无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 15-21.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210480
所属专题: 【能源环境】CO2绿色转换
• 专栏: CO 2 绿色转化(特邀编辑: 欧阳述昕, 王文中) • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2021-07-29
修回日期:2021-08-17
出版日期:2022-01-20
网络出版日期:2021-09-27
通讯作者:
张 宁, 副教授. E-mail: nzhang@csu.edu.cn
作者简介:刘 彭(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 203112101@csu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIU Peng( ), WU Shimiao, WU Yunfeng, ZHANG Ning(
), WU Shimiao, WU Yunfeng, ZHANG Ning( )
)
Received:2021-07-29
Revised:2021-08-17
Published:2022-01-20
Online:2021-09-27
Contact:
ZHANG Ning, associate professor. E-mail: nzhang@csu.edu.cn
About author:LIU Peng (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 203112101@csu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
利用光催化技术将CO2转化为燃料有望解决能源危机和温室效应。Zn1-2x(CuGa)xGa2S4具有可见光响应及较高的导带电势, 从热力学上看是较为理想的CO2还原材料, 但是其光催化CO2还原活性仍然较低, 亟待从动力学角度提高其活性。本研究采用Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4与不同比例的CdS纳米颗粒复合, 制备了Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS异质结半导体材料。通过材料表征证明CdS在Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4微米颗粒上均匀生长并形成了全固态Z型异质结的复合结构。这种结构有效抑制了电子空穴对的复合, 保持了较高的还原电势, 有利于提高光催化性能。在溶液体系中, 所制备的Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS能够有效地将CO2光催化还原为CO。研究表明, 当Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4与CdS的摩尔比为2 : 1时, 样品的光催化活性达到最优, 是Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4材料的1.7倍, CdS材料的1.6倍。本工作通过构造异质结构, 提高了Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4半导体材料的光催化CO2还原活性, 对人工光合成材料的设计与制备具有较大的参考价值。
中图分类号:
刘彭, 吴仕淼, 吴昀峰, 张宁. Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS光催化材料的制备及其CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 15-21.
LIU Peng, WU Shimiao, WU Yunfeng, ZHANG Ning. Synthesis of Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS Photocatalyst for CO2 Reduction[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 15-21.
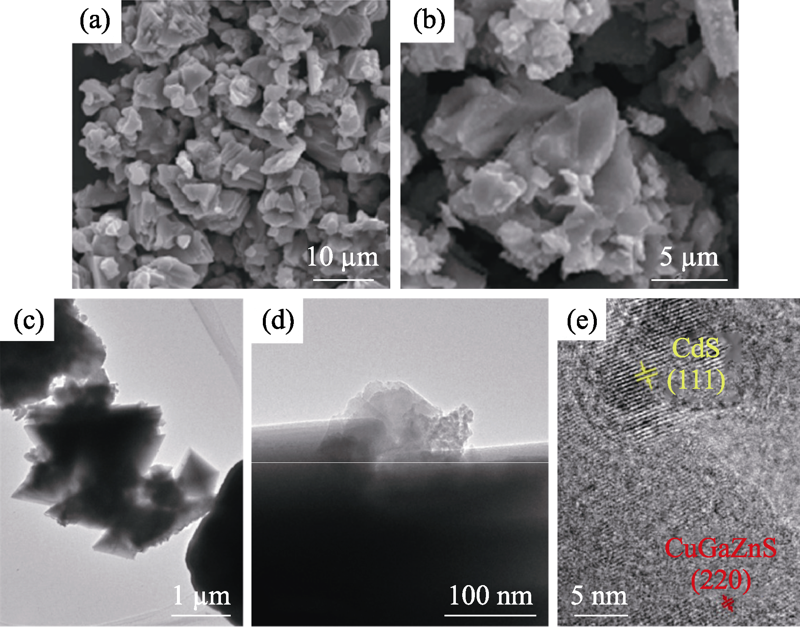
图2 Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1的(a,b)SEM照片, (c,d)TEM照片和(e)HRTEM照片
Fig. 2 (a,b) SEM images, (c,d) TEM images, (e) HRTEM image of Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1
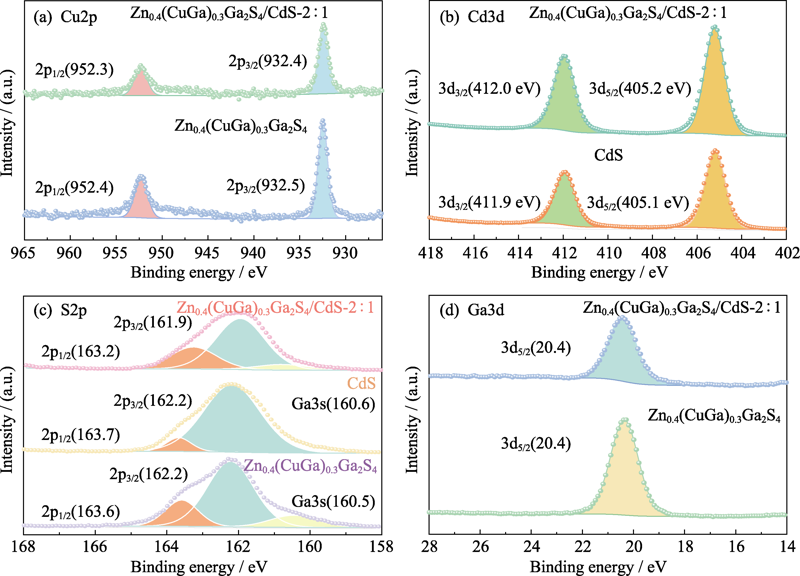
图4 样品Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1、Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4和CdS的(a)Cu2p, (b)C3d, (c)S2p, (d)Ga3d的XPS图谱
Fig. 4 (a) Cu2p, (b) C3d, (c) S2p, (d) Ga3d XPS spectra of Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1, Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4 and CdS
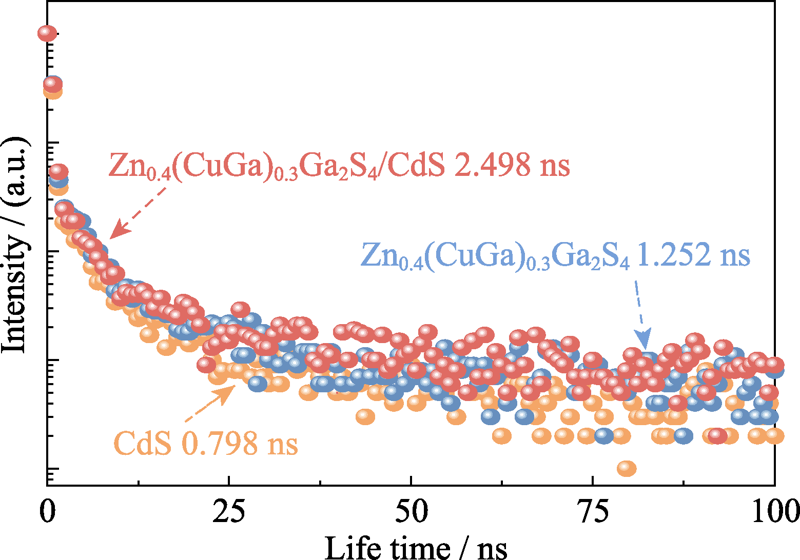
图8 样品Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1、Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4和CdS的时间分辨光致发光光谱
Fig. 8 TRPL spectra of samples Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1, Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4 and CdS Colorful figures are available on website
