performance aqueous lithium ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(2):593-599. |
| [91] | 张华民, 王怀清, 冯凯, 等. 一种阴离子掺杂的磷酸钛锂负极材料及其制备和应用. ZL201610490240.3. 2016. 6. 29. |
| [92] | LUO H, TANG Y, XIANG Z,et al. Cl-doping strategy to boost the lithium storage performance of lithium titanium phosphate. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2020,8:349. |
| [93] | JIANG Z, LI Y H, HAN C,et al. Endowing LiTi2(PO4)3/C with excellent electrochemical performances through rational crystal doping. Ceramics International, 2019,45(17):23406-23410. |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [11] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [12] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [13] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | 刘岩, 张珂颖, 李天宇, 周菠, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 陶瓷材料电场辅助连接技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | 谢兵, 蔡金峡, 王铜铜, 刘智勇, 姜胜林, 张海波. 高储能密度聚合物基多层复合电介质的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||