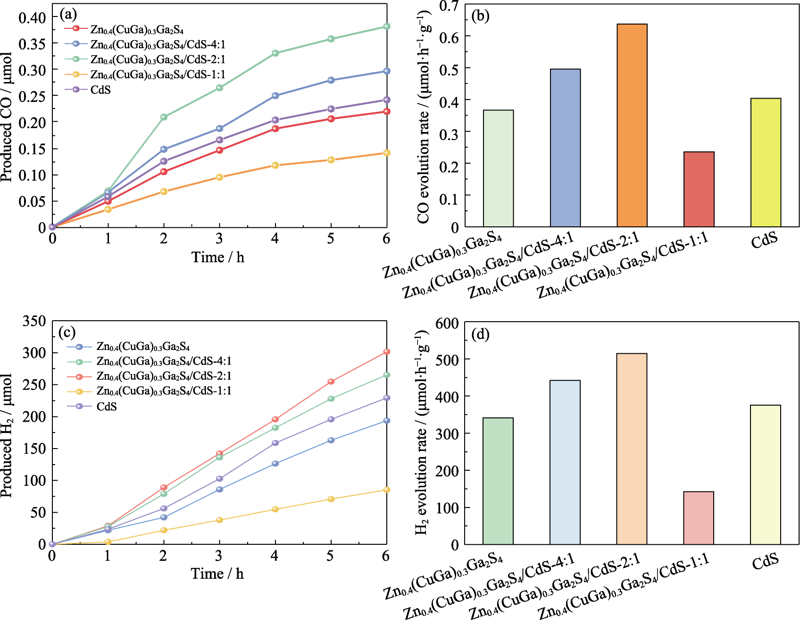
图9 样品Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-4 : 1、Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1、Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-1 : 1、Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4和CdS的(a)CO动力学曲线, (b)CO产率柱状图, (c) H2动力学曲线和(d) H2产率柱状图
Fig. 9 (a) CO evolution vs. irradiation time, (b) CO evolution rate, (c) H2 evolution vs. irradiation time, and (d) H2 evolution rate over Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-4 : 1, Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-2 : 1, Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS-1 : 1, Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4, and CdS Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] |
CHU S, MAJUMDAR A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature, 2012, 488(7411):294-303.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 霍景沛, 林冲, 陈桂煌 等. 光催化二氧化碳还原催化体系研究进展. 化学推进剂与高分子材料, 2020, 18(3):8-14. |
| [3] |
LI K, PENG B S, PENG T Y. Recent advances in heterogeneous photocatalytic CO2 conversion to solar fuels . ACS Catal, 2016, 6:7485-7527.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 赵志强, 张贺, 焦畅, 等. 全球CCUS技术和应用现状分析. 现代化工, 2021, 41(4):5-10. |
| [5] | 王冰, 赵美明, 周勇, 等. 光催化还原二氧化碳制备太阳燃料研究进展及挑战. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2017, 47(3):286-296. |
| [6] |
MIKKELSEN M, JØRGENSEN M, KREBS F C. The teraton challenge. A review of fixation and transformation of carbon dioxide. Energy and Environmental Science, 2010, 3(1):43-81.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ARAI T, SATO S, KAJINO T, et al. Solar CO2 reduction using H2O by a semiconductor/metal-complex hybrid photocatalyst: enhanced efficiency and demonstration of a wireless system using SrTiO3 photoanodes. Energy and Environmental Science, 2013, 6(4):1274-1282.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HASHIMOTO K, IRIE H, FUJISHIMA A. TiO2 photocatalysis: a historical overview and future prospects. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 44(12):8269-8285.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LONG R, LI Y, SONG L, et al. Coupling solar energy into reactions: materials design for surface plasmon-mediated catalysis. Small, 2015, 11(32):3873-3889.
DOI URL |
| [10] | HUANG H, ZHOU J, ZHOU J, et al. Structure-retentive synthesis of a highly ordered mesoporous Nb2O5/N-doped graphene nanocomposite with superior interfacial contacts and improved visible- light photocatalysis. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(13):3373-3379. |
| [11] |
ZHANG H, CHEN Y, ZHU X, et al. Mn2+-doped Zn2GeO4 for photocatalysis hydrogen generation. International Journal of Energy Research, 2019, 43(9):5013-5019.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG J, LI W, LI Y, et al. Self-optimizing bifunctional CdS/Cu2S with coexistence of light-reduced CuO for highly efficient photocatalytic H2 generation under visible-light irradiation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 217:30-36.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MANZI A, SIMON T, SONNLEITNER C, et al. Light-induced cation exchange for copper sulfide based CO2 reduction. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(44):14007-14010.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHAO M, HUANG F, LIN H, et al. CuGaS2-ZnS p-n nanoheterostructures: a promising visible light photo-catalyst for water-splitting hydrogen production. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(37):16670-16676.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
KAGA H, KUDO A. Cosubstituting effects of copper(I) and gallium (III) for ZnGa2S4 with defect chalcopyrite structure on photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 310:31-36.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 王宗鹏, 林志萍, 申士杰, 等. 异质结光催化材料的新进展. 催化学报, 2021, 42(5):710-730. |
| [17] | 董虹星, 刘秋平, 贺跃辉. BiVO4基纳米异质结光催化材料的研究进展. 材料导报, 2018, 32(10):3358-3367. |
| [18] |
SARKAR D, GHOSH C K, MUKHERJEE S, et al. Three dimensional Ag2O/TiO2 type-II (p-n) nanoheterojunctions for superior photocatalytic activity. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2013, 5(2):331-337.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG H, ZHANG L, CHEN Z, et al. Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: design, construction, and photocatalytic performances. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(15):5234-5244.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
PANMAND R P, SETHI Y A, et al. In situ fabrication of highly crystalline CdS decorated Bi2S3 nanowires (nano-heterostructure) for visible light photocatalyst application. RSC Advances, 2016, 6:23508-23517.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
GUO F, SHI W, LI M, et al. 2D/2D Z-scheme heterojunction of CuInS2/g-C3N4 for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity towards the degradation of tetracycline. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 210:608-615.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
TADA H, MITSUI T, KIYONAGA T, et al. All-solid-state Z-scheme in CdS-Au-TiO2 three-component nanojunction system. Nature Materials, 2006, 5(10):782-786.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
HE Y, ZHANG L, TENG B, et al. New application of Z-scheme Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 composite in converting CO2 to fuel. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 49(1):649-656.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHOU Q, KANG S Z, LI X, et al. One-pot hydrothermal preparation of wurtzite CuGaS2 and its application as a photoluminescent probe for trace detection of l-noradrenaline. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2015, 465:124-129.
DOI URL |
| [25] | LIANG Q, JIANG G, ZHAO Z, et al. CdS-decorated triptycene- based polymer: durable photocatalysts for hydrogen production under visible-light irradiation. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2015, 5(6):3368-3374. |
| [26] |
WU S, PANG H, ZHOU W, et al. Stabilizing CuGaS2 by crystalline CdS through an interfacial Z-scheme charge transfer for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction under visible light. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(16):8693-8700.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
MA F, ZHAO G, LI C, et al. Fabrication of CdS/BNNSs nanocomposites with broadband solar absorption for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. CrystEngComm, 2016, 18(4):631-637.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHENG Z, ZHANG N, WANG T, et al. Ag1.69Sb2.27O6.25 coupled carbon nitride photocatalyst with high redox potential for efficient multifunctional environmental applications. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 487(March):82-90.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SIMON T, BOUCHONVILLE N, BERR M J, et al. Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods. Nature Materials, 2014, 13(11):1013-1018.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 吴唯, 周勇, 刘尚军, 等. InAs量子点低温盖层对其发光特性的影响. 半导体光电, 2020, 41(1):89-92. |
| [1] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | 马心全, 李喜宝, 陈智, 冯志军, 黄军同. S型异质结BiOBr/ZnMoO4的构建及光催化降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [3] | 陈瀚翔, 周敏, 莫曌, 宜坚坚, 李华明, 许晖. CoN/g-C3N4 0D/2D复合结构及其光催化制氢性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [4] | 薛虹云, 王聪宇, MAHMOOD Asad, 于佳君, 王焱, 谢晓峰, 孙静. 二维g-C3N4与Ag-TiO2复合光催化剂降解气态乙醛抗失活研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [5] | 洪佳辉, 马冉, 仵云超, 文涛, 艾玥洁. MOFs自牺牲模板法制备CoNx/g-C3N4纳米材料用作高效光催化还原U(VI)[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [6] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [7] | 王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [8] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [9] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [10] | 张弦, 张策, 姜文君, 冯德强, 姚伟. 四元BiMnVO5的合成、电子结构与可见光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [11] | 高娃, 熊宇杰, 吴聪萍, 周勇, 邹志刚. 基于超薄纳米结构的光催化二氧化碳选择性转化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 3-14. |
| [12] | 王潇, 朱智杰, 吴之怡, 张城城, 陈志杰, 肖梦琦, 李超然, 何乐. 钴等离激元超结构粉体催化剂的制备及其光热催化应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 22-28. |
| [13] | 刘雪晨, 曾滴, 周沅逸, 王海鹏, 张玲, 王文中. 改性氮化碳光催化剂在生物质氧化反应中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [14] | 杨东旺, 罗婷婷, 苏贤礼, 吴劲松, 唐新峰. 基于熵工程及SHS动力学的BiAgSeS本征低热导率起源探究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 991-998. |
| [15] | 王路平, 卢占会, 魏鑫, 方明, 王祥科. 改进的灰色模型在光催化数据预测中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 871-876. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